Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
ECG With Image
Enviado por
mathavanDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ECG With Image
Enviado por
mathavanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH (ECG)
This is the technique by which the electrical activities of the heart are studied.
Electrocardiograph:
This is the instrument by which the electrical activities of the heart are recorded.
Electrocardiogram:
This is the record or graphical registration of electrical activities of the heart.
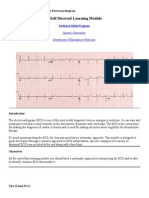
1. ECG Waveforms
P Wave
Q Wave
R Wave
S Wave
T Wave
2. Einthoven Triangle
3. Bipolar limb leads or Standard leads or Einthoven lead system
Lead I
Lead II
Lead III
4. Augmented unipolar limb lead or Wilson Lead System
Augmented Voltage Right Arm (aVR)
Augmented Voltage Left Arm (aVL)
Augmented Voltage Foot (aVF)
5. Unipolar chest leads
6. ECG Recording Method
Defibrillator Protection Circuit
Lead Selection Logic
Calibration Circuit
Pre Amplifier
Power Amplifier
Auxiliary Amplifier
Feedback Network
Display Unit
N.Mathavan || AP – ECE – NSCET
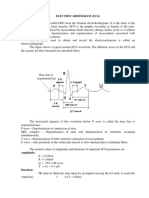
ECG Waveforms
Einthoven was the inventor of the first device capable of printing the ECG on paper.
Einthoven named the waves using five capital letters from the alphabet: P, Q, R, S &T.
The width of a wave on the horizontal axis represents a measure of time.
The height and depth of a wave represent a measure of voltage.
An upward deflection of a wave is called positive deflection
A downward deflection is called negative deflection.
S. Amplitude Duration
Wave/ Segment Cause
No (mV) (sec)
1 P Wave Depolarization of atria 0.25 0.12 to 0.22
R Wave Re-polarization of atria and Depolarization of
2 ventricles 1.6 0.07 to 0.1
(QRS Complex)
3 T Wave Re-polarization of ventricles 0.1 to 0.5 0.05 to0.15
Slow re-polarization of
4 U Wave <0.1 0.2
Intra ventricular(Purkinje fibers) system
N.Mathavan || AP – ECE – NSCET
Einthoven Triangle
The closed path RA to LA to LL and back to RA is called as Einthoven Triangle.
The vector sum of the projections on all the three sides is equal to zero.
Applying KVL, the R wave amplitude of lead II is equal to the sum of the R wave
amplitudes of Lead I and Lead III.
The R wave nominal voltage from different
lead is as given below.
Lead I - 0.53 mv (0.07 - 1.13) mv
Lead II - 0.71 mv (0.18 - 1.68) mv
Lead III - 0.38 mv (0.03 - 1.31) mv
By KVL VII = VI + VIII
Bipolar limb leads or Standard Leads or Einthoven lead system
In this lead system, the potentials are tapped from four locations of our body.
They are: i) Right arm (RA) ii) Left arm (LA) iii) Right Leg (RL) iv) Left Leg (LL)
The Right Leg (RL) electrode acts as the reference electrode.
Lead I:
It is a lead obtained between a
negative electrode placed on the
right arm (RA) and a positive
electrode placed on the
left arm (LA). It gives voltage VI
the voltage drop from the
left arm (LA) to the
right arm (RA).
Lead II:
It is a lead obtained between a negative electrode placed on the right arm (RA) and a
positive electrode placed on the left leg (LL). It gives voltage VII, the voltage drop from
the left leg (LL) to the right arm (RA).
N.Mathavan || AP – ECE – NSCET
Lead III:
It is a lead obtained between a negative electrode placed on the left arm (LA) and
a positive electrode placed on the left Leg (LL). It gives voltage VIII, the voltage drop
from the left leg (LL) to the left arm (LA).
Augmented Unipolar Limb Leads
Wilson introduced augmented unipolar limb lead system. The electrocardiogram is
recorded between a single electrode and the central terminal, which has a potential
corresponding to the center of the body.
Thus, two equal and large resistors are connected to a pair of limb electrodes and the
center of this resistive network.
The remaining limb electrode acts as exploratory single electrode.
By means of augmented ECG lead connections, a small increase in the ECG voltage
can be realized.
The augmented lead connections are,
Augmented voltage Right arm (aVR)
It is a lead obtained between the average signal obtained from three negative electrodes
(left arm, left leg and right foot) and the signal obtained from a positive electrode placed on
the right arm
Augmented voltage Left arm (aVL)
It is a lead obtained between the average signal obtained from three negative electrodes
(right arm, left foot and right foot) and the signal obtained from a positive electrode placed
on the left arm
Augmented voltage Foot arm (aVF)
It is a lead obtained between the average signal obtained from three negative electrodes
(left arm, right arm and right foot) and the signal obtained from a positive electrode placed
on the left foot
N.Mathavan || AP – ECE – NSCET
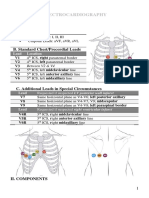
Unipolar Chest Lead
In unipolar chest leads, the exploratory electrode is obtained from one of the chest
electrodes. The chest electrodes are placed at six different points on the chest close to the
heart.
By connecting 3 equal large resistors to RA, RL, LL, a central terminal is obtained. This
lead system is known as Wilson lead system.
Vl: is a lead obtained between the reference negative electrode and a positive electrode
placed on the chest in the V1 position
V2: is a lead obtained between the reference negative electrode and a positive electrode
placed on the chest in the V2 position
V3: is a lead obtained between the reference negative electrode and a positive electrode
placed on the chest in the V3 position
V4: is a lead obtained between the reference negative electrode and a positive electrode
placed on the chest in the V4 position
V5: is a lead obtained between the reference negative electrode and a positive electrode
placed on the chest in the V5 position.
N.Mathavan || AP – ECE – NSCET
V6: is a lead obtained between the reference negative electrode and a positive electrode
placed on the chest in the V6 position.
ECG Recording Method
Defibrillator Protection Circuit
The protection circuit
Employs
• Buffer Amplifier
(To Increase I/P Impedance)
• Over Voltage Protection Circuits
(Protect Pre & Power Amplifier
from over voltage)
Lead Selection Logic
It s used to select Lead type either
Bipolar or Augmented
Calibration Circuit
While selecting lead some artifact is introduce at output, by using calibration circuit can
calibrate the O/P unit.
Pre Amplifier
From the lead selector switch, the ECG signal goes to a preamplifier, a differential
amplifier with high common-mode rejection. It is ac-coupled to avoid problems with
N.Mathavan || AP – ECE – NSCET
small dc voltages that may originate from polarization of the electrodes.
Power Amplifier
The preamplifier is followed by a dc amplifier called the power (Pen) amplifier, which
provides the power to drive the pen motor that records the actual ECG trace.
Auxiliary Amplifier
Pre Amplifier are not sufficient for eliminate the common mode signal, because impedance
of all electrodes are not equal. So auxiliary amplifier is used.
Feedback Network
Feedback N/W consist of R-C circuit. It provides necessary damping to the pen motor
Display Unit
CRO or Paper chart recorder is used as O/P unit, generally, paper chart is used.
Electrocardiograms are recorded at a paper speed of 25 mm/sec
N.Mathavan || AP – ECE – NSCET
Você também pode gostar
- ECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasNo EverandECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- BDSM List FixedDocumento4 páginasBDSM List Fixedchamarion100% (3)
- Nursing Practice Skills: Adult Intensive Care Unit PatientsDocumento10 páginasNursing Practice Skills: Adult Intensive Care Unit PatientsMona Doria67% (3)
- ECG WorldDocumento139 páginasECG WorldsatyaAinda não há avaliações
- ABS Rules For Cable SizingDocumento2 páginasABS Rules For Cable SizingMohammed JassimAinda não há avaliações
- Modul EKGDocumento101 páginasModul EKGAjeng Dwik01Ainda não há avaliações
- ECG InterpretationDocumento48 páginasECG InterpretationKervayse St.ClairAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Module PrintableDocumento39 páginasECG Module PrintableAbu HibbaanAinda não há avaliações
- Building SOR 01.12.2020 Volume 1Documento437 páginasBuilding SOR 01.12.2020 Volume 1Shiv Shankar Shukla82% (11)
- Ecg 111029102429 Phpapp01Documento103 páginasEcg 111029102429 Phpapp01Vickry WahidjiAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Interpretation: DR S J Bhosale DM, FPCC (Canada) Associate Professor Tata Memorial CentreDocumento90 páginasECG Interpretation: DR S J Bhosale DM, FPCC (Canada) Associate Professor Tata Memorial Centrevaishali TayadeAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrocardiogramDocumento52 páginasElectrocardiogramTuong HoangManhAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg PresentationDocumento42 páginasEcg PresentationAnwar SiddiquiAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg in DogsDocumento107 páginasEcg in DogsPLABITA GOSWAMI100% (2)
- Didactics ECGDocumento87 páginasDidactics ECGGenesis Poblacion100% (1)
- Street Design Manual NYCDocumento312 páginasStreet Design Manual NYCgonleoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To ECG For NursingDocumento75 páginasIntroduction To ECG For NursingRashid AlHamdan100% (1)
- Electrical TimeDocumento14 páginasElectrical TimeNithyaa SathishAinda não há avaliações
- REM Geo&Man Comp 2016Documento350 páginasREM Geo&Man Comp 2016youungAinda não há avaliações
- Electrocardiography: I. Leads A. Limb LeadsDocumento11 páginasElectrocardiography: I. Leads A. Limb LeadsJoezelle0% (1)
- Compressed Air Pressure Drop DiagramDocumento4 páginasCompressed Air Pressure Drop DiagramycemalAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg Physio LectureDocumento60 páginasEcg Physio LectureAninze Chidera100% (1)
- Electrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGDocumento76 páginasElectrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGInnocent Clifford MaranduAinda não há avaliações
- Biomedical Instrumentation (BM8502)Documento34 páginasBiomedical Instrumentation (BM8502)1011 BMEAinda não há avaliações
- Bio SignalDocumento20 páginasBio SignalThiyagu RajanAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrocardiographDocumento5 páginasElectrocardiographGeorge MagedAinda não há avaliações
- Biopotential AmplifiersDocumento94 páginasBiopotential AmplifiersAhmed Magdy HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Waleed Abdel Aziz Salem Attia - ECG (L1-L2-L3)Documento57 páginasWaleed Abdel Aziz Salem Attia - ECG (L1-L2-L3)Mandy745Ainda não há avaliações
- Project 2 Electrocardiography: Practical TasksDocumento16 páginasProject 2 Electrocardiography: Practical TasksFahad ShahidAinda não há avaliações
- Lab ManualDocumento33 páginasLab Manualg8248418302Ainda não há avaliações
- Ec 8073 - Medical Electronics Unit - I Electro - Phisiology and Bio Potential RecordingDocumento9 páginasEc 8073 - Medical Electronics Unit - I Electro - Phisiology and Bio Potential RecordingJackie SparrowAinda não há avaliações
- 2020 EcgDocumento49 páginas2020 EcgHannah HalimAinda não há avaliações
- The Physiological Basis of The EkgDocumento87 páginasThe Physiological Basis of The EkgYS NateAinda não há avaliações
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Base Line or Isopotential LineDocumento15 páginasElectrocardiogram (Ecg) : Base Line or Isopotential Linegyspsunshine girlAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11-The Normal ElectrocardiogramDocumento18 páginasChapter 11-The Normal Electrocardiogrammuna s100% (1)
- Characteristics of Blood FlowDocumento11 páginasCharacteristics of Blood FlowPriyamvada VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Electrophysiology of The HeartDocumento27 páginasElectrophysiology of The HeartTsegaye HailuAinda não há avaliações
- The Electrocardiogram: Ecg: by Gaurishi Agarwal, 32Documento17 páginasThe Electrocardiogram: Ecg: by Gaurishi Agarwal, 32Gaurishi AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- 6 7 8 Biopotential AmplifiersDocumento67 páginas6 7 8 Biopotential Amplifiersahmed kakaAinda não há avaliações
- EcgDocumento18 páginasEcgmyla adapAinda não há avaliações
- A Guide TO: Noob'SDocumento103 páginasA Guide TO: Noob'SAgleema AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) : This Is The Lecture No. 4Documento51 páginasElectrocardiogram (ECG) : This Is The Lecture No. 4Aboodsha ShAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg PrsentationDocumento33 páginasEcg Prsentationtehillahkabwe100Ainda não há avaliações
- MEDICAL ELECTRONICS New AssignmentDocumento10 páginasMEDICAL ELECTRONICS New AssignmentChandan ChandanAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiologia - EletrocardiografiaDocumento40 páginasCardiologia - EletrocardiografiaDANIEL ALEJANDROAinda não há avaliações
- ECG - Module - Printable Analysis and Interpretation of ECGDocumento37 páginasECG - Module - Printable Analysis and Interpretation of ECGPankaj PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Auskultation. ECG - LastDocumento5 páginasAuskultation. ECG - LastAndreyAinda não há avaliações
- 05 - ElektrokardiogramDocumento39 páginas05 - ElektrokardiogramNauval Zilal FananyAinda não há avaliações
- SaikatDocumento50 páginasSaikatSaurabh MondalAinda não há avaliações
- SBM1301Documento84 páginasSBM1301g8248418302Ainda não há avaliações
- ECGDocumento62 páginasECGSanju TanwarAinda não há avaliações
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg) Introduction of Basic Principles: Dian Puspita SariDocumento47 páginasElectrocardiogram (Ecg) Introduction of Basic Principles: Dian Puspita SariArie Krisnayanti Ida AyuAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Conduction Pathway: Course Lesson Student Email Atika - Salsabila91@ui - Ac.idDocumento12 páginasElectrical Conduction Pathway: Course Lesson Student Email Atika - Salsabila91@ui - Ac.idlemon kyuteaAinda não há avaliações
- THE Electrocardiogram (ECG)Documento13 páginasTHE Electrocardiogram (ECG)Bander Binjabaan Al-QahtaniAinda não há avaliações
- ECG All LeadsDocumento25 páginasECG All LeadsVIJAYKUMAR AAinda não há avaliações
- How Procedure Is Performed: ElectrocardiogramDocumento10 páginasHow Procedure Is Performed: ElectrocardiogramJonathan AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg Engl Large 126Documento125 páginasEcg Engl Large 126Andreea-Sânziana StanciuAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology Seminar: ElectrocardiographyDocumento42 páginasPhysiology Seminar: ElectrocardiographyRajesh SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- REAL Time ECG TRAINER MANUALDocumento15 páginasREAL Time ECG TRAINER MANUALSHANKARAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrocardiogramDocumento40 páginasElectrocardiogramDhvij KmlAinda não há avaliações
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAMDocumento50 páginasELECTROCARDIOGRAMamitava2010Ainda não há avaliações
- CCApostol ECGDocumento115 páginasCCApostol ECGAlanis ApostolAinda não há avaliações
- Omd551/Basics of Biomedical Instrumentation Two Marks With Answer Unit I Bio Potential Generation and Electrodes TypesDocumento13 páginasOmd551/Basics of Biomedical Instrumentation Two Marks With Answer Unit I Bio Potential Generation and Electrodes TypesAleesha100% (1)
- EcgDocumento29 páginasEcgSouvikDattaAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Intracardiac EGMs: A Patient Centered GuideNo EverandUnderstanding Intracardiac EGMs: A Patient Centered GuideAinda não há avaliações
- 3160 5485 1 SMDocumento19 páginas3160 5485 1 SMQuoc MaiAinda não há avaliações
- Phonocardiography (PCG) : NSCET - Medical Electronics (EC8073)Documento6 páginasPhonocardiography (PCG) : NSCET - Medical Electronics (EC8073)mathavanAinda não há avaliações
- EEG With ImageDocumento6 páginasEEG With ImagemathavanAinda não há avaliações
- DC Question BankDocumento8 páginasDC Question BankmathavanAinda não há avaliações
- ED EC 8252 - 2 Mark Final QBDocumento2 páginasED EC 8252 - 2 Mark Final QBmathavanAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Electronics Question BankDocumento3 páginasMedical Electronics Question BankmathavanAinda não há avaliações
- Beee Question BankDocumento4 páginasBeee Question BankmathavanAinda não há avaliações
- Beee Question BankDocumento4 páginasBeee Question BankmathavanAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Communication Question BankDocumento2 páginasDigital Communication Question BankmathavanAinda não há avaliações
- Acute and Chronic Gastrointestinal BleedingDocumento7 páginasAcute and Chronic Gastrointestinal BleedingMarwan M.100% (1)
- Manual de Servico Samsung Sgh-I677-Eplis-11Documento10 páginasManual de Servico Samsung Sgh-I677-Eplis-11Anselmo Antunes0% (1)
- Bleeding Disorders and Periodontology: P V & K PDocumento13 páginasBleeding Disorders and Periodontology: P V & K PAdyas AdrianaAinda não há avaliações
- Manuel Alava 01-12-10 PLDocumento3 páginasManuel Alava 01-12-10 PLAshley RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- T/PR/DIS/5.10.1: Work Procedure ForDocumento38 páginasT/PR/DIS/5.10.1: Work Procedure ForAnant RubadeAinda não há avaliações
- Aspirating Smoke Detector: Technical DescriptionDocumento115 páginasAspirating Smoke Detector: Technical DescriptionSecuriton ArgentinaAinda não há avaliações
- Ded Deliverable List: As Per 19-08-2016Documento2 páginasDed Deliverable List: As Per 19-08-2016Isna MuthoharohAinda não há avaliações
- Flood RateDocumento367 páginasFlood RatetpktpkAinda não há avaliações
- Fact Sheeton Canola OilDocumento15 páginasFact Sheeton Canola OilMonika ThadeaAinda não há avaliações
- Artikel Penelitian Annisa Humairah IbrahimDocumento15 páginasArtikel Penelitian Annisa Humairah Ibrahimisma nurhandayaniAinda não há avaliações
- Total Aircraft Washing System: Mudmaster Mudmaster MudliteDocumento2 páginasTotal Aircraft Washing System: Mudmaster Mudmaster MudliteAli Abu ShhiwaAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM333 Syllabus 2020 2021Documento4 páginasCHEM333 Syllabus 2020 2021lina kwikAinda não há avaliações
- Al Khudari Company Profile FP PDFDocumento14 páginasAl Khudari Company Profile FP PDFAnonymous bgYdp4Ainda não há avaliações
- 365-M - City Bus Route & Timings, Bangalore (BMTC) Map, First & Last BusDocumento10 páginas365-M - City Bus Route & Timings, Bangalore (BMTC) Map, First & Last BusER Aditya DasAinda não há avaliações
- Journal of Environmental Management: Ajay Singh TDocumento7 páginasJournal of Environmental Management: Ajay Singh TNestor Garay CahuanaAinda não há avaliações
- Nfpa 13d 2007 IndexDocumento3 páginasNfpa 13d 2007 Indexsaladin1977Ainda não há avaliações
- VisakhapatnamDocumento27 páginasVisakhapatnamCherukupalli Gopala KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- IJHIM 6 - Nur Husnina (36 SD 42)Documento7 páginasIJHIM 6 - Nur Husnina (36 SD 42)RSU Sayang BundaAinda não há avaliações
- Scan&SolveDocumento24 páginasScan&SolveAtul ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Approved Reading List Editions 2019ff As of 01 19 2023 2Documento9 páginasApproved Reading List Editions 2019ff As of 01 19 2023 2nikolAinda não há avaliações
- 96-09302-00-01 Reva Technical Manual Inogen One G5Documento18 páginas96-09302-00-01 Reva Technical Manual Inogen One G5Paula Andrea MarulandaAinda não há avaliações
- J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9010-9016Documento8 páginasJ. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9010-9016Jatyr OliveiraAinda não há avaliações
- Architecture of HimalayasDocumento3 páginasArchitecture of HimalayasAndrea CaballeroAinda não há avaliações