Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Course 9
Enviado por
faster123Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Course 9
Enviado por
faster123Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Course 9.
Digital Circuits and Systems (Video Course)
Faculty Coordinator(s) :
1. Prof. S. Srinivasan
Department of Electrical Engineering
Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
Chennai- 600036
Email : srini@ee.iitm.ernet.in
Telephone : (91-44) Off : 22578374
22579374
Detailed Syllabus :
1. Introduction
Digital Systems; Data representation and coding; Logic circuits, integrated circuits;
Analysis, design and implementation of digital systems; CAD tools.
2. Number Systems and Codes
Positional number system; Binary, octal and hexadecimal number systems; Methods of
base conversions; Binary, octal and hexadecimal arithmetic; Representation of signed
numbers; Fixed and floating point numbers; Binary coded decimal codes; Gray codes;
Error detection and correction codes - parity check codes and Hamming code.
3. Combinatorial Logic Systems
Definition and specification; Truth table; Basic logic operation and logic gates.
4. Boolean Algebra and Switching Functions
Basic postulates and fundamental theorems of Boolean algebra; Standard
representation of logic functions - SOP and POS forms; Simplification of switching
functions - K-map and Quine-McCluskey tabular methods; Synthesis of combinational
logic circuits.
5. Logic families
Introduction to different logic families; Operational characteristics of BJT in saturation
and cut-off regions; Operational characteristics of MOSFET as switch; TTL inverter -
circuit description and operation; CMOS inverter - circuit description and operation;
Structure and operations of TTL and CMOS gates; Electrical characteristics of logic
gates – logic levels and noise margins, fan-out, propagation delay, transition time,
power consumption and power-delay product.
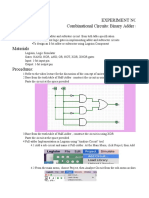
6. Combinational Logic Modules and their applications
Decoders, encoders, multiplexers, demultiplexers and their applications; Parity circuits
and comparators; Arithmetic modules- adders, subtractors and ALU; Design examples.
7. Sequential Logic systems:
Definition of state machines, state machine as a sequential controller; Basic sequential
circuits- latches and flip-flops: SR-latch, D-latch, D flip-flop, JK flip-flop, T flip-flop;
Timing hazards and races; Analysis of state machines using D flip-flops and JK flip-
flops; Design of state machines - state table, state assignment, transition/excitation
table, excitation maps and equations, logic realization; Design examples
8. State machine design approach
Designing state machine using ASM charts; Designing state machine using state
diagram; Design examples
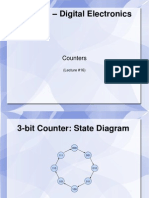
9. Sequential logic modules and their applications
Multi-bit latches and registers, counters, shift register, application examples.
10. Memory
Read-only memory, read/write memory - SRAM and DRAM
11.Programmable Logic Devices:
PLAs, PALs and their applications; Sequential PLDs and their applications; State-
machine design with sequential PLDs; Introduction to field programmable gate arrays
(FPGAs)
Você também pode gostar
- Practical Design of Digital Circuits: Basic Logic to MicroprocessorsNo EverandPractical Design of Digital Circuits: Basic Logic to MicroprocessorsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- CP203 Digital Logic & DesignDocumento2 páginasCP203 Digital Logic & Designviral patelAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Digital Systems: Modeling, Synthesis, and Simulation Using VHDLNo EverandIntroduction to Digital Systems: Modeling, Synthesis, and Simulation Using VHDLAinda não há avaliações
- Scheme of Examination & Syllabus: M. Sc. ElectronicsDocumento24 páginasScheme of Examination & Syllabus: M. Sc. ElectronicsJacob B ChackoAinda não há avaliações
- Bebop to the Boolean Boogie: An Unconventional Guide to ElectronicsNo EverandBebop to the Boolean Boogie: An Unconventional Guide to ElectronicsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- Common Recruitment Examination June 2013: DeityDocumento10 páginasCommon Recruitment Examination June 2013: DeitydannycbsAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to 6800/6802 Microprocessor Systems: Hardware, Software and ExperimentationNo EverandIntroduction to 6800/6802 Microprocessor Systems: Hardware, Software and ExperimentationAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Electronics TEE: CO1 CO2 CO3 CO4 CO5 CO6Documento2 páginasDigital Electronics TEE: CO1 CO2 CO3 CO4 CO5 CO6Anonymous HyOfbJ6Ainda não há avaliações
- MR3391 SyllabusDocumento1 páginaMR3391 Syllabusadmission1.gojanAinda não há avaliações
- Microprocessor System Design: A Practical IntroductionNo EverandMicroprocessor System Design: A Practical IntroductionAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Electronics Combinational and Sequential Circuit DesignDocumento2 páginasDigital Electronics Combinational and Sequential Circuit DesignjeevaAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mathematics - Iv CODE: 10 MAT 41 IA Marks: 25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam HRS: 03 Total HRS: 52 Exam Marks:100 Part-A Unit-I: Numerical Methods - 1Documento14 páginasEngineering Mathematics - Iv CODE: 10 MAT 41 IA Marks: 25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam HRS: 03 Total HRS: 52 Exam Marks:100 Part-A Unit-I: Numerical Methods - 1HmmTell TellAinda não há avaliações
- ISRO SCIENTISTS/ENGINEERS (SC) SYLLABUS OVERVIEWDocumento5 páginasISRO SCIENTISTS/ENGINEERS (SC) SYLLABUS OVERVIEWVIVEK SINGHAinda não há avaliações
- Digital SystemsDocumento390 páginasDigital SystemsKetan PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Documento3 páginasGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Alok MauryaAinda não há avaliações
- DSD Syll - Merged DSD GtuDocumento8 páginasDSD Syll - Merged DSD GtuSandeep kumarAinda não há avaliações
- GTU Digital Electronics Syllabus Explains Concepts & DesignDocumento3 páginasGTU Digital Electronics Syllabus Explains Concepts & Designsjbv.hardik582Ainda não há avaliações
- Number System and RepresentationDocumento4 páginasNumber System and RepresentationVani telluriAinda não há avaliações
- Digital ElectronicsDocumento228 páginasDigital ElectronicsMujeeb AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Documento4 páginasGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19useless9925Ainda não há avaliações
- Syllabi Special Computer Full 17E and Above Nov2020Documento88 páginasSyllabi Special Computer Full 17E and Above Nov2020Vinodh LahiruAinda não há avaliações
- RGPV Syllabus Cbgs Ec 3 Sem All SubjectsDocumento8 páginasRGPV Syllabus Cbgs Ec 3 Sem All SubjectsAyushAinda não há avaliações
- Vlsi DesignDocumento12 páginasVlsi DesignTanveer AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Swttching Theory and Logic Design PDFDocumento2 páginasSwttching Theory and Logic Design PDFgoutamkrsahooAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Logic Design-SyllabusDocumento2 páginasDigital Logic Design-SyllabusSri MathiAinda não há avaliações
- TNPSC Assistant System Engineer and Analyst SyllabusDocumento10 páginasTNPSC Assistant System Engineer and Analyst SyllabussoundaryaAinda não há avaliações
- PDFDocumento4 páginasPDFArpit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Vlsi System DesignDocumento12 páginasVlsi System DesignMahender GoudAinda não há avaliações
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad M.Tech. Digital Electronics & Communication Systems Course Structure and SyllabusDocumento12 páginasJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad M.Tech. Digital Electronics & Communication Systems Course Structure and Syllabustejaswi.mAinda não há avaliações
- CS III and IV Sem SyllabusDocumento31 páginasCS III and IV Sem Syllabusjoshituhina9Ainda não há avaliações
- Logic DesignDocumento3 páginasLogic DesignHarsh BharadwajAinda não há avaliações
- EtrxDocumento16 páginasEtrxapi-236544093Ainda não há avaliações
- Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocumento3 páginasElectronics and Communication EngineeringPurvaAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus PDFDocumento1 páginaSyllabus PDFJitha VargheseAinda não há avaliações
- MTech VLSI Design 1st Sem SyllabusDocumento5 páginasMTech VLSI Design 1st Sem SyllabusPrakash Sinha100% (1)
- Annexure - I (A) : Syllabus For Preliminary Written Test Technical Paper (Objective Type) (200 Questions)Documento7 páginasAnnexure - I (A) : Syllabus For Preliminary Written Test Technical Paper (Objective Type) (200 Questions)KumarJinneAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Circuits and SystemsDocumento3 páginasDigital Circuits and SystemsAayush JainAinda não há avaliações
- Demulti Plexer and MultiolexerDocumento7 páginasDemulti Plexer and Multiolexerkaran007_mAinda não há avaliações
- GTU Digital Logic DesignDocumento2 páginasGTU Digital Logic DesignChirag PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus CODocumento7 páginasSyllabus COAshwini MateAinda não há avaliações
- Vit Ece 5th Year SyllabusDocumento16 páginasVit Ece 5th Year Syllabuspranavateja12399Ainda não há avaliações
- EC1303 Digital System Design Course OverviewDocumento2 páginasEC1303 Digital System Design Course OverviewMohamed Abdul RahimAinda não há avaliações
- Es IiDocumento16 páginasEs IiSivasankar YalavarthyAinda não há avaliações
- Cu 1st SemDocumento4 páginasCu 1st SemCOMPUTER SCIENCE BGCAinda não há avaliações
- Cse1003 Digital-logic-And-Design Eth 1.1 47 Cse1003Documento8 páginasCse1003 Digital-logic-And-Design Eth 1.1 47 Cse1003Shiva Charan0% (1)
- Btech New SyllabusDocumento8 páginasBtech New SyllabusDrBhoopal RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Analog SyllabusDocumento8 páginasAnalog SyllabusSonam SainiAinda não há avaliações
- syllabusTNPSC Ase Asa SyllabusDocumento9 páginassyllabusTNPSC Ase Asa SyllabusVaikunthan SAinda não há avaliações
- EC8395 Digital ElectronicsDocumento1 páginaEC8395 Digital ElectronicsScientist SakthivelAinda não há avaliações
- SyllabusDocumento3 páginasSyllabusUttam DeshpandeAinda não há avaliações
- Ine 312:: Microprocessors and Interfacing: Course OutcomeDocumento4 páginasIne 312:: Microprocessors and Interfacing: Course OutcomeVineeth KumarAinda não há avaliações
- 04 Syllabus M.tech ESD Final - AmbpsDocumento21 páginas04 Syllabus M.tech ESD Final - Ambpsnikky234Ainda não há avaliações
- M.tech Vlsi Syllabus: D.A.John & K.Martin, Analog Integrated Circuit Design, Wiley, 1997Documento5 páginasM.tech Vlsi Syllabus: D.A.John & K.Martin, Analog Integrated Circuit Design, Wiley, 1997Garth RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Design SyllabusDocumento3 páginasDigital Design SyllabusRahul KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture PlanDocumento1 páginaLecture Planlaviniaandronicus9Ainda não há avaliações
- BEEE206L - DIGITAL-ELECTRONICS - TH - 1.0 - 67 - Digital ElectronicsDocumento3 páginasBEEE206L - DIGITAL-ELECTRONICS - TH - 1.0 - 67 - Digital ElectronicsNithish kumar RajendranAinda não há avaliações
- Switching Theory and Logic Design PDFDocumento159 páginasSwitching Theory and Logic Design PDFSai TejaswiniAinda não há avaliações
- New VLSIDocumento2 páginasNew VLSIRanjit KumarAinda não há avaliações
- VLSI SyllabusDocumento13 páginasVLSI SyllabusNagabhushanam KoduriAinda não há avaliações
- DTE Imp QuestionsDocumento2 páginasDTE Imp QuestionsPushkar rane 1oth,B,ROLL NO.47Ainda não há avaliações
- Fast and Ls TTL Data (Thong So IC So)Documento727 páginasFast and Ls TTL Data (Thong So IC So)Nguyễn Đặng Tấn TàiAinda não há avaliações
- LAB 1 Boolean Operations - SimulationDocumento9 páginasLAB 1 Boolean Operations - SimulationazrieAinda não há avaliações
- VHDL DOCUMENTATIONDocumento41 páginasVHDL DOCUMENTATIONB. MeenakshiAinda não há avaliações
- FPGA Architecture, Technologies, and Tools: Neeraj Goel IIT DelhiDocumento63 páginasFPGA Architecture, Technologies, and Tools: Neeraj Goel IIT DelhiAnuj BhattAinda não há avaliações
- 4-BIT SYNCHRONOUS COUNTERDocumento6 páginas4-BIT SYNCHRONOUS COUNTERTuhinAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture #32 Registers, Counters EtcDocumento21 páginasLecture #32 Registers, Counters EtcRajan GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- Latches & Flip Flops: Understanding the DifferenceDocumento19 páginasLatches & Flip Flops: Understanding the DifferenceTaran ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Logic Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento63 páginasDigital Logic Multiple Choice QuestionsSalman ManiAinda não há avaliações
- Decoders & MuxDocumento69 páginasDecoders & Muxshivam007Ainda não há avaliações
- Aditya College of Engineering: Answer ALL QuestionsDocumento1 páginaAditya College of Engineering: Answer ALL QuestionsK V BALARAMAKRISHNAAinda não há avaliações
- Home Assgn4 BEE 3BCDocumento4 páginasHome Assgn4 BEE 3BCDaniyal Yasin0% (1)
- Lab Session 08Documento7 páginasLab Session 08Priyanshu KumarAinda não há avaliações
- ECE 301 - Digital Electronics: CountersDocumento25 páginasECE 301 - Digital Electronics: CountersHayan FadhilAinda não há avaliações
- De - Lab ExperimentsDocumento62 páginasDe - Lab ExperimentssaipraneethpAinda não há avaliações
- MD Rakibul Islam Rakib - Lab Report 2Documento4 páginasMD Rakibul Islam Rakib - Lab Report 2A H MAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Logic Design 6th Edition Chapter 12Documento10 páginasFundamentals of Logic Design 6th Edition Chapter 12Huy HoangAinda não há avaliações
- DSD Importanat Question Unit Wise Unit 1Documento2 páginasDSD Importanat Question Unit Wise Unit 1siddharthgrgAinda não há avaliações
- VLSI Design (Online Lectures) Assignment-1Documento3 páginasVLSI Design (Online Lectures) Assignment-1TarushiAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Sheet LAB E3 DIGITAL MODULE - FLIP FLOP AND COUNTERDocumento7 páginasAnswer Sheet LAB E3 DIGITAL MODULE - FLIP FLOP AND COUNTERBen EdwardAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Electronics Lab ManualDocumento191 páginasDigital Electronics Lab Manuallavanyavinayagam1985Ainda não há avaliações
- Nor Gate As Universal Gate:: Power Supply, IC 7400, 7402, LEDDocumento4 páginasNor Gate As Universal Gate:: Power Supply, IC 7400, 7402, LEDNkAinda não há avaliações
- Concepts in VLSI Design: Combinational CircuitsDocumento38 páginasConcepts in VLSI Design: Combinational CircuitsAbhishek BhardwajAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3Documento34 páginasChapter 3Alazar GetachewAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No 3 Combinational Circuits: Binary Adder and Subtractor Circuits Learning ObjectivesDocumento20 páginasExperiment No 3 Combinational Circuits: Binary Adder and Subtractor Circuits Learning ObjectivesSHELPTSAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Logic Circuit Design Experiemnet 8Documento8 páginasDigital Logic Circuit Design Experiemnet 8fahadAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational Logic Circuits - PPTDocumento36 páginasCombinational Logic Circuits - PPTAllanki Sanyasi RaoAinda não há avaliações
- VLSI Design Lab PDFDocumento109 páginasVLSI Design Lab PDFKvnsumeshChandraAinda não há avaliações
- Mech Lab ManualDocumento43 páginasMech Lab ManualTamil SelvanAinda não há avaliações
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyNo EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (227)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyNo EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (82)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002No EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionNo Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (6)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersNo EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102No EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Model-based System and Architecture Engineering with the Arcadia MethodNo EverandModel-based System and Architecture Engineering with the Arcadia MethodAinda não há avaliações
- From Cell Phones to VOIP: The Evolution of Communication Technology - Technology Books | Children's Reference & NonfictionNo EverandFrom Cell Phones to VOIP: The Evolution of Communication Technology - Technology Books | Children's Reference & NonfictionAinda não há avaliações
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XNo EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (2)
- Hacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxNo EverandHacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxAinda não há avaliações
- Creative Selection: Inside Apple's Design Process During the Golden Age of Steve JobsNo EverandCreative Selection: Inside Apple's Design Process During the Golden Age of Steve JobsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (49)
- Dancing with Qubits: How quantum computing works and how it can change the worldNo EverandDancing with Qubits: How quantum computing works and how it can change the worldNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- 2018 (40+) Best Free Apps for Kindle Fire Tablets: +Simple Step-by-Step Guide For New Kindle Fire UsersNo Everand2018 (40+) Best Free Apps for Kindle Fire Tablets: +Simple Step-by-Step Guide For New Kindle Fire UsersAinda não há avaliações
- Cancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionNo EverandCancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)