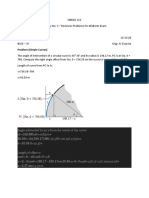
Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Summative Test All
Enviado por
Lairepmi EmjaneTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Summative Test All
Enviado por
Lairepmi EmjaneDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
PLEASE READ!!!
REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,2,3,4,5,6,7
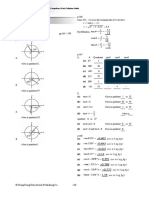
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 2, and 3.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#1, letters a and b.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 8,9,10,11,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 4, 5, and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#1, letters c and d.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,3,5,7,9,11,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 3, and 5.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#1, letters a and e.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,3,6,8,10,12
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 2, 4, and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#1, letters b and c.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 4,7,8,9,10,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 5, and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#1, letters d and e.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,2,3,5,6,11,12
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 2, 3 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters a and b.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 3,6,7,10,11,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 3 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters c and d.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,2,4,5,8,9,12
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
Tangent
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 2 and 5.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters a and e.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 3,6,7,9,10,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,2,4,5,8,11
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 3 and 4..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters d and e.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,5,7,8,9,11
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 2 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
Answer # 4 and 5.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,3,4,6,10,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
Tangent
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 2, 5 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 139
Answer # 6 and 7.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 3,4,5,7,8,9
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 2 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 139
Answer # 8 and 9.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,2,6,10,11,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 5 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138-139
Answer #4 and 9.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,3,4,7,8,9,10
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1,2,3,4,5 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,5,6,11,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 2, 4 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters a,b,c, d and e.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 4,6,8,9,10,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 3 and 4.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#4 and #5
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,2,3,5,7,11
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 2, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
Answer #4 and #8
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,5,6,7,8,9
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 3, 4 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
Answer # 5 and #7.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’ 1,3,4,10,11,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
Answer #7 and #8.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,4,6,7,9,10,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 5 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 139
Answer #6 and #9
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,3,5,8,11,12
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 3, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 139
Answer #5 and 9.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,3,6,7,9,10,11
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 2, 3 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
Answer all under #2.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,4,5,8,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 2 and 4.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
Answer #4 and #8
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 3,6,9,10,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 3, 4, 5 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters a, b,and c.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,2,4,5,7,8,11
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 2, 3, 4 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,6,7,8,9,10
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 4 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#3 and #4
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,3,4,5,11,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1,2,3, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters a and c.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 3,6,7,9,10,11,12
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1,3, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b,c, and e.
#3 and #4
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,2,4,5,8,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1 up to 6
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters a up to e.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,5,6,8,9,10
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 4 , 5 and 6.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#3 and #4
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,3,4,7,11,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 2 to 4.
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b, c and d.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,5,7,10,11,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1,2, 3 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#3, #4 and #5.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,3,4,6,8,9,12
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 139
Answer #6 up to #9
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 4,7,8,10,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#3, #4 and #5.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,2,3,5,6,9,11
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1,2, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters a to e.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,5,6,8,10,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#3 to #7.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,3,4,7,9,11,12
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,4,6,7,9,10,11
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1 up to 6
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
Answer #2 and #3.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,3,5,8,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#3
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,3,5,8,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
Answer #6 to #8
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,2,5,7,9,10,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1,3, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters a to d.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 3,4,6,8,11,12
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 2,3, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, #4 and #6.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,4,6,9,11,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#3 and #7.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,3,5,7,8,10
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1,2, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
Answer from #3 to #8.
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 2,9,10,11,12,13
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 2,3, 4 and 5..
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 138
#2, letters b and c.
#3 and #4
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Summative test: pages 101-103
Answer the following: show all the solutions. (Short bond paper, and compile in a
short white folder)
#’s 1,3,4,5,6,7,8
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve formed by a set of points on a plane that
are the same distance from its center O. That distance is known as the radius of
the circle.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the
circle and has its endpoints on the circle. All the diameters of the same circle have
the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with both endpoints on the circle. The diameter is a
special chord that passes through the center of the circle. The diameter would be
the longest chord in the circle.
Radius
The radius of the circle is a line segment from the center of the circle to a point on
the circle. The plural of radius is radii.
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A tangent is
perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. The point of tangency is where
a tangent line touches the circle.
Parts of a Circle
The following video gives the definitions of a circle, a radius, a chord, a diameter,
secant, secant line, tangent, congruent circles, concentric circles, and intersecting
circles.
A secant line intersects the circle in two points.
A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at one point.
A point of tangency is where a tangent line touches or intersects the circle.
Congruent circles are circles that have the same radius but different centers.
Concentric circles are two circles that have the same center, but a different radii.
Intersecting Circles: Two circles may intersect at two points or at one point. If
they intersect at one point then they can either be externally tangent or internally
tangent.
Two circles that do not intersect can either have a common external tangent or
common internal tangent.
In the common external tangent, the tangent does not cross between the two
circles.
In the common internal tangent, the tangent crosses between the two circles.
Arc of a Circle
An arc is any connected part of the circumference of a circle.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
PLEASE READ!!! REFER TO YOUR MATHEMATICS BOOK FOR THE ACTIVITIES
(DON’T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME AND SECTION)
An arc could be a minor arc, a semicircle or a major arc.
A semicircle is an arc that is half a circle.
A minor arc is an arc that is smaller than a semicircle.
A major arc is an arc that is larger than a semicircle.
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle.
Arc Measure
The measure of a semicircle is 180°.
The measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that
intercepts the arc. We can also say that the measure of a minor arc is equal to the
measure of the central angle that is subtended by the arc.
Circles Worksheets:
Answer activity # 2 page 137
#’s 1 up to #4
And answer questions a and b.
Activity # 3 page 139
#7 up to #9
List all the POSTULATES, AXIOMS and THEOREMS involving CIRCLES.
SHOW ALL POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS AND PROCESS.
Você também pode gostar
- Theorems On Two Intersecting ChordsDocumento5 páginasTheorems On Two Intersecting ChordsJayAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Resource Package: Quarter I Subject: MATH Date: - Day: 1 Content StandardDocumento12 páginasMathematics Resource Package: Quarter I Subject: MATH Date: - Day: 1 Content StandardLowie D GacetaAinda não há avaliações
- Math DLP 16 Q1Documento3 páginasMath DLP 16 Q1Norjana Otto Medal-MadaleAinda não há avaliações
- Illustrating and Differentiating Terms Related To AlgebraDocumento7 páginasIllustrating and Differentiating Terms Related To AlgebraNico ValeraAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 10 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level 10 Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Quarter SecondDocumento11 páginasGrade 10 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level 10 Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Quarter SecondMichael Beniga0% (1)
- DLP CombinationDocumento10 páginasDLP CombinationAlexis Magana100% (1)
- Weekly Home Learning Plan For Mathematics 10 (Modular Distance Learning)Documento2 páginasWeekly Home Learning Plan For Mathematics 10 (Modular Distance Learning)Rochelle100% (1)
- PermutationDocumento6 páginasPermutationKaren DamasoAinda não há avaliações
- III-Day 2Documento4 páginasIII-Day 2Rainman InsanityAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 1-12 Daily Lesson Log: Learning PlanDocumento8 páginasGrade 1-12 Daily Lesson Log: Learning PlanJesusa Salvador JardinelAinda não há avaliações
- Range and Standard Deviation Lesson PlanDocumento7 páginasRange and Standard Deviation Lesson Planapi-266325800Ainda não há avaliações
- Fourth Periodical Test in Math 10 2019 2020Documento5 páginasFourth Periodical Test in Math 10 2019 2020Jaycelyn Magboo BritaniaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson PlanDocumento5 páginasLesson PlanMark John Dy Dayto100% (2)
- The Following Are The Steps in Constructing Perpendicular Bisector of A Segment Using A Compass and A StraightedgeDocumento4 páginasThe Following Are The Steps in Constructing Perpendicular Bisector of A Segment Using A Compass and A StraightedgeAnjelo Amar BarcenasAinda não há avaliações
- Mod Geo - Lesson 2Documento15 páginasMod Geo - Lesson 2Saudia Charylle Clent VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Distance & Midpoint Formula, Coordinate ProofDocumento2 páginasDistance & Midpoint Formula, Coordinate Proofben muddasir100% (1)
- Math - Grade7 Q1 Module 4 - Expresses Rational Numbers From Fraction Form To Decimal Form and Vice Versa.Documento11 páginasMath - Grade7 Q1 Module 4 - Expresses Rational Numbers From Fraction Form To Decimal Form and Vice Versa.Kitty GengAinda não há avaliações
- M103 Detailed Lesson Plan Undefined TermsDocumento4 páginasM103 Detailed Lesson Plan Undefined TermsQaillah Shane Quilla100% (1)
- Lesson 30 (Geometry) - Basic Concepts and Terms - LGDocumento10 páginasLesson 30 (Geometry) - Basic Concepts and Terms - LGSwag Mooshroom100% (1)
- DLP 3Documento2 páginasDLP 3Pablo JimeneaAinda não há avaliações
- Mastery Test in Mathematics 10 Quarter 3 Weeks 1 & 2: San Guillermo National High SchoolDocumento9 páginasMastery Test in Mathematics 10 Quarter 3 Weeks 1 & 2: San Guillermo National High SchoolSheila Mauricio GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Q4 A.S. Measures of Position For Grouped DataDocumento9 páginasQ4 A.S. Measures of Position For Grouped Datasunshine batoyAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocumento8 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsResa MaeAinda não há avaliações
- 2023 Lesson Exemplar in Mathematics 10 PermutationDocumento3 páginas2023 Lesson Exemplar in Mathematics 10 PermutationRoxan OndoyAinda não há avaliações
- Math10 - q2 - Mod3of8 - Theorems On Chords Arcs Central Angles and Inscribed Angles - v2Documento21 páginasMath10 - q2 - Mod3of8 - Theorems On Chords Arcs Central Angles and Inscribed Angles - v2Ledesma, Elijah O.Ainda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocumento8 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsHazel Recites Bernaldez100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Measures of PositionDocumento11 páginasChapter 4 - Measures of PositionFLIPTOP ANALYSISAinda não há avaliações
- Week 3-Day2 DLP (Asuncion, Alwin C.)Documento12 páginasWeek 3-Day2 DLP (Asuncion, Alwin C.)Chello Ann Pelaez AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Cot 2Documento5 páginasCot 2Alfredo Macadangdang Angel Jr.Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson ExemplarDocumento5 páginasLesson ExemplarMsVange A LptAinda não há avaliações
- Measure of Central TendencyDocumento2 páginasMeasure of Central TendencykiahjessieAinda não há avaliações
- Group 8: Grade 7 Mathematics Fourth QuarterDocumento17 páginasGroup 8: Grade 7 Mathematics Fourth QuarterChang CarelAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics: Quarter 4 - Module 34 Measures of Position of Grouped DataDocumento31 páginasMathematics: Quarter 4 - Module 34 Measures of Position of Grouped DataZT EstreraAinda não há avaliações
- EASE Module 3 Triangle CongruenceDocumento25 páginasEASE Module 3 Triangle CongruenceVengie PamanAinda não há avaliações
- MATH10 QUARTER 2 Week 2 DLLDocumento8 páginasMATH10 QUARTER 2 Week 2 DLLkich100% (2)
- K To 12 Curriculum Guide: MathematicsDocumento18 páginasK To 12 Curriculum Guide: Mathematicseiz catAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1 Probability BingoDocumento4 páginasLesson 1 Probability Bingoapi-253261408Ainda não há avaliações
- Percentile Rank Worksheet 5Documento2 páginasPercentile Rank Worksheet 5Era BarrientosAinda não há avaliações
- GRABSUM School Inc. Inc.: Flexible Instructional Delivery PlanDocumento3 páginasGRABSUM School Inc. Inc.: Flexible Instructional Delivery PlanLavander BlushAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan On Statistical Mini-Research - Used Research BasedDocumento2 páginasLesson Plan On Statistical Mini-Research - Used Research Basedgilbert immoliapAinda não há avaliações
- E - Portfolio in Mathematics 10: Submitted By: Binas, Ayumi A. 10 Rizal Submitted To: Ma'am Evelyn ResuelloDocumento11 páginasE - Portfolio in Mathematics 10: Submitted By: Binas, Ayumi A. 10 Rizal Submitted To: Ma'am Evelyn ResuelloAyumi BiñasAinda não há avaliações
- Stem Basic Calculus CGDocumento5 páginasStem Basic Calculus CGapi-323289375Ainda não há avaliações
- Addition Hills Integrated School: A. Content Standard B. Performance Standard C. Learning CompetenciesDocumento5 páginasAddition Hills Integrated School: A. Content Standard B. Performance Standard C. Learning CompetenciesAnonuevo Louie100% (1)
- Instructional Plan On Probability: Simple EventsDocumento2 páginasInstructional Plan On Probability: Simple EventsMAE CAinda não há avaliações
- Module 7.other Formative AssessmentDocumento17 páginasModule 7.other Formative AssessmentMaria Janna Ivy MontejoAinda não há avaliações
- 2022 Stat Analysis Module 4 Parametric Test RDocumento18 páginas2022 Stat Analysis Module 4 Parametric Test RArsenio N. RojoAinda não há avaliações
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 8 Mathematics ON Basic Concepts of ProbabilityDocumento5 páginasA Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 8 Mathematics ON Basic Concepts of ProbabilityRachel Mae Roque EnarioAinda não há avaliações
- LeaP Math G10 Week 8 Q3Documento3 páginasLeaP Math G10 Week 8 Q3Aldos, Jayacinzyra P.Ainda não há avaliações
- DLP 29Documento4 páginasDLP 29Pablo JimeneaAinda não há avaliações
- New Math Grade 10 Quiz Quartile Decile PercentileDocumento7 páginasNew Math Grade 10 Quiz Quartile Decile PercentilePaul PollAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Math 9 Lesson PlanDocumento10 páginasDetailed Math 9 Lesson PlanGraceRasdas0% (1)
- Grade 7 Math PolynomialsDocumento1 páginaGrade 7 Math PolynomialsLeigh YahAinda não há avaliações
- MATH 8 SLHT, Q3, Wk1-2 M8GE-IIIa-1 & M8GE-IIIa-c-1Documento15 páginasMATH 8 SLHT, Q3, Wk1-2 M8GE-IIIa-1 & M8GE-IIIa-c-1Zia Belle Bedro - LuardoAinda não há avaliações
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF M11GM-Ih-i-1 (Week Nine - Day One)Documento2 páginasDAILY LESSON LOG OF M11GM-Ih-i-1 (Week Nine - Day One)Nelson MaraguinotAinda não há avaliações
- DLP (Ndkc-Ibed) in Grade 10Documento4 páginasDLP (Ndkc-Ibed) in Grade 10cathline austriaAinda não há avaliações
- The Learner : Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan Second Quarter Topic Title: Content Standard Performance StandardsDocumento2 páginasThe Learner : Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan Second Quarter Topic Title: Content Standard Performance StandardsMGrace P. VergaraAinda não há avaliações
- Math 7 - Q4, WK2 LasDocumento4 páginasMath 7 - Q4, WK2 LasNiña Romina G. NavaltaAinda não há avaliações
- Semi - Finals in Math 10Documento3 páginasSemi - Finals in Math 10Mari Zechnas OsnolaAinda não há avaliações
- April 13 Applies Triangle Congruence To Construct PerpendicularDocumento3 páginasApril 13 Applies Triangle Congruence To Construct PerpendicularryanAinda não há avaliações
- Circles ModifiedDocumento134 páginasCircles ModifiedHermione ClydeAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation1 (Geometric Sequence)Documento28 páginasPresentation1 (Geometric Sequence)Lairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Write An Essay and Reaction Paper of Each of The FollowingDocumento14 páginasWrite An Essay and Reaction Paper of Each of The FollowingLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Supervision Communication LettersDocumento6 páginasSupervision Communication LettersLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Remainder TheoremDocumento12 páginasRemainder TheoremLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Arcs of A Circles: Strategic Intervention Materials in Mathematics 10Documento2 páginasArcs of A Circles: Strategic Intervention Materials in Mathematics 10Lairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- The Effect of Digital Apparatus On Mathematics Learning Among Grade 10-Bronze Students of Malangas National High SchoolDocumento20 páginasThe Effect of Digital Apparatus On Mathematics Learning Among Grade 10-Bronze Students of Malangas National High SchoolLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Simplify The Following Polynomials and Evaluate at XDocumento3 páginasSimplify The Following Polynomials and Evaluate at XLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Ungrouped DataDocumento5 páginasUngrouped DataLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Remaining Topics For 1st QuarterDocumento2 páginasRemaining Topics For 1st QuarterLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- The Role of The Principal in SchoolsDocumento3 páginasThe Role of The Principal in SchoolsLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocumento3 páginasRepublic of The PhilippinesLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Educational PsychologyDocumento8 páginasWhat Is Educational PsychologyLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Supervision Reflection PaperDocumento1 páginaSupervision Reflection PaperLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Grouped DataDocumento3 páginasWhat Is Grouped DataLairepmi EmjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Module 2a (Tension Members With Staggered Holes)Documento4 páginasModule 2a (Tension Members With Staggered Holes)Jordan BalagotAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus Test For Wedensday 003Documento7 páginasCalculus Test For Wedensday 003Prisha ShettyAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE 7 Symmetry WS1Documento4 páginasCBSE 7 Symmetry WS1sumita ghoshAinda não há avaliações
- Modeling, Estimation and Attitude Control of An Octorotor Using PID and L1 Adaptive Control TechniquesDocumento137 páginasModeling, Estimation and Attitude Control of An Octorotor Using PID and L1 Adaptive Control TechniquesColDfireAinda não há avaliações
- The Quarry Device of Ed LeedskalninDocumento16 páginasThe Quarry Device of Ed Leedskalninoveryounity0% (1)
- Pstricks: User'S GuideDocumento338 páginasPstricks: User'S GuideJeff Pratt100% (4)
- Adams Tire Mdr3 Help-152Documento388 páginasAdams Tire Mdr3 Help-152Thu DaoAinda não há avaliações
- Hw7 SolutionsDocumento12 páginasHw7 SolutionsDivya pandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Problem 2.1: SolutionDocumento161 páginasProblem 2.1: SolutionFernanda MorenoAinda não há avaliações
- Weekly Home Learning Plan 1st Distribution 4th QuarterDocumento4 páginasWeekly Home Learning Plan 1st Distribution 4th QuarterRichelle Cayubit Dela Peña-LosdoAinda não há avaliações
- Class 6 MathsDocumento2 páginasClass 6 Mathsfgh ijkAinda não há avaliações
- Bk5 Sol C14 EDocumento36 páginasBk5 Sol C14 EMa Ka YiAinda não há avaliações
- Trigo PreboardDocumento26 páginasTrigo PreboardMichael Beltran100% (1)
- Tau ManifestoDocumento29 páginasTau ManifestoLeighton DawsonAinda não há avaliações
- Problem (Simple Curves)Documento9 páginasProblem (Simple Curves)arvin paruliAinda não há avaliações
- WeeblyDocumento6 páginasWeeblyapi-383617357Ainda não há avaliações
- 2 - Terminology of Directional Drilling - 27!10!2022Documento42 páginas2 - Terminology of Directional Drilling - 27!10!2022علي سعيد سعودAinda não há avaliações
- Spe 84246 MSDocumento16 páginasSpe 84246 MSGilberto Garcia de la PazAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Manual Activities For Term-IIDocumento12 páginasLab Manual Activities For Term-IImistique707Ainda não há avaliações
- Horizontal Curves-Superelevation-And Geometric Design StandardsDocumento41 páginasHorizontal Curves-Superelevation-And Geometric Design Standardsmannie edet100% (1)
- Caie Checkpoint Mathematics Geometry and Measure v1Documento10 páginasCaie Checkpoint Mathematics Geometry and Measure v1Shame BopeAinda não há avaliações
- Math 10 - Lines, Segments and Arcs Associated With CircleDocumento102 páginasMath 10 - Lines, Segments and Arcs Associated With CirclePhilodox xodolihP100% (1)
- IS - ISO 16322-1 (2005) - Textiles - Determination of Spirality After Laundering, Part 1 - Percentage of Wale Spirality Change in Knitted GarmentsDocumento11 páginasIS - ISO 16322-1 (2005) - Textiles - Determination of Spirality After Laundering, Part 1 - Percentage of Wale Spirality Change in Knitted GarmentsCella ChenAinda não há avaliações
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizDocumento32 páginasWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizDima TabeshAinda não há avaliações
- Azimuth ChangeDocumento4 páginasAzimuth ChangeLazuardhy Vozicha Futur0% (1)
- Analytical and Experimental Characterisation of High-Precision Flexural Pivots Subjected To Lateral LoadsDocumento8 páginasAnalytical and Experimental Characterisation of High-Precision Flexural Pivots Subjected To Lateral LoadssharanbietAinda não há avaliações
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 9Documento2 páginasSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 9Patrick Aniro67% (3)
- Lesson Plan On Theorems On Angles FormedDocumento5 páginasLesson Plan On Theorems On Angles Formedmarygrace idanan100% (5)
- Calculation For Angle of ListDocumento3 páginasCalculation For Angle of ListMohd RahmatAinda não há avaliações
- WING SPAR PresentationDocumento67 páginasWING SPAR Presentationdillikannan007Ainda não há avaliações