Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Osteoarthritis
Enviado por
caanhil0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
28 visualizações1 páginaDireitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
28 visualizações1 páginaOsteoarthritis
Enviado por
caanhilDireitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
Osteoarthritis-(OA) is the most common form of arthritis, with up to 40 million people in the US
having been diagnosed with it.
-Also known as degenerative joint disease
-generally considered to be noninflammatory.
-the same cytokines and interleukins seen in inflammatory arthritis are also seen inosteoarthritis,
although in lesser quantity.
-Theories of etiology include both primary biomechanical, or primary biochemical effects
andsecondary biomechanical-derived effects leading to a gradual loss of articular cartilage.
-Many patients do not have a clearly identifiable source for their OA
-Other patients may demonstrate problems such as chronic instability, malalignment, priorinjury,
crystalline disease, past history of meniscectomy, or excessive and repetitive loading
-A genetic predisposition is present in some patients.
O The knee is the most commonly affected joint.
O Radiographic evidence of OA is common by age 40 years, but clinically significantosteoarthritis is
less common until about age 60 years
-Typical findings on a radiographic examination reveal loss of articular cartilage shown by
"jointnarrowing" especially on weight-bearing films.
-Osteophytes and subchondral cysts are common radiographic findings.
-Physical examination reveals pain upon walking (an antalgic gait pattern) or motion of theinvolved
joint.
-Patients have some degree of limitation of motion, pain and/or crepitus with that motion.
-Usually there is an effusion in the joint.
-The initial treatment includes
O activity modification
O weight reduction if indicated
O the use of a cane for lower-extremity problems
O nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and nonnarcotic analgesic medications if required.
-Patients should be encouraged to maintain their joint motion and muscular strength.
-Rarely, an intra-articular corticosteroid injection can be used for an acutely painful joint, but it is
only a temporary solution
-Surgical options are based on the dramatic success of joint replacement to relieve pain andrestore
function to the arthritic joint.
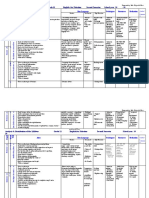
Synovial Fluid Analysis
Clinical Example Normal Noninflammatory(Osteoarthrosis) Inflammatory(Rheumatoid) Septic (Bacterial)
Color Clear Clear yellow Opalescent yellow Turbid yellow to
green
Viscosity High High Low Low
WBC/mm3 200 200– 2000 200– 100,000 >100,000
% PMM leukocytes <25% <25% >50% >75%
Culture Negative Negative Negative Positive
Mucin clot Firm Firm Friable Friable
Glucose 100% 100% 50–75% <50%
(% of serumglucose)
Total protein Normal Normal Elevated Elevated
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Mms Health Recovery Guidebook 1 October 2016Documento346 páginasMms Health Recovery Guidebook 1 October 2016omar hazard94% (50)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Myths and Truths About Transcendental MeditationDocumento11 páginasThe Myths and Truths About Transcendental MeditationMeditation Fix100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Fractures NoteDocumento31 páginasFractures NoteNoor AlblushiAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Aromaterapia Español PDFDocumento60 páginasManual Aromaterapia Español PDFPablo Andrés Mora SolísAinda não há avaliações
- Shape Up BusyBee CarysDocumento16 páginasShape Up BusyBee CarysElena HorodincaAinda não há avaliações
- YakultDocumento15 páginasYakultMlb T. De TorresAinda não há avaliações
- English Teacher's NotesDocumento24 páginasEnglish Teacher's NotesPrincess KimAinda não há avaliações
- An Electromyographical Analysis of Sumo and Conventional Style DeadliftsDocumento8 páginasAn Electromyographical Analysis of Sumo and Conventional Style DeadliftsRafael EscamillaAinda não há avaliações
- Prevention and Control of Infectious Disease Act 1988Documento16 páginasPrevention and Control of Infectious Disease Act 1988smuf_2Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12 Rev QuestionsDocumento3 páginasChapter 12 Rev QuestionsLidia DominguezAinda não há avaliações
- Advancements in The Bbutilization of Azolla Anabaena System in RelationDocumento17 páginasAdvancements in The Bbutilization of Azolla Anabaena System in Relationryana_soesantieAinda não há avaliações
- HCM 239Documento199 páginasHCM 239Mohit VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Official ResumeDocumento1 páginaOfficial ResumeBrianna DallalAinda não há avaliações
- 21.JMM Promotion and Management, Inc. vs. Court of AppealsDocumento3 páginas21.JMM Promotion and Management, Inc. vs. Court of AppealsnathAinda não há avaliações
- Extended and Expanded Roles of Nurses 2Documento1 páginaExtended and Expanded Roles of Nurses 2Sivaprasad SAinda não há avaliações
- Assisting For Endotracheal IntubationDocumento16 páginasAssisting For Endotracheal IntubationSREEDEVI T SURESH100% (1)
- Experiment 9 - Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesDocumento2 páginasExperiment 9 - Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesJuren LasagaAinda não há avaliações
- NURS FPX 6030 Assessment 6 Final Project SubmissionDocumento11 páginasNURS FPX 6030 Assessment 6 Final Project Submissionzadem5266Ainda não há avaliações
- Nso AblaparotomyDocumento3 páginasNso AblaparotomyAleeya SarajanAinda não há avaliações
- The Ethics of Helping Transgender Men and Women Have ChildrenDocumento16 páginasThe Ethics of Helping Transgender Men and Women Have ChildrenAnonymous 75M6uB3OwAinda não há avaliações
- Nitroimidazole Wps OfficeDocumento10 páginasNitroimidazole Wps OfficeCamelle DiniayAinda não há avaliações
- SR.# Weight (KG) Height (FT) Age (Yrz) Others RecommendationsDocumento2 páginasSR.# Weight (KG) Height (FT) Age (Yrz) Others RecommendationsshaniAinda não há avaliações
- (ENGLISH) Perbandingan Khasiat Cetirizine Dan LoratadinDocumento9 páginas(ENGLISH) Perbandingan Khasiat Cetirizine Dan Loratadinintan nabilah pratiwiAinda não há avaliações
- STD.: Xi Practice Test - 2016 Date: 0 14 - 10 - 2016 SUBJECT: Zoology Animal HusbandryDocumento2 páginasSTD.: Xi Practice Test - 2016 Date: 0 14 - 10 - 2016 SUBJECT: Zoology Animal HusbandryDr-Atin Kumar SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- 3 5 18 950 PDFDocumento3 páginas3 5 18 950 PDFBang AthanAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Fitness Test Individual Score CardDocumento12 páginasPhysical Fitness Test Individual Score CardJunessa TadinaAinda não há avaliações
- Ifosfamide Nephrotoxicity - UpToDateDocumento7 páginasIfosfamide Nephrotoxicity - UpToDateZurya UdayanaAinda não há avaliações
- 10 1007@s00068-mfjrbtDocumento14 páginas10 1007@s00068-mfjrbtJGunar VasquezAinda não há avaliações
- Break The Cycle Activity GuidesDocumento19 páginasBreak The Cycle Activity GuidesJuanmiguel Ocampo Dion SchpAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis & Distribution of The Syllabus Grade 11 English For Palestine Second Semester School Year: 20 - 20Documento3 páginasAnalysis & Distribution of The Syllabus Grade 11 English For Palestine Second Semester School Year: 20 - 20Nur IbrahimAinda não há avaliações