Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Acute Glomerulonephritis
Enviado por
Ayrheen Fornoles0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
117 visualizações1 páginaTítulo original
ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
117 visualizações1 páginaAcute Glomerulonephritis
Enviado por
Ayrheen FornolesDireitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS DRUG THERAPY:
1. Diuretics: metolazone (zaroxlyn), Furoseonide
Also called acute poststreptococcal glumeronephtriris, (lasix) to reduce extracellualr fluid overload
AGN is a relatively common bilateral infection in the 2. Antihypertensives: hydralazine
glomeruli, the kidney’s blood vessels. It follows a
streptococcal infection of the respiratory tract or, less RELATED LABORATORY FINDINGS:
often a skin infection such as impetigo. 1. Blood Test: crea
2. 24-hr urine sample: crea clearance and imparied
CAUSES: glomerular filtration
1. Trapped antigen-antibody complexes (produced 3. Antitreptolysin-O titers (in 80% of patients)
as an immunologic mechanism in response to streptozyme and anti-Dnase B titers
streptococci) in the glomenular capillary serum complement levels verify recent strep infxn
membrames; including infalmmatory damage 4. Renal Biopsy: may confitm that dx may be used to
and impeding glomenular function. asses renal tissue status
5. Renal Utz: may show normal/enlarged kidney
2. Untreated pharyngitis,/ tonsilitis,impetigo,and 6. Throat Culture: (+) group A beta-hemolytic strep
scarlet fever. 7. Urinalysis: typically reveals protenuiria and
hematuria. RBCs, WBCs and mixed cell casts are
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS: common findingsin urinary sediment
Azotemia ( nitrogen in blood) 8. KUB X-ray: bilateral kidney enlargement
Edema
Fatigue NURSING MANAGEMENT :
Hematuria 1. Check VS and electrolyte values. Monitor I&O daily
Oliguria wt. Asses renal function daily through serum crea
Protenuria and BUN levels and urine creatine clearance.
BP (NS is BP) Watch out for signs of acute renal failure (oliguria,
ozotemia, acidosis) These measures detect early
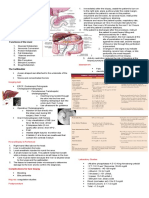
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY signs of complications and help guide the
treatment plan.
Antigen (group A-Beta hemolytic streptococcus) 2. Consult the dietitian to provide a diet cal, pro,
Na, K and limited fluids.
Antibody-antigen complex formation in glomerolus 3. Provide good nutrition, use good hygienic
technique and prevent contact with infected
Inflammation of glomerular basement membrane people. To protect thedebilitated patient from
secondary infection.
blood supply and oxygen in the glomeruli membrane 4. Bed rest. Bed rest is a necessary during the acute
phase. Encourage the pt. To gradually resume
necrosis and injury to glomerulus normal activities as aymptoms subside to prevent
fatigue.
space in glomerular membrane 5. Provide emotional support for the pt. and family. If
the pt. Is on dialysis, explain the procedure fully.
glomerular filtration rate Theses measures may help ease the pts.anviety.
6. The need for frewuent medical evaluation in
protein can pass through to the filter pregnant pts. With a hx of AGN.
7. The possibility of orthostatic hypotentsion when
proteniuria taking diuretics and the need to change position
slowly.
hypoprotenuria 8. The need for regular blood pressure, urinary
protien and venal fcn asssessments during the
capillary oncotic pressure convalesent months to detect recurrence.
9. The importance of immediately reporting signs of
shifting of fluid into interstitial space infxn, such as fever and sore throat.
10. The importance of follow-up examinations to
edema detect chronic renal failure.
Você também pode gostar
- GU Blackboard OutlineDocumento15 páginasGU Blackboard Outlinedlneisha61Ainda não há avaliações
- PERITONITISDocumento27 páginasPERITONITISTiffany Adrias100% (1)
- Med Surg 2 - 7 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic Disorders 2Documento7 páginasMed Surg 2 - 7 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic Disorders 2Maxinne RoseñoAinda não há avaliações
- Aki CR 1Documento3 páginasAki CR 1AmeldaAinda não há avaliações
- Broodbank & Christian. Renal Tubular Disorders. 2018.Documento10 páginasBroodbank & Christian. Renal Tubular Disorders. 2018.Jéssica Hilário BonomoAinda não há avaliações
- Glomerular Disease - Dr. LuDocumento8 páginasGlomerular Disease - Dr. LuMACATANGAY, GAELLE LISETTEAinda não há avaliações
- Hepatology - 1983 - Viola - Exudative Ascites in The Course of Acute Type B HepatitisDocumento3 páginasHepatology - 1983 - Viola - Exudative Ascites in The Course of Acute Type B HepatitisAudryaAinda não há avaliações
- Glomerulonephritis and The Acute Nephritic Syndrome: Chapter ObjectivesDocumento10 páginasGlomerulonephritis and The Acute Nephritic Syndrome: Chapter ObjectivesMiguel AngelAinda não há avaliações
- Flgastro 2018 101102Documento8 páginasFlgastro 2018 101102carolina pulidoAinda não há avaliações
- Adult Pyloric Stenosis Masquerading as Acute Renal FailureDocumento2 páginasAdult Pyloric Stenosis Masquerading as Acute Renal FailurezapomannAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0929644112000057 MainDocumento4 páginas1 s2.0 S0929644112000057 MainAisahAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Guide To The Management of Acute Pancreatitis: George Goodchild, Manil Chouhan, Gavin J JohnsonDocumento8 páginasPractical Guide To The Management of Acute Pancreatitis: George Goodchild, Manil Chouhan, Gavin J JohnsonRene CordovaAinda não há avaliações
- Reviews: Fluid Balance and Acute Kidney InjuryDocumento9 páginasReviews: Fluid Balance and Acute Kidney InjuryNestor Torres MarinaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathology 5.01.1 Kidney I - Dr. MesinaDocumento14 páginasPathology 5.01.1 Kidney I - Dr. MesinaShaira Aquino VerzosaAinda não há avaliações
- The Acinar-Ductal Tango in The Pathogenesis of Acute PancreatitisDocumento10 páginasThe Acinar-Ductal Tango in The Pathogenesis of Acute Pancreatitispruebaprueba321765Ainda não há avaliações
- At Two: Was SeDocumento3 páginasAt Two: Was Seida ayu agung WijayantiAinda não há avaliações
- Accessory OrgansDocumento6 páginasAccessory OrgansNadia AbdurasidAinda não há avaliações
- Intrahepatic Pancreatic Pseudocyst Wayward Cyst 2024 International JournalDocumento4 páginasIntrahepatic Pancreatic Pseudocyst Wayward Cyst 2024 International JournalRonald QuezadaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocumento8 páginasNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Tutorial 1Documento38 páginasRenal Tutorial 1luckyswiss7776848Ainda não há avaliações
- Management of Acute Renal FailureDocumento12 páginasManagement of Acute Renal FailureAlamsyah TegarAinda não há avaliações
- Piis0085253815527324 PDFDocumento5 páginasPiis0085253815527324 PDFdodong skyroseAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis: Report of Two Cases: M. Turan, M. S En, R. EgılmezDocumento3 páginasPneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis: Report of Two Cases: M. Turan, M. S En, R. EgılmezzixdiddyAinda não há avaliações
- Renal BiopsyDocumento4 páginasRenal BiopsyDeshan AdikariAinda não há avaliações
- Brown C (2013) Patient Care Report For Feline Patient With Urethral ObstructionDocumento5 páginasBrown C (2013) Patient Care Report For Feline Patient With Urethral ObstructionRob PAinda não há avaliações
- 174965-Article Text-447758-1-10-20180723Documento2 páginas174965-Article Text-447758-1-10-20180723fwinterholdAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnosis Biomarkers in Acute Intestinal Ischemic InjuryDocumento13 páginasDiagnosis Biomarkers in Acute Intestinal Ischemic InjuryrizkyAinda não há avaliações
- Connally2003 Lavado Peritoneal DiagnosticoDocumento6 páginasConnally2003 Lavado Peritoneal Diagnosticoandres silvaAinda não há avaliações
- Anestesi Pada Penyakit GinjalDocumento16 páginasAnestesi Pada Penyakit GinjalCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaAinda não há avaliações
- 28-Year-Old Man With Crohn Disease and Hematuria: Residents ' ClinicDocumento5 páginas28-Year-Old Man With Crohn Disease and Hematuria: Residents ' ClinicDesi HutapeaAinda não há avaliações
- Atypical Renal Presentation in Severe LeptospirosisDocumento3 páginasAtypical Renal Presentation in Severe LeptospirosisADIAinda não há avaliações
- Unusual Cause of Feeding Intolerance in A Term Infant: PresentationDocumento6 páginasUnusual Cause of Feeding Intolerance in A Term Infant: PresentationAsma AlwiAinda não há avaliações
- Visceral Leishmaniasis Turning into Chronic Liver DiseaseDocumento4 páginasVisceral Leishmaniasis Turning into Chronic Liver DiseasePratyay HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Educational Case: Kidney Transplant Rejection: Kevin Kuan, MD and Daniel Schwartz, MDDocumento7 páginasEducational Case: Kidney Transplant Rejection: Kevin Kuan, MD and Daniel Schwartz, MDL AAinda não há avaliações
- Struvite Urolithiasis With Infection: A Case: Corynebacterium UrealyticumDocumento2 páginasStruvite Urolithiasis With Infection: A Case: Corynebacterium UrealyticumSandra Liliana Rojas ArevaloAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S187952261200053X MainDocumento8 páginas1 s2.0 S187952261200053X MainRobert ChristevenAinda não há avaliações
- Subhepatic Appendix: An Ectopic Topography Not To Be Disregarded: A Case ReportDocumento4 páginasSubhepatic Appendix: An Ectopic Topography Not To Be Disregarded: A Case ReportPawan MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Use Only: Investigating A Rare Cause of Intestinal OcclusionDocumento2 páginasUse Only: Investigating A Rare Cause of Intestinal OcclusionDannyMichelleAinda não há avaliações
- Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine 2003 Kashif 535 7Documento9 páginasCleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine 2003 Kashif 535 7shiloinAinda não há avaliações
- Efusi Pleura MaskellDocumento10 páginasEfusi Pleura MaskellYessica Chrystie Dian SinurayaAinda não há avaliações
- Aguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningDocumento9 páginasAguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningSophia Kaye AguinaldoAinda não há avaliações
- M1 - Urinary DisordersDocumento2 páginasM1 - Urinary DisordersjuiceAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)Documento13 páginasAcute Kidney Injury (AKI)Valenshya AlfaAinda não há avaliações
- Extreme Highserum Ca 19-9 in ApxwithasinglebiliarystoneDocumento3 páginasExtreme Highserum Ca 19-9 in ApxwithasinglebiliarystoneRony RonyAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Malabsorption Due Child With Immunoglobulin DeficiencyDocumento3 páginasChronic Malabsorption Due Child With Immunoglobulin DeficiencyCentro De Copiado Luna RtAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Impaired Cerebral Tissue PerfussionDocumento4 páginasNCP Impaired Cerebral Tissue PerfussionYvonne Ronamae100% (2)
- The Significance Malbuminuria" (Proteinuria) : CompletelyDocumento3 páginasThe Significance Malbuminuria" (Proteinuria) : CompletelyAmanuel MaruAinda não há avaliações
- Pancreatitis Cronica Dog-CatDocumento14 páginasPancreatitis Cronica Dog-CatSamantha Orozco PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- Saturday: Acid/schiffDocumento4 páginasSaturday: Acid/schiffmedAinda não há avaliações
- DM Nefro1Documento9 páginasDM Nefro1Teddy Alexander MorinAinda não há avaliações
- Altered LocDocumento19 páginasAltered Locgeeeelzy07Ainda não há avaliações
- Severe Peritonitis Case Report Highlights Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute PancreatitisDocumento2 páginasSevere Peritonitis Case Report Highlights Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute PancreatitisJune Faith HacheroAinda não há avaliações
- 2018-10 - Ischemic Cholangiopathy 11 Years After Liver Transplantation From Asymptomatic Chronic Hepatic Artery ThrombosisDocumento3 páginas2018-10 - Ischemic Cholangiopathy 11 Years After Liver Transplantation From Asymptomatic Chronic Hepatic Artery ThrombosisNawzad SulayvaniAinda não há avaliações
- Case Report: Peritonitis in Patients With Scrub TyphusDocumento3 páginasCase Report: Peritonitis in Patients With Scrub TyphusJasleen KaurAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Pharmacy Nephrotic Syndrome: ChildrenDocumento2 páginasClinical Pharmacy Nephrotic Syndrome: ChildrenKristine AbrahamAinda não há avaliações
- t2 Kidney DiseaseDocumento52 páginast2 Kidney Diseasewany.fyza54Ainda não há avaliações
- About A Case Report of Giant HydronephrosisDocumento4 páginasAbout A Case Report of Giant HydronephrosisgilangAinda não há avaliações
- 1999-07 - Intraductal Papillary-Mucinous Tumor of The Pancreas - Presentation in A Young Adult PDFDocumento4 páginas1999-07 - Intraductal Papillary-Mucinous Tumor of The Pancreas - Presentation in A Young Adult PDFNawzad SulayvaniAinda não há avaliações
- Z - 2009-08 - Pancreatic Pseudocyst With Pancreatolithiasis and Intracystic Hemorrhage Treated With Distal Pancreatectomy - A Case ReportDocumento5 páginasZ - 2009-08 - Pancreatic Pseudocyst With Pancreatolithiasis and Intracystic Hemorrhage Treated With Distal Pancreatectomy - A Case ReportNawzad SulayvaniAinda não há avaliações
- KwashiorkorDocumento1 páginaKwashiorkorAyrheen FornolesAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 Computer Software and SystemsDocumento40 páginasChapter 5 Computer Software and SystemsAyrheen FornolesAinda não há avaliações
- Hirschsprung EDocumento2 páginasHirschsprung EAyrheen FornolesAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing InterventionDocumento2 páginasNursing InterventionAyrheen FornolesAinda não há avaliações
- Answers and Rationales For NCLEX Style Review QuestionsDocumento12 páginasAnswers and Rationales For NCLEX Style Review QuestionsJacinth Florido Fedelin50% (2)
- Microteaching PresentationDocumento13 páginasMicroteaching Presentationapi-217735356Ainda não há avaliações
- 8 - Hair Disorders (Updated)Documento14 páginas8 - Hair Disorders (Updated)haytham aliAinda não há avaliações
- Coagulation Problems PPTDocumento69 páginasCoagulation Problems PPTBao NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation in Functional Recovery of Patients With Strokea Review PDFDocumento3 páginasEffect of Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation in Functional Recovery of Patients With Strokea Review PDFHana Ayu RamadhaniaAinda não há avaliações
- Visual Acuity Measurement Snellen Chart) : 3/20/2019 PHSC 1Documento25 páginasVisual Acuity Measurement Snellen Chart) : 3/20/2019 PHSC 1Birhanu AyenewAinda não há avaliações
- Internship of Summer Training ON Study of Opd Services in A Hospital Submitted By:-Salony Saha REGISTRATION NO.:-1476020 (FROM-1 July To 31Th August)Documento14 páginasInternship of Summer Training ON Study of Opd Services in A Hospital Submitted By:-Salony Saha REGISTRATION NO.:-1476020 (FROM-1 July To 31Th August)yugalkishorAinda não há avaliações
- Foa, 2010. CBT of OCD PDFDocumento9 páginasFoa, 2010. CBT of OCD PDFmariobar17636Ainda não há avaliações
- Weaning from Parenteral Nutrition: Strategies and ConsiderationsDocumento26 páginasWeaning from Parenteral Nutrition: Strategies and ConsiderationsJosebeth RisquezAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 05: Oral Medications Mulholland: The Nurse, The Math, The Meds, 3rd EditionDocumento14 páginasChapter 05: Oral Medications Mulholland: The Nurse, The Math, The Meds, 3rd EditionadenAinda não há avaliações
- HypokalemiaDocumento3 páginasHypokalemiaSergeiAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases Seminar 4 yDocumento18 páginas3 Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases Seminar 4 yPrasenjit SarkarAinda não há avaliações
- MAGNETOM Flash Special Neuro Edition 1800000004672617Documento45 páginasMAGNETOM Flash Special Neuro Edition 1800000004672617Hyd HydAinda não há avaliações
- Cathcart Robert FDocumento10 páginasCathcart Robert FFilipos Constantin100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Louise O. Reponte BSN-3CDocumento12 páginasNursing Care Plan: Louise O. Reponte BSN-3CLouise MurphyAinda não há avaliações
- DK2X - 04 Reflective QuestionaireDocumento9 páginasDK2X - 04 Reflective QuestionaireSttucs IvelAinda não há avaliações
- Serum IL6 AdhdDocumento7 páginasSerum IL6 AdhdZaenab AzzahraAinda não há avaliações
- Causes and prevention of ledging and blockages in root canalsDocumento19 páginasCauses and prevention of ledging and blockages in root canalsBunga Erlita RosaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Davao Doctors College Nursing Program Progress NotesDocumento17 páginasDavao Doctors College Nursing Program Progress NotesABBEYGALE JOYHN GALANAinda não há avaliações
- Dialog Dental PatientDocumento2 páginasDialog Dental PatientLiza ChumikaAinda não há avaliações
- 2022-05-03 Duron Letter To FPPCDocumento2 páginas2022-05-03 Duron Letter To FPPCCalifornia Stem Cell ReportAinda não há avaliações
- Dipake 2Documento19 páginasDipake 2AriWahyuAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Therapy Practice QuestionsDocumento53 páginasPhysical Therapy Practice QuestionsJohn Ryan ParisAinda não há avaliações
- Pulmonary Cryptococcal Infections CaseDocumento61 páginasPulmonary Cryptococcal Infections CaseAnna DananjayaAinda não há avaliações
- Hemodialysis NCPDocumento2 páginasHemodialysis NCPAfia Tawiah100% (1)
- Causes of Albuminocytological Dissociation and TheDocumento8 páginasCauses of Albuminocytological Dissociation and TheAbdur rehman100% (1)
- Nursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationDocumento1 páginaNursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationOmar IzzoAinda não há avaliações
- Blepharitis: Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocumento11 páginasBlepharitis: Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentmohamadAinda não há avaliações
- Fatigue and Sleeplessness On The RiseDocumento10 páginasFatigue and Sleeplessness On The Risemaria espindolaAinda não há avaliações
- 8 19 Management of Snake Bites PDFDocumento12 páginas8 19 Management of Snake Bites PDFdawnkuruvillaAinda não há avaliações