Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Project
Enviado por
Shivam BhatiaDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Project
Enviado por
Shivam BhatiaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
96 F E B R U A R Y 2 0 0 5 E LEC T R O N IC S F O R YO U
W W W . E F Y M A G . C O M
CIRCUIT
IDEAS
S.C.DWIVEDI
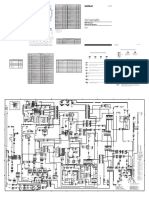
T his charger for series-connected
4-cell AA batteries automatically
disconnects from mains to stop charging when the batteries are fully charged. It can be used to charge par - tially discharged
cells as well.
The circuit is simple and can be
divided into AC-to-DC converter, relay
driver and charging sections.
In the AC-to-DC converter section, transformer X1 steps down mains 230V AC to 9V AC at 750 mA, which is rec - tified by a full-wave
rectifier compris- ing diodes D1 through D4 and filtered by capacitor C1. Regulator IC LM317 (IC1) provides the required 12V DC charging
voltage. When you press switch S1 momentarily, the charger starts operating and the power -on LED1 glows to indicate that the charger is
µon.¶
The relay driver section uses pnp
transistors T1, T2 and T3 (each BC558)
Y .M . A N A N D A V A R D H A N A
toenergise electromagnetic relay RL1. Relay RL1 is connected to the collec- tor of transistor T1. Transistor T1 is driven by pnp transistor
T2, which, in turn, is driven by pnp transistor T3. Resistor R4 (10 -ohm, 0.5W) is con- nected between the emitter and base of transistor
T3.
When a current of over 65 mA
flows through the 12V line, it causes a
voltage drop of about 650 mV across resistor R4 to drive transistor T3 and cut off transistor T2. This, in turn, turns transistor T1 µon¶ to energise
relay RL1. Now even if the pushbutton is re- leased, mains is still available to the primary of the transformer through its normally open (N/O)
contacts.
In the charging section, regulator IC1 is biased to give about 7.35V. Pre - set VR1 is used for adjusting the bias voltage. Diode D6
connected between the output of IC1 and battery limits the output voltage to about 6.7V, which is used for charging the batt ery.
AUTO TURN-OFF
BATTERY CHARGER
Pushing switch S1 latches relay RL1 and the battery cells start charg- ing. As the voltage per cell increases beyond 1.3V, the
voltage drop across resistor R4 starts decreasing. When it falls below 650 mV, transistor T3 cuts off to drive transistor T2 and, in turn, cuts
off transistor T3. As a result, re- lay RL1 de-energises to cut off the charger and red LED1 turns off.
You may determine the charging voltage depending on the NiCd cell specifications by the manufacturer. Here, we¶ve set the
charging voltage at 7.35V for four 1.5V cells. Nowadays, 700mAH cells are available in the mar - ket, which can be charged at 70 mA for
10 hours. The open-circuit voltage is about 1.3V.
The shut-off voltage point is deter- mined by charging the four cells fully (at 70 mA for 14 hours). After measur - ing the output
voltage, add the diode drop (about 0
Você também pode gostar
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Data Warehousing Quick GuideDocumento66 páginasData Warehousing Quick Guidejacktheking2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- SVT-RM10: Remote Control UnitDocumento2 páginasSVT-RM10: Remote Control UnitJOGITELEAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- How Does A Blueprint Work?Documento5 páginasHow Does A Blueprint Work?Eumieh Jane AlfonsoAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Qdoc - Tips Bs en Iso 19285 2017 Non Destructive Testing of WeDocumento30 páginasQdoc - Tips Bs en Iso 19285 2017 Non Destructive Testing of WeDave CheungAinda não há avaliações
- Planeur Tres Simple PDFDocumento3 páginasPlaneur Tres Simple PDFAhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Work at Height Questions For Height PassDocumento3 páginasWork at Height Questions For Height PassPravash Mohanty100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Ibell RH26-26Documento18 páginasIbell RH26-26SangaAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Assign Chap 8Documento3 páginasAssign Chap 8nishedhAinda não há avaliações
- Iv2906 Iveco Ad380t42h 6x4Documento2 páginasIv2906 Iveco Ad380t42h 6x4أبو خالد الأثرىAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- LoftplanDocumento1 páginaLoftplanapi-228799117Ainda não há avaliações
- Cables TheoryDocumento15 páginasCables TheorytceterexAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Sop 4590Documento230 páginasSop 4590Mike WilliamAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- 80312A-ENUS Error LogDocumento10 páginas80312A-ENUS Error LogSafdar HussainAinda não há avaliações
- d8n Wiring HardnessDocumento2 páginasd8n Wiring HardnessandraAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Test PDFDocumento6 páginasTest PDFDr. L. Bhanuprakash Reddy100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
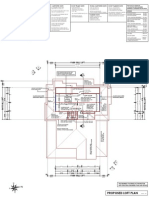
- Column Marking For G+4 Hostel Building: All Dimensions Are in MeterDocumento1 páginaColumn Marking For G+4 Hostel Building: All Dimensions Are in Metergowtham gowdaAinda não há avaliações
- Comb - Chemkin - Format PDFDocumento5 páginasComb - Chemkin - Format PDFMUHAMMAD FAREEZ IZWAN BIN ABDUL JALILAinda não há avaliações
- Gen00036-04 Wa600-6 Wheel LoaderDocumento98 páginasGen00036-04 Wa600-6 Wheel LoaderJuan Araya BarrazaAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Gold Alloy Spinnerets For The Production of Viscose RayonDocumento8 páginasGold Alloy Spinnerets For The Production of Viscose RayonPhan MHanhAinda não há avaliações
- Guide To The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (Sebok), Version 1.1Documento51 páginasGuide To The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (Sebok), Version 1.1António FerreiraAinda não há avaliações
- Data Sheet For Toys TestDocumento2 páginasData Sheet For Toys TestAnonymous TYGiADAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- When Good Engineers Deliver Bad FEADocumento17 páginasWhen Good Engineers Deliver Bad FEAJarad Wilson100% (1)
- Computation For Concrete Mix 120221Documento3 páginasComputation For Concrete Mix 120221MASGRO BUILDERSAinda não há avaliações
- Aqueous EquilibriumDocumento7 páginasAqueous EquilibriumWONG TSAinda não há avaliações
- SWOT Analysis of Viyellatex Spinning LimitedDocumento81 páginasSWOT Analysis of Viyellatex Spinning LimitedHossain RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier Series - MATLAB & Simulink PDFDocumento7 páginasFourier Series - MATLAB & Simulink PDFWanderson Antonio Sousa SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- B766Documento9 páginasB766marriolavAinda não há avaliações
- Project 3 FinalDocumento15 páginasProject 3 Finalapi-285419046Ainda não há avaliações
- Ione-Aa00-Pe-Cm-0005 Hse Procedure For Pre Start-Up Safety Review - Rev. ADocumento21 páginasIone-Aa00-Pe-Cm-0005 Hse Procedure For Pre Start-Up Safety Review - Rev. AYusuf100% (2)
- 180 W PC Main SFX Supply - PHPDocumento2 páginas180 W PC Main SFX Supply - PHPCici Icic100% (1)