Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
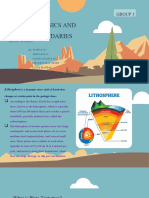
Summary About Plate Tectonics
Enviado por
Christine Khong100%(2)100% acharam este documento útil (2 votos)
362 visualizações2 páginasPlates on the Earth's surface move or change shape due to the convection of the asthenosphere which can cause changes in the topography of the Earth. Divergence, either between two continental plates or two oceanic plates, move away from each other when magma rises to the surface between them. Transform fault boundaries happen when one plate slides laterally past another causing massive amounts of energy to be released.
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoPlates on the Earth's surface move or change shape due to the convection of the asthenosphere which can cause changes in the topography of the Earth. Divergence, either between two continental plates or two oceanic plates, move away from each other when magma rises to the surface between them. Transform fault boundaries happen when one plate slides laterally past another causing massive amounts of energy to be released.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
100%(2)100% acharam este documento útil (2 votos)
362 visualizações2 páginasSummary About Plate Tectonics
Enviado por
Christine KhongPlates on the Earth's surface move or change shape due to the convection of the asthenosphere which can cause changes in the topography of the Earth. Divergence, either between two continental plates or two oceanic plates, move away from each other when magma rises to the surface between them. Transform fault boundaries happen when one plate slides laterally past another causing massive amounts of energy to be released.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
Christine Khong
Duncan
APES- Period 2
13 December 2010
Summary About Plate Tectonics
Proposed by Alfred Wegener, the theory of continental drift stated that
all of the land masses on Earth had once formed one supercontinent which
broke apart and drifted to different locations. Evidence such as fossil
evidence, rock evidence, and that the continents can virtually fit together
like a puzzle supports this idea thus leading to the theory of plate tectonics.
The ‘floating’ plates on the Earth’s surface move or change shape due to the
convection of the asthenosphere which can cause changes in the topography
of the Earth, change the location/size of a continent, alter the climate, and/or
cause isolation between species as land is split up which may lead to the
evolution of a new species.
Three types of plate boundaries include: divergent, convergent, and
transform fault boundaries. Divergence, either between two continental
plates or two oceanic plates, move away from each other when magma rises
to the surface between them which can cause ocean ridges, seafloor
spreading, and rift zones. Rift zones can lead to a large system of faults and
could eventually tear a continent in half, currently happening in Africa in the
Red Sea. Continental- continental convergence happens when equal density
plates collide with one another, forming mountain ranges. Oceanic-
continental convergence happens when a denser oceanic plate collides with
a continental plate, plunges below the continental play, creating a
subduction zone. When the oceanic plate descends below the overriding
plate, it heats up and the friction causes the overlying rock to melt forming
magma. The magma is less dense than the rock around it so it rises to the
surface causing volcanic eruptions. Some surface features that can be found
near subduction zones are volcanoes, mountain ranges, and rugged
coastlines. Forming from oceanic- continental convergence are oceanic
trenches and volcanoes. Oceanic-oceanic convergence happens as two
oceanic plates collide, one sliding beneath the other and a similar pattern of
volcanic formations and ocean trench formations happens as in the oceanic-
continental convergence. A transform fault boundary happens when one
plate slides laterally past another. This movement can cause massive
amounts of energy to build up which can cause earthquakes. New
continental crust is created in ocean ridges and can be destroyed at
subduction zones as the ocean floor rips from the ridge and plunges at the
subduction zone.
As we can see, the movements of the tectonic plates are continuously
changing the Earth’s topography and can affect the diversity of life on Earth
by isolating or combining landmasses. The resulting activity of the tectonic
cycle also affects the Earth with earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and
tsunamis.
Você também pode gostar
- PermeabilityDocumento29 páginasPermeabilityF.a.AlfredThomAinda não há avaliações
- Fossil A-Z BookDocumento6 páginasFossil A-Z Bookapi-236358005Ainda não há avaliações
- Design Examples For The Eurocode 7Documento12 páginasDesign Examples For The Eurocode 7milan_popovic_2100% (3)
- Chapter 2Documento1 páginaChapter 2api-523871804Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 1 Earth SubsystemsDocumento33 páginasModule 1 Earth SubsystemsClemente Montilla100% (1)
- History of Soil MechanicsDocumento9 páginasHistory of Soil Mechanicsleah yadaoAinda não há avaliações
- Review Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?Documento43 páginasReview Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?maris100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Geology PDFDocumento38 páginasChapter 1 - Introduction To Geology PDFZulaikha Kamal50% (4)
- Grade 6 Reading Practice Test: Nebraska Department of Education 20 09Documento10 páginasGrade 6 Reading Practice Test: Nebraska Department of Education 20 09Aubrey Celine PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Well Logging 2Documento32 páginasWell Logging 2Irish Pales CosidonAinda não há avaliações
- Cone Penetration TestDocumento14 páginasCone Penetration Testgabriel chinechenduAinda não há avaliações
- 100 Soal Soal Text NarativveDocumento27 páginas100 Soal Soal Text NarativveKertiasihAinda não há avaliações
- GEN. - ED. - EXAM - DRILL - I - QA - Doc Filename - UTF-8''GEN. ED. EXAM DRILL I QADocumento7 páginasGEN. - ED. - EXAM - DRILL - I - QA - Doc Filename - UTF-8''GEN. ED. EXAM DRILL I QAJoey AltecheAinda não há avaliações
- Earth & Life Science Lesson 3: The Three Main Categories of RocksDocumento30 páginasEarth & Life Science Lesson 3: The Three Main Categories of RocksTeacher MelAinda não há avaliações
- Instructional Competence of Teachers: Basis For Learning Action Cell SessionsDocumento4 páginasInstructional Competence of Teachers: Basis For Learning Action Cell SessionsZacky CadornaAinda não há avaliações
- Law On Insurance: University of Santo TomasDocumento94 páginasLaw On Insurance: University of Santo TomasRona AnyogAinda não há avaliações
- Rock CycleDocumento2 páginasRock CyclesharulazriAinda não há avaliações
- Science 10 ReviewerDocumento4 páginasScience 10 ReviewerArgie Mabag100% (2)
- By:Julie Miezejeski, Liz Lynde, Caitlin Monahan, Marissa TrantinoDocumento11 páginasBy:Julie Miezejeski, Liz Lynde, Caitlin Monahan, Marissa Trantinoronado100% (1)
- 4 Reproductive Health-NotesDocumento3 páginas4 Reproductive Health-NotesKamalAinda não há avaliações
- Dacasin V DacasinDocumento9 páginasDacasin V DacasinAbi GieAinda não há avaliações
- NSTP PDFDocumento14 páginasNSTP PDFJanine ChachiAinda não há avaliações
- Land Bank of The Philippines Vs Eugenio Dalauta DigestDocumento2 páginasLand Bank of The Philippines Vs Eugenio Dalauta DigestLawrence Y. CapuchinoAinda não há avaliações
- LAB EXERCISE Blastula and GastrulaDocumento8 páginasLAB EXERCISE Blastula and GastrulaJOSHUA MOLO100% (1)
- Applied Econ Parallel Assessment Module 1 & 2Documento6 páginasApplied Econ Parallel Assessment Module 1 & 2Issachar BarezAinda não há avaliações
- Accountancy Notes Computer in AccountingDocumento3 páginasAccountancy Notes Computer in AccountingYashKhanijo100% (1)
- Defining Intercultural CompetenceDocumento16 páginasDefining Intercultural CompetenceChristina PilleAinda não há avaliações
- Social Science-General EducationDocumento8 páginasSocial Science-General EducationDENNIS AFABLEAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet - Chapter 1Documento2 páginasWorksheet - Chapter 1api-252972327Ainda não há avaliações
- Local Government & Electoral SystemDocumento2 páginasLocal Government & Electoral Systemzanderhero30Ainda não há avaliações
- Umali v. ComelecDocumento7 páginasUmali v. ComelecVernie TinapayAinda não há avaliações
- Voluntary Rehab DOHDocumento15 páginasVoluntary Rehab DOHFebiana Bayacsan100% (1)
- Qualitative Research Quantitative Research.: What Is Research: DefinitionDocumento5 páginasQualitative Research Quantitative Research.: What Is Research: DefinitionClarette GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - Project and It's BackgroundDocumento15 páginasChapter 1 - Project and It's Backgroundcharimaine hernandezAinda não há avaliações
- History of Philippine LiteratureDocumento25 páginasHistory of Philippine LiteratureMark Joseph AcidAinda não há avaliações
- Increasing Need For Doctoral Education: Doctor of Nursing PracticeDocumento3 páginasIncreasing Need For Doctoral Education: Doctor of Nursing PracticeTrisha Ysobelle M. MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- Modified TRUE or FALSEDocumento23 páginasModified TRUE or FALSErenz ian dacoronAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Little ThingsDocumento5 páginas12 Little ThingsJose Emmanuel Sarumay ManingasAinda não há avaliações
- 109 Ways To Conserve Water.Documento8 páginas109 Ways To Conserve Water.NellyAinda não há avaliações
- Regional Competitiveness Index An Understanding of The MethodologyDocumento83 páginasRegional Competitiveness Index An Understanding of The MethodologyAyaz Mahmood GhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Endocrine System (Pancreas & Thyroid Gland)Documento5 páginasAnatomy & Physiology of The Endocrine System (Pancreas & Thyroid Gland)Joanna DuapaAinda não há avaliações
- Disaster ManagementDocumento63 páginasDisaster ManagementLyrMa NCAinda não há avaliações
- Updated Copy of CHED DOH GUIDELINES On Limited F2F Classes v33 20 January 2021Documento75 páginasUpdated Copy of CHED DOH GUIDELINES On Limited F2F Classes v33 20 January 2021Faye G.Ainda não há avaliações
- 2b GP Essay-2Documento8 páginas2b GP Essay-2api-448767375Ainda não há avaliações
- Development On The Academic Performance in ScienceDocumento14 páginasDevelopment On The Academic Performance in ScienceAngel Mae Bornea MondejarAinda não há avaliações
- Essay On HungerDocumento4 páginasEssay On HungerJacobAinda não há avaliações
- 33 Metro Iloilo Water District Vs CADocumento6 páginas33 Metro Iloilo Water District Vs CAKingAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Surgical Nursing Review NotesDocumento20 páginasMedical Surgical Nursing Review NotesFerreze AnnAinda não há avaliações
- Chem1017 Pos JmsDocumento7 páginasChem1017 Pos JmsPRC BoardAinda não há avaliações
- Intramurals Opening ReflectionDocumento1 páginaIntramurals Opening ReflectionPrincess Angel LucanasAinda não há avaliações
- Case Digest - Baranda Vs GustiloDocumento1 páginaCase Digest - Baranda Vs GustiloJoena GeAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 3Documento2 páginasAssignment 3KennethSuttonAinda não há avaliações
- Noynoy AquinoDocumento32 páginasNoynoy AquinoHarold Dela Fuente100% (1)
- Avoiding Communication BreakdownDocumento4 páginasAvoiding Communication BreakdownDANGVIENAinda não há avaliações
- Origin of The Universe Origin of The Solar SystemDocumento1 páginaOrigin of The Universe Origin of The Solar SystemJane AmadAinda não há avaliações
- An Exercise To Determine Your Educational PhilosophyDocumento3 páginasAn Exercise To Determine Your Educational PhilosophyJulie LusuegroAinda não há avaliações
- The Anticoagulation of Allium Cepa and Allium Sativum Within Blood Type ODocumento26 páginasThe Anticoagulation of Allium Cepa and Allium Sativum Within Blood Type OLUNA PARALLELAinda não há avaliações
- Sci ReviewerDocumento7 páginasSci ReviewerBxbble BerriAinda não há avaliações
- MilesDocumento13 páginasMilesRichel Escalante MaglunsodAinda não há avaliações
- Synthèse Unit 3 Leçon 1 - 6 A) The Earth's Structure and CompositionDocumento7 páginasSynthèse Unit 3 Leçon 1 - 6 A) The Earth's Structure and CompositionJoey CarlAinda não há avaliações
- Plate TectonicsDocumento4 páginasPlate TectonicsSandroAinda não há avaliações
- Earth Science Group 3Documento17 páginasEarth Science Group 3reignchan640Ainda não há avaliações
- Hand OutsDocumento6 páginasHand OutsMJ DejosAinda não há avaliações
- Science Plate BoundariesDocumento3 páginasScience Plate BoundariesAshley VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Plate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3ADocumento5 páginasPlate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3AMark Rienzo HingpisAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer 8 ScienceDocumento16 páginasReviewer 8 ScienceJhanna Gil BuctolanAinda não há avaliações
- Continental Drift TheoryDocumento35 páginasContinental Drift TheoryCarmela Del MarAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristics of Plate BoundariesDocumento2 páginasCharacteristics of Plate BoundariesIsla VermilionAinda não há avaliações
- Tectonic Plates NotesDocumento3 páginasTectonic Plates NotesAngelica CamilonAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 4Documento10 páginasLecture 4D KrishanaAinda não há avaliações
- V-NOTCH en 04 V Notch Flow MetersDocumento5 páginasV-NOTCH en 04 V Notch Flow MetersSDLCAinda não há avaliações
- Blast Vibration Study To Analyse The Response of A Wind Tower Close To An Open Pit MineDocumento8 páginasBlast Vibration Study To Analyse The Response of A Wind Tower Close To An Open Pit MinehectorAinda não há avaliações
- 5 BogosavljevicDocumento16 páginas5 BogosavljevicLuka PustahijaAinda não há avaliações
- A Preliminary Sub-Basin Scale Evaluation FrameworkDocumento17 páginasA Preliminary Sub-Basin Scale Evaluation FrameworkSohini ChatterjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Crowded Coasts Lesson 10Documento31 páginasCrowded Coasts Lesson 10hooriakhan68Ainda não há avaliações
- Marine Geodesy-Karl Rinner PDFDocumento50 páginasMarine Geodesy-Karl Rinner PDFFirAinda não há avaliações
- Evolution and Origin of Biodiversity 2Documento30 páginasEvolution and Origin of Biodiversity 2Vincent FloraAinda não há avaliações
- River Restoration: Prepared By: SURIPIN For KBK Hidro Seminar, October 16, 2009Documento39 páginasRiver Restoration: Prepared By: SURIPIN For KBK Hidro Seminar, October 16, 2009sinduAinda não há avaliações
- Earthquake Resistant BuildingsDocumento18 páginasEarthquake Resistant BuildingsXaid IbrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Hazard Risk MapsDocumento5 páginasHazard Risk MapsHarrison Jara InfantesAinda não há avaliações
- Urine Preservatives - SLUDocumento2 páginasUrine Preservatives - SLUShana Flame Haze0% (1)
- 1469189474variability of Selected Soil Properties of A River Slope in Amaigbo Southeastern NigeriaDocumento9 páginas1469189474variability of Selected Soil Properties of A River Slope in Amaigbo Southeastern Nigeriauba ucheAinda não há avaliações
- Three Cities in Russia PDFDocumento570 páginasThree Cities in Russia PDFEmre AygünAinda não há avaliações
- Avinash Et Al. 2011 Geocarto InternationalDocumento25 páginasAvinash Et Al. 2011 Geocarto InternationalNiranjanAryanAinda não há avaliações
- 3D Flood Modelling With LIDARDocumento200 páginas3D Flood Modelling With LIDARJavied BhattiAinda não há avaliações
- Earthquake EngineeringDocumento117 páginasEarthquake EngineeringAllaineAinda não há avaliações
- Neutron Activation Analysis (INAA and RNAA)Documento4 páginasNeutron Activation Analysis (INAA and RNAA)Marco Antonio Enriquez QuirogaAinda não há avaliações
- Mine Wastes PDFDocumento18 páginasMine Wastes PDFDavidRuizAinda não há avaliações
- Intertek Minerals: Geochemistry ServicesDocumento4 páginasIntertek Minerals: Geochemistry ServicesVictor LusamboAinda não há avaliações
- Chrysocolla: Chrysocolla Is A Hydrated CopperDocumento9 páginasChrysocolla: Chrysocolla Is A Hydrated CoppermelprvnAinda não há avaliações