Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Report 2
Enviado por
jave louriseTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Report 2
Enviado por
jave louriseDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Infinitesimal
o Everything would work out fine if the interval could be made infinitely small
o in mathematics, a quantity less than any finite quantity yet not zero. Even though no such
quantity can exist in the real number system, many early attempts to justify calculus were based
on sometimes dubious reasoning about infinitesimals: derivatives were defined as ultimate
ratios of infinitesimals, and integrals were calculated by summing rectangles of infinitesimal
width. As a result, differential and integral calculus was originally referred to as the infinitesimal
calculus. This terminology gradually disappeared as rigorous concepts of limit, continuity, and
the real numbers were formulated
so the humanity was curious about calculus
HOW MATHEMATICS IS USED IN:
Calculus
o the mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of
shape and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
o Providing tools that let scientists calculate what nature is doing
o Providing new questions for mathematicians to sort out their own satisfaction
Applied Mathematics
o Applied mathematics is the application of mathematical methods by different fields such as
science, engineering, business, computer science, and industry.
Pure mathematics
o Pure mathematics is the study of mathematical concepts independently of any application
outside mathematics.
nature
Monk Gregor Mendel
o through his work on pea plants, discovered the fundamental laws of inheritance. He deduced
that genes come in pairs and are inherited as distinct units, one from each parent.
o He tracked the segregation of parental genes and their appearance in the offspring as dominant
or recessive traits. He recognized the mathematical patterns of inheritance from one generation
to the next.
Erwin Chargaff
o was one of those men, making two discoveries that led James Watson and Francis Crick to the
double helix structure of DNA.
o noticed that DNA, whether taken from a plant or animal, contained equal amounts of adenine
and thymine and equal amounts of cytosine and guanine.
o These equalities provided clues into the chemical pairings that make up the double helix.
o In addition, Chargaff also found that amounts of guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymine vary by
species – an indication that DNA, not protein, might be the genetic material for life.
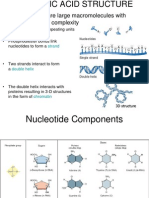
DNA
o Has double helical structure consists of two spiral chains of deoxyribonucleic acid. The shape is
similar to that of a spiral staircase.
o is a nucleic acid composed of nitrogenous bases (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine), a
five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and phosphate molecules
o . The nucleotide bases of DNA represent the stair steps of the staircase, and the deoxyribose
and phosphate molecules form the sides of the staircase.
Você também pode gostar
- Unit 1Documento47 páginasUnit 1Ansh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Basic Molecular Biology: Gene StructureDocumento36 páginasBasic Molecular Biology: Gene StructureLutfil HadiAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Fluorescent and Colorimetric Sensors For Detection of Lead, Cadmium, and Mercury IonsDocumento36 páginasFluorescent and Colorimetric Sensors For Detection of Lead, Cadmium, and Mercury IonskawtherahmedAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Molecular Biology Lecture NotesDocumento7 páginasMolecular Biology Lecture NotesChristineAinda não há avaliações
- The Bacterial RecA Protein and Recombinationlal Dna Repair of Stalled Replication ForksDocumento32 páginasThe Bacterial RecA Protein and Recombinationlal Dna Repair of Stalled Replication ForksHaru SahaAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Greatest Medical Discoveries of The MillenniumDocumento10 páginasThe Greatest Medical Discoveries of The MillenniumKatie JusayAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Philippe Cluzel, Anne Lebrun, Christoph Heller, Richard Lavery, Jean-Louis Viovy, Didier Chatenay and François Caron - DNA: An Extensible MoleculeDocumento4 páginasPhilippe Cluzel, Anne Lebrun, Christoph Heller, Richard Lavery, Jean-Louis Viovy, Didier Chatenay and François Caron - DNA: An Extensible MoleculeUylrikkAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Watson and Crick Model of DNADocumento22 páginasWatson and Crick Model of DNAGanesh V Gaonkar100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- BCH 323 NotesDocumento41 páginasBCH 323 NotesvictorAinda não há avaliações
- Dna 2Documento27 páginasDna 2Louis FortunatoAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Plutarch's ParableDocumento93 páginasPlutarch's ParableLR Young100% (3)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Bioinspired and Biomimetic Supramolecular ChemistryDocumento653 páginasBioinspired and Biomimetic Supramolecular ChemistryFGHAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Exercise On Chemical Composition of The CellDocumento7 páginasExercise On Chemical Composition of The CellNorliyana Ali100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A, B and Z DnaDocumento24 páginasA, B and Z DnaUtkarsh SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Genetics Analysis and Principles 5th Edition Brooker Solutions ManualDocumento6 páginasGenetics Analysis and Principles 5th Edition Brooker Solutions Manualariadneamelindasx7e100% (26)
- Model BuildingDocumento5 páginasModel BuildingFarhanBaqiAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Cot CurvesDocumento4 páginasCot CurvesVenkateswarlu Yadavalli100% (2)
- Supercoiling of Knotted and Unknotted DNA Plasmids Contact in Kirchhoff Rods With Applications To Theory of SelfDocumento20 páginasSupercoiling of Knotted and Unknotted DNA Plasmids Contact in Kirchhoff Rods With Applications To Theory of SelfLokosooAinda não há avaliações
- Lab3 Winter2016Documento3 páginasLab3 Winter2016ENAinda não há avaliações
- Dna StructureDocumento7 páginasDna StructurehoneyworksAinda não há avaliações
- BP605T Unit 4-6Documento482 páginasBP605T Unit 4-6Gyampoh SolomonAinda não há avaliações
- Amilopektin PDFDocumento29 páginasAmilopektin PDFmasdalifahAinda não há avaliações
- DNADocumento37 páginasDNAGhafoor AzamAinda não há avaliações
- Philosophy of ScienceDocumento8 páginasPhilosophy of ScienceBenjamin MariAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Dna Double Helical Structure WatsonDocumento11 páginasDna Double Helical Structure Watsonabhijeetgoyal16Ainda não há avaliações
- Chem 205 Lecture 5: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids (Derived From Voet, 2011)Documento37 páginasChem 205 Lecture 5: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids (Derived From Voet, 2011)Rab BaloloyAinda não há avaliações
- Nadrian C. Seeman - From Genes To Machines: DNA Nanomechanical DevicesDocumento7 páginasNadrian C. Seeman - From Genes To Machines: DNA Nanomechanical DevicesLpeo23Ainda não há avaliações
- IV. Nucleic AcidsDocumento44 páginasIV. Nucleic AcidsAngel Hope MacedaAinda não há avaliações
- Metal in MedecineDocumento20 páginasMetal in MedecineMaikeru Turaven KyuseshuAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- 11.1 Nucleic Acid Chemistry Part 1Documento7 páginas11.1 Nucleic Acid Chemistry Part 1ChonaAinda não há avaliações