Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
ECII Fill in The Blanks
Enviado por
prabraghu0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
295 visualizações5 páginasThis document contains 100 fill-in-the-blank questions and answers related to electronics concepts such as rectifiers, transistor biasing, amplifiers, oscillators, digital circuits, memory devices, and counters. The questions cover topics like half wave and full wave rectification, transistor operating points, classes of power amplifiers, feedback in amplifiers, oscillator conditions, binary addition, flip-flops, counters, memory types (RAM, ROM, PROM, EEPROM), analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion, multiplexers, decoders, and more. The document is intended as a study guide to help learn and review these important electronics topics.
Descrição original:
Título original
ECII Fill in the Blanks
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document contains 100 fill-in-the-blank questions and answers related to electronics concepts such as rectifiers, transistor biasing, amplifiers, oscillators, digital circuits, memory devices, and counters. The questions cover topics like half wave and full wave rectification, transistor operating points, classes of power amplifiers, feedback in amplifiers, oscillator conditions, binary addition, flip-flops, counters, memory types (RAM, ROM, PROM, EEPROM), analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion, multiplexers, decoders, and more. The document is intended as a study guide to help learn and review these important electronics topics.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
295 visualizações5 páginasECII Fill in The Blanks
Enviado por
prabraghuThis document contains 100 fill-in-the-blank questions and answers related to electronics concepts such as rectifiers, transistor biasing, amplifiers, oscillators, digital circuits, memory devices, and counters. The questions cover topics like half wave and full wave rectification, transistor operating points, classes of power amplifiers, feedback in amplifiers, oscillator conditions, binary addition, flip-flops, counters, memory types (RAM, ROM, PROM, EEPROM), analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion, multiplexers, decoders, and more. The document is intended as a study guide to help learn and review these important electronics topics.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 5
ECII: 100 Fill in the blanks questions and answers
1. The disadvantage of half wave rectifier is that the output is
difficult to filter.
2. If the ac input to a half wave rectifier has an rms value of 400/√2
volts, then diode PIV rating is 400V.
3. The ripple factor of a half wave rectifier is 1.21.
4. There is a need of transformer for center-tap full wave
rectifier.
5. The PIV rating of each diode in a bridge rectifier is one half that
of the equivalent centre tap rectifier.
6. For the same secondary voltage, the output voltage from a
centre tap rectifier is one-half than that of bridge rectifier.
7. If the PIV rating of a diode is exceeded, the diode is
destroyed.
8. The maximum efficiency of a half wave rectifier is 40.6%.
9. The most widely used rectifier is bridge full wave rectifier.
10.The maximum efficiency of a full wave rectifier is 81.2%.
11.The ripple factor of a full wave rectifier is 0.48
12.Transistor biasing represents dc conditions.
13.Transistor biasing is done to keep proper direct current in
the circuit.
14.Operating point represents zero signal values of Ic and Vce.
15.If biasing is not done in the amplifier circuit, it results in
unfaithful amplification.
16.Transistor biasing is generally provided by a biasing circuit.
17.For faithful amplification by a transistor circuit, the value of Vbe
should not fall below 0.7 V for silicon transistor.
18. For faithful amplification by a transistor circuit, the value of Vce
should not fall below 1 V for silicon transistor.
19.The circuit that provides the best stabilization of operating point
is potential divider bias.
20.For proper amplification by a transistor circuit, the operating
point should be located at the middle of the dc load line.
21.Thermal runaway occurs when the transistor is not biased.
22.When the temperature changes, the operating point is shifted
due to change in ICBO.
23.Transformer coupling is generally used in power amplifiers.
24.A class A power amplifier uses one transistor.
25.Class C power amplifier has the highest collector efficiency.
NRAM Polytechnic, Nitte 1/5
ECII: 100 Fill in the blanks questions and answers
26.A 2 transistor class B power amplifier is commonly called push-
pull amplifier.
27.When a negative voltage feedback is applied to an amplifier, its
voltage gain is reduced.
28.A feedback circuit usually employs resistive network.
29.The gain of an amplifier with feedback is known as closed loop
gain.
30.Negative feedback is employed in amplifiers.
31.The name op-amp stand for operational amplifiers.
32.The basic purpose of applying negative feedback is to reduce
distortion.
33.An oscillator converts dc power into ac power.
34.An oscillator produces undamped oscillations.
35.An oscillator employs positive feedback.
36.An oscillator differs from an amplifier because it requires no
input signal.
37.One condition for oscillation is a phase shift around a feedback
loop is 0°.
38.A second condition for oscillations is a gain of 1 around the
feedback loop.
39.Crystal oscillator is a fixed frequency oscillator.
40.In a summing amplifier the output voltage is negative sum of
all input voltages.
41.A circuit in which the output voltage is the integral of the input
voltage is the integrator.
42.The current to voltage converter is used in digital to analog
converters.
43.The filter circuit which uses transistors or opamps in addition to
resistors and capacitors are called as active filters.
44.The frequency at which the gain decreases down by 3dB is
called the cut-off frequency.
45.NE/SE555 is a monolithic timing circuit that can produce
accurate and highly stable time delays or oscillations.
46.The supply voltage for IC 555 is of +5V to +18V.
47.A monostable multivibrator is also called as a one-shot
multivibrator.
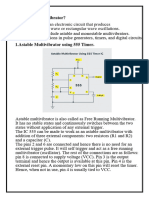
48.An Astable multivibrator is also called as a free-running
multivibrator
NRAM Polytechnic, Nitte 2/5
ECII: 100 Fill in the blanks questions and answers
49.Arithmetic circuits, such as adders and subtractors are called
combinational circuits.
50.The basic addition circuit is called a half adder.
51.Adders can be wired together to form parallel adders.
52.A 4 bit parallel adder adds two 4 –bit binary numbers at one
time.
53.A half adder circuit is used for adding only the 1s column of a
binary addition problem.
54.A full adder must be used for the 2s,4s, 8s and more significant
bits in binary addition.
55.The RS flip-flop has active LOW inputs.
56.The set and reset inputs of the clocked RS flipflop are active
HIGH inputs.
57.When both JK inputs are HIGH then JK flipflop in toggle mode.
58.When both JK inputs are HIGH then JK flipflop in HOLD mode.
59.In ripple counters the JK flip flop is operated in toggle mode.
60.The decade counter is also called as mod-10 counter.
61.A counter that triggers all the flip flops at the same instant is
called a synchronous counter.
62.Clock inputs are connected in parallel on a synchronous
counter.
63.The clear (CLR) input to the shift register is active LOW.
64.The decimal number 29 is the same as 11101 in binary.
65. The decimal number 29 is same as 0010 1001 in 8421 BCD
code.
66. The 74147 encoder has a priority feature.
67.The letter LED stands for Light Emitting Diode.
68. The power for the LED segments in a LED display is given by a
display driver IC.
69. A decoder is a code translator.
70. The RBI and RBO inputs of the 7447 are commonly used for
blanking leading zeroes on calculators.
71.The lamp test, blanking and zero blanking inputs of the 7447 are
active LOW inputs.
72. The letters RAM stands for Random Access Memory.
73.A RAM is also called a read/ write memory.
74.A disadvantage of the RAM is that it is volatile; it loses data
when the power is turned off.
NRAM Polytechnic, Nitte 3/5
ECII: 100 Fill in the blanks questions and answers
75.Copying information into a storage location is called writing
into memory.
76. ROM stand for Read Only Memory.
77. ROM never forget data and are called non-volatile memory.
78. The letter PROM stands for programmable Read Only
Memory.
79.The letter EPROM stands for Erasable programmable Read
Only Memory.
80.The letter EEPROM stands for Electrically Erasable
programmable Read Only Memory.
81. Erasing EPROMs can be done by shining ultraviolet light
through a special window in the top of the IC.
82.A special encoder that converts from analog to digital
information is called analog-to-digital-converter.
83.A special decoder that converts from digital to analog
information is called digital-to-analog converter.
84.A D/A converter consist of a resistor network and a summing
amplifier.
85. One application for an A/D converter is a digital voltmeter.
86.A logic circuit that gates one out of several inputs to single
output is known as a multiplexer.
87. A demultiplexer is a logic circuit that accepts one data input
and distributes it over several outputs.
88. The minimum number of selection inputs required for selecting
one out of 32 inputs is 5.
89. A logic circuit required for converting BCD code to 7 segment
code is known as BCD to 7 segment decoder.
90. Flip flop is a memory element.
91.Number of flip flops required for storing n-bit of information is n.
92. In as SR flip flop S=R=1 is not permitted.
93. Preset and clear inputs are used in flip flops for making Q=1
and 0 respectively.
94. A flip flop has two states.
95. Registers and counters can be designed using flip-flops.
96. The minimum number of flip-flops required for a decade counter
is 4.
97. The modulo of a 4 bit binary counter is 16.
98. The count of a 4 bit down counter is 0000. When clock is
applied its count will be 1111.
NRAM Polytechnic, Nitte 4/5
ECII: 100 Fill in the blanks questions and answers
99.The speed of an asynchronous counter is lower than that of a
synchronous counter.
100. A ripple counter is asynchronous sequential counter.
ALL THE BEST!!
NRAM Polytechnic, Nitte 5/5
Você também pode gostar
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignNo EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Ainda não há avaliações
- TSR 9294 DLA3 Dragons RestDocumento78 páginasTSR 9294 DLA3 Dragons RestLéo Duarte100% (4)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorNo Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Nota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (3)
- 00 Table of ContentsDocumento26 páginas00 Table of ContentsNana Agyeman AntwiAinda não há avaliações
- Inverter Explanation Cd4047Documento7 páginasInverter Explanation Cd4047Sruthi ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Integrated Circuits Course Outline PDFDocumento49 páginasLinear Integrated Circuits Course Outline PDFSarvjeet Singh SohalAinda não há avaliações
- Heroic Tales Core Rules 1.1.0Documento33 páginasHeroic Tales Core Rules 1.1.0Melobajoya MelobajoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Creation of A Piano Using A 555 Timer ICDocumento9 páginasCreation of A Piano Using A 555 Timer ICPruthvi Trinath100% (1)
- Linear Integrated CircuitsDocumento17 páginasLinear Integrated CircuitsShahrruck SAinda não há avaliações
- Module 8 - Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingDocumento4 páginasModule 8 - Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingSheila Mae Paltep100% (3)
- 3250-008 Foundations of Data Science Course Outline - Spring 2018Documento6 páginas3250-008 Foundations of Data Science Course Outline - Spring 2018vaneetAinda não há avaliações
- ECS 3390 - Business and Technical CommuncationsDocumento293 páginasECS 3390 - Business and Technical CommuncationsEliseo Robles0% (3)
- D - Jayakumar Ece Ece Ece Viva Questions-JkDocumento20 páginasD - Jayakumar Ece Ece Ece Viva Questions-Jktinku990056% (9)
- Crowd Management - Model Course128Documento117 páginasCrowd Management - Model Course128alonso_r100% (4)
- Power Electronics MCQ & Short QaDocumento19 páginasPower Electronics MCQ & Short QaAngamuthu Ananth100% (2)
- Module: ELEC 03 Total Questions: 100 Total Recorded: 100: AnswerDocumento6 páginasModule: ELEC 03 Total Questions: 100 Total Recorded: 100: AnswerJhasper ManagyoAinda não há avaliações
- IJSRDV2I3100Documento10 páginasIJSRDV2I3100Yash KalraAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Integrated Circuits Lab Viva-Voce QuestionsDocumento8 páginasLinear Integrated Circuits Lab Viva-Voce QuestionsNithin SAinda não há avaliações
- Elex Module 2Documento6 páginasElex Module 2Chemuel Mardie G. ObedencioAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Circuits 1 Ec1203Documento13 páginasElectronic Circuits 1 Ec1203ainugiri100% (2)
- Electronic Circuits I 2 Marks Question AnswersDocumento13 páginasElectronic Circuits I 2 Marks Question Answersbala_smAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Electronics &communication Engineering: B C Co BEDocumento11 páginasDepartment of Electronics &communication Engineering: B C Co BEKishoth kumar.AAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Integrated CircuitsDocumento15 páginasLinear Integrated CircuitsAISWARYA MAinda não há avaliações
- EC I 2marks PDFDocumento13 páginasEC I 2marks PDFPetrishia ArockiasamyAinda não há avaliações
- Function of U1 CA555Documento7 páginasFunction of U1 CA555sjnl100% (1)
- Unit-3 - Function Generator Using IC 8038Documento10 páginasUnit-3 - Function Generator Using IC 8038yp2401553Ainda não há avaliações
- ADE - Pspice Lab ManualDocumento12 páginasADE - Pspice Lab ManualShashiAinda não há avaliações
- Module: ELEC 4 Total Questions: 100 Total Recorded:: AnswerDocumento4 páginasModule: ELEC 4 Total Questions: 100 Total Recorded:: AnswerJhasper ManagyoAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics Module 4Documento4 páginasElectronics Module 4light cloudAinda não há avaliações
- Silicon Wafer (Substrate) Preparation 2. Epitaxial Growth 3. Oxidation 4. Photolithography 5. Diffusion 6. Ion Implantation 7. Isolation Techniques 8. MetallizationDocumento21 páginasSilicon Wafer (Substrate) Preparation 2. Epitaxial Growth 3. Oxidation 4. Photolithography 5. Diffusion 6. Ion Implantation 7. Isolation Techniques 8. MetallizationMangaiyarkarasi VengatachalamAinda não há avaliações
- Frequency To Voltage Converter ReportDocumento5 páginasFrequency To Voltage Converter ReportEssa SiddiquiAinda não há avaliações
- Ade Lab ManualDocumento104 páginasAde Lab Manualsrinureddy2014Ainda não há avaliações
- DEPT Lab Question2Documento10 páginasDEPT Lab Question2Mostofa Al MuradAinda não há avaliações
- Piano ReportDocumento9 páginasPiano ReportMaryam TariqAinda não há avaliações
- ElectronicsDocumento8 páginasElectronicsmadhu chandrikaAinda não há avaliações
- EE51POWER ELECTORNICS EzDocumento20 páginasEE51POWER ELECTORNICS EzAnonymous m8oCtJBAinda não há avaliações
- Module 16Documento3 páginasModule 16Jojo TakatoAinda não há avaliações
- Ee 3101 Electronics I Laboratory Experiment 2 Lab Manual Power Supply Design ConsiderationsDocumento8 páginasEe 3101 Electronics I Laboratory Experiment 2 Lab Manual Power Supply Design ConsiderationsAnurag PatelAinda não há avaliações
- SPEED CONTROL OF SINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR" BY USING TRIAC - PPTDocumento30 páginasSPEED CONTROL OF SINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR" BY USING TRIAC - PPTGökhan KAYA100% (2)
- Experiment No.4: FM Using 555 IcDocumento3 páginasExperiment No.4: FM Using 555 IcSree DhanyaAinda não há avaliações
- Ec 36 Electronics Circuits-IDocumento15 páginasEc 36 Electronics Circuits-IHania UmarAinda não há avaliações
- Multi VibratorDocumento3 páginasMulti VibratorGayathri SwethaAinda não há avaliações
- Micro Controller Base Satelite TrackingDocumento67 páginasMicro Controller Base Satelite TrackingYuvraj ChaudhariAinda não há avaliações
- Ica Lab (135) Iii-IDocumento87 páginasIca Lab (135) Iii-IesesesAinda não há avaliações
- Ic Lab Planer 8-7-13Documento55 páginasIc Lab Planer 8-7-13NaveenkAinda não há avaliações
- AND8099/D 5.0 V, 2.0 A Flyback Converter: Application NoteDocumento8 páginasAND8099/D 5.0 V, 2.0 A Flyback Converter: Application NoteIgor MairinckAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics Exercise 2: The 555 Timer and It's Applications: ObjectiveDocumento5 páginasElectronics Exercise 2: The 555 Timer and It's Applications: ObjectiveMichael AjayiAinda não há avaliações
- PWM Signal GeneratorsDocumento3 páginasPWM Signal GeneratorsjalalhAinda não há avaliações
- Analog Communications Laboratory (Experiment: 7Documento5 páginasAnalog Communications Laboratory (Experiment: 7Yogesh GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- Traffic Light Control SystemDocumento12 páginasTraffic Light Control SystemVinay ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- DiDocumento5 páginasDiByron DamaniaAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Channel IR Remote Control System Using MicrocontrollerDocumento5 páginas5 Channel IR Remote Control System Using MicrocontrollerKoushik MaityAinda não há avaliações
- PWM Signal Generators: Testing Status: Mixed. Some Untested, Some SPICE SimulatedDocumento15 páginasPWM Signal Generators: Testing Status: Mixed. Some Untested, Some SPICE SimulatedSivareddy MudiyalaAinda não há avaliações
- Analog and Digital Ic'S Short Questions With AnswersDocumento41 páginasAnalog and Digital Ic'S Short Questions With Answerspriya adhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Microcontroller Based Low Cost Controlled Rectifiers Training Module For Power Electronics LaboratoryDocumento4 páginasMicrocontroller Based Low Cost Controlled Rectifiers Training Module For Power Electronics LaboratoryJubari FikriAinda não há avaliações
- Oscillator ManualDocumento22 páginasOscillator ManualckooipgAinda não há avaliações
- Power Electronics Short Questions and AnswersDocumento21 páginasPower Electronics Short Questions and AnswersPalak Ariwala75% (4)
- ClocksDocumento4 páginasClocksluizcpimentaAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Marks Ldica NotesDocumento8 páginas2 Marks Ldica NotesRAJOLI GIRISAI MADHAV100% (2)
- Cycloconverter ManualDocumento6 páginasCycloconverter ManualShankar ArunmozhiAinda não há avaliações
- Digital To Analog: R R D V 2R DDocumento13 páginasDigital To Analog: R R D V 2R DRudra MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Techniques Micro-ProjectDocumento11 páginasDigital Techniques Micro-ProjectRonit PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Ee 3101 Electronics I Laboratory Experiment 9 Lab Manual Applications of Ic Building BlocksDocumento5 páginasEe 3101 Electronics I Laboratory Experiment 9 Lab Manual Applications of Ic Building BlocksPriyanshu KumawatAinda não há avaliações
- Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College HospitalDocumento3 páginasShaheed Suhrawardy Medical College HospitalDr. Mohammad Nazrul IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Health Concerns in The 21st CenturyDocumento4 páginasCritical Health Concerns in The 21st CenturykelleybrawnAinda não há avaliações
- VukcevicEtAl GhostFluidMethodInPolyhedralFV AnnotatedDocumento19 páginasVukcevicEtAl GhostFluidMethodInPolyhedralFV AnnotatedputhenkulamAinda não há avaliações
- Edagogy of Anguages: VerviewDocumento54 páginasEdagogy of Anguages: VerviewMukesh MalviyaAinda não há avaliações
- Edwards SVV HandoutDocumento2 páginasEdwards SVV HandoutossinAinda não há avaliações
- Warranties Liabilities Patents Bids and InsuranceDocumento39 páginasWarranties Liabilities Patents Bids and InsuranceIVAN JOHN BITONAinda não há avaliações
- PWC - Digital Pocket Tax Book 2023 - SlovakiaDocumento52 páginasPWC - Digital Pocket Tax Book 2023 - SlovakiaRoman SlovinecAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Report: Patient Name: Pranav Chauhan PRANM050319990B 0009VA060799Documento2 páginasDiagnostic Report: Patient Name: Pranav Chauhan PRANM050319990B 0009VA060799pranav chauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter - 01 Geography The Earth in The Solar SystemDocumento10 páginasChapter - 01 Geography The Earth in The Solar SystemKarsin ManochaAinda não há avaliações
- Note 15-Feb-2023Documento4 páginasNote 15-Feb-2023Oliver ScissorsAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 Learning PrinciplesDocumento2 páginasModule 1 Learning PrinciplesAngela Agonos100% (1)
- Yealink Meeting Server Administrator Guide V10.23.0.5 PDFDocumento97 páginasYealink Meeting Server Administrator Guide V10.23.0.5 PDFFatima PérezAinda não há avaliações
- Removal of Chloride in The Kraft Chemical Recovery CycleDocumento8 páginasRemoval of Chloride in The Kraft Chemical Recovery CycleVeldaa AmiraaAinda não há avaliações
- Myplan Assessment Skills Profiler Report Summary AnalysisDocumento5 páginasMyplan Assessment Skills Profiler Report Summary Analysisapi-338283524Ainda não há avaliações
- Causal Relationships WorksheetDocumento2 páginasCausal Relationships Worksheetledmabaya23Ainda não há avaliações
- Asia Pacific SAR Plan V2.0Documento38 páginasAsia Pacific SAR Plan V2.0Joci SimõesAinda não há avaliações
- 热虹吸管相变传热行为CFD模拟 王啸远Documento7 páginas热虹吸管相变传热行为CFD模拟 王啸远小黄包Ainda não há avaliações
- Programmable Logic Controllers: Basic Ladder Logic ProgrammingDocumento9 páginasProgrammable Logic Controllers: Basic Ladder Logic Programminganuradha19Ainda não há avaliações
- Watt AC-DC Converters: FeaturesDocumento3 páginasWatt AC-DC Converters: FeatureskofidAinda não há avaliações
- PostmanPat Activity PackDocumento5 páginasPostmanPat Activity PackCorto Maltese100% (1)
- Continuous Improvement SYMPOSIUM SCRIPTDocumento3 páginasContinuous Improvement SYMPOSIUM SCRIPTChanda Marie AsedillaAinda não há avaliações
- New York LifeDocumento38 páginasNew York LifeDaniel SineusAinda não há avaliações
- Preparatory Newsletter No 3 2013Documento22 páginasPreparatory Newsletter No 3 2013SJC AdminAinda não há avaliações
- Bilge Günsel TEL531E Detection and Estimation Theory W #1-2Documento25 páginasBilge Günsel TEL531E Detection and Estimation Theory W #1-2ahmetAinda não há avaliações