Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Problem 11
Enviado por
Anonymous GtcMxTDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Problem 11
Enviado por
Anonymous GtcMxTDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Problem 11: Soil Mechanics, Weight-Volume Relationship (CE May 2003)
The following data was obtained from laboratory tests for a cohesive specimen: moisture
content, w, was 22.5%; G = 2.60; and to determine the approximate unit weight, a sample having
a mass of 224 g was placed in a 500 cm^3 container with 382 cm^3 of water required to fill the
container.
a. What is the total unit weight of the soil sample in kN/m^3?
b. What is the void ratio (e)?
c. What is the dry unit weight of the soil sample in kN/m^3?
Answers:
e = 0.678
Problem 10: Soil Mechanics, Weight-Volume Relationship (CE Nov 2002)
Given the following characteristics of a soil sample:
Volume = 0.5 cubic ft
Mass = 56.7 pound mass
The solids have specific gravity of 2.69. After oven drying, the mass of the soil was 48.7 pounds.
a. What is the density of the in-situ soil?
b. What is the porosity of the in-situ soil?
c. What is the degree of the saturation of the in-situ soil?
Answers:
n = 42%
S = 61.018%
Problem 9: Soil Mechanics, Weight-Volume Relationship (CE Nov 2001)
A 480 cc soil sample taken from the site weighs 850.5 grams. After oven drying it, it weighed
59.4 grams. If the specific gravity of solids is 2.72, determine the void ratio of the soil.
Answers:
e = 1.195
Problem 12: Soil Mechanics, Properties of Soil (CE May 2000)
A sample of moist sand taken from the field was found to have a moisture content of 14% and a
porosity of 38%. In a laboratory test that stimulates field conditions, it was found that at its
densest state, its void ratio is 85% and at its looses state its void ratio is 40%. Determine the
relative of the sand.
Answers:
Physical Properties of Soil
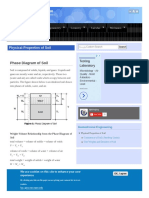
Soil is composed of solids, liquids, and gases. Liquids and gases are mostly water and air,
respectively. These two (water and air) are called voids which occupy between soil particles. The
figure shown below is an idealized soil drawn into phases of solids, water, and air.
Weight-Volume Relationship from the Phase Diagram of Soil
total volume = volume of soilds + volume of voids
volume of voids = volume of water + volume of air
total weight = weight of solids + weight of water
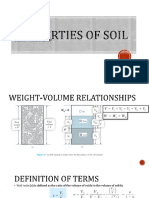
Soil Properties
Void Ratio, e
Void ratio is the ratio of volume of voids to the volume of solids.
Porosity, n
Porosity is the ratio of volume of voids to the total volume of soil.
Degree of Saturation, S
Degree of saturation is the ratio of volume of water to the volume of voids.
Water Content or Moisture Content, w
Moisture content, usually expressed in terms of percentage, is the ratio of the weight of water to
the weight of solids.
Unit Weight, γ
Unit weight is the weight of soil per unit volume. Also called bulk unit weight (γ), and moist unit
weight (γm).
Dry Unit Weight, γd
Dry unit weight is the weight of dry soil per unit volume.
Saturated Unit Weight, γsat
Saturated unit weight is the weight of saturated soil per unit volume.
Effective Unit Weight, γ'
Effective unit weight is the weight of solids in a submerged soil per unit volume. Also called
buoyant density or buoyant unit weight (γb).
Specific Gravity of Solid Particles, G
Specific gravity of solid particles of soil is the ratio of the unit weight of solids (γs) to the unit
weight of water (γw).
Formulas for Properties of Soil
Symbols and Notations
= void ratio
= porosity
= moisture content, water content
= specific gravity of any substance
= specific gravity of solids
= degree of saturation
= volume of soil mass
= volume of air
= volume of water
= volume of solids
= volume of voids
= total weight of soil
= weight of water
= weight of solids
= relative density
= unit weight of soil mass, moist unit weight, bulk unit weight
= unit weight of soil solids
= unit weight of water
= = buoyant unit weight, submerged unit weight
= = dry unit weight
= saturated unit weight
= liquid limit
= plastic limit
= liquidity index
= plasticity index
= group index
Basic Formulas
Unit weight,
Weight,
Specific gravity,
Physical Properties of Soil
Total weight,
Total volume,
Volume of voids,
Void ratio, , Note:
Porosity, , Note:
Relationship between e and n, and
Water content or moisture content, , Note:
Degree of saturation, , Note:
Relationship between G, w, S, and e,
Moist unit weight or bulk unit weight,
, also or
Dry unit weight, and
Saturated unit weight,
Submerged or buoyant unit weight, or
Critical hydraulic gradient, or
Relative Density, or
Atterberg Limits
Plasticity index,
Liquidity index,
Shrinkage index,
Activity of clay, , where = soil finer than 0.002 mm in percent
Other Formulas
Volume of voids,
Volume of solids,
Volume of water,
Weight of water,
Weight of soil,
Dry unit weight,
Relationship between specific gravity of solids, moisture content, degree of saturation, and
void ratio
The relationship between , , , and is given by the following
G = specific gravity of solid particles
w = moisture content or water content
S = degree of saturation
e = void ratio
The formula above can be derived as follows:
Thus, as stated above.
Relationship between void ratio and porosity
The relationship between and is given by
and
Derivation is as follows
→ void ratio
→ n = Vv / V
(okay!)
→ porosity
→ e = Vv / Vs
Você também pode gostar
- Problem 11Documento6 páginasProblem 11Elbrent Paul M ObedencioAinda não há avaliações
- Soil FormulasDocumento7 páginasSoil FormulasJunrey MaweAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3Documento18 páginasChapter 3anon_749279665Ainda não há avaliações
- Geotechnical Engineering 1 T2Documento16 páginasGeotechnical Engineering 1 T2ERJEAN SILVERIOAinda não há avaliações
- Soil Engineering Chapter - 2-2Documento15 páginasSoil Engineering Chapter - 2-2Bhavya zaveriAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Three Phase RelationshipsDocumento11 páginasChapter Three Phase Relationshipshussein darwishAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2-1Documento36 páginasChapter 2-1Chalachew MesfinAinda não há avaliações
- Module 2. Physical Properties of SoilDocumento24 páginasModule 2. Physical Properties of SoilMark Andykenn Liaga MaglinteAinda não há avaliações
- 003 - Weight-Volume RelationshipDocumento29 páginas003 - Weight-Volume RelationshipCristina Marie Pegarro AlfaroAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 - Physical Properties of SoilDocumento50 páginasChapter 3 - Physical Properties of SoilChristian BonoanAinda não há avaliações
- GeotechDocumento27 páginasGeotechGina ClamorAinda não há avaliações
- GTEL01E: Physical Properties of Soil: Modules inDocumento14 páginasGTEL01E: Physical Properties of Soil: Modules inHatsuieeAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3 Index PropertiesDocumento26 páginasLecture 3 Index PropertiesMd. Ariful IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Composition of SoilDocumento38 páginasComposition of SoilRegina MerasAinda não há avaliações
- MODULE 1 Unit 4 (Week 7 and 8) For Soil MechanicsDocumento6 páginasMODULE 1 Unit 4 (Week 7 and 8) For Soil MechanicsMark Ruby OpawonAinda não há avaliações
- Geo - Technical Engineering Question Bank by MR Sukriti DanDocumento13 páginasGeo - Technical Engineering Question Bank by MR Sukriti Dansukritidan1990100% (1)
- MKCP 3313 Week 2 SynchronousDocumento21 páginasMKCP 3313 Week 2 SynchronousXen GamesAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Soil MechanicsDocumento30 páginasBasic Soil MechanicsAfham AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter2 WeightvolumerelationshipDocumento35 páginasChapter2 WeightvolumerelationshipAbuAinda não há avaliações
- Permeability and Seepage: Course Code: Course Title: Credit HoursDocumento15 páginasPermeability and Seepage: Course Code: Course Title: Credit HoursSHAHRIER NAZIM SHUVROAinda não há avaliações
- Soil MechanicsDocumento30 páginasSoil MechanicsShivang VivekAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 - Weight Volume RelationshipDocumento30 páginasChapter 2 - Weight Volume RelationshipShahrull Rule50% (2)
- Lecture 03Documento23 páginasLecture 03Zakawat SadiAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment Weight Volumn RelationshipDocumento8 páginasAssignment Weight Volumn RelationshipAbdulrauf Ismail BusayoAinda não há avaliações
- 5 - Weight Volume RelationshipsDocumento32 páginas5 - Weight Volume Relationshipsmaame25Ainda não há avaliações
- Weight Volume RelationshipDocumento9 páginasWeight Volume RelationshipFervid Prim01Ainda não há avaliações
- Geotech 1Documento167 páginasGeotech 1Clariselle MarisgaAinda não há avaliações
- Weight Volume RelationshipsDocumento32 páginasWeight Volume Relationshipssyedumairali100% (1)
- Lec 4 - Soil Composition and Index Properties F22Documento23 páginasLec 4 - Soil Composition and Index Properties F22tyler bradfordAinda não há avaliações
- C. Weight-Volume RelationshipsDocumento35 páginasC. Weight-Volume RelationshipsKerby Brylle GawanAinda não há avaliações
- Phase Relations: (Das, Chapter 3) Sections: All Except 3.6Documento12 páginasPhase Relations: (Das, Chapter 3) Sections: All Except 3.6javier100% (1)
- 2chapter-2 PPT - (Final)Documento61 páginas2chapter-2 PPT - (Final)Muhe JsAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter TwoDocumento25 páginasChapter TwoJannica Delos ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Handout Minggu 02b Mektan - Soil Index and Gravimetry-1Documento19 páginasHandout Minggu 02b Mektan - Soil Index and Gravimetry-1IkeAinda não há avaliações
- Geotecheng Module 01 Chapter 02Documento32 páginasGeotecheng Module 01 Chapter 02Ace De GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Weight-Volume Relationships: MohammadDocumento33 páginasWeight-Volume Relationships: MohammadAadolf ElÿasAinda não há avaliações
- Geotechnical EngineeringDocumento7 páginasGeotechnical EngineeringWherlyne Lyka IslaAinda não há avaliações
- Geotechnical Engineering 1Documento31 páginasGeotechnical Engineering 1Ranajit MajhiAinda não há avaliações
- Geotechnical Engineering FormulasDocumento15 páginasGeotechnical Engineering FormulasJp TobiasAinda não há avaliações
- Ce 122 Chapter 2 PDFDocumento11 páginasCe 122 Chapter 2 PDFJeisther Timothy GalanoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Two Physical Characteristics of SoilsDocumento32 páginasChapter Two Physical Characteristics of SoilsHiwot DemisseAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Geology University of Liberia Semester II-2019-2020Documento37 páginasDepartment of Geology University of Liberia Semester II-2019-2020Edwin BallahAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-II-physical Characteristics of SoilDocumento34 páginasChapter-II-physical Characteristics of SoilVijaykumar NagnaikAinda não há avaliações
- Symbols and NotationsDocumento1 páginaSymbols and NotationsE SAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of SoilDocumento10 páginasProperties of SoilJommarVocalTagalogAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Properties of Soil PDFDocumento16 páginasPhysical Properties of Soil PDFAshish MittalAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 2Documento27 páginasLesson 2jrAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Phase ModelsDocumento24 páginas3 Phase Modelsfaroukm91Ainda não há avaliações
- 02 Chapter 3 - Weight Volume RelationshipsDocumento42 páginas02 Chapter 3 - Weight Volume RelationshipsLeandrow BacolodAinda não há avaliações
- 02 Chapter 3 - Weight Volume Relationships PDFDocumento42 páginas02 Chapter 3 - Weight Volume Relationships PDFAbd El Rhman Mohamed50% (2)
- Instructor: Dipanjan Basu: Civil & Environmental Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo, ON, CanadaDocumento29 páginasInstructor: Dipanjan Basu: Civil & Environmental Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo, ON, CanadaDamilare OlaniyanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Weight Volume Relationships For StudentsDocumento35 páginasChapter 3 Weight Volume Relationships For StudentsHahahahahahahahahaAinda não há avaliações
- Lec 2Documento32 páginasLec 2ahmed alhajAinda não há avaliações
- Geotechnical Module 1Documento52 páginasGeotechnical Module 1athira100% (2)
- Civil Engineering Formulas 2Documento3 páginasCivil Engineering Formulas 2Jonathan100% (3)
- Soil ParticlesDocumento48 páginasSoil ParticlesbookAinda não há avaliações
- Plate 1 in Soil MechanicsDocumento8 páginasPlate 1 in Soil MechanicsjulspdAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - Soil ClassificationDocumento74 páginasChapter 1 - Soil ClassificationEyntan Iera100% (1)
- Soils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationNo EverandSoils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationGuilhem BourrieAinda não há avaliações
- s16 PDFDocumento84 páginass16 PDFAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- Bill of MaterialsDocumento4 páginasBill of MaterialsAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- Hypergeometric DistributionDocumento16 páginasHypergeometric DistributionAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- Modular Arithmetic/introductionDocumento8 páginasModular Arithmetic/introductionAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- 0 - Preliminaries - 2Documento6 páginas0 - Preliminaries - 2Anonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Reinforced ConcreteDocumento1 páginaDesign of Reinforced ConcreteAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- Design - of - Reinforced - Concrete-Www - Parsafar.com - 22 PDFDocumento1 páginaDesign - of - Reinforced - Concrete-Www - Parsafar.com - 22 PDFAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- 1.4 Historical Background: Economy of Reinforced Concrete Structures, The Major Emphasis Is On Reducing Formwork CostsDocumento1 página1.4 Historical Background: Economy of Reinforced Concrete Structures, The Major Emphasis Is On Reducing Formwork CostsAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- An Instructor's Solutions Manual To Accompany: Principles of Geotechnical Engineering, 7 Edition, SIDocumento6 páginasAn Instructor's Solutions Manual To Accompany: Principles of Geotechnical Engineering, 7 Edition, SIAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- Terzaghi Bearing Capacity FactorsDocumento1 páginaTerzaghi Bearing Capacity FactorsAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- 23 FHDDocumento3 páginas23 FHDAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- When I Was 4 Years Old My Sister Was Half My Age, Now Am 100 How Old Is My Sister?Documento1 páginaWhen I Was 4 Years Old My Sister Was Half My Age, Now Am 100 How Old Is My Sister?Anonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- TOP 10 EarthquakeDocumento2 páginasTOP 10 EarthquakeAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- Africa Dams EngDocumento190 páginasAfrica Dams EngAnonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- According To Logarithm : So The Answer Is 3. Correct Answer Is Given at Option E)Documento1 páginaAccording To Logarithm : So The Answer Is 3. Correct Answer Is Given at Option E)Anonymous GtcMxTAinda não há avaliações
- Docker Tutorial: Anthony BaireDocumento99 páginasDocker Tutorial: Anthony BairesuderAinda não há avaliações
- Student Ought To Possess To Produce Clean-Up and In-Between DrawingsDocumento2 páginasStudent Ought To Possess To Produce Clean-Up and In-Between Drawingscristian friasAinda não há avaliações
- FTP Booster Training Plan OverviewDocumento1 páginaFTP Booster Training Plan Overviewwiligton oswaldo uribe rodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Quantum Data-Fitting: PACS Numbers: 03.67.-A, 03.67.ac, 42.50.DvDocumento6 páginasQuantum Data-Fitting: PACS Numbers: 03.67.-A, 03.67.ac, 42.50.Dvohenri100Ainda não há avaliações
- Chirimuuta, Mazviita - Outside Color - Perceptual Science and The Puzzle of Color in Philosophy-The MIT Press (2017)Documento263 páginasChirimuuta, Mazviita - Outside Color - Perceptual Science and The Puzzle of Color in Philosophy-The MIT Press (2017)Karishma borgohainAinda não há avaliações
- Business ProblemsDocumento5 páginasBusiness ProblemsMaureen GarridoAinda não há avaliações
- Fall 2015 The Language of Anatomy PDFDocumento14 páginasFall 2015 The Language of Anatomy PDFpikminixAinda não há avaliações
- Case For Overhead and DistributionDocumento2 páginasCase For Overhead and DistributionBhargav D.S.Ainda não há avaliações
- Particle FilterDocumento16 páginasParticle Filterlevin696Ainda não há avaliações
- Reconductoring Using HTLS Conductors. Case Study For A 220 KV Double Circuit Transmission LINE in RomaniaDocumento7 páginasReconductoring Using HTLS Conductors. Case Study For A 220 KV Double Circuit Transmission LINE in RomaniaJose ValdiviesoAinda não há avaliações
- 10 TazmahalDocumento12 páginas10 TazmahalSifat E Noor SahibaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Recycling of Textile PolymersDocumento8 páginasChemical Recycling of Textile PolymersVaishali RaneAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook Essentials of Kumar Clarks Clinical Medicine PDF Full Chapter PDFDocumento67 páginasEbook Essentials of Kumar Clarks Clinical Medicine PDF Full Chapter PDFjanet.cochran431100% (19)
- Mindset For IELTS Level 1 Student's Book PDF English As A Second or Foreign Language International English Language TestinDocumento1 páginaMindset For IELTS Level 1 Student's Book PDF English As A Second or Foreign Language International English Language TestinhiAinda não há avaliações
- Euronext Derivatives How The Market Works-V2 PDFDocumento106 páginasEuronext Derivatives How The Market Works-V2 PDFTomAinda não há avaliações
- Board Resolution On Assigning Signatories in The Voucher ProgramDocumento2 páginasBoard Resolution On Assigning Signatories in The Voucher ProgramavinmanzanoAinda não há avaliações
- Pipe Support Reference 8-29-14Documento108 páginasPipe Support Reference 8-29-14HITESHAinda não há avaliações
- AVR On Load Tap ChangerDocumento39 páginasAVR On Load Tap ChangerInsan Aziz100% (1)
- Javascript PrefiDocumento66 páginasJavascript Prefiguendelyn omegaAinda não há avaliações
- Sacramento County Compensation Survey Board of SupervisorsDocumento13 páginasSacramento County Compensation Survey Board of SupervisorsCBS13Ainda não há avaliações
- Sense and NonsenseDocumento263 páginasSense and NonsenseAbdulRehmanKhilji100% (1)
- The Definitive Guide On How To Build A High Status Social CircleDocumento46 páginasThe Definitive Guide On How To Build A High Status Social CircleCecilia Teresa Grayeb SánchezAinda não há avaliações
- Lab5.ipynb - ColaboratoryDocumento8 páginasLab5.ipynb - ColaboratoryMin YAinda não há avaliações
- The Impact of Teaching PracticeDocumento14 páginasThe Impact of Teaching PracticemubarakAinda não há avaliações
- CS 2400 - 2500 BrochureDocumento8 páginasCS 2400 - 2500 BrochureOo Kenx OoAinda não há avaliações
- The London SchoolDocumento3 páginasThe London SchoolKhawla Adnan100% (5)
- Concept PaperDocumento4 páginasConcept Paperjanet a. silosAinda não há avaliações
- NTCC Project - Fake News and Its Impact On Indian Social Media UsersDocumento41 páginasNTCC Project - Fake News and Its Impact On Indian Social Media UsersManan TrivediAinda não há avaliações
- Legal Aspects of Construction Ethics PaperDocumento11 páginasLegal Aspects of Construction Ethics PaperbikaresAinda não há avaliações
- Sow and Learning ObjectivesDocumento14 páginasSow and Learning ObjectivesEhsan AzmanAinda não há avaliações