Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Pathophysiology of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS
Enviado por
Erika Nena Castillo AlamoDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Pathophysiology of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS
Enviado por
Erika Nena Castillo AlamoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
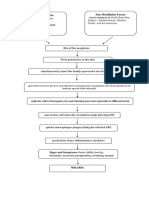
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of STAPHYLOCOCCAL SCALDED SKIN SYNDROME (SSSS)
PREDISPOSING FACTORS PRECIPITATING FACTORS
> Environment > Poor hand hygiene
> Weak Immune system
> Poor renal clearance
S. Aureus produces exotoxins (Epidermolytic A and B) in the skin
Exotoxins produces serine proteases
This cleaves the desmosomal proteins desmoglein 1 in the zona granulosa of the epidermis
Causing keratinocytes to detach from one another
and from the underlying basement membrane
S/Sx:
(+)skin exfoliation Exfoliation of the skin Blisters
(diffuse sheetlike desquamation) (thin walled, sterile cloudy fluid to
frank yellow pus fluid-filled bullae)
Rupture of lesions leaves denuded skin
(also known as Nikolsky’s Sign)
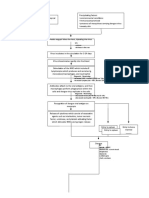
S/Sx:
rash, heat, pain Local Inflammatory Response of the body
Exofoliative toxins are spread hematogenously
widespread loss of superficial epidermis
Loss of barrier function of the skin
S/Sx:
(+) fever Systemic Inflammatory Response of the body
S. aureus skin infection
Complications Signs and Symptoms
Sepsis Fussiness
Cellulitis Tiredness
Severe infections Redness of the skin
Pneumonia Fluid-filled blisters
Nikolsky sign
Sheet-like desquamation of skin
Painful, erythematous rash with
wrinkled tissue paper life consistency
Você também pode gostar
- BFCDocumento8 páginasBFCIrene GunongAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Hepatitis B Virus InfectionDocumento9 páginasPathophysiology of Hepatitis B Virus InfectionDianne G Ignacio100% (4)
- Science As Human Endeavour TaskDocumento2 páginasScience As Human Endeavour Taskyolanda Sitepu100% (1)
- Annotated Group 2 Impetigo Concept Mapping 1Documento30 páginasAnnotated Group 2 Impetigo Concept Mapping 1DHANE ANN CAMPOSANOAinda não há avaliações
- OTITIS Concept MapDocumento7 páginasOTITIS Concept MapElleAinda não há avaliações
- Precipitating Environmental Factors and Pathophysiology of Dengue VirusDocumento4 páginasPrecipitating Environmental Factors and Pathophysiology of Dengue VirusKathleen DimacaliAinda não há avaliações
- HPV Virus Causes Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis in BoyDocumento21 páginasHPV Virus Causes Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis in BoyDaffa IbnurasyAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionStephanie GapuzAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology: School OF Health AND Allied Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing - Level IiiDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology: School OF Health AND Allied Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing - Level IiiLadybelle GototosAinda não há avaliações
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisDocumento1 páginaSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma CaseDocumento6 páginasThyroid Papillary Carcinoma CaseRandy F BabaoAinda não há avaliações
- Dengue PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaDengue PathophysiologyRafael Miguel Alon Protacio50% (2)
- Case 1 Pedia Henoch Schonlein PurpuraDocumento45 páginasCase 1 Pedia Henoch Schonlein PurpuraJefferson Gumiran100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Pediatric Community Acquired PneumoniaDocumento35 páginasNursing Care Plan for Pediatric Community Acquired PneumoniaJose Bryan NacillaAinda não há avaliações
- DOH ProgramsDocumento6 páginasDOH ProgramsMichael VillavertAinda não há avaliações
- Amoebiasis PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginasAmoebiasis PathophysiologyApril CornejoAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocumento2 páginasNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitAinda não há avaliações
- PathophysiologyDocumento5 páginasPathophysiologyJessyl GirayAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Fever and Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Dengue Fever and Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverKenrick Randell IbanaAinda não há avaliações
- ChickenpoxDocumento7 páginasChickenpoxJennevy Buque100% (1)
- Case AnalysisDocumento12 páginasCase AnalysisFroilan TaracatacAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map On Acute PainDocumento1 páginaConcept Map On Acute PainKatherine Conlu Bengan0% (1)
- 1.05 General Pathology - Diseases of The Immune System (Part 2) - Dr. AleraDocumento13 páginas1.05 General Pathology - Diseases of The Immune System (Part 2) - Dr. AleraCherry RahimaAinda não há avaliações
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Etiology, Types, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento6 páginasMycobacterium Tuberculosis Etiology, Types, Diagnosis and TreatmentChloé Jane HilarioAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocumento5 páginasChronic PyelonephritisIsak ShatikaAinda não há avaliações
- Age - Weather: Aspiration of Secretions Containing MicrobesDocumento4 páginasAge - Weather: Aspiration of Secretions Containing Microbeslouie john abilaAinda não há avaliações
- Schematic Diagram BA HAP HRDocumento2 páginasSchematic Diagram BA HAP HRMika MinsalanAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study SSSSDocumento37 páginasCase Study SSSSsplakener100% (1)
- Pcap PathoDocumento2 páginasPcap PathoLardel CarayAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionSTORAGE FILEAinda não há avaliações
- USC Case 04 - SinusitisDocumento9 páginasUSC Case 04 - SinusitisDisti Damelia SebayangAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology PTBDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology PTBNikki Galvez Braganza100% (2)
- TB Case StudyDocumento2 páginasTB Case StudyReisabelle LabianoAinda não há avaliações
- CellulitisDocumento5 páginasCellulitisaimigdragonAinda não há avaliações
- OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY Case Study on Post Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocumento20 páginasOUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY Case Study on Post Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisMikaCasimiroBalunanAinda não há avaliações
- Patho BAIAEDocumento2 páginasPatho BAIAECatherine Ann EaAinda não há avaliações
- Diarrhea 2016Documento37 páginasDiarrhea 2016oli garkiAinda não há avaliações
- MDRTB Case StudyDocumento35 páginasMDRTB Case StudyFejlean Angelica AntineoAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Amoebiasis: Ingestion to ExcretionDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of Amoebiasis: Ingestion to ExcretionCathy AcquiatanAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Syphilis & GonorrheaDocumento14 páginasPathophysiology of Syphilis & GonorrheasourabhAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Gastroenteritis Case StudyDocumento42 páginasAcute Gastroenteritis Case StudyGelah DacanayAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisDocumento9 páginasPathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisIrish EspinosaAinda não há avaliações
- Bronchial Asthma Exacerbation PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginasBronchial Asthma Exacerbation PathophysiologyKing TrixieAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumonia Case Study FinalllDocumento56 páginasPneumonia Case Study Finalllbethrice melegritoAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology of HyperthyroidismKitty YuffieAinda não há avaliações
- Patho DengueDocumento3 páginasPatho DengueLindy Shane BoncalesAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology Hypokalemia Periodic ParalysisDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology Hypokalemia Periodic Paralysisloyea0% (2)
- Path o Physiology of SyphilisDocumento1 páginaPath o Physiology of Syphilis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.Ainda não há avaliações
- Journal Pcap CDocumento3 páginasJournal Pcap CKit LaraAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology Dengue 2Documento4 páginasPathophysiology Dengue 2KatherineAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study of Community Acquired PneumoniaDocumento14 páginasCase Study of Community Acquired PneumoniaRachelAinda não há avaliações
- GonorrheaDocumento7 páginasGonorrheaEköw Santiago JavierAinda não há avaliações
- Cavite State University: I. ObjectivesDocumento7 páginasCavite State University: I. ObjectivesChamy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Vii. Pathophysiology A. AlgorithmDocumento2 páginasVii. Pathophysiology A. AlgorithmJonna Mae TurquezaAinda não há avaliações
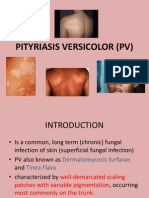
- Pityriasis Versicolor Part 1Documento9 páginasPityriasis Versicolor Part 1Sopna Zenith0% (1)
- Staphylococcal Infection Concept Map PDFDocumento2 páginasStaphylococcal Infection Concept Map PDFAna VillarandaAinda não há avaliações
- BurnsDocumento1 páginaBurnsasdfghjAinda não há avaliações
- Term Example Discoloration Flat,: Patch ( 1cm) Papule ( 1cm)Documento4 páginasTerm Example Discoloration Flat,: Patch ( 1cm) Papule ( 1cm)Almira PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatology Lectures JRRMMCDocumento10 páginasDermatology Lectures JRRMMCGi Em100% (1)
- Skin and MSK EverythingDocumento31 páginasSkin and MSK EverythingBernard HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary System GlossaryDocumento3 páginasIntegumentary System GlossaryLarissa ShevchenkoAinda não há avaliações
- Nplex Micro ChartDocumento12 páginasNplex Micro Chartapi-26938624100% (2)
- Tutor Imun HBsAg KuantitatifDocumento27 páginasTutor Imun HBsAg Kuantitatifv_mayasari100% (1)
- Reticuloendothelial System (Macrophage System) : MacrophagesDocumento4 páginasReticuloendothelial System (Macrophage System) : MacrophagesJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerAinda não há avaliações
- Interpretations of SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG Antibody Titers in TheDocumento7 páginasInterpretations of SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG Antibody Titers in TheYunita AnggrainiAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 - TransDocumento8 páginasModule 1 - TransJohanna Kate DiestroAinda não há avaliações
- Bacteria PDFDocumento13 páginasBacteria PDFJohn Christopher LucesAinda não há avaliações
- Conjunctivitis, Eye (Conjunctivitis), Pink EyeDocumento1 páginaConjunctivitis, Eye (Conjunctivitis), Pink EyeTudorel PoalelungiAinda não há avaliações
- CDC 1st Quar. REPORT 2015Documento67 páginasCDC 1st Quar. REPORT 2015abdi qanoAinda não há avaliações
- HIV Awareness BrochureDocumento2 páginasHIV Awareness BrochureLoraine Antonette CupoAinda não há avaliações
- Case Report Tinea Corporis - Salsabilla Sahara - 22004101052Documento25 páginasCase Report Tinea Corporis - Salsabilla Sahara - 22004101052Salsabilla SaharaAinda não há avaliações
- No Diagnosa Menurut Kki Level Kode Kode Diagnosa AskesDocumento5 páginasNo Diagnosa Menurut Kki Level Kode Kode Diagnosa Askesashri hikmatullohAinda não há avaliações
- Health Assessment FormDocumento2 páginasHealth Assessment FormJessa MaeAinda não há avaliações
- Measles Basic Info EnglishDocumento2 páginasMeasles Basic Info EnglishSinclair Broadcast Group - EugeneAinda não há avaliações
- s4 l3 Nematodes IIDocumento14 páginass4 l3 Nematodes II2013SecB100% (1)
- Research ProposalDocumento3 páginasResearch Proposalapi-345809869Ainda não há avaliações
- YELLOW FEVER CAUSED BY AEDES AEGYPTI MOSQUITODocumento12 páginasYELLOW FEVER CAUSED BY AEDES AEGYPTI MOSQUITOAkinsoun MotunrayoAinda não há avaliações
- Test Result Normal Range Interpreta Tion Implicatio NDocumento11 páginasTest Result Normal Range Interpreta Tion Implicatio NSitty Aizah MangotaraAinda não há avaliações
- Degenerative Disc DiseaseDocumento13 páginasDegenerative Disc DiseaseSisuka CeritaAinda não há avaliações
- The Effect of Inflammation On BoneDocumento14 páginasThe Effect of Inflammation On BoneKelas CAinda não há avaliações
- Argument Essay ReflectionDocumento5 páginasArgument Essay Reflectionapi-509671089Ainda não há avaliações
- Origin, Transmission, Diagnosis and Management of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)Documento6 páginasOrigin, Transmission, Diagnosis and Management of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)Alfitrah NurjayaAinda não há avaliações
- Antirheumatic and Antigout DrugsDocumento66 páginasAntirheumatic and Antigout DrugsBadri KarkiAinda não há avaliações
- Neonatal Skin Disorders and The Emergency Medicine Physician PDFDocumento10 páginasNeonatal Skin Disorders and The Emergency Medicine Physician PDFsamerdkhAinda não há avaliações
- Precipitation and Agglutination ReactionsDocumento3 páginasPrecipitation and Agglutination ReactionsakiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 44 STIDocumento5 páginasChapter 44 STIRebeccaAinda não há avaliações
- ABO Blood TypesDocumento4 páginasABO Blood TypesKBS100% (1)
- HPV Immunisation - MalaysiaDocumento13 páginasHPV Immunisation - MalaysiaMadeline TanAinda não há avaliações
- Leflet Asmpid New-3Documento1 páginaLeflet Asmpid New-3TheAru21Ainda não há avaliações
- CHN Immunization NotesDocumento9 páginasCHN Immunization NotesJustin AncogAinda não há avaliações