Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Sources of Air Pollution
Enviado por
mohdjamiljohan0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
62 visualizações2 páginasIndustrialization or just everyday routines has become added burden to the existing air pollution loading. In 2004, nearly 14 million vehicles were registered in Malaysia, almost double the number from a decade ago. The number of vehicles will increase in the next few years with higher disposable incomes, rural-urban migration and lack of efficient public transport systems.
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoIndustrialization or just everyday routines has become added burden to the existing air pollution loading. In 2004, nearly 14 million vehicles were registered in Malaysia, almost double the number from a decade ago. The number of vehicles will increase in the next few years with higher disposable incomes, rural-urban migration and lack of efficient public transport systems.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
62 visualizações2 páginasSources of Air Pollution
Enviado por
mohdjamiljohanIndustrialization or just everyday routines has become added burden to the existing air pollution loading. In 2004, nearly 14 million vehicles were registered in Malaysia, almost double the number from a decade ago. The number of vehicles will increase in the next few years with higher disposable incomes, rural-urban migration and lack of efficient public transport systems.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
Sources of Air Pollution
• Sources of Air Pollution§
Sources of Air Pollution(An overview)
There are many natural sources of air pollution such as eruption of volcanoes, biological
decay and lightning-caused forest fire. Naturally, the Earth already has its own air
pollution loading. However, industrialization or just everyday routines has become added
burden to the existing air pollution loading. Sources of air pollution are as explained
below :-
Industrial and development activities
Malaysia’s economic growth is mainly based on its manufacturing (especially
electronics), chemical and rubber industries. But higher production rates also lead to
higher emissions of organic and inorganic gases, chemicals and dust.
Different industries emit different pollutants. For example, the chemical industry releases
emissions that contain many nitrogen and sulphur compounds while refineries discharge
sulphur dioxide and hydrocarbons. The metal working industry is partially responsible for
the emissions of sulphur dioxide and large amounts of toxic dust. Human activities have
resulted in harmful substances and polluting emissions being released into the air. They
endanger our health and our natural ecosystem, and lead to an additional greenhouse
effect. (Text : 'Clean Air For Our Cities, 2006, by DOE Malaysia & German Technical
Co-operation)
Besides emissions of toxic dust, unplanned and uncontrolled development of industrial
premises or zones leads to noise pollution and vibration disturbance. The use of
conventional piling methods and the sound of exhaust fans in factories are some of the
common activities that generate high sound level.
Motor vehicles
Modern society is highly dependent on motorized transportation such as cars, trucks, and
railways. Movement of people and goods requires energy which relies mostly on the
burning of fossil fuels, thus causing emissions and noise with adverse local effects.
The air quality of the different transport modes depends on the kind of energy, engine
technology and the amount of energy consumed. Within the transport sector motorized
road traffic is the main emission source while public transport is environmentally
friendlier than passenger cars.
In 2004, nearly 14 million vehicles were registered in Malaysia, almost double the
number from a decade ago.The number will increase in the next few years, with higher
disposable incomes, rural-urban migration and the lack of efficient public transport
systems. (Text : 'Clean Air For Our Cities, 2006, by DOE Malaysia & German Technical
Co-operation)
Power Generation
Most of the energy is produced in conventional power plants burning fossil fuels like
natural gas, oil or coal. The effectiveness of these power plants is about 35 to 40 per cent
with the remaining chemical energy converted into heat.
At the moment, Malaysia produces 86% of its electricity in conventional power plants
and 14% in hydroelectric power plants.(Text : 'Clean Air For Our Cities, 2006, by DOE
Malaysia & German Technical Co-operation)
Everyday Routine
Household contribute to air pollution mainly through the use of energy that is required to
run machines and electrical appliances such as refrigerators. Refrigerators and air
conditioners not only consume energy but they pollute the environment when their
coolant fluids release Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) into the atmosphere. Chemicals used in
houses and gardens are also sources of pollution as well as toxic waste. (Text : 'Clean Air
For Our Cities, 2006, by DOE Malaysia & German Technical Co-operation)
Open Burning
Burning of older existing plantations for re-planting creates large amounts of soot
particles. These soot particles can be blown over long distances and are mainly
responsible for the haze that often covers the sky above Malaysia. These fires not only
pollute the air but also destroy the rich habitat of the flora and fauna. (Text : 'Clean Air
For Our Cities, 2006, by DOE Malaysia & German Technical Co-operation)
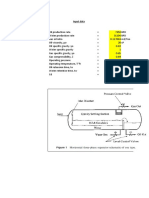
(Graphs and figures of Air Pollution Sources in Malaysia)§
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Slo Review Standard 2Documento3 páginasSlo Review Standard 2api-305204604Ainda não há avaliações
- Renewable Energy Heating SectorDocumento12 páginasRenewable Energy Heating SectorAkash BhattacharyyaAinda não há avaliações
- Element Air - Guide - Tribe RedleafDocumento15 páginasElement Air - Guide - Tribe RedleafhancilloAinda não há avaliações
- Proof of Life - How Would We Recognize An Alien If We Saw One - Reader ViewDocumento3 páginasProof of Life - How Would We Recognize An Alien If We Saw One - Reader ViewBlazing BooksAinda não há avaliações
- Specific Objectives: Pressure QuestionsDocumento6 páginasSpecific Objectives: Pressure QuestionsBadmind JnrAinda não há avaliações
- Cenozoic Tectonics of Indonesia Problems and Models: Robert HallDocumento32 páginasCenozoic Tectonics of Indonesia Problems and Models: Robert Hallarie_stoner13Ainda não há avaliações
- Earth's Timeline (Earth & Life ScienceDocumento4 páginasEarth's Timeline (Earth & Life ScienceRUTH DEBORAH PECIOAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Law GuideDocumento5 páginasEnvironmental Law GuideStuti BaradiaAinda não há avaliações
- Geotechnical Formulas and Conversion FactorsDocumento35 páginasGeotechnical Formulas and Conversion Factorsdrh31415100% (1)
- Introductory AstronomyDocumento7 páginasIntroductory AstronomyJeko Betguen PalangiAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento253 páginasUntitledKathy LuoAinda não há avaliações
- PerformanceDocumento2 páginasPerformanceTenny SupAinda não há avaliações
- An Investigation On The Power System Stability of Photovoltaic Grid Integrated SystemDocumento4 páginasAn Investigation On The Power System Stability of Photovoltaic Grid Integrated SystemaeaAinda não há avaliações
- VLL Separator - Train1Documento9 páginasVLL Separator - Train1yamen-691904Ainda não há avaliações
- Dino Kraspedon - My Contact With Flying SaucersDocumento46 páginasDino Kraspedon - My Contact With Flying Saucersgolliwoghc0% (1)
- IGCSE - Bio - Worksheet 10 - Plants and FoodDocumento10 páginasIGCSE - Bio - Worksheet 10 - Plants and FoodSyed Muhammad FaiqAinda não há avaliações
- Scuttlers, Black Goo, and The Biogenic FieldDocumento27 páginasScuttlers, Black Goo, and The Biogenic FieldIan Beardsley100% (1)
- Soil Mechanics Permeability ProblemsDocumento4 páginasSoil Mechanics Permeability Problemsbasel ibrahimAinda não há avaliações
- 00Documento40 páginas00ShōyōHinataAinda não há avaliações
- Curriculum Vitae: Dr. Tapas LahaDocumento8 páginasCurriculum Vitae: Dr. Tapas LahaDeepak KAinda não há avaliações
- Inorganic Chemistry: Duward Shriver and Peter AtkinsDocumento65 páginasInorganic Chemistry: Duward Shriver and Peter AtkinsMilano TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Fisa Tehnica Panou Fotovoltaic Hyundai 485W HiE S485VI GreenCostal 1Documento2 páginasFisa Tehnica Panou Fotovoltaic Hyundai 485W HiE S485VI GreenCostal 1subtirelu lucianAinda não há avaliações
- 325C1 2005Documento9 páginas325C1 2005Rajat SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 2 Materials 2A FluidsDocumento3 páginasTopic 2 Materials 2A Fluidsmaram shbairAinda não há avaliações
- EnergyNext Vol 03 Issue 8 Aug 2013Documento68 páginasEnergyNext Vol 03 Issue 8 Aug 2013IndiaNextAinda não há avaliações
- Domestic Building Compliance Guide - 2010Documento129 páginasDomestic Building Compliance Guide - 2010Heronildes OliveiraAinda não há avaliações
- Informe 11Documento31 páginasInforme 11JHON ALBERT CASTILLO VENTOCILLAAinda não há avaliações
- Sustainability - The Role of Mineral Processing and Extractive MetallurgyDocumento9 páginasSustainability - The Role of Mineral Processing and Extractive MetallurgyakshukAinda não há avaliações
- Hybrid Power Systems Based On Renewable Energies-A Suitable and Cost-Competitive Solution For Rural Electrification PDFDocumento7 páginasHybrid Power Systems Based On Renewable Energies-A Suitable and Cost-Competitive Solution For Rural Electrification PDFbdsrlAinda não há avaliações