Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
1
Enviado por
Rene Uy0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
12 visualizações4 páginasMore than one half of the respondents are in the age bracket of 60 years and above, most of them are female, married and high school level / graduate. A continuous self-monitoring system should be continuously monitor their blood glucose level as well as control their diet accordingly. Patients should exercise on at least three non consecutive days each week to maximize benefits.
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoMore than one half of the respondents are in the age bracket of 60 years and above, most of them are female, married and high school level / graduate. A continuous self-monitoring system should be continuously monitor their blood glucose level as well as control their diet accordingly. Patients should exercise on at least three non consecutive days each week to maximize benefits.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
12 visualizações4 páginas1
Enviado por
Rene UyMore than one half of the respondents are in the age bracket of 60 years and above, most of them are female, married and high school level / graduate. A continuous self-monitoring system should be continuously monitor their blood glucose level as well as control their diet accordingly. Patients should exercise on at least three non consecutive days each week to maximize benefits.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 4
1.
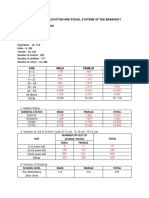
More than one half of the respondents are in the
age bracket of 60 years and above, most of them are
female, married and high school level/graduate.
2. Generally the respondents were excellent with their
foot care compared with their diet, exercise and
medication.
3. The respondents’ age do not influence the lifestyle
practices as to diet, exercise and foot care.
4. The respondents’ gender does not influence the
lifestyle practices as to diet, exercise,
medication and foot care.
5. The respondents’ marital status does not influence
the lifestyle practices as to diet, exercise,
medication and foot care.
6. The respondents educational attainment does not
influence the lifestyle practices as to diet,
exercise, medication and foot care.
7. The respondents’ age influence the lifestyle
practices as to medication.
8.3 Recommendations.
As a result of this study, several recommendations are
presented.
1. Health care providers should have a patient-
centered, and provide advice when patients are
ready to hear and learn more about the diabetic
treatment.
2. A continuous self-monitoring system should be
continuously monitor their blood glucose level as
well as control their diet accordingly.
3. It is also recommended that the hospital diabetic
educator should develop a diabetes education
program to ensure to improve patient knowledge and
care about diabetes.
4. Families should cooperate and give support to the
patient in order for the patient to comply with
his/her regimen such as diet, medication, and
exercise.
5. Studies on similar context but with wider scope
and much larger sample size is recommended to
confirm findings of this study and to further
explore other relevant factors especially factors
influencing lifestyle practices.
6. Patients should exercise on at least three non
consecutive days each week to maximize benefits.
Individual sessions should be at least 10
minutes each or longer.
7. Exercise counseling is needed to assess and
adjust levels of physical activity and provide
motivation and support. Telephone counseling is
economical, practical and effective.
8. Obese older adults with diabetes may benefit from
modest energy restriction and an increase in
physical activity; energy requirement may be
less than for a younger individual of a similar
weight.
9. Individuals with type 2 diabetes are encouraged
to implement lifestyle modifications that reduce
intakes of energy, saturated and trans fatty
acids, cholesterol, and sodium and to increase
physical activity in an effort to improve
glycemia, dyslipidemia, and blood pressure.
10. Have a routine for taking your medications. If
there is a chance that you can become confused
about when to take your medications, or that you
will miss a medication, consider getting a pill
box that is marked with the days of the week.
Fill the pill box at the beginning of each week
to make it easier for you to remember.
11. Keeping a medicine calendar/log book might help
you to remember if you have taken your
medication.
12. Avoid activities that can injure the feet — Some
activities increase the risk of foot injury are
not recommemended including walking barefoot,
using a heating pad or hot water bottle on the
feet, and stepping into the bathtub before
testing the temperature.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Aerobics Unit PlanDocumento28 páginasAerobics Unit PlanGino Al Ballano BorinagaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Summative Test in HOPE 1Documento1 página1 Summative Test in HOPE 1Ervin BaladjayAinda não há avaliações
- Copar DataDocumento4 páginasCopar DataDan HizonAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition Unit I 2021Documento145 páginasNutrition Unit I 2021Anuchithra RadhakrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- Meticore Healthy Metabolism SupportDocumento6 páginasMeticore Healthy Metabolism SupportAbdul MateenAinda não há avaliações
- NEBOSH Assignment 2 - 30th April 2016Documento1 páginaNEBOSH Assignment 2 - 30th April 2016Nazneen AliAinda não há avaliações
- Living in Camp Accommodation RA-R9-01-010-01Documento1 páginaLiving in Camp Accommodation RA-R9-01-010-01cmrig74Ainda não há avaliações
- IMAM Guidelines Final VersionDocumento137 páginasIMAM Guidelines Final VersionRian Apriza0% (1)
- Fit Over 40 GuideDocumento29 páginasFit Over 40 GuideAngelaAinda não há avaliações
- EXCI 202 Case Study PDFDocumento4 páginasEXCI 202 Case Study PDFHayaAinda não há avaliações
- Jeff Cadge/the Image Bank/Getty ImagesDocumento48 páginasJeff Cadge/the Image Bank/Getty ImagesdmcoombsAinda não há avaliações
- Jason Ferruggia's Renegade FitnessDocumento9 páginasJason Ferruggia's Renegade FitnessNeevAinda não há avaliações
- Food & NutritionDocumento21 páginasFood & NutritionSalman Preeom88% (24)
- Organizational Structure BnapDocumento15 páginasOrganizational Structure BnapHenry Kahal Orio Jr.Ainda não há avaliações
- Functional Foods and Nutraceutical History NewDocumento22 páginasFunctional Foods and Nutraceutical History NewKinza SarfrazAinda não há avaliações
- Blue and Purple Mental Health Modern User Information BrochureDocumento1 páginaBlue and Purple Mental Health Modern User Information BrochureJohn Carl B. BungarAinda não há avaliações
- Pathfit 2: Exercise and Fitness GuidelinesDocumento11 páginasPathfit 2: Exercise and Fitness GuidelinesKeen Jude CaminosAinda não há avaliações
- Pathfit 1Documento15 páginasPathfit 1Keziah Bless Palma SalvadorAinda não há avaliações
- Stunting Pada Balita Dipengaruhi KesehatDocumento6 páginasStunting Pada Balita Dipengaruhi KesehatSara TonapaAinda não há avaliações
- Module 21: Health and Nutrition in A Child's DevelopmentDocumento10 páginasModule 21: Health and Nutrition in A Child's DevelopmentŞterbeţ RuxandraAinda não há avaliações
- Homework 2 Unit 1Documento5 páginasHomework 2 Unit 1David MayAinda não há avaliações
- ConditionalDocumento25 páginasConditionalAtziri García VélezAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Fitness and Gymnastics: Asian Development Foundation College P. Burgos St. Tacloban, CityDocumento6 páginasPhysical Fitness and Gymnastics: Asian Development Foundation College P. Burgos St. Tacloban, CityJessa Moster0% (1)
- Nutritional Status-Consolidated-2021-2022Documento1 páginaNutritional Status-Consolidated-2021-2022Laarni Kiamco Ortiz EpanAinda não há avaliações
- Austin and Seebohar - Performance Nutrition. Nutrient TimingDocumento200 páginasAustin and Seebohar - Performance Nutrition. Nutrient Timingmax7booxAinda não há avaliações
- Maps ProgramsDocumento1 páginaMaps Programssergio viquez50% (4)
- Ganesh BeediDocumento2 páginasGanesh BeediAnkitTiwariAinda não há avaliações
- PE - MODULE-3 - QTR 1 YeahDocumento14 páginasPE - MODULE-3 - QTR 1 YeahJunjun AfableAinda não há avaliações
- MilletsDocumento5 páginasMilletsTanish GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- PDFDocumento6 páginasPDFAhmad Arbi AninditoAinda não há avaliações