Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Solid Mensuration
Enviado por
Keiffer MangomaDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Solid Mensuration
Enviado por
Keiffer MangomaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ENGG MATH 1 – Precalculus
SOLID MENSURATION Diagonal is a line that connects two non-adjacent vertices
LESSON EIGHT:
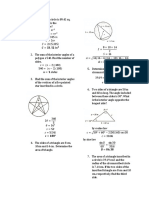
I. SOLID MENSURATION Number of diagonals of a given polygon:
A. Plane Figures The term “geometry” was derived from the Greek words Sum of Interior angles: Where: n is the
𝑛 number of sides of
B. Solids for which V=Bh “ge” meaning earth and “metria” meaning measurement. 𝐷𝑖𝑎𝑔𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑙𝑠 = (𝑛 − 3) 𝑆 = (𝑛 − 2) 180°
2 the polygon
1. Cube Solid geometry is the traditional name for the geometry of
2. Rectangular Parallelepiped three-dimensional Euclidean space. Stereometry deals with
3. Prism
4. Cylindrical Surface the measurements of volumes of various solid figures
5. Cylinder including pyramids, prisms and other polyhedrons.
6. Circular Cylinder Mensuration also means the measuring of geometric
7. Right Circular Cylinder
C. Solids for which V = Bh / 3 magnitudes, lengths, areas and volumes.
1. Pyramid
2. Regular Pyramid PLANE FIGURES
3. Similar Figures
4. Conical Surfaces POLYGON – a closed plane figure with three or more angles.
5. Cone There are as many sides as angles in a polygon. The term
6. Right Circular Cone “polygon” comes from the Greek words “poly” meaning many
D. Sphere
and “gonia” meaning angle. Polygons are named according
OBJECTIVES: to the number of sides or vertices.
At the end of the lesson, the
student should be able to:
TLO 8: Analyze and solve
Regular polygon – having all sides equal and all interior
problems involving Plane
angles equal
Figures, Solids for which
V=BH, Solids for which V =
3 Triangle 9 Nonagon
(Bh)/3 and spheres 4 Quadrilateral or 10 Decagon
Tetragon
References: 5 Pentagon 11 Undecagon
Solid Geometry by Lara and 6 Hexagon 12 Dodecagon
Ymas 7 Heptagon 1000 Chilliagon
Solid Mensuration. Kern. and 8 Octagon n n-gon
Bland
Convex polygon – having each interior angle less than 180°
Concave polygon – having one interior angle greater than 180°
Prepared by: Engr. Caroline Bautista-Moncada ENGGMATH 1
EXERCISES: EXERCISES:
1. A window glass is 4 ft. 2 in. by 2 ft. 10 in. Find its area. 1. Find the length of the diagonal of the section ABCD (diagonal of
Ans. 1700 sq. inches the cube) in the figure.
2. Find the area of the largest circle which can be cut from 2. How much material was used in the manufacture of 24,000
a square of edge 4 inches. What is the area of the celluloid dice, if each die has an edge of 1/4 inch?
material wasted? Ans. 12.5664 in2 3. Find the volume and total area of the largest cube of wood that
3. A metal washer 1 in. in diameter is pierced by a ½-in can be cut from a log of circular cross section whose radius is 12.7
hole. What is the area of one face of the washer? in. Ans. V=3.3528 ft3 , A = 13.4408 ft2
Ans. 0.589 in2 4. A vegetable bin built in the form of a cube with an edge of 6 ft. is
4. A sail has a spread of canvas as shown in the figure. Find divided by a vertical partition which passes through two diagonally
the surface area of one side of the sail. opposite edges. Find the lateral surface of either compartment. Ans.
Ans. 136.4864 sq. ft 122.9117 ft2
5. Find the area of a triangle whose vertex is at the midpoint of an upper
SOLIDS FOR WHICH V = Bh edge of a cube of edge a and whose base coincides with the diagonally
opposite edge of the cube. Ans. 0.7071a2
SOLID – any limited portion of space, bounded by surfaces
SECTION – of a solid is the plane figure cut from the solid by passing a plane through it. B. RECTANGULAR PARALLELEPIPED
- A polyhedron whose six faces are all rectangles
PROPERTIES:
a. The parallel edges of a rectangular
parallelepiped are equal.
b. The opposite lateral faces of a
rectangular parallelepiped are equal
and parallel.
c. Any two opposite faces of a rectangular
parallelepiped may be taken as the
bases.
POLYHEDRON – a solid bounded by planes. d. Every section of a rectangular
EDGES – intersection of the bounding planes parallelepiped made by a plane parallel
FACES – portions of the bounding planes included by the edges. The faces are polygons. to the base is equal in are to that of the base.
VERTICES – intersections of the edges EXERCISES:
1. Counting 38 cu. ft. of coal to a ton, how many tons will a coal bin 19 ft. long, 6 ft. wide
and 9 ft. deep contain, when level is full? Ans. 27 tons
2. Building bricks are closely stacked in a pile 7 ft. high, 36 ft. long, and 12 ft. wide. If the
bricks are 2 in. by 4 in. by 9 in. , how many bricks are in the pile? Ans. 72,576
3. How many cubic yards of material are needed for the foundation of a barn 40 by 80 ft.,
if the foundation is 2 ft. thick and 12 ft. high?
A. CUBE Ans. 206.22 yd3
- A cube is a polyhedron whose six faces are all squares 4. The edges of a trunk are 3 ft., 4 ft., 6 ft. A second
Properties: trunk is twice as long; the other edges are 3 ft., 4
a. The three dimensions of a cube are equal to each ft. How do their volumes compare? Ans. V2 = 2V1
other. Therefore, all edges are equal. 5. A solid concrete porch consists of 3 steps and a
b. All the faces of a cube are congruent squares. landing. The steps have a tread of 11 in., a rise of
7 in., and a length of 7 ft; the landing is 6 ft. by 7
Total area = sum of the areas of its faces Volume , 𝑽 = 𝒂𝟑 ft. How much material was used in its
𝑻 = 𝟔𝒂𝟐 where a = edge construction? Ans. 120.46 cu. ft
Prepared by: Engr. Caroline Bautista-Moncada ENGGMATH 1
D. CYLINDRICAL SURFACE , CYLINDER, CIRCULAR CYLINDER, AND RIGHT CIRCULAR
C. PRISM CYLINDER
- A polyhedron of which two faces are equal polygons in parallel planes, and the other - Cylindrical Surface: A surface generated by a moving straight line (generator) which is
faces are parallelograms. always parallel to a fixed line, and which always intersects a fixed plane curve (directrix)
PROPERTIES: not in the plane with the fixed line.
1. The bases are the equal polygons; the lateral - Cylinder: Solid bounded by a closed cylindrical surface and two parallel planes.
area is the sum of the areas of the remaining - Circular Cylinder: A cylinder which has a circular right section.
faces. - Right Circular Cylinder: A circular cylinder whose elements are perpendicular to its base.
2. The intersection of the lateral faces are called
the lateral edges
3. The sections of a prism made by parallel
planes cutting all the lateral edges are equal
polygons.
4. The altitude of the prism is the perpendicular
distance between the planes of its bases.
5. A right section of a prism is a section
perpendicular to the lateral edges.
6. A right prism is a prism whose lateral edges
are perpendicular to its bases; its lateral faces
are rectangles.
Circular Cylinder
LATERAL AREA = lateral edge x perimeter of LA = perimeter of right
the right section section x element ,
S = pKe
𝑺 = 𝒆𝒑𝑲
Volume = Base x height,
VOLUME = base x altitude = Bh V = Bh
VOLUME = right section x lateral edge = Ke Volume = right section x
element,
V = Ke
Exercises:
1. A lead pencil whose ends are regular hexagons was cut from a cylindrical piece of wood,
with the least waste. If the original piece was 8 in. long and ½ in. in diameter, find the
volume of the pencil. Ans. 1.2990 in2
2. A trench is 180 ft. long and 12 ft deep, 7 ft. wide at the top and 4 ft. at the bottom. How
many cubic yards of earth have to be removed? Ans. 440 yd3
3. A trough is formed by nailing together, edge to edge, two boards 11 ft. in length, so that Exercises:
the right section is a right triangle. If 15 gal. of water are poured into the trough and if 1. During a rain, 1/4 in. of water fell. Find how many gallons of water fell on a level 10-acre
the trough is held level so that a right park. (1 cu. ft = 7.48 gal, 1 acre=43560 sq. ft.) Ans. 67,881 gal
section of the water is an isosceles right 2. A smokestack of a ship is 25 ft. long with a rake aft ( angle of the stack’s inclination from
triangle, how deep is the water? (231 cu. the vertical) so that its top rises 24 ft. above the deck. The cross section of the fleu is a
in. = 1 gal.) Ans. 5.1235 in. circle with a diameter of 3 ½ ft. Completely encircling the fleu is a protective stack. The
4. A contractor agrees to build a dam, 180 distance between two stacks is 6 in. Find the space enclosed between the two stacks and
ft long and 20 ft high, 12 ft wide at the also the outerside painting surface of the protective stack. (neglect the thickness of the
bottom and 8 ft wide at the top, for metal) Ans. 157.08 cu. ft, 353 sq. ft.
$9.75 a cubic yard. Find his profit if his 3. The diameter of a well is 6 ft. and the water is 7 ft deep. How many gallons of water are
costs were $10,000. Ans. $3,000.00 there in the well, reckoning 7.48 gal to the cubic foot? Ans. 1480.44 gal.
Prepared by: Engr. Caroline Bautista-Moncada ENGGMATH 1
SOLIDS FOR WHICH V = 1/3 Bh inscribed in the lower base of the cube. If the edge of the cube is 12 in., find the
volume of the cone. Ans. 452. 39 in3
A. PYRAMID
C. RIGHT CIRCULAR CONE – circular cone whose axis is perpendicular to its base.
1. A pile of sand is in the form of a right circular cone of altitude 7 ft. and slant height
25 ft. What is the weight of the sand, if the sand weighs 107.5 lb. per cu. ft? Ans.
453,897.3066 lb.
2. How many square yards of canvas will be required to make a conical tent 15 ft.
high and 18 ft. in diameter, if 10 percent of the material is wasted? Ans.60.45 yd2
THE SPHERE
A sphere is a solid bounded by a closed surface every point of which is equidistant from a fixed
point called the center.
REGULAR PYRAMID – pyramid whose base is a regular polygon whose center coincides
with the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the vertex to the base.
Lateral area = ½ perimeter of the base x slant height
𝟏
𝑺= 𝒑𝒍
𝟐
1. If there are 1 ¼ cu. ft in a bushel, what is the capacity (in bushels) of a hopper in the
shape of an inverted pyramid 12 ft. deep and 8 ft. square at the top? Ans. 204.8 bu
2. A church spire in the form of a regular hexagonal pyramid whose base edge is 8 ft. and
whose altitude is 75 ft. is to be painted at a cost of 22 cents per square yard. What is
the total cost? Ans. $44.25
B. CONE – solid bounded by a conical surface (lateral surface) whose directrix is a closed
Area = area of 4 great circles
curve, and a plane (base) which cuts all the elements.
𝑺 = 𝟒𝝅𝑹𝟐
Volume
𝟒
𝑽= 𝝅 𝑹𝟑
𝟑
1. Find the weight of a snowball 4 ft. in diameter if the wet compact snow of which this
ball is made weighs 30 lb. per cu. ft. Ans. 1005.31 lb.
2. The surface of a hemispherical dome whose diameter is 36 ft. is to be covered with gold
1. The crater of a volcano is approximately in the shape of a
leaf which costs 15 cents per square in. What must be paid for the gold leaf? Ans.
cone of base 3.1416 sq. mi. The crater’s depth is 1500 ft.
$43,972.24
How many cubic yards of earth would be required to fill this
3. A spherical balloon is inflated so that its diameter is 40 ft. Find the surface area of the
cavity? Ans. 16.219 x 108 cu. yd
balloon’s covering and the volume of the gas. Ans. S=5026.55 ft2, V=33,510.3216 ft3
2. The vertex of the cone shown in the figure is at the midpoint
of an upper edge of the cube; the base of the cone is a circle
Prepared by: Engr. Caroline Bautista-Moncada ENGGMATH 1
Você também pode gostar
- Archemidian SolidsDocumento22 páginasArchemidian Solidspositron999100% (1)
- New Century Maths Advanced 9 - Chapter 6. Geometry PDFDocumento30 páginasNew Century Maths Advanced 9 - Chapter 6. Geometry PDFOlivia Ngo100% (1)
- Year 3 Maths FulDocumento133 páginasYear 3 Maths Fulmohdzarrin77Ainda não há avaliações
- Prmo Daily Practice Problems: Sub.: Mathematics DPP: 14Documento19 páginasPrmo Daily Practice Problems: Sub.: Mathematics DPP: 14sudhir singh100% (3)
- Solid Mensuration ExamDocumento2 páginasSolid Mensuration ExamDanilo Albay0% (1)
- Solid Mensuration - Chapter 1Documento76 páginasSolid Mensuration - Chapter 1Christian Esteban80% (10)
- Solid MensurationDocumento60 páginasSolid MensurationBenePicar100% (2)
- Solid Mensuration Module 1Documento9 páginasSolid Mensuration Module 1Azha Clarice Villanueva100% (2)
- Engineering Drawing 1 and Plans: ENSC 20112Documento55 páginasEngineering Drawing 1 and Plans: ENSC 20112Christel GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Review MODULE: - Elementary and Higher SurveyingDocumento3 páginasReview MODULE: - Elementary and Higher SurveyingTatingJainar100% (1)
- MATH13 CoursewaresDocumento163 páginasMATH13 CoursewaresPaolo Gochingco75% (4)
- Integral Calculus SyllabusDocumento3 páginasIntegral Calculus SyllabusSpica Dim100% (5)
- Solid MensurationDocumento108 páginasSolid MensurationVittorio Navarro100% (2)
- Statics of Rigid Bodies PDFDocumento8 páginasStatics of Rigid Bodies PDFBESAY REUELAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Functions, Limits and ContinuityDocumento6 páginas1 Functions, Limits and ContinuityReign dropping100% (1)
- 8$20 AreaDocumento26 páginas8$20 AreaBaskaran SeetharamanAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Geom - JFMDocumento26 páginasSolid Geom - JFMJane MañiboAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3 Polyhedrons: Week 5 Math 13 Solid MensurationDocumento21 páginasLesson 3 Polyhedrons: Week 5 Math 13 Solid MensurationDan Casurao100% (1)
- Solid Mensuration MATH 005 (TIP Reviewer)Documento14 páginasSolid Mensuration MATH 005 (TIP Reviewer)James Lindo80% (5)
- Civil Engineering OrientationDocumento16 páginasCivil Engineering OrientationTrishia Mae Patalinghug50% (2)
- Reviewer - Solid MensurationDocumento6 páginasReviewer - Solid MensurationLorenz ArdienteAinda não há avaliações
- Solid MensurationDocumento32 páginasSolid MensurationEdgar Kenneth100% (1)
- Lesson 4 MATH13-1Documento22 páginasLesson 4 MATH13-1akladffja100% (1)
- Lesson 3 MATH13-1Documento23 páginasLesson 3 MATH13-1akladffja100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Math 13-1Documento53 páginasLesson 1 Math 13-1akladffja100% (1)
- Course Syllabus in EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERINGDocumento9 páginasCourse Syllabus in EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERINGRamil S. ArtatesAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Mensuration Problems and Answers PDFDocumento3 páginasSolid Mensuration Problems and Answers PDFjungatbunton100% (1)
- Plane and Solid Geometry Rev 1-20Documento67 páginasPlane and Solid Geometry Rev 1-20Sheila Mae GuadAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Mensuration Problems and AnswersDocumento3 páginasSolid Mensuration Problems and AnswersMaureen Galingan67% (9)
- Prism and CylinderDocumento36 páginasPrism and CylinderCharous Vaughn FabriaAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Mensuration-CHAPTER 4Documento16 páginasSolid Mensuration-CHAPTER 4Daniella Sabac100% (1)
- MATH13 Course SyllabusDocumento5 páginasMATH13 Course SyllabusBryx William GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- And Its Implementing Rules and RegulationsDocumento79 páginasAnd Its Implementing Rules and RegulationsHabyer47100% (1)
- Easy Plane GeometryDocumento2 páginasEasy Plane Geometrylakr lamaAinda não há avaliações
- Topics 1 Solid MensurationDocumento1 páginaTopics 1 Solid MensurationRiel De MesaAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Module - Numerical Solutions To CE Problems - Physical Meaning of Derivatives and IntegralsDocumento12 páginas1st Module - Numerical Solutions To CE Problems - Physical Meaning of Derivatives and IntegralsELSA M. ARCIBAL100% (1)
- Solid Mensuration ReviewDocumento6 páginasSolid Mensuration ReviewUlquiorra GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- SOLIDMensuration Finals TopicsDocumento25 páginasSOLIDMensuration Finals Topicsresolution8878100% (3)
- Mthn14e Lec 2Documento26 páginasMthn14e Lec 2Aly BueserAinda não há avaliações
- Analytic Geometry Module 1Documento3 páginasAnalytic Geometry Module 1John Joshua Montañez100% (3)
- MODULE 4 Plane Geometry Composite FiguresDocumento9 páginasMODULE 4 Plane Geometry Composite FiguresCyndelleAinda não há avaliações
- Two Special Points 1Documento6 páginasTwo Special Points 1Swapnaneel Bhattacharyya100% (1)
- Symmetry, Rotation, Translation, ReflectionDocumento15 páginasSymmetry, Rotation, Translation, ReflectionAnurag Singh100% (1)
- Problem SetDocumento10 páginasProblem SetAnnaAinda não há avaliações
- Solids For Which V BHDocumento26 páginasSolids For Which V BHindaiAinda não há avaliações
- Lectures 7 - Solids (V BH)Documento48 páginasLectures 7 - Solids (V BH)Sandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Solids (V 1) 3bh) ConeDocumento13 páginasSolids (V 1) 3bh) ConeSandra Enn Bahinting0% (1)
- Solids For Which V (Mean B) HDocumento21 páginasSolids For Which V (Mean B) HindaiAinda não há avaliações
- Math 139-1 Lesson 1 and 2 (Latest-Latest)Documento56 páginasMath 139-1 Lesson 1 and 2 (Latest-Latest)Marielle Ansherine GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Mensuration: Solids For Which Volume, V BHDocumento35 páginasSolid Mensuration: Solids For Which Volume, V BHKate ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- M1 +Review+of+Mathematical+FoundationsDocumento4 páginasM1 +Review+of+Mathematical+FoundationsKpop HarteuAinda não há avaliações
- Analytic and Solid Mensuration FINALSDocumento6 páginasAnalytic and Solid Mensuration FINALSJacky Boy Endencio Atienza100% (4)
- Birds Comp EM Sol To Exerc Chap 29 2017Documento35 páginasBirds Comp EM Sol To Exerc Chap 29 2017MarkAinda não há avaliações
- Solid MensurationDocumento13 páginasSolid MensurationJann Michael Carpio100% (1)
- CIVIL ENGINEERING ORIENTATION - Module 5 PDFDocumento7 páginasCIVIL ENGINEERING ORIENTATION - Module 5 PDFAntonio RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- Area ComputationDocumento11 páginasArea ComputationRubie FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Solid MensurationDocumento44 páginasSolid MensurationKay PorrasAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 8 9 - Solid MensurationDocumento9 páginasLecture 8 9 - Solid MensurationJames Phillip CustodioAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 15 - Mathematical Systems PDFDocumento2 páginasLesson 15 - Mathematical Systems PDFPeter EcleviaAinda não há avaliações
- REVIEW MODULE (Plane and Solid Geometry V2)Documento4 páginasREVIEW MODULE (Plane and Solid Geometry V2)Lenielle Amatosa100% (1)
- Module 1 Measurement VectorDocumento25 páginasModule 1 Measurement VectorGreen BrainAinda não há avaliações
- Lustre SurveyingHWDocumento3 páginasLustre SurveyingHWJhon Christian De GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Solid MensurationDocumento5 páginasSolid MensurationJenny E. Forcadilla100% (1)
- MODULE 1 Analytic GeometryDocumento8 páginasMODULE 1 Analytic Geometrysimonjohn spanglerAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Data AnalysisDocumento5 páginasEngineering Data AnalysisJoshuaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Part 1Documento16 páginasChapter 3 Part 1KokieAinda não há avaliações
- Archmath1.Module 2Documento27 páginasArchmath1.Module 2ruthzieAinda não há avaliações
- Angle PropertiesDocumento5 páginasAngle PropertiesCatalin SapariucAinda não há avaliações
- Geometry EOC Practice Test: Division of Mathematics. Office of Academics and TransformationDocumento41 páginasGeometry EOC Practice Test: Division of Mathematics. Office of Academics and TransformationJohn SmithAinda não há avaliações
- 1 3 1 5 2Documento42 páginas1 3 1 5 2Himanshu GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- A Polyhedral Compound Is A Polyhedron That Is Itself Composed of Several Other Polyhedra Sharing A Common CentreDocumento6 páginasA Polyhedral Compound Is A Polyhedron That Is Itself Composed of Several Other Polyhedra Sharing A Common CentrepomzAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Polygo-WPS OfficeDocumento5 páginasTypes of Polygo-WPS OfficeChrishelle Grace CamanianAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd Quarterly Exam in Mathematics 4Documento9 páginas3rd Quarterly Exam in Mathematics 4Jaycer De MesaAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Education: 2 QUARTER Summative Test Grade 8 Carpentry Multiple Choice: Directions: Select The BestDocumento5 páginasDepartment of Education: 2 QUARTER Summative Test Grade 8 Carpentry Multiple Choice: Directions: Select The Bestlouie vertudazoAinda não há avaliações
- 6-Introduction To PolygonsDocumento4 páginas6-Introduction To PolygonsAymenAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Triangle Congruence PacketDocumento5 páginas7 Triangle Congruence Packetapi-243405443Ainda não há avaliações
- PT - Mathematics 5 - Q3Documento7 páginasPT - Mathematics 5 - Q3Glenford dela TorreAinda não há avaliações
- Miles C. Hartley - Patterns of PolyhedronsDocumento50 páginasMiles C. Hartley - Patterns of PolyhedronsneweliAinda não há avaliações
- Quarter 3 QuizDocumento8 páginasQuarter 3 QuizEdimar RingorAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 5 - Worksheet 3 QuadrilateralsDocumento4 páginasGrade 5 - Worksheet 3 QuadrilateralsHasan FarazAinda não há avaliações
- Activities 3rdDocumento11 páginasActivities 3rdJassim MagallanesAinda não há avaliações
- Pogchamp 2020Documento2 páginasPogchamp 2020Ashok DargarAinda não há avaliações
- Good Hope School - 16 21 2B Ch.10 Angles Related To Triangles and Polygons CQDocumento3 páginasGood Hope School - 16 21 2B Ch.10 Angles Related To Triangles and Polygons CQLincolnAinda não há avaliações
- The New Version of The Tangram Puzzle: Lecturer Wen-Hsien SUNDocumento191 páginasThe New Version of The Tangram Puzzle: Lecturer Wen-Hsien SUNMAUREEN LAVARIASAinda não há avaliações
- ShapesDocumento70 páginasShapesdarlene bianzonAinda não há avaliações
- Triangles: Equilateral, Isosceles and ScaleneDocumento8 páginasTriangles: Equilateral, Isosceles and ScaleneRoyuss SokooAinda não há avaliações
- Perimeter and AreaDocumento12 páginasPerimeter and AreaElaikah Keith Dato-onAinda não há avaliações
- Polygons: Submitted By, Reshma S Ravi Mathematics OptionDocumento15 páginasPolygons: Submitted By, Reshma S Ravi Mathematics OptionPrasant NatarajanAinda não há avaliações
- WWW Nexuslearning Net Books Ml-Geometry Chapter4 ML Geometry Chapter 4 Review-TestDocumento4 páginasWWW Nexuslearning Net Books Ml-Geometry Chapter4 ML Geometry Chapter 4 Review-Testapi-232613595Ainda não há avaliações