Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Atherosclerosis
Enviado por
froilanjalotjotDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Atherosclerosis
Enviado por
froilanjalotjotDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
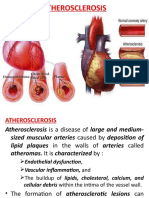
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
abnormal accumulation of lipid, or fatty, substances and fibrous tissue in the vessel wall.
A form of arteriosclerosis, it is the reduction in blood flow through the arteries caused by greasy
deposits called atheroma or plaque that form on the insides of arteries and partially restrict the flow of
blood.
Plaque deposits are associated with high concentrations of cholesterol in the blood. Recent studies have
also shown an association between inflammation and plaque deposits.
Blood flow is often further reduced by the formation of blood clots (Thrombosis), which are most likely
to form where the artery walls have been roughened by plaque.
Reduction in blood flow can cause organ damage. A heart attack occurs when a coronary artery
becomes blocked and heart muscle is destroyed.
The anatomic structure of the coronary arteries makes them particularly most susceptible to the
mechanisms of atherosclerosis.
Risk factors that contribute to atherosclerosis include physical inactivity, smoking, a diet high in fat, high
blood pressure, and diabetes mellitus.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CORONARY ATHEROSCLEROSIS
Lipid or fatty deposits in the intima of the arterial wall
Macrophagest ingest lipid then die
Proliferation of smooth muscle cells to form a fibrous cap
Atheromas or Plaques Lipid core may grow leading to rupture of the fibrous cap
Narrowing of BV and obstruction to BF Thrombus formation
↓ Blood flow to the heart
↓ O2 Supply
Ischemia of myocardial cells
↑ Lactic Acid
Pain
Myocardial Infarction
Você também pode gostar
- 1 Henry McCraeDocumento4 páginas1 Henry McCraeAbdullah RajaAinda não há avaliações
- Atherosclerosis: A Brief SummaryDocumento7 páginasAtherosclerosis: A Brief Summarynan doeAinda não há avaliações
- Atherosclerosis and Myocardial InfractionDocumento26 páginasAtherosclerosis and Myocardial InfractionElina GAinda não há avaliações
- AtherosclerosisDocumento23 páginasAtherosclerosisPoonam soniAinda não há avaliações
- Myocardial InfarctionDocumento2 páginasMyocardial InfarctionAmyAinda não há avaliações
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromoboembolism and ShockDocumento10 páginasHemodynamic Disorders, Thromoboembolism and ShockMarinelle TumanguilAinda não há avaliações
- AterosklerosisDocumento40 páginasAterosklerosisIda Benecia DeseAinda não há avaliações
- Kel 10 Diseases and Disorders of The Circulatory SystemDocumento16 páginasKel 10 Diseases and Disorders of The Circulatory SystemocktiAinda não há avaliações
- Patomorfologia Prezentacja - KopiaDocumento14 páginasPatomorfologia Prezentacja - KopiaOlgaAinda não há avaliações
- SG 4,5,6Documento20 páginasSG 4,5,6Itadori YujiAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular Systems - 2 (Blood and Lymphatic Vessel)Documento37 páginasCardiovascular Systems - 2 (Blood and Lymphatic Vessel)RezaAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular Pathology 2024Documento132 páginasCardiovascular Pathology 2024Chen HouyuAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocumento5 páginasCardiovascular DisordersAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniAinda não há avaliações
- Pa Tho Physiology of Angina PectorisDocumento2 páginasPa Tho Physiology of Angina PectorisChristine Elaine Batusin IlaganAinda não há avaliações
- Hypertension: Synthesis of The Disease For Coronary Artery Disease (Book-Based) b.1. Definition of The DiseaseDocumento9 páginasHypertension: Synthesis of The Disease For Coronary Artery Disease (Book-Based) b.1. Definition of The DiseaseAnnAinda não há avaliações
- Book Cardio ConceptDocumento29 páginasBook Cardio ConceptJulia Rae Delos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- AtherosclerosisDocumento56 páginasAtherosclerosissilentdestruction100% (1)
- AtherosclerosisDocumento24 páginasAtherosclerosisnabilaAinda não há avaliações
- Sirkulasi Koroner: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocumento36 páginasSirkulasi Koroner: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraYohanna SinuhajiAinda não há avaliações
- Pathology 2 Block 1 NotesDocumento11 páginasPathology 2 Block 1 NotesJason KaplanAinda não há avaliações
- PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginasPathophysiologyJosh LazoAinda não há avaliações
- Diseases and Disorders of The Human Circulatory SystemDocumento18 páginasDiseases and Disorders of The Human Circulatory SystemvvAinda não há avaliações
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocumento3 páginasSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Cardiovascular DiseasesDocumento11 páginasBio Cardiovascular DiseasesSoon ElaineAinda não há avaliações
- Atherosclerosis 1Documento45 páginasAtherosclerosis 1MoonAIRAinda não há avaliações
- Atherosclerosis P 30 - 31Documento2 páginasAtherosclerosis P 30 - 31Shiv DattaAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Clotting Mechanisms and AtherosclesrosisDocumento11 páginasBlood Clotting Mechanisms and AtherosclesrosisGizelle Iwo BatkoAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDocumento43 páginasCardiovascular DiseasesApple Mae AlmoniaAinda não há avaliações
- Disorders of TheDocumento2 páginasDisorders of ThewiniindrianiAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD) : AtherosclerosisDocumento4 páginasCardiovascular Diseases (CVD) : Atherosclerosisnan doeAinda não há avaliações
- The Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocumento15 páginasThe Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosisviper121Ainda não há avaliações
- Assign PDFDocumento4 páginasAssign PDFAhmedA.SharafAinda não há avaliações
- Hemodinamik Dan Penyakit Thrombosis (MU) HEMODINAMIK DAN PENYAKIT THROMBOSISDocumento59 páginasHemodinamik Dan Penyakit Thrombosis (MU) HEMODINAMIK DAN PENYAKIT THROMBOSISflowerpearlyAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiology 3 F2018Documento34 páginasCardiology 3 F2018TkAinda não há avaliações
- 4 CVDDocumento19 páginas4 CVDYousef WardatAinda não há avaliações
- CALIXTRO, LJM Coronary AtherosclerosisDocumento2 páginasCALIXTRO, LJM Coronary AtherosclerosisKim SunooAinda não há avaliações
- Narrative PathophysiologyDocumento18 páginasNarrative PathophysiologyNica Georgelle Maniego SamonteAinda não há avaliações
- Defense Againts Infectious Diseases ClassworkDocumento2 páginasDefense Againts Infectious Diseases ClassworkSofia OrtizAinda não há avaliações
- Ischemic StrokeDocumento3 páginasIschemic StrokerimarahmadiptaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Atherosclerosis?: Smoking - This Can Damage and TightenDocumento2 páginasWhat Is Atherosclerosis?: Smoking - This Can Damage and TightenAly AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- 141 - PDFsam - Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9eDocumento20 páginas141 - PDFsam - Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9eRizky Angga PerdanaAinda não há avaliações
- Coronart Artery DiseasesDocumento26 páginasCoronart Artery DiseasesakashAinda não há avaliações
- Peripheral Arterial Disease 1Documento1 páginaPeripheral Arterial Disease 1Pauline TayabanAinda não há avaliações
- Hemodynamic Disorders NotesDocumento12 páginasHemodynamic Disorders NotesavidadarkestevilAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis and EmbolismDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology of Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis and EmbolismKeshant Samaroo100% (1)
- Group3 JatiDocumento8 páginasGroup3 JatiAmsyidi AsmidaAinda não há avaliações
- Atherosclerosis 2 2017 (Modified)Documento64 páginasAtherosclerosis 2 2017 (Modified)Remo B AbyAinda não há avaliações
- Arteriosclerosis & AtherosclerosisDocumento29 páginasArteriosclerosis & AtherosclerosisblossomkdcAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System: Vascular DiseaseDocumento5 páginasCirculatory System: Vascular DiseaseRabbyiatul Al AdawiaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is The Function of TriglyceridesDocumento5 páginasWhat Is The Function of Triglyceridesrosidin_551390Ainda não há avaliações
- Arterial Thrombosis by AbrarDocumento20 páginasArterial Thrombosis by AbrarZain HadiAinda não há avaliações
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis and ShockDocumento40 páginasHemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis and ShockAndi Tri NugrahaAinda não há avaliações
- 5 - Pathology of CADDocumento58 páginas5 - Pathology of CADregeti bhargavAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular Changes Group 5Documento16 páginasCardiovascular Changes Group 5Andrea Albester GarinoAinda não há avaliações
- Disorders of The Circulatory SystemDocumento3 páginasDisorders of The Circulatory SystemCondurache Ilie-AndreiAinda não há avaliações
- Ailments of The Circulatory SystemDocumento1 páginaAilments of The Circulatory SystemJovita Projemo HolandaAinda não há avaliações
- Praktikum Cardiovaskular DiseaseDocumento38 páginasPraktikum Cardiovaskular DiseaseJAQUELINEAinda não há avaliações
- Atherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo EverandAtherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações