Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Uneb - Taxonomy - of - PPP Estagio 1
Enviado por
afroviviTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Uneb - Taxonomy - of - PPP Estagio 1
Enviado por
afroviviDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
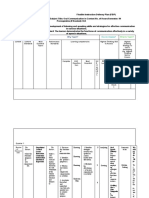
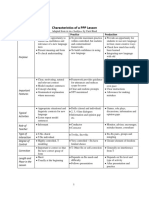
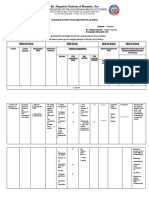
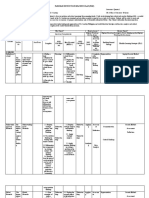
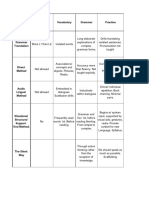
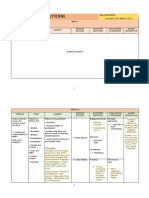
TAXONOMY OF KINDS OF PRACTICE – UNEB / 2006.
II – Profº Robélio Caria Filho
HIGHL Y CONTROLLED LESS HIGHL Y LESS CONTROLLED FREER PRACTICE FLUENCY PRACTICE
PRACTICE CONTROLLED PARCTICE PRACTICE
Accurate production of Opportunity for recall Practice in choice-making Practice in choice-making Build on communicative
Target Lang, orally Reinforce meaning through Reinforce meaning through Exposing ss to competence
Fluid oral production of new context new context umpredictability and Opportunity for risk-taking
AIMS Target Lang More pronunciation Experimenting with allowing them to deal experimenting creativity
Manipulation of sounds, practice communicative of with it Render the teacher
stress, intonation Some practice in choice- Target Lang Opportunity for self- redundant
Confidence - building making Practice in dealing with expression
Confidence- building umpredictability Internalization of Target
Manipulation of form Lang.
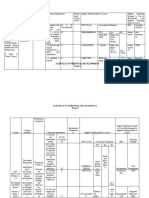
FOCUS LANG____ ¤ or ¤ ¤ ¤ ¤ ¤
_________COMMU.? L C L C L C L C L C
None- Teacher Very limited – If the activity has Broader – This is where Lots. If the Target Lang …not Leamers’ entire
Imposes all lang- practiced. been devised properly, only leamers compare target Lang prompted- But during lead-in to language repertoire
Target Lang should be poss, to other lang with which this the task students are No discussion of appropriate
RANGE OF LANG. but is not actually imposed. could be confused. encouraged to think lang
CHOICE: Pron. Work concentrates on appropriate to the task. All communication strategies
intonation for conveying mood. encouraged.
Sts are given “communication
strategies”.
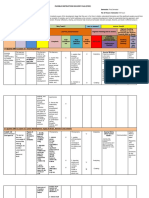
-st -st -st -st -st
T -st mostly T -st initially T -st at organization stage T -st at organization stage T -st at organization stage
INTERACTION -st -st - st -st -st
¤ ¤ ¤ ¤ -st ¤
St - st; st – st St - st; st - st St - st; pairs / groups St - st; pairs / groups St - st; pairs / groups
Modeling / demonstrating Organizing Monitor / helper during In setting up task: checking Setting up
Leading Monitoring preparation communication strategies/ Monitoring
Participating Intervening Emergency intervention comp. of instructions for the
TEACHER’S ROLE Monitoring Resource(for expressions task.
Intervening requested). During task discrete
monitoring
Listening out for correct ss
use of Target Lang in the
context.
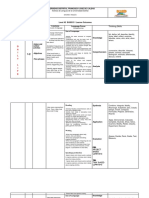
Error inadmissible T – st Prompts for self-correction Intervention only where st A Post-activity errors analysis?
Rigorous correction of all St – st T – st ´s Reminder appropriate language
DEALING WITH ERROR errors in production of Target Self St – st Unintelligibility inhibits st B
Lang Still no room for error here Error only dealt with if it T makes a not major errors
Mostly teacher-centred obscures intelligibility for post-activity comment
Choral repetition Open pairs Highly cued role-play Role-play
Individual repetition Elicited/ dialogues Relating stories Discussion –
Backchaining drill monologues Describe & for/against
Mutter drill Cued dialogues do/make/draw/compare “If I were…”
EXAMPLES Substitution drill Narrative – build “Communication games” Problem – solving
Transformation drill “Controlled” info. Gap Describe and…
Imposed Dialogue Text survey Relating personal
(B/B; book tape) 4/5- line drills experiences.
Question & answer “Drill” + personalized end
drill
close
Você também pode gostar
- Performance Task Lesson PlanDocumento6 páginasPerformance Task Lesson Planapi-288713007100% (1)
- Planing 25 de MarzoDocumento13 páginasPlaning 25 de MarzoFrancesca DownerAinda não há avaliações
- PPP TableDocumento6 páginasPPP TableMartha MarthaAinda não há avaliações
- Fidp Oral Comm Q1Documento9 páginasFidp Oral Comm Q1MIKKIENNAAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Approaches To Language TeachingDocumento3 páginasSummary of Approaches To Language TeachingSiyeon YeungAinda não há avaliações
- Quarter 1&2 - Flexible Instruction Delivery PlanDocumento8 páginasQuarter 1&2 - Flexible Instruction Delivery PlanKrizza Jane SingcuyaAinda não há avaliações
- Englis Test Item BankDocumento2 páginasEnglis Test Item Bankeliezar PayusanAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Theories Chart: Pav20 /L 4105) and Humans (CITATION Wat20 /L 4105)Documento3 páginasLearning Theories Chart: Pav20 /L 4105) and Humans (CITATION Wat20 /L 4105)Jose AlvaradoAinda não há avaliações
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan TemplateDocumento2 páginasFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan Templatemaryluz ederAinda não há avaliações
- Trends q1 FidpDocumento6 páginasTrends q1 FidpAubrae Frances BannawiAinda não há avaliações
- EL Strategies ChartDocumento1 páginaEL Strategies ChartturnfoxAinda não há avaliações
- Principles in Language Teaching - A SummaryDocumento4 páginasPrinciples in Language Teaching - A SummaryAlejandra ParedesAinda não há avaliações
- Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan TemplateDocumento6 páginasFlexible Instructional Delivery Plan TemplaterenzpaulorodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Weinstein Strategic Learning ModelDocumento1 páginaWeinstein Strategic Learning ModelGerardo Bañales FazAinda não há avaliações
- Communicating Change 1: Building SupportDocumento8 páginasCommunicating Change 1: Building SupportLe NamAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Principles in Language TeachingDocumento3 páginasSummary of Principles in Language TeachingCarolina BarbaAinda não há avaliações
- Tp://t.me/amerwna HTDocumento159 páginasTp://t.me/amerwna HTAshwaq.Alqarni A-AAinda não há avaliações
- Narrative Writing ModuleDocumento138 páginasNarrative Writing ModuleKureen FreddieAinda não há avaliações
- Scope and SequencesDocumento4 páginasScope and SequencesTrung HiếuAinda não há avaliações
- Methods L1 Vocabulary Grammar PracticeDocumento6 páginasMethods L1 Vocabulary Grammar PracticeSonya BladeAinda não há avaliações
- From Communicative To Action Oriented - Theory Into PracticeDocumento9 páginasFrom Communicative To Action Oriented - Theory Into PracticeUxueAinda não há avaliações
- Finished Fidp OralcomDocumento6 páginasFinished Fidp OralcomAira CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- Apresentação Sobre A CAADocumento73 páginasApresentação Sobre A CAAMonalisa CostaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 01 Business CommunicationDocumento48 páginasCH 01 Business CommunicationMUHAMMAD USAMAAinda não há avaliações
- Curriculum Map For Values 7Documento23 páginasCurriculum Map For Values 7Jesah CambongaAinda não há avaliações
- What To Teach?Documento6 páginasWhat To Teach?Keneth Rose FagtananAinda não há avaliações
- Task-Based Learning at A GlanceDocumento2 páginasTask-Based Learning at A GlanceLuiz Otávio Barros, MA100% (2)
- A Look at 4 Different Age GroupsDocumento4 páginasA Look at 4 Different Age GroupsluisAinda não há avaliações
- Taguite Elementary School/Leyte Oliver A. Lampayan Interpersonal Skills (Relationships & Community Buliding Skills) 1st QuarterDocumento9 páginasTaguite Elementary School/Leyte Oliver A. Lampayan Interpersonal Skills (Relationships & Community Buliding Skills) 1st QuarterTom CroslandAinda não há avaliações
- TEACHERS' NAMES: Rosario Guadalupe Zepeda, Silvia Melissa Aguilar Fernández. LEVEL: INTERMEDIATE 1 MODULE: 1 TEXTBOOKDocumento3 páginasTEACHERS' NAMES: Rosario Guadalupe Zepeda, Silvia Melissa Aguilar Fernández. LEVEL: INTERMEDIATE 1 MODULE: 1 TEXTBOOKMelissa AguilarAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus Iii - 2024 EnglishDocumento10 páginasSyllabus Iii - 2024 EnglishAbigail Bravo de RuedaAinda não há avaliações
- Model As A MASTER PAL OverviewDocumento18 páginasModel As A MASTER PAL OverviewClara Laosa CamposAinda não há avaliações
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map: Alegria, Murcia, Negros OccidentalDocumento8 páginasClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map: Alegria, Murcia, Negros OccidentalRolyn RolynAinda não há avaliações
- Rubric For Speaking Skills EditedDocumento2 páginasRubric For Speaking Skills EditedizawanyAinda não há avaliações
- RWS - Action PlanDocumento88 páginasRWS - Action Planvimar fabonanAinda não há avaliações
- ACidDocumento3 páginasACidJonard OrcinoAinda não há avaliações
- Fidp - Per-DevDocumento3 páginasFidp - Per-DevIn SanityAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Nursing-Care-Plan SchizoDocumento6 páginas4 Nursing-Care-Plan SchizoJai GoAinda não há avaliações
- The Go To Page Word Fillable - TWDocumento4 páginasThe Go To Page Word Fillable - TWapi-537263106Ainda não há avaliações
- Basico I PDFDocumento14 páginasBasico I PDFChristian LinaresAinda não há avaliações
- Eng2p Media AssignmentDocumento2 páginasEng2p Media Assignmentapi-308070012100% (1)
- Concept MapDocumento2 páginasConcept MapGeraldine FloresAinda não há avaliações
- RubricsDocumento2 páginasRubricsellin bagsacAinda não há avaliações
- Met 5.1Documento3 páginasMet 5.1Saul NabenaAinda não há avaliações
- Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (Fidp) : What To Teach?Documento4 páginasFlexible Instructional Delivery Plan (Fidp) : What To Teach?Rosalie CarmeloAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 5 SlidesDocumento17 páginasTopic 5 SlidesSARA MARIN LOPEZAinda não há avaliações
- 22-23 Planificare Pe Unitati de Invatare Fairyland 3Documento9 páginas22-23 Planificare Pe Unitati de Invatare Fairyland 3Mădălina LunguAinda não há avaliações
- Mslessonplan221 24Documento3 páginasMslessonplan221 24api-329779328Ainda não há avaliações
- Flexible Instruction Delivery PlanDocumento2 páginasFlexible Instruction Delivery PlanMarc Christian NicolasAinda não há avaliações
- Fidp Oral ComDocumento4 páginasFidp Oral ComElmerAinda não há avaliações
- Methods ChartDocumento2 páginasMethods ChartDani JesusAinda não há avaliações
- CM - English 9Documento7 páginasCM - English 9Yuri IssangAinda não há avaliações
- Integrative Assessment: Master Teacher Grade Level ChairmanDocumento6 páginasIntegrative Assessment: Master Teacher Grade Level Chairmanmarco medurandaAinda não há avaliações
- ELEMTBL Activity 4 PrelimDocumento3 páginasELEMTBL Activity 4 PrelimRosette LumbresAinda não há avaliações
- TMP - 29682-Cameron, L & Bandler, D.G & Lebeau, M - The Emprint Method-62977549Documento147 páginasTMP - 29682-Cameron, L & Bandler, D.G & Lebeau, M - The Emprint Method-62977549Ambaejo96Ainda não há avaliações
- Summative Assessment 2015-16 Ad RubricDocumento2 páginasSummative Assessment 2015-16 Ad Rubricapi-353859154100% (1)
- English 8 w3Documento3 páginasEnglish 8 w3joshua souribioAinda não há avaliações
- Group 5 Summary of Language Teaching MethodsDocumento7 páginasGroup 5 Summary of Language Teaching MethodsPhan Xuân Yến NhiAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Language Teaching ApproachesDocumento1 páginaSummary of Language Teaching Approachesdiya100% (1)
- Noticing and Learning Collocation ETP Issue40 Sept 2005Documento3 páginasNoticing and Learning Collocation ETP Issue40 Sept 2005Camila Selarin100% (2)
- Education Is A Social Process: - EDITORIALDocumento1 páginaEducation Is A Social Process: - EDITORIALKim JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Cimle: Curriculum Integration: An OverviewDocumento5 páginasCimle: Curriculum Integration: An OverviewyusnaidarAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Education Faculty of Social Sciences Air University, IslamabadDocumento6 páginasDepartment of Education Faculty of Social Sciences Air University, IslamabadAliza ArifAinda não há avaliações
- PerDev SHS Learning Plan Lesson 10Documento3 páginasPerDev SHS Learning Plan Lesson 10Daniel John ArboledaAinda não há avaliações
- MOOC Design Toolkit: How To Use ADDIE To Build Your Massive Open Online Course (MOOC)Documento40 páginasMOOC Design Toolkit: How To Use ADDIE To Build Your Massive Open Online Course (MOOC)Aland MediaAinda não há avaliações
- Rosynanda Nur FauziahDocumento2 páginasRosynanda Nur FauziahWahdi Luthfi RamadhanAinda não há avaliações
- The Lexicon School, Hadapsar: 1 September 2020 Dear ParentsDocumento2 páginasThe Lexicon School, Hadapsar: 1 September 2020 Dear ParentsdineshbabupsgAinda não há avaliações
- Monitoring and Evaluation Tool 2022 2023Documento7 páginasMonitoring and Evaluation Tool 2022 2023amelia lagatAinda não há avaliações
- School Learning Action Cell (SLAC)Documento3 páginasSchool Learning Action Cell (SLAC)Reyes C. ErvinAinda não há avaliações
- Sri Vidya College of Enginnering & Technology Course Material (Lecture Notes)Documento35 páginasSri Vidya College of Enginnering & Technology Course Material (Lecture Notes)priya dharshiniAinda não há avaliações
- Adult Learning Syllabus MSUDocumento12 páginasAdult Learning Syllabus MSUGinny M. JonesAinda não há avaliações
- Ipcrf Portfolio Template Rainbow ChevronDocumento21 páginasIpcrf Portfolio Template Rainbow ChevronAbigail Fritz GoloAinda não há avaliações
- Teori Barbara ResnickDocumento20 páginasTeori Barbara Resnickrully annisaAinda não há avaliações
- 955 1654 1 SMDocumento11 páginas955 1654 1 SMStefanus LigaAinda não há avaliações
- The Effects of The Directed Reading Thinking Activity On Second GDocumento45 páginasThe Effects of The Directed Reading Thinking Activity On Second GMîšš ÄĥłèmAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Assessment Map PECsDocumento1 páginaUnit Assessment Map PECsNikki Joyce Cabansag CuranAinda não há avaliações
- E1 Effective Exam PreparationDocumento2 páginasE1 Effective Exam PreparationWendy GuAinda não há avaliações
- Visual Literacy Lesson PlanDocumento3 páginasVisual Literacy Lesson Planapi-664554628Ainda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary QueriesDocumento1 páginaVocabulary QueriesLuis Enrique Simancas HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Yr 7 Lesson Plans Set 1Documento5 páginasYr 7 Lesson Plans Set 1api-524992148Ainda não há avaliações
- rtl2 Assignment 2 FinalisedDocumento15 páginasrtl2 Assignment 2 Finalisedapi-408480165Ainda não há avaliações
- Lan6271 Unit Plan 1.ip 2021Documento24 páginasLan6271 Unit Plan 1.ip 2021thao leAinda não há avaliações
- Complied Tws - Kristen HernandezDocumento48 páginasComplied Tws - Kristen Hernandezapi-240280548100% (1)
- Grade 2 q4 Week 2 All Subjects DAY 5Documento2 páginasGrade 2 q4 Week 2 All Subjects DAY 5marife olmedoAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Module 33 Visualizing Addition or Subtraction of Similar Fractions RevisedDocumento17 páginasMathematics Module 33 Visualizing Addition or Subtraction of Similar Fractions RevisedCharlene Mhae100% (2)
- Recommendations For Students With High Functioning Autism by Kerry Hogan - TEACCH - UNC School of MedicineDocumento9 páginasRecommendations For Students With High Functioning Autism by Kerry Hogan - TEACCH - UNC School of MedicinedelekatalaAinda não há avaliações
- PRACTICALDocumento11 páginasPRACTICALJayvee Loyd R. DizonAinda não há avaliações
- Teacher CompetenciesDocumento15 páginasTeacher CompetenciesVipinAinda não há avaliações