Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
3 FRICTION Equilibrium of The Body On Ladder
Enviado por
RAMAKANT RANA77%(13)77% acharam este documento útil (13 votos)
8K visualizações2 páginasA ladder consists of two long uprights of wood or iron and connected by a number of cross bars. These cross bars are called rungs and provide steps for climbing. A ladder is acted upon by the following set of forces: (1) Weight W acting downwards at its mid point. (2) Normal reaction Rb and friction force Fb = uRb at the end B leaning against the wall. Since the ladder has a tendency to slip downwards, the friction force will be acting upwards
Descrição original:
Título original
3 FRICTION Equilibrium of The Body on Ladder
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoA ladder consists of two long uprights of wood or iron and connected by a number of cross bars. These cross bars are called rungs and provide steps for climbing. A ladder is acted upon by the following set of forces: (1) Weight W acting downwards at its mid point. (2) Normal reaction Rb and friction force Fb = uRb at the end B leaning against the wall. Since the ladder has a tendency to slip downwards, the friction force will be acting upwards
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
77%(13)77% acharam este documento útil (13 votos)
8K visualizações2 páginas3 FRICTION Equilibrium of The Body On Ladder
Enviado por
RAMAKANT RANAA ladder consists of two long uprights of wood or iron and connected by a number of cross bars. These cross bars are called rungs and provide steps for climbing. A ladder is acted upon by the following set of forces: (1) Weight W acting downwards at its mid point. (2) Normal reaction Rb and friction force Fb = uRb at the end B leaning against the wall. Since the ladder has a tendency to slip downwards, the friction force will be acting upwards
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
FRICTION ((LADDER PROBLEMS) MAIT
Q. 1: What is ladder friction? How many forces are acting on a ladder?
Solution:
A ladder is an arrangement used for climbing on the
walls It essentially consists of two long uprights of
wood or iron and connected by a number of cross bars.
These cross bars are called rungs and provide steps for
climbing.
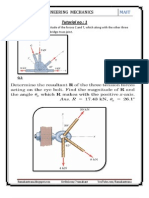
Fig shows a ladder AB with its end A resting on the
ground and end B leaning against a wall. ll. The ladder is
acted upon by the following set of forces:
(1) Weight W acting downwards at its mid point.
(2) Normal reaction Rb and friction force Fb = µRb
at the end B leaning against the wall. Since the
ladder has a tendency to slip downwards, the
friction force will be acting upwards. If the
wall is smooth (µ = 0), the friction force will
be zero.
(3) Normal reaction Ra and friction force Fa =µRa at the end A resting on the floor. Since the ladder, upon
slipping, tends to move away from the wall, the direction of friction force will be towards the wall.
Applying equilibrium conditions, the algebraic sum of the horizontal and vertical component of forces would be
zero.
Q. 2: A ladder 5m long rests on a horizontal ground and leans
against a smooth vertical wall at an angle 70° with the horizontal.
The weight of the ladder is 900N and acts at its middle. The ladder
is at the point of sliding, when a man weighing 750N stands 1.5m
from the bottom of the ladder. Calculate coefficient of friction
between the ladder and the floor.
Solution:
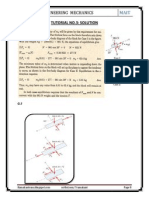
Forces acting on the ladder is shown in fig 9.62
Resolving all the forces vertically,
RV = R – 900 – 750 = 0
R = 1650N ...(ii)
Now taking moment about point B,
R × 5sin20° – Fr × 5cos20°
– 900 × 2.5sin20° – 750 × 3.5sin20° = 0
Since Fr = µR, and R = 1650N; Fr = 1650µ
Putting, the value of R and Fr
µ = 0.127 .......ANS (see Fig.)
Q. 3: A uniform ladder of length 13m and weighing 250N is placed
against a smooth vertical wall with its lower end 5m from the wall.
The coefficient of friction between the ladder and floor is 0.3. Show
that the ladder will remain in equilibrium in this position. What is the
frictional force acting on the ladder at the point of contact between
the ladder and the floor?
Solution:
Since the ladder is placed against a smooth vertical wall, therefore there
will be no friction at the point of contact between the ladder and wall.
Compiled by: RAMAKANT RANA “ramakantrana@blogspot.com” Page 1
FRICTION ((LADDER PROBLEMS) MAIT
Resolve all the forces horizontally and vertically.
∑H = 0,
Fr – R2 = 0 ...(i)
∑V = 0,
R1 – 250 ...(ii)
From the geometry of the figure, BC = 12m
Taking moment about point B,
R1 × 5 – Fr × 12 – 250 × 2.5 = 0
Fr = 52N .......ANS
For equilibrium of the ladder, Maximum force of friction available at the point of contact between the ladder and the
floor = µR
= 0.3 × 250 = 75N .......ANS
Thus we see that the amount of the force of friction available at the point of contact (75N) is more than force of
friction required for equilibrium (52N). Therefore, the ladder will remain in equilibrium in this position.
Q. 4: A uniform ladder of 7m rests against a vertical wall with which it makes an angle of 45º, the coefficient
of friction between the ladder and the wall is 0.4 and that between ladder and the floor is 0.5. If a man, whose
weight is one half of that of the ladder, ascends it, how high will it be when the ladder slips?
Solution:
Let,
X = Distance between A and the man, when the ladder is at the
point of slipping.
W = Weight of the ladder
Weight of man = W/2 = 0.5W
Fr1 = 0.5R1 ...(i)
Fr2 = 0.4R2 ...(ii)
Resolving the forces vertically
R1 + Fr2 – W – 0.5W = 0
R1 + 0.4R2 = 1.5W ...(iii)
Resolving the forces Horizontally
R2 – Fr1 = 0; R2 = 0.5RR1 ...(iv)
Solving equation (iii) and (iv), we get
R2 = 0.625W, Fr2 = 0.25
0.25W
Now taking moment about point A,
W × 3.5cos45° + 0.5W W × xcos45° – R2 ×
7sin45° – Fr2 × 7cos45°
Putting the value of R2 and Fr2, we get
X = 5.25m .......ANS
Compiled by: RAMAKANT RANA “ramakantrana@blogspot.com” Page 2
Você também pode gostar
- ENGINEERING MECHANICS - FRICTION FORCESDocumento25 páginasENGINEERING MECHANICS - FRICTION FORCESAbigail SiatrezAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 04Documento78 páginasChapter 04Bikash Chandra DasAinda não há avaliações
- Correlation 1: DynamicsDocumento14 páginasCorrelation 1: DynamicsLaurence Ciervo0% (1)
- RMK Engineering College mechanical engineering tutorial problemsDocumento22 páginasRMK Engineering College mechanical engineering tutorial problemskalirajgurusamy33% (3)
- Calculating Stress in Bridge Truss MembersDocumento32 páginasCalculating Stress in Bridge Truss Members안혜영Ainda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics: Numerical ExamplesDocumento36 páginasEngineering Mechanics: Numerical Examplessaxenaarpita41100% (1)
- Method of Members - Frames Containing Three-Force MembersDocumento75 páginasMethod of Members - Frames Containing Three-Force MembersAna May DocotAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 13.3: SolutionDocumento3 páginasPROBLEM 13.3: Solutionnicky1213aAinda não há avaliações
- SeriesIIProblems ENG1440Documento92 páginasSeriesIIProblems ENG1440Sumit Ghai100% (2)
- PRPC324 Module 5Documento40 páginasPRPC324 Module 5holeeshet holeeshetAinda não há avaliações
- Torsion of Circular ShaftsDocumento7 páginasTorsion of Circular ShaftsJoshua John Julio100% (1)
- Equilibrium of Force SystemDocumento89 páginasEquilibrium of Force SystemKimberly TerogoAinda não há avaliações
- CH-3 Strength of MaterialsDocumento33 páginasCH-3 Strength of Materialsethiopia ethiopia100% (2)
- Problem 431Documento12 páginasProblem 431Cheska FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- F.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER STATICS EXAMDocumento3 páginasF.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER STATICS EXAMAve de GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Kirchoffs Law With Cramers RuleDocumento14 páginasKirchoffs Law With Cramers RuleRoy BernardAinda não há avaliações
- CHP 06Documento22 páginasCHP 06Abhiram Reddy100% (5)
- Engineering MechanicsDocumento4 páginasEngineering MechanicsDonna MelgarAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 1Documento2 páginasTutorial 1Eddy FazwanAinda não há avaliações
- RCD Assignment 1Documento5 páginasRCD Assignment 1Camille Semilla100% (1)
- Chap. 3-PbsDocumento54 páginasChap. 3-PbsAlias HedgeAinda não há avaliações
- RCD SA4 GuideDocumento15 páginasRCD SA4 GuideDionne Rhenzo MontalesAinda não há avaliações
- Problems Set 04 With SolutionsDocumento10 páginasProblems Set 04 With Solutionsjutt4all100% (1)
- FINAL EXAMINATION in Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocumento1 páginaFINAL EXAMINATION in Dynamics of Rigid BodiesRochelle TugadeAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics Problems On WedgesDocumento21 páginasEngineering Mechanics Problems On WedgesJeremy RimandoAinda não há avaliações
- CE Board Problems in PhysicsDocumento4 páginasCE Board Problems in PhysicsGinto Aquino50% (4)
- Problem Set 1Documento9 páginasProblem Set 1Ron Julienne RebugioAinda não há avaliações
- WorkoutDocumento2 páginasWorkoutWei Shen100% (1)
- FRICTION FORCESDocumento7 páginasFRICTION FORCESJasmeetSinghAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Materials 6th Beer Chapter8Documento116 páginasMechanics of Materials 6th Beer Chapter8최혜원Ainda não há avaliações
- Ejercicios TimothyDocumento32 páginasEjercicios TimothyvanessaAinda não há avaliações
- 07 03ChapGereDocumento14 páginas07 03ChapGereChristina BuckleAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter VI - Force System in SpaceDocumento11 páginasChapter VI - Force System in SpaceJommarVocalTagalogAinda não há avaliações
- Static-Couples - Equilibrium - Moment PDFDocumento9 páginasStatic-Couples - Equilibrium - Moment PDFBryant Villarin Baldivicio100% (6)
- G17 - Dynamics - Work and Energy - ProblemsDocumento22 páginasG17 - Dynamics - Work and Energy - ProblemsWilson Chaparro100% (1)
- Sample Problem 4.1: Free-Body DiagramDocumento4 páginasSample Problem 4.1: Free-Body DiagramAlbert MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Prestressed-Concrete Chapter 4Documento17 páginasPrestressed-Concrete Chapter 4Renz Ryan Dolor50% (2)
- Steel Design Problem SetxzDocumento35 páginasSteel Design Problem SetxzMiah N. PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Q3Documento4 páginasQ3Ritsu Tainaka0% (1)
- Chapter 4 Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDocumento12 páginasChapter 4 Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyWilliam JugalbotAinda não há avaliações
- StaticsDocumento5 páginasStaticslakr lama100% (1)
- CSU-Cabadbaran Advance Review For EE: Topic: Mechanics 1 - StaticsDocumento10 páginasCSU-Cabadbaran Advance Review For EE: Topic: Mechanics 1 - StaticsCinderella WhiteAinda não há avaliações
- Module 02: Approximate Analysis of Indeterminate Structures: Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO's)Documento41 páginasModule 02: Approximate Analysis of Indeterminate Structures: Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO's)Mac KYAinda não há avaliações
- CH 14 Kinetics of Particles Work and EnergyDocumento19 páginasCH 14 Kinetics of Particles Work and EnergyKhaled Obeidat100% (2)
- Exercises: Ans. F = 1404.917 N; θ = 7.05ºDocumento3 páginasExercises: Ans. F = 1404.917 N; θ = 7.05ºRhey LuceroAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 2.124: SolutionDocumento14 páginasPROBLEM 2.124: SolutionCharbel Abou KhalilAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Design II (Steel/Timber) Lab: Prepared By: Cedrick L. AngelesDocumento122 páginasStructural Design II (Steel/Timber) Lab: Prepared By: Cedrick L. AngelesPascasio PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- Motion Diagrams:: Interval. V Interval. SDocumento3 páginasMotion Diagrams:: Interval. V Interval. Sruel_galutan100% (1)
- 1) Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocumento18 páginas1) Dynamics of Rigid Bodiesnicolo agustinAinda não há avaliações
- 3d Force System PDFDocumento31 páginas3d Force System PDFprofamarAinda não há avaliações
- ES 12 - Chapter 17 - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Energy and Momentum MethodsDocumento50 páginasES 12 - Chapter 17 - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Energy and Momentum Methodscriscab12345Ainda não há avaliações
- Truss - Problems With Solution (Structural)Documento10 páginasTruss - Problems With Solution (Structural)BESTINAinda não há avaliações
- Structural design problems and solutionsDocumento6 páginasStructural design problems and solutionsPaulo ValderamaAinda não há avaliações
- Arches and CablesDocumento21 páginasArches and CablesAriel Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- FRICTION FORCES AND COEFFICIENTSDocumento12 páginasFRICTION FORCES AND COEFFICIENTSLesther James CastroAinda não há avaliações
- 1 T 2Documento16 páginas1 T 2Mr. Sambath LimAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Frictin Rough Inclined PlaneDocumento7 páginas2 Frictin Rough Inclined PlaneRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Solution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Documento18 páginasSolution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Gulshan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Engg Graphics 2 Edition PrefaceDocumento16 páginasEngg Graphics 2 Edition PrefaceRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing Lab ManualDocumento52 páginasEngineering Drawing Lab ManualRAMAKANT RANA93% (15)
- SOME Write UPDocumento3 páginasSOME Write UPRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Recent Advances in Mechanical Engineering RAME-2016 (Proceedings)Documento768 páginasRecent Advances in Mechanical Engineering RAME-2016 (Proceedings)RAMAKANT RANA100% (4)
- Assignment Instrumentation V Sem EveningDocumento5 páginasAssignment Instrumentation V Sem EveningRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Electrochemical Machining ECMDocumento11 páginasElectrochemical Machining ECMRAMAKANT RANA100% (1)
- Electrochemical Machining (ECM)Documento11 páginasElectrochemical Machining (ECM)RAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Manufacturing Process SyllabusDocumento4 páginasManufacturing Process SyllabusRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Mechatronics Lab ManualDocumento32 páginasMechatronics Lab ManualRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Ultrasonic Machining (Usm)Documento12 páginasUltrasonic Machining (Usm)RAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- CupolaDocumento3 páginasCupolaRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- EMM Lecture Unit VIDocumento7 páginasEMM Lecture Unit VIRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Course 17Documento4 páginasCourse 17getprize4surveyAinda não há avaliações
- Robotics Practical FileDocumento131 páginasRobotics Practical FileRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Laser Beam Machining (LBM)Documento10 páginasLaser Beam Machining (LBM)RAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Advanced AMethods of MachiningDocumento3 páginasIntroduction To Advanced AMethods of MachiningRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions To The Tutorial (No. 3) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !Documento5 páginasSolutions To The Tutorial (No. 3) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !RAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Discharge MachiningDocumento13 páginasElectrical Discharge MachiningRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial No. 5Documento1 páginaTutorial No. 5RAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions To The Tutorial (No. 2) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !Documento4 páginasSolutions To The Tutorial (No. 2) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !RAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation of Drilling Machine by Anil Dahiya SirDocumento72 páginasPresentation of Drilling Machine by Anil Dahiya SirRAMAKANT RANA100% (1)
- Engineering Graphics Lab ManualDocumento51 páginasEngineering Graphics Lab ManualRAMAKANT RANA63% (8)
- Solutions To The Tutorial (No. 4) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !Documento3 páginasSolutions To The Tutorial (No. 4) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !RAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial No. 4Documento2 páginasTutorial No. 4RAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Graphics Viva QuestionsDocumento1 páginaEngineering Graphics Viva QuestionsRAMAKANT RANA75% (4)
- Tutorial No 1Documento3 páginasTutorial No 1RAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Sessional SyllabusDocumento2 páginas2nd Sessional SyllabusRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical SwitchesDocumento1 páginaMechanical SwitchesRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Graphics by RAMAKANT RANADocumento1 páginaEngineering Graphics by RAMAKANT RANARAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Mecha Syllabus Point WiseDocumento2 páginasMecha Syllabus Point WiseRAMAKANT RANAAinda não há avaliações
- Two Sides of Effective Oral CommunicationDocumento17 páginasTwo Sides of Effective Oral CommunicationSharath KumarAinda não há avaliações
- PSM641UX TechnicalManua-V1.03Documento128 páginasPSM641UX TechnicalManua-V1.03arulsethuAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Kabbalah: Jewish Mysticism, Meditation and MoralityDocumento4 páginasPractical Kabbalah: Jewish Mysticism, Meditation and MoralityJoyce Choombe MulengaAinda não há avaliações
- DefenseDocumento20 páginasDefenseManny De MesaAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition Kolb Test BankDocumento26 páginasFundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition Kolb Test BankDanielYoungabrn100% (60)
- Thank You LetterDocumento2 páginasThank You LetterFathina57% (7)
- Lec23 PDFDocumento44 páginasLec23 PDFSyed YousufuddinAinda não há avaliações
- Vodafone - Market Research ProposalDocumento4 páginasVodafone - Market Research ProposalNikita Sanghvi100% (2)
- Cunningham S Book of Shadows PDFDocumento258 páginasCunningham S Book of Shadows PDFAngela C. Allen100% (10)
- What Is The Advantages and Disadvantages of Analog and Digital InstrumentDocumento22 páginasWhat Is The Advantages and Disadvantages of Analog and Digital Instrumentabishek_bhardwa866645% (20)
- In Sunni IslamDocumento5 páginasIn Sunni IslamMk AkangbeAinda não há avaliações
- Function Point and Cocomo ModelDocumento31 páginasFunction Point and Cocomo ModelParinyas SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Wildlife Ecology - Unit 14 - Week (12) - RevisionDocumento1 páginaWildlife Ecology - Unit 14 - Week (12) - RevisionAdityaAinda não há avaliações
- # Law and MoralityDocumento16 páginas# Law and MoralityBRYAN LING PING YEE UnknownAinda não há avaliações
- Peta I Think Fizik t4Documento18 páginasPeta I Think Fizik t4Yk TayAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 22 NDocumento6 páginasLecture 22 Ncau toanAinda não há avaliações
- Management Review, 32: 794-816.: Daftar PustakaDocumento8 páginasManagement Review, 32: 794-816.: Daftar PustakaNurulsalamah28Ainda não há avaliações
- COOKERY Grade 9 (Q1-W1)Documento2 páginasCOOKERY Grade 9 (Q1-W1)Xian James G. YapAinda não há avaliações
- PrisonerDocumento10 páginasPrisonerAbdi ShakourAinda não há avaliações
- CS201 Midterm Solved MCQs With ReferenceDocumento4 páginasCS201 Midterm Solved MCQs With Referencegenome companyAinda não há avaliações
- Living Water by David FeddesDocumento44 páginasLiving Water by David FeddesBenjaminFigueroaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 - Risk and ReturnDocumento67 páginasChapter 3 - Risk and ReturnPhuonganh LeAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Course Alagappa UniversityDocumento10 páginasMathematics Course Alagappa UniversityTirthajit SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Competencies For English - Grades 11-12Documento5 páginasLearning Competencies For English - Grades 11-12Neo Artajo100% (1)
- Ideation For Product Innovation What Are The BestDocumento9 páginasIdeation For Product Innovation What Are The BestLIVIA MARILIA CHIARIAinda não há avaliações
- Vaishali Ancient City Archaeological SiteDocumento31 páginasVaishali Ancient City Archaeological SiteVipul RajputAinda não há avaliações
- Individual Assignment I Google Search Network CampaignDocumento15 páginasIndividual Assignment I Google Search Network CampaignMokshita VajawatAinda não há avaliações
- Fraud under Indian Contract Act - Essentials and Exceptions to Mere SilenceDocumento6 páginasFraud under Indian Contract Act - Essentials and Exceptions to Mere SilenceabhilashAinda não há avaliações
- Demand for Money Theory ExplainedDocumento31 páginasDemand for Money Theory Explainedrichard kapimpaAinda não há avaliações