Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ineffective Airway Clearance
Enviado por
Arabelle GODescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ineffective Airway Clearance
Enviado por
Arabelle GODireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
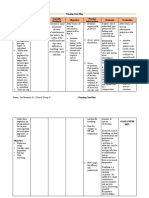
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DATA DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Ineffective airway Inflammation of the lung After 1 hour of nursing 1. Assess and 1. Tachypnea is
“Madali laak kapoyun, clearance r/t Pneumonia parenchyma results to intervention the patient monitor usually present
napabulig nala ak kun as evidenced by O2sat of accumulation of will be able to: respiratory rate. to some degree
nabuhat or kun 93% secretion restricting 1. Maintain patent Note inspiratory- and may be
mabaktas tikadto ha CR” oxygen exchange and airway with to expiratory pronounced on
as verbalized due to the inflammation breath sounds ratio. admission,
bronchial constriction clear or clearing. during stress, or
Objective: occurs in which the 2. Demonstrate during
O2sat of 93% airway system narrows behaviors to concurrent acute
causing decreased improve airway infectious
passage of oxygen clearance process.
entering the lungs for Respirations may
utilization. be shallow and
rapid, with
prolonged
Source: Nursing Care expiration in
Plans pg. 272 comparison to
inspiration.
2. Auscultate 2. Some degree of
breath sounds. bronchospasm is
Note present with
adventitious obstructions in
breath sounds airway and may
such as wheezes, or may not be
crackles, or manifested in
rhonchi. adventitious
breath sounds,
such as
scattered, moist
crackles
(bronchitis); faint
sounds, with
expiratory
wheezes
(emphysema); or
absent breath
sounds (severe
asthma).
3. Note presence 3. Respiratory
and degree of dysfunction is
dyspnea, for variable
example, reports depending on
of “air hunger,” the underlying
restlessness, process, for
anxiety, example,
respiratory infection, allergic
distress, and use reaction, and the
of accessory stage of
muscles. chronicity in a
client with
established
COPD.
4. Assist client to 4. Elevation of the
maintain a head of the bed
comfortable facilitates
position to respiratory
facilitate function using
breathing by gravity; however,
elevating the client in severe
head of bed, distress will seek
leaning on over- the position that
bed table, or most eases
sitting on edge of breathing.
bed. Supporting arms
and legs with
table, pillows,
and so on helps
reduce muscle
fatigue and can
aid chest
expansion.
5. Encourage and 5. Provides client
assist with with some
abdominal or means to cope
pursed-lip with and control
breathing dyspnea and
exercises. reduce air-
trapping.
6. Increase fluid 6. Hydration helps
intake to 3000 decrease the
mL/day within viscosity of
cardiac secretions,
tolerance. facilitating
Provide warm or expectoration.
tepid liquids. Using warm
Recommend liquids may
intake of fluids decrease
between, instead bronchospasm.
of during, meals Fluids during
meals can
increase gastric
distention and
pressure on the
diaphragm.
Você também pode gostar
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPFARAH MAE MEDINAAinda não há avaliações
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDocumento2 páginasStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaJhasmine MocnanganAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPRoger Jr PumarenAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short-Term: Independent: A) Elevated Head of A) To TakeDocumento2 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short-Term: Independent: A) Elevated Head of A) To TakeANGEL AKIRA TORRESAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationEllee HadesAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationEllee HadesAinda não há avaliações
- NURSING CARE PLAN Impaired Breathing PatternDocumento3 páginasNURSING CARE PLAN Impaired Breathing PatternChie Hyun-AeAinda não há avaliações
- Iudmc ActivityDocumento10 páginasIudmc ActivityJeraldine GumpalAinda não há avaliações
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDocumento2 páginasStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaNur SanaaniAinda não há avaliações
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDocumento2 páginasStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaJojo MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento8 páginasCamarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationEdelweiss Marie CayetanoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: (NoDocumento19 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: (NoKen BaxAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Cough 1Documento3 páginasNCP For Cough 1Ro VinAinda não há avaliações
- Innefective Airway Clearance NCPDocumento4 páginasInnefective Airway Clearance NCPAllen Vincent Cauton TulaganAinda não há avaliações
- RusheDocumento1 páginaRusheCallie ParkAinda não há avaliações
- Eent Case: Diagnosis: Septic Shock, Pneumonia in Pre Immunocompromised Host, Oropharyngeal CA Stage IVDocumento7 páginasEent Case: Diagnosis: Septic Shock, Pneumonia in Pre Immunocompromised Host, Oropharyngeal CA Stage IVYram Yoj ZeraujAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMel Izhra N. MargateAinda não há avaliações
- Performance Task # 9Documento6 páginasPerformance Task # 9Aileen Reign MalonzoAinda não há avaliações
- NCPPDocumento11 páginasNCPPAngelo Miguel MuñozAinda não há avaliações
- CopdDocumento6 páginasCopdapi-3717941100% (2)
- Data NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoDocumento3 páginasData NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoClaudineAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentWyeth Earl Padar EndrianoAinda não há avaliações
- D. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in BreathingDocumento2 páginasD. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in BreathingReinette LastrillaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocumento5 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMica OmotsosircAinda não há avaliações
- Tetanus NCPDocumento3 páginasTetanus NCPMarc Jayson TobiasAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationNichol John MalabananAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan (Pedia)Documento5 páginasNursing Care Plan (Pedia)JA BerzabalAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento4 páginasUntitledPie CanapiAinda não há avaliações
- NCP FinalDocumento16 páginasNCP FinalEuleen Tria PadrigoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Patient: Mrs. K Age: 68 Diagnosis: Community Acquired PneumoniaDocumento6 páginasNursing Care Plan Patient: Mrs. K Age: 68 Diagnosis: Community Acquired PneumoniaKerks Von Gladiel NapaoAinda não há avaliações
- MCN NCPDocumento4 páginasMCN NCPPEARL CHRISTINE CUDALAinda não há avaliações
- NCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento5 páginasNCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternMicaela CrisostomoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento4 páginasNCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternPRINCESS KOBAYASHIAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento13 páginasNursing Care PlanJan DamesAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For PneumoniaDocumento3 páginasNCP For PneumoniaLeogalvez BedanoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDDocumento7 páginasNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDMa. Elaine Carla Tating67% (3)
- NCP (Darping, Alimansor M. 4BSN-C)Documento14 páginasNCP (Darping, Alimansor M. 4BSN-C)Alimansor M. DarpingAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Marife: 45 Years Old Assessment Diagnosis Background Study/ Planning Implementation Rationale Expected Outcome/ EvaluationDocumento6 páginasNursing Care Plan Marife: 45 Years Old Assessment Diagnosis Background Study/ Planning Implementation Rationale Expected Outcome/ EvaluationAngelica Malacay RevilAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPCelline Isabelle ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Scenario 4 - NCPDocumento15 páginasScenario 4 - NCPVian RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 páginaIneffective Airway ClearancejomerdalonaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaDocumento2 páginasNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaFaith CalimlimAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Scenario BreathingDocumento4 páginasNCP For Scenario Breathingmy moznAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Ineffective AirwayDocumento1 páginaNCP Ineffective AirwayRainier IbarretaAinda não há avaliações
- Community Nursing Care PlanDocumento6 páginasCommunity Nursing Care Plantansincos93% (14)
- Goal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionDocumento4 páginasGoal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionWyen CabatbatAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 páginaIneffective Airway Clearancerozj0750% (2)
- NCP (Ineffective Airway)Documento2 páginasNCP (Ineffective Airway)Angeline CasabuenaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan 1Documento2 páginasNursing Care Plan 1Niña Loirence CajusayAinda não há avaliações
- To KeithDocumento16 páginasTo Keith3C SAVELLA, Glaiza Marie RAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento9 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKen IgnacioAinda não há avaliações
- Asthma NCPDocumento3 páginasAsthma NCPjaijai magbanuaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento7 páginasAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDanica Kate GalleonAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department NAME:R.D.RDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department NAME:R.D.Rcen janber cabrillosAinda não há avaliações
- Fibromyalgia SyndromeDocumento1 páginaFibromyalgia SyndromeArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY marLONDocumento4 páginasANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY marLONArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Cholera: Period of CommunicabilityDocumento1 páginaCholera: Period of CommunicabilityArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- WHO Surgical Safety ChecklistDocumento1 páginaWHO Surgical Safety ChecklistArabelle GO100% (1)
- Human Papilloma Virus: Incubation PeriodDocumento4 páginasHuman Papilloma Virus: Incubation PeriodArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine Function HCG: TH THDocumento4 páginasEndocrine Function HCG: TH THArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 23 ContinuationDocumento7 páginasChapter 23 ContinuationArabelle GO100% (1)
- MOTIVATIONDocumento25 páginasMOTIVATIONArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Activity PlanDocumento1 páginaActivity PlanArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Postnatal Care of The Mother and NewbornDocumento15 páginas11 Postnatal Care of The Mother and NewbornArabelle GO100% (1)
- Conduct DisorderDocumento26 páginasConduct DisorderArabelle GO100% (1)
- Exercise and Dance Therapies For PsychiaDocumento4 páginasExercise and Dance Therapies For PsychiaArabelle GO100% (1)
- Dance Therapy SummaryDocumento1 páginaDance Therapy SummaryArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- OBJECTIVES: After The Seminar, The Students Will Be Able ToDocumento4 páginasOBJECTIVES: After The Seminar, The Students Will Be Able ToArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Forearm SplintingDocumento6 páginasForearm SplintingArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Anti Anemia DrugsDocumento36 páginasAnti Anemia DrugsArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- By: Yzobelle RedondoDocumento4 páginasBy: Yzobelle RedondoArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Fluticasone Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasFluticasone Drug StudyArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentDocumento2 páginasCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Types of InsulinpptDocumento7 páginasTypes of InsulinpptArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Fibromyalgia SyndromeDocumento1 páginaFibromyalgia SyndromeArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Sternal Angle 2 Ic Superior Border Right Border Sternum DiaphragmDocumento18 páginasSternal Angle 2 Ic Superior Border Right Border Sternum DiaphragmArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Candesartan Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasCandesartan Drug StudyArabelle GO100% (1)
- Doxofylline Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasDoxofylline Drug StudyArabelle GO67% (3)
- Acetylcysteine Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasAcetylcysteine Drug StudyArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- Learning ProcessDocumento24 páginasLearning ProcessArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- The Biological Perspective 1Documento18 páginasThe Biological Perspective 1Radhey SurveAinda não há avaliações
- Ask An Expert: The Benefits of Aerobic ExerciseDocumento3 páginasAsk An Expert: The Benefits of Aerobic ExercisePrincess Villasis BaciaAinda não há avaliações
- Soal ATLSDocumento12 páginasSoal ATLSarditya galaxy100% (1)
- Sepsis: Texts: Text ADocumento18 páginasSepsis: Texts: Text AInsta GlobalAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ CPRDocumento2 páginasMCQ CPRAzmal Kabir Sarker75% (16)
- Chrono PharmacologyDocumento4 páginasChrono PharmacologyArun DavesarAinda não há avaliações
- Seahorse XF AnalyzerDocumento83 páginasSeahorse XF AnalyzerYash WaliaAinda não há avaliações
- 77 Nursing Abbreviations Cheat SheetDocumento4 páginas77 Nursing Abbreviations Cheat SheetGregory UtupoAinda não há avaliações
- المختصر الجم في فحص الدمDocumento116 páginasالمختصر الجم في فحص الدمmanni1001Ainda não há avaliações
- ScienceDocumento33 páginasScienceI am JAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Card For Who Emergency Unit Form GeneralDocumento2 páginasReference Card For Who Emergency Unit Form GeneralGideon BahuleAinda não há avaliações
- 2.8 Bio Starter 21.03.23 Malak PDFDocumento4 páginas2.8 Bio Starter 21.03.23 Malak PDFMalak AAinda não há avaliações
- CH-21 Neural Control and Coordination.......Documento16 páginasCH-21 Neural Control and Coordination.......Irmin HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of NursingDocumento27 páginasFundamentals of NursingRobeth OrbisoAinda não há avaliações
- Exam 1 Will Consist of 50 QuestionsDocumento1 páginaExam 1 Will Consist of 50 QuestionsVrunda PatelAinda não há avaliações
- MPAH SCDocumento3 páginasMPAH SCBernard ChanAinda não há avaliações
- Australasian Emergency Care: Jeremy Pallas, John-Paul SmilesDocumento3 páginasAustralasian Emergency Care: Jeremy Pallas, John-Paul Smileszaenal abidinAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems: Chapter TestDocumento6 páginasCirculatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems: Chapter TestJunior SencionAinda não há avaliações
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Dr. Sachana KC 1 Year Resident Department of AnesthesiaDocumento67 páginasAntiarrhythmic Drugs: Dr. Sachana KC 1 Year Resident Department of AnesthesiaKshitizma GiriAinda não há avaliações
- SDL Respiratory Care Modalities LOPEZ BSN 3CDocumento3 páginasSDL Respiratory Care Modalities LOPEZ BSN 3CMaria Niña Angela LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Hormones: Siti Zulaika Binti KasmatDocumento21 páginasHormones: Siti Zulaika Binti KasmatikaAinda não há avaliações
- Notes Calvin CycleDocumento2 páginasNotes Calvin Cycleneelp331Ainda não há avaliações
- Elitox PPT ENG CompressedDocumento18 páginasElitox PPT ENG CompressedTom ArdiAinda não há avaliações
- EMGBS Bio G11 U5 NoteDocumento80 páginasEMGBS Bio G11 U5 NoteDaniel GtsadkanAinda não há avaliações
- Diagram Human Heart Kel 1Documento3 páginasDiagram Human Heart Kel 1Rahma SafitriAinda não há avaliações
- Final Project - Vanessa Fuerstenberg P.2Documento9 páginasFinal Project - Vanessa Fuerstenberg P.2nessaAinda não há avaliações
- Volibris MOA Storyboard v1 1Documento4 páginasVolibris MOA Storyboard v1 1shyamchepurAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiotonics & Inotropic Drugs PDFDocumento10 páginasCardiotonics & Inotropic Drugs PDFZehra AmirAinda não há avaliações
- Toolkit For Sleep: Andrew D. Huberman, PH.DDocumento6 páginasToolkit For Sleep: Andrew D. Huberman, PH.DFlori100% (1)
- Human HeartDocumento2 páginasHuman HearthaniimanAinda não há avaliações