Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
Enviado por
Ziyad100%(1)100% acharam este documento útil (1 voto)
223 visualizações2 páginasDireitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF ou leia online no Scribd
100%(1)100% acharam este documento útil (1 voto)
223 visualizações2 páginasAcyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
Enviado por
ZiyadDireitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
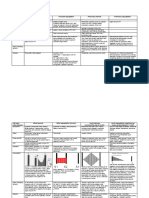
Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease (CHD)
Group Etio. Epid. Clinical Man. Imaging Treatment Comments
LTR VSD 25% Most Pansystolic murmur (LLSB), split S2 ECG: LAH, LVH ⅓ close spontaneously Perimembranous VSD most
shunts common common (67%)
CHD Small VSD: Asymptomatic, loud murmur CXR: Cardiomegaly, Small: no closure required
(P.P) Moderate-to-large VSD: fatigue, diaphoresis LVH Moderate-to-large: Diuretics, Asymptomatic at birth ( PVR)
with feedings, poor growth HF. Pulmonary HT RVH digoxin, afterload reduction
Large shunts: Mid-diastolic murmur at apex, Poor growth, pulmonary HT, or
large VSD: surgical closure.
ASD 10% Rarely symptomatic ECG: RAD, RVH R/I unless significant defect by 3y Secundum (foramen ovale)
Systolic ejection murmur (I-II), fixed split S2, RV CXR: Cardiomegaly, Secundum: closure device (cath.) defect most common
impulse (LLSB) RAH, prominent PA Primum, sinus venosus: surgical c.
PDA 10% Widened pulse pressure, continuous machine- CXR: full PA silhouette, Diuretics initially, but requires Imaging may be normal
like murmur (left infraclavicular area, left back, increases pulmonary closure (indomethacin?) Premature infants excluded in
radiates along PA), splitting of S2, thrill vascularity Cath lab: Coil embolization, incidence (occurs more)
Large shunts: Mid-diastolic murmur at apex, ECG: LVH, RVH (P.HT) closure device. Uncorrected PDA results in
hyperdynamic pericordium cyanosis in lower extremities
AVCD - Complete defect: primum ASD + posterior VSD, Dx: Echocardiography Initially: diuretics ± digoxin, Some Down syndrome
leaflet clefts in mitral & tricuspid valves ± AV CXR: cardiomegamly, afterload reduction (for HF) children have complete
valve insufficiency enlargement of all Ultimately surgical repair required endocardial cushion defect
HF in first 6-8 w, P.HT, poor growth chambers
Large VSD component: single S2 ECG: LAX, combined VH
Ob. Les. PS 10% Mild: asymptomatic ECG: RAD, RVH Balloon valvuloplasty Newborn with severe stenosis
may be cyanotic due to atrial
(n P.P) Mod-to-Sev: Exertional dyspn., easy fatigability CXR: prominent main PA Surgical repair: if unsuccessful or right-to-left shunt
SEM (left 2nd intercostal, radiates to back), thrill, Echo: site of stenosis, subvalvular (muscular) stenosis
widely split S2 with quite pulmonary degree of hypertrophy, Valvular PS does not progress
component, impulse at LLSB (RVH), Click pressure gradient
(valvular stenosis, varies with respiration)
AS 5% Mild-to-moderate: Asymptomatic ECG: LVH Serial follow up with Echo Degree of aortic stenosis
Severe: easy fatigability, exertional chest pain, CXR: Poststenotic Balloon valvuloplasty 1st interv. progresses with growth and
syncope, infants can present with HF dilation of ascending (less successful than PSBV) age
SEM (Rt 2nd ICS along sternum, radiating to aorta or aortic knob Surgical repair: failed BV, Aortic insufficiency often
neck), systolic ejection click (valvular Echo: same as PS development of valve develops
stenosis), thrill (RUSB, suprasternal notch) insufficiency ( risk with BV)
COA 10% Infant: Poor feeding, respiratory distress, shock Infant ECG, CXR: RVH, Infant presenting with cardiac Almost always juxtaductal
before 2 w, femoral pulse/BP/timing < radial cardiomegaly, decompensation: IV (preductal)
Older children: asymptomatic, hx of leg pulmonary edema prostaglandin E1, inotropic Symptoms develop after PDA
discomfort with exercise, headache, epistaxis, Older children ECG, agents, diuretics, balloon closes
HT in upper extremity. CXR: LVH, mildly angioplasty, surgical repair (m/c) Most commonly associated
Murmur (left interscapular area of back), enlarged heart, rib Older children: ballooning, with bicuspid aortic valve
collaterals present continuous mumur notching (>8yr with stenting, surgical repair (m/c) Associated with Turner
throughout chest large collaterals) syndrome
Abnormal aortic valve (50%): SEM, SEC
LTR. Left-to-right shunt; P.P, pulmonary pressure; CHD: congenital heart disease; LLSB, Left Lower Sternal Border; A/VH, atrial/ventricular hypertrophy, PVR, pulmonary vascular resistance; SEM/C, systolic ejection murmur/click, AVCD, atrioventricular canal defect
Você também pode gostar
- UWorld Notes - Peds 2Documento38 páginasUWorld Notes - Peds 2Dylan GerlachAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento3 páginasCongenital Heart DiseaseKarisaAinda não há avaliações
- Peds Shelf NotesDocumento73 páginasPeds Shelf NotesTanyaMusonza100% (1)
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Pediatric Cardiology Division University of Sumatera UtaraDocumento40 páginasAcyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Pediatric Cardiology Division University of Sumatera UtaraHanda YaniAinda não há avaliações
- Peds Shelf NotesDocumento88 páginasPeds Shelf Notesγιαννης παπαςAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart Diseases ReviewDocumento2 páginasCongenital Heart Diseases ReviewQworldAinda não há avaliações
- Pediatric Cardiology Part 2Documento3 páginasPediatric Cardiology Part 2carlosAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart Defects - CyanoticDocumento3 páginasCongenital Heart Defects - Cyanoticr5ss7pq9tpAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiology CardiovascularExaminationDocumento5 páginasCardiology CardiovascularExaminationSalifyanji SimpambaAinda não há avaliações
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasesDocumento7 páginasAcyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasesAlvin De LunaAinda não há avaliações
- K9. Penyakit Kardiovaskuler BawaanDocumento70 páginasK9. Penyakit Kardiovaskuler Bawaanjulis muharamAinda não há avaliações
- MAA Paeds Conditions - CardioDocumento13 páginasMAA Paeds Conditions - CardioThistell ThistleAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento6 páginasCongenital Heart DiseaseSamah KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of Cardiac Malformations: Daniel Bernstein's (Clinical + Physiopathological)Documento28 páginasClassification of Cardiac Malformations: Daniel Bernstein's (Clinical + Physiopathological)Sandyka AleAinda não há avaliações
- Pedia Cardiology 2Documento5 páginasPedia Cardiology 2Medisina101Ainda não há avaliações
- 02 - Kuliah Mhs Unsri 2015Documento55 páginas02 - Kuliah Mhs Unsri 2015warriordc1995Ainda não há avaliações
- Clinical Congenital Heart Disease: Prof M S Ranjit MD DCH Senior Consultant Paed. Cardiologist ChennaiDocumento78 páginasClinical Congenital Heart Disease: Prof M S Ranjit MD DCH Senior Consultant Paed. Cardiologist ChennaiAnişoara FrunzeAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart Disease UHNDocumento46 páginasCongenital Heart Disease UHNFaisalAinda não há avaliações
- Valvular Heart Disease: Chalinee Pravarnpat, M.DDocumento49 páginasValvular Heart Disease: Chalinee Pravarnpat, M.DChalee InkateAinda não há avaliações
- Anak 2Documento107 páginasAnak 2Nency PurmayaAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento25 páginasCongenital Heart DiseaserizkyAinda não há avaliações
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento48 páginasAcyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasenabillagusrinaAinda não há avaliações
- Penyakit Jantung Bawaan Pada AnakDocumento27 páginasPenyakit Jantung Bawaan Pada AnakPisangEpeAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart Disease.: Sadath Ali KhanDocumento9 páginasCongenital Heart Disease.: Sadath Ali Khandr_alfuAinda não há avaliações
- PANCE Word Associations PDFDocumento27 páginasPANCE Word Associations PDFkatAinda não há avaliações
- 35 Years Old Female Presented To The OPD With Fatigue and Dyspnea On ExertionDocumento2 páginas35 Years Old Female Presented To The OPD With Fatigue and Dyspnea On ExertionAbdulrahman KatibAinda não há avaliações
- Peds Shelf NotesDocumento74 páginasPeds Shelf NotesRandy BornmannAinda não há avaliações
- Word Association PANCEDocumento31 páginasWord Association PANCEnevmerka100% (1)
- Congenital Heart Disease - Dr. HabibieDocumento43 páginasCongenital Heart Disease - Dr. HabibieNanda Kurnia RamadhanAinda não há avaliações
- DMDudzinski EKG Algorithm4Documento1 páginaDMDudzinski EKG Algorithm4nate simmons100% (1)
- Tips and Tricks in Management of Patients With CHDDocumento46 páginasTips and Tricks in Management of Patients With CHDDrMarcus KeyboardAinda não há avaliações
- Penyakit Jantung Bawaan Pada AnakDocumento26 páginasPenyakit Jantung Bawaan Pada AnakDellaAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Cardiovascular DisordersDocumento4 páginasCongenital Cardiovascular DisordersMika SaldañaAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart Defects - AcyanoticDocumento6 páginasCongenital Heart Defects - Acyanoticr5ss7pq9tpAinda não há avaliações
- Approach Cyanosis FinalDocumento31 páginasApproach Cyanosis Finalsuheena.CAinda não há avaliações
- 10 1016@j CCL 2020 04 008Documento12 páginas10 1016@j CCL 2020 04 008Linda Silvana SariAinda não há avaliações
- Clin Med For PAsDocumento32 páginasClin Med For PAsMaryNguyen100% (2)
- Cardio My Opa Thies ChartDocumento2 páginasCardio My Opa Thies ChartSolomon Seth SallforsAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah KardioDocumento62 páginasKuliah KardioJardinia DianAinda não há avaliações
- ASD Aortic StenosisDocumento3 páginasASD Aortic Stenosis[161]Shuaib AktherAinda não há avaliações
- Ongenital Eart Iseases: Iman Sulaiman Al-Hatmi 85569Documento63 páginasOngenital Eart Iseases: Iman Sulaiman Al-Hatmi 85569Anişoara FrunzeAinda não há avaliações
- Obstructive LesionsDocumento7 páginasObstructive LesionsMaikka IlaganAinda não há avaliações
- (Medbook4u Com) IllBaby1Documento693 páginas(Medbook4u Com) IllBaby1Certificate SurrenderAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Mohammad Shaikhani. Sulaimani University, College of Medicine. Sulaimanya-Iraqi KurdistanDocumento51 páginasDr. Mohammad Shaikhani. Sulaimani University, College of Medicine. Sulaimanya-Iraqi KurdistanHNINAinda não há avaliações
- Top Ten (Or 11) EKG KillersDocumento84 páginasTop Ten (Or 11) EKG KillersphausknechtAinda não há avaliações
- Stenotic Lesions AaDocumento7 páginasStenotic Lesions Aaprem kotiAinda não há avaliações
- Aortic Regurgitation CaseDocumento38 páginasAortic Regurgitation CaseIka MagfirahAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Diagnosis CVS BCCM Second Year Lecture MARKMDDocumento26 páginasPhysical Diagnosis CVS BCCM Second Year Lecture MARKMDJoseph De JoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Right To Left Shunts TableDocumento5 páginasRight To Left Shunts TableIgwe SolomonAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart Disease-2Documento57 páginasCongenital Heart Disease-2Deepika LamichhaneAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Ika Prasetya W, SPPD: Divisi Kardiologi Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FKUI/RSCM JakartaDocumento39 páginasDr. Ika Prasetya W, SPPD: Divisi Kardiologi Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FKUI/RSCM JakartaStefani Astari Dewi AryaniAinda não há avaliações
- Achd Ug OriginalDocumento43 páginasAchd Ug OriginalchristyAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. RSK - Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento44 páginasDr. RSK - Cyanotic Congenital Heart Diseasemanjunath182019Ainda não há avaliações
- Arteriolar Dilator Decreases After Load Ejection FractionDocumento1 páginaArteriolar Dilator Decreases After Load Ejection FractionJack GuccioneAinda não há avaliações
- Arrythmias and Cardiac TumorsDocumento30 páginasArrythmias and Cardiac TumorsRabea DiaAinda não há avaliações
- Mumurs Summary PDFDocumento6 páginasMumurs Summary PDFykteo323Ainda não há avaliações
- Family Medicine Study GuideDocumento240 páginasFamily Medicine Study GuideJeremy Christmann100% (1)
- 14 - Toronto Notes 2011 - GynecologyDocumento52 páginas14 - Toronto Notes 2011 - GynecologyZiyad100% (4)
- Fluid Management in PediatricsDocumento3 páginasFluid Management in PediatricsZiyadAinda não há avaliações
- EndometriosisDocumento1 páginaEndometriosisZiyad100% (1)
- Instruments & IndicationsDocumento11 páginasInstruments & IndicationsZiyad100% (2)
- Obstetric BleedingDocumento1 páginaObstetric BleedingZiyadAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid DiseaseDocumento1 páginaThyroid DiseaseZiyadAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary IncontinenceDocumento1 páginaUrinary IncontinenceZiyad100% (1)
- BreechDocumento1 páginaBreechZiyadAinda não há avaliações
- Heart Valve DiseaseDocumento67 páginasHeart Valve DiseaseSaba SivaAinda não há avaliações
- Stoelting Anasthesia and Co Existing Disease PDFDocumento28 páginasStoelting Anasthesia and Co Existing Disease PDFEgidia SetyaAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular Examination:: General InspectionDocumento6 páginasCardiovascular Examination:: General InspectionPhysician AssociateAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology Practical 1: (Heart Sounds)Documento12 páginasPhysiology Practical 1: (Heart Sounds)Dratosh KatiyarAinda não há avaliações
- Saudi License Exam (SLE) 3rd Edt. UQUDocumento445 páginasSaudi License Exam (SLE) 3rd Edt. UQUkingmedic98% (41)
- Normal Sinus RhythmDocumento97 páginasNormal Sinus RhythmNatasha LiberisAinda não há avaliações
- Atrial FibrillationDocumento19 páginasAtrial FibrillationAnwari MuhammadAinda não há avaliações
- PericarditisDocumento45 páginasPericarditisJorge Luis Ibarra NaranjoAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Audit On Code BlueDocumento7 páginasClinical Audit On Code BlueSunny AnthonyAinda não há avaliações
- Progress - AMS Study ErbelDocumento19 páginasProgress - AMS Study ErbelmarksteckelAinda não há avaliações
- Joglar Et Al 2023 2023 Acc Aha Accp Hrs Guideline For The Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation A Report ofDocumento156 páginasJoglar Et Al 2023 2023 Acc Aha Accp Hrs Guideline For The Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation A Report ofCorina DiaconescuAinda não há avaliações
- Echocardiography (Cardiac Echography, Heart Sonography)Documento2 páginasEchocardiography (Cardiac Echography, Heart Sonography)Broc Il SerbatoioAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S2772930322004367 MainDocumento15 páginas1 s2.0 S2772930322004367 MainVimal NishadAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Life SupportDocumento35 páginasBasic Life SupportCitra Kartikasari100% (1)
- Comparison of STEMI and NSTEMI Patients in The Emergency DepartmentDocumento4 páginasComparison of STEMI and NSTEMI Patients in The Emergency DepartmentazizhaAinda não há avaliações
- Schedule D: List of Life Saveing or Life Sustaining Medical DevicesDocumento5 páginasSchedule D: List of Life Saveing or Life Sustaining Medical DevicesAasma RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- An Uncommon Stemi Masquerader: A Case of Imipramine Induced Brugada Phenocopy (BRP)Documento5 páginasAn Uncommon Stemi Masquerader: A Case of Imipramine Induced Brugada Phenocopy (BRP)IJAR JOURNALAinda não há avaliações
- Echo Basic Protocol (ENG)Documento15 páginasEcho Basic Protocol (ENG)stoicea_katalinAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiology Laboratory TestsDocumento2 páginasCardiology Laboratory TestsBeatrice SalgadoAinda não há avaliações
- 2012 MitraClip For The Treatment of Mitral RegurgitationDocumento11 páginas2012 MitraClip For The Treatment of Mitral RegurgitationThanh BinhAinda não há avaliações
- Catheter Ablation in End Stage Heart FailureDocumento10 páginasCatheter Ablation in End Stage Heart FailureJose Gomez MorenoAinda não há avaliações
- DNB (Post MBBS) January 2017 Admission Session - Seat Allotment Details (Round-1)Documento49 páginasDNB (Post MBBS) January 2017 Admission Session - Seat Allotment Details (Round-1)Karan KalraAinda não há avaliações
- S 0272638606005543Documento89 páginasS 0272638606005543Dima NicoletaAinda não há avaliações
- One Stop Doc Cardiology - Aggarwal, RishiDocumento145 páginasOne Stop Doc Cardiology - Aggarwal, RishiCosmin Neagu100% (5)
- Previous Question Paper 2 Cardiology PDFDocumento6 páginasPrevious Question Paper 2 Cardiology PDFDeepthi D100% (1)
- Rapidly Progressive IgA Nephropathy Leads To End-Stage Renal Disease A Case ReportDocumento3 páginasRapidly Progressive IgA Nephropathy Leads To End-Stage Renal Disease A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Etiology of Chronic Kidney Disease CKD in Saudi Arabia PDFDocumento6 páginasEtiology of Chronic Kidney Disease CKD in Saudi Arabia PDFDimas RizkyAinda não há avaliações
- Echocardiography in TAVI ProcedureDocumento26 páginasEchocardiography in TAVI ProcedurejshAinda não há avaliações
- V. Complications of CVDDocumento26 páginasV. Complications of CVDJan Federick BantayAinda não há avaliações
- DR Tejas Patel cv-1 PDFDocumento18 páginasDR Tejas Patel cv-1 PDFnarasimhahanAinda não há avaliações