Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
M-S I Case Study Hirschsprungs
Enviado por
cot_byDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
M-S I Case Study Hirschsprungs
Enviado por
cot_byDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MIAMI DADE COLLEGE
MEDICAL CENTER CAMPUS
SCHOOL OF NURSING
NUR 2310L: Pediatric Nursing Clinical Laboratory
Pre-Assignment Worksheet
Student’s Name _Chandrasekhar ____________ DATE ____10/05/2010_________________ Time:____________________________________
Client’s Initial: ___DK__ Admission Date _____10/03/2010________ Allergies:____NKDA______________________ Religion:_________________________________
Age: __11yr__ Sex: __M__ Race:________________________________ Diet:__Clear Liquid______________ Activity: ___As tolerated____________________
Admitting Medical Diagnosis (es) ___Hirschsprung's disease, Chronic constipation__________________________________________________________________________
Past medical History (include past surgical history)___Chronic constipation _______________________________________________________________________________
Present Surgical Procedures (include date):_________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Client’s understanding of illness:_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
History of present Illness: ___Client has chronic constipation since birth and newly diagnosed with Hirschsprung's disease. Constipation has been worsening past 1 week
What medications are you taking you at home? Laxatives
Medications Time(s) Why?
______D5 ½ Normal Saline + 20 Meq KCL___ _____84 ml/hr_______________ _ To maintain nutritional & hydration status .
______MiraLax________________________ _____17 gr PO daily prn _____ _Constipation___________________________________
______Golytely _______________________ _____4000ml x 1 _________ _Stimulate bowel movements______________________
Are your medications causing any discomfort? _____NO_______________________________________
M-S I Forms/Case History 1
Medications (s) Worksheet (Topical, PO, IM, SQ, IV)
CLASSIFICATION DOSE/ ROUTE/FREQUENCY MECHANISM INDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS AND
NAME SAFE RANGE OF ACTION PATIENT EDUCATION
D5 ½ Normal Saline + 84 ml per hour IV Provides calories Provides Fluid overload, Explain purpose of administration to patient
20 Meq KCL & replace K+ that hydration and hypokalemia, and parents
caloric sources are passed from calories hypomagnesemia, Administer slowly to prevent phlebitis or
the body in the hypophosphatemia, sclerosis of the vein.
stool. glycosuria, Assess IV site frequently.
hyperglycemia Rapid infusions may cause hyperglycemia or
fluid shifts.
Assess for s/s of water intoxication
MiraLax 17 gr PO daily prn Acts as an Constipation Abdominal bloating, Assess patient for abdominal distention,
Laxatives osmotic agent, cramping, presence of bowel sounds, and usual pattern of
drawing water flatulence, nausea bowel function
into the lumen of Assess color, consistency, and amount of stool
the GI tract produced
GoLYTELY 4000ml x1 Increases the Constipation, Severe stomach pain Do not use this medication if allergic to
(Polyethylene glycol amount of water clean the bowel or bloating, gagging, polyethylene glycol or any other electrolyte
electrolyte solution) in the intestinal before choking, or solutions (such as Pedialyte or Gatorade), or
Laxative tract to stimulate colonoscopy, a vomiting, mild with a perforated bowel; a bowel obstruction or
bowel barium x-ray, or stomach cramps, severe constipation; or colitis or toxic
movements. other intestinal gas, rectal pain or megacolon
procedures irritation.
M-S I Forms/Case History 2
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY- BRIEF TEXTBOOK PICTURE WITH CLIENT COMPARISON
Definition, Etiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnostic tests, Sign & Symptoms, Medical treatments & (3) References (Using APA format)
Hirschsprung disease is a developmental disorder of the enteric nervous system and is characterized by an absence of ganglion cells in the distal colon resulting in a
functional obstruction.
Causes: Congenital aganglionosis of the distal bowel defines Hirschsprung disease. Aganglionosis begins with the anus, which is always involved, and continues
proximally for a variable distance. Both the myenteric (Auerbach) plexus and the submucosal (Meissner) plexus are absent, resulting in reduced bowel peristalsis and
function. The precise mechanism underlying the development of Hirschsprung disease is unknown.
Symptoms: Delayed passage of meconium, abdominal distension and Constipation are classic symptoms of this disease.
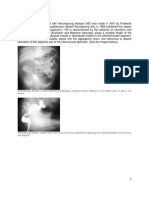
Diagnosis: A barium enema is the mainstay of diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s, though a rectal biopsy showing the lack of ganglion cells is the only certain method of
diagnosis.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
M-S I Forms/Case History 3
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
X-RAY/ CT SCAN/ ULS/ MRI/EKG etc. RESULTS (Please include date of tests results)
KUB Modified fecal retention, obstruction in unspecified bowel gas pattern
10/04/10
Barium Enema Yet to perform the test.
10/04/10
M-S I Forms/Case History 4
CHEMISTRY NORMAL CLIENT’S VALUES HEMATOLOGY NORMAL CLIENT’S VALUES
PROFILE VALUES VALUES
DATE DATE DATE DATE DATE DATE
SODIUM WBC 4.8-10.8
POTASSIUM RBC 4.70-6.10
CHLORIDE HGB 12-16
CO2 HCT 36-48
CALCIUM MCV 80-96
GLUCOSE MCH 27-31
BUN MCHC 32-36
CREATININE PLATELETS 150-400
PHOSPHORUS
CHOLESTEROL DIFFERENTIAL
TOTAL PROTEIN 6.4-8.3 NEUTROPHILS 38-70
ALBUMIN 3.5-5.0 SEGMENTS 2-8
ALBUMIN/
GLOBULIN RATIO BANDS
AST (SGOT) < 31 LYMPHOCYTES 21-49
ALT (SGPT) < 41 EOSINOPHILS 0-7
TOTAL
BILIRUBIN <1.0 BASOPHILS 0-1
AMYLASE 28-100 MONOCYTES 0-7
LIPASE 13-60
COAGULATION STUDIES
PTT 23-35 sec
LIPID PROFILE PT 10.5-13.5
TOTAL INR 0.76-1.25
CHOLESTEROL
TRIGLYCERIDES BLEEDING TIME
HDL
LDL
CHO/HDLC Ratio
GGT
M-S I Forms/Case History 5
URINALYSIS NORMAL CLIENT’S VALUES
VALUES DATE DATE DATE
URINALYSIS
COLOR
APPEARANCE
SP. GRAVITY MISCELLANEOUS TEST
PH TEST NORMAL CLIENT’S VALUES
VALUES DATE DATE DATE
GLUCOSE
KETONE
OCCULT BLOOD
PROTEIN
BILIRUBIN
UROBILINOGEN
NTRITE
LEUCOCYTE
CAST
WBC
RBC
CRYSTALS
SQUAMOUS CELLS/
EPITHELIAL CELLS
Relate the clinical significance of abnormal lab values above:
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_
M-S I Forms/Case History 6
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_
M-S I Forms/Case History 7
REFERENCES
Deglin, Judith, & Vallerand, April. (2007). Davis Drug Guide for Nurses (10th ed). Philadelphia:
F A Davis Co.
Beers, Mark, & Porter, Robert. (2006). The Merck manual of diagnosis and therapy. New Jersey:
Merck & Co., Inc..
Smeltzer, Suzanne, Bare, Brenda, Hinkle, Janice, & Cheever, Kerry. (2008). Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing.
Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins
M-S I Forms/Case History 8
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- NBME Peds Form 2 AnswersDocumento27 páginasNBME Peds Form 2 Answersjohndoe199580% (5)
- Surgery Reviosn NotesDocumento41 páginasSurgery Reviosn Noteshy7tn100% (1)
- Pediatric Surgery MCQDocumento8 páginasPediatric Surgery MCQMohamed Al-zichrawy100% (1)
- Gastroenterology Best RDocumento23 páginasGastroenterology Best RfrabziAinda não há avaliações
- Pediatric RadiologyDocumento82 páginasPediatric Radiologyabakferro0% (1)
- Nclex 100 Questions and Answers With Rationale (Pediatric Nursing)Documento206 páginasNclex 100 Questions and Answers With Rationale (Pediatric Nursing)maj91% (242)
- Pedia 102 MIDTERM EXAMSDocumento15 páginasPedia 102 MIDTERM EXAMSquidditch07Ainda não há avaliações
- NCM 116 W1 Reading HandoutDocumento13 páginasNCM 116 W1 Reading Handoutriza sarmientoAinda não há avaliações
- Short Bowel Syndrome in The NICUDocumento16 páginasShort Bowel Syndrome in The NICUChanAinda não há avaliações
- Hirschsprung Disease (Aganglionic Megacolon)Documento6 páginasHirschsprung Disease (Aganglionic Megacolon)Julliza Joy PandiAinda não há avaliações
- (CGPT) B11M4.1Documento12 páginas(CGPT) B11M4.1adriennemartha.barrientosAinda não há avaliações
- Motility Disorders of The GITDocumento57 páginasMotility Disorders of The GITMahmoud AjinehAinda não há avaliações
- Complications in Hirschsprung'S DiseaseDocumento4 páginasComplications in Hirschsprung'S DiseaseHayati Rizki PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Maternal and Child Nursing Part 3Documento20 páginasMaternal and Child Nursing Part 3Edralee VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Unusual Cause of Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction: Zikavska T Brucknerova I Cervenova O Vidiscak M Hustavova LDocumento4 páginasUnusual Cause of Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction: Zikavska T Brucknerova I Cervenova O Vidiscak M Hustavova LanillodepeneAinda não há avaliações
- January - Hirschsprung's Disease in Africa 21 CenturyDocumento27 páginasJanuary - Hirschsprung's Disease in Africa 21 CenturyVita MadmoAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation of Hirschsprung's DiseaseDocumento2 páginasPresentation of Hirschsprung's DiseaseMarcela Di VincenzoAinda não há avaliações
- Hirschsprung Disease: Case StudyDocumento4 páginasHirschsprung Disease: Case StudytifaniAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care of The Child With Gastrointestinal DisordersDocumento50 páginasNursing Care of The Child With Gastrointestinal Disordersمهند الرحيليAinda não há avaliações
- Hischsprug Disease by HamadDocumento31 páginasHischsprug Disease by HamadALIEF MUTHIAAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Test Pediatric Nursing 100 ItemsDocumento17 páginasPractice Test Pediatric Nursing 100 Itemsjaxski13Ainda não há avaliações
- Hirschsprung Disease ImagingDocumento9 páginasHirschsprung Disease ImagingScalpel LancetAinda não há avaliações
- Hirschsprung's Disease - AthigamanDocumento128 páginasHirschsprung's Disease - Athigamanprived100% (4)
- A Pattern Based Approach To The Bowel Obstruction in The NewbornDocumento12 páginasA Pattern Based Approach To The Bowel Obstruction in The Newborntiosam59100% (1)
- Hirschsprung's Disease (Aganglionic Megacolon)Documento3 páginasHirschsprung's Disease (Aganglionic Megacolon)JOANMA_NEWAinda não há avaliações
- 19-Pediatric SurgeryDocumento39 páginas19-Pediatric Surgerycallisto3487Ainda não há avaliações
- 11.0 Pediatrics Flashcards Oct 2023Documento13 páginas11.0 Pediatrics Flashcards Oct 2023Shane Laika Bay DugayAinda não há avaliações
- Hirschsprung PathophysiologyDocumento4 páginasHirschsprung PathophysiologyJona SuarezAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Newborn Care: Fluid (Green Amniotic Fluid) ) To Prevent AspirationDocumento17 páginasEssential Newborn Care: Fluid (Green Amniotic Fluid) ) To Prevent AspirationthadzamingAinda não há avaliações
- Hirschsprung Disease Case Study ScenarioDocumento2 páginasHirschsprung Disease Case Study ScenarioKrizzia Angela BacotocAinda não há avaliações