Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Disease Summary Sheet
Enviado por
robgardner1Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Disease Summary Sheet
Enviado por
robgardner1Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
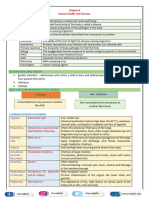
Biology Summary Sheet:
Disease
Health is a state of physical, mental and social well Disease is a departure from good health. A
being. Free from disease and infirmity, balanced diet malfunction in the body or mind which causes
and suitably housed with proper sanitation. physical or mental symptoms. Impairs the normal
functioning of an organism
An infectious disease is a disease caused by living
organisms and can be passed from individual to
individual. Eg- Malaria, HIV and TB
A pathogen is an organism which causes damage to A parasite is an organism which lives in or on
another organism it infects. Live by taking nutrition another living organism. It gets nutrition from the
from their host and in the process cause damage. host and benefits at the expense of the host.
Bacteria, Fungi and Viruses are pathogens. Tapeworms and Head Lice are parasites.
Bacteria: Prokaryote, reproduce rapidly, cause disease by damaging
cells or releasing waste which is toxic.
Eg. Cholera (Vibrio Cholerae), TB (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis)
Fungi: Lives in the skin. Release reproductive hyphae which grow on
surface of skin and release spores. Cause rash and irritation.
Eg.Athletes foot & Ringworm (Tinea)
Viruses: Invade cells. Take over genetic machinery and organelles. Cause
cell to manufacture copies. Host cell bursts releasing Viruses.
Eg.Influenza, HIV/AIDS
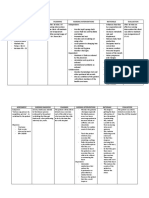
Malaria (parasite)
• Caused by a single celled eukaryotic parasite called plasmodium.
• Transmitted by Female Anopheles Mosquitoes. They carry the disease but donʼt cause it (called Vectors)
• Feed on blood of infected person - suck up parasite gametes.
• Zygotes develop in mosquito stomach- infective stages move to salivary glands.
• Mosquito bites another person - injects a little saliva.
• Plasmodium infects liver and multiply before passing into blood again.
• Infect red blood cells.
• Also passed on by unhygienic medical practices, placenta from mother to child, unscreened blood transfusions.
HIV/AIDS (Virus)
• Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) enters body.
• Attacks and destroys T helper cells in the immune system - cells which normally help prevent infection.
• HIV leads to Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome - Immune system deteriorates and fails due to loss of WBCs.
• Left vulnerable to pathogens which may enter body - may contract a range of opportunistic infections.
• These diseases are what kills AIDS suffers.
• Passed on in a number of ways: Exchange of bodily fluids, Unprotected sexual intercourse, unscreened blood
transfusions, unsterilised surgical equipment, sharing needles, across placenta (mother to child), Breast feeding.
Tuberculosis (Bacteria)
• Lung disease caused by bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• Spread by droplet infection - When an infected person coughs/sneezes etc, tiny droplets of saliva and mucus are
thrown out. Some of these droplets will contain the bacteria.
• Another person may inhale these droplets and so the bacteria is now inside their bodies too.
• Many people with TB donʼt show symptoms. But if they are weakened by another disease or malnutrition, the
infection can become active. Theyʼll show the symptoms and be able to pass on the bacteria.
• Usually takes close prolonged contact with an infected person to contract TB.
• Contraction is made more likely by: overcrowding, poor ventilation, poor health, poor diet, homelessness.
Você também pode gostar
- Alwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 10. Diseases and Immunity NotesDocumento35 páginasAlwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 10. Diseases and Immunity NotesMohammed HelmyAinda não há avaliações
- Microorganisms Lesson - 3Documento28 páginasMicroorganisms Lesson - 3aishaAinda não há avaliações
- Summary Science Unit 5, Lesson 1Documento3 páginasSummary Science Unit 5, Lesson 1Yohana ChuaAinda não há avaliações
- Why Do We Fall Ill - Part IiDocumento12 páginasWhy Do We Fall Ill - Part IiChhaya GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Bio HazardsDocumento11 páginasBio HazardsMahaprasad RathAinda não há avaliações
- Bio HazardsDocumento11 páginasBio HazardsMahaprasad RathAinda não há avaliações
- Disease and Its Impact On HumansDocumento21 páginasDisease and Its Impact On HumansJodell CampbellAinda não há avaliações
- Why Do We Fall Ill?Documento10 páginasWhy Do We Fall Ill?Ninja NinjaAinda não há avaliações
- Reasons For Falling IllDocumento22 páginasReasons For Falling IllNarayanaAinda não há avaliações
- Infection and Infectious Process Power PointDocumento44 páginasInfection and Infectious Process Power PointNitesh BhuraAinda não há avaliações
- Roos Obs Lesson #12 2022 2Documento41 páginasRoos Obs Lesson #12 2022 2JIMENA MAGALY JARAMILLO CORDOVAAinda não há avaliações
- HSBDocumento4 páginasHSBCarlos WebsterAinda não há avaliações
- Infection and Infectious ProcessDocumento44 páginasInfection and Infectious Processpandey omkarAinda não há avaliações
- Microorganisms: What Is A Disease?Documento8 páginasMicroorganisms: What Is A Disease?Rosa -Ainda não há avaliações
- Why Do We Fall IllDocumento6 páginasWhy Do We Fall IllMonika Mehan100% (10)
- Infection & Disease: Gcse BiologyDocumento39 páginasInfection & Disease: Gcse BiologyMaryam NaeemAinda não há avaliações
- Bacteria and Viruses PowerPointDocumento43 páginasBacteria and Viruses PowerPointGastonMuñozAzulGmgAinda não há avaliações
- Class 9 - How Do We Fall Ill - ScienceDocumento9 páginasClass 9 - How Do We Fall Ill - Scienceamir anwarAinda não há avaliações
- II ME NRP B SS 26. Human Health and DiseaseDocumento9 páginasII ME NRP B SS 26. Human Health and DiseaseAmit RavindhraAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 30Documento42 páginasChapter 30Konishko Dey100% (1)
- SFH - Module 5Documento4 páginasSFH - Module 5Vishal KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 Why Do We Fall IllDocumento43 páginasGrade 9 Why Do We Fall IllMehala Sri AurobindoAinda não há avaliações
- Infection: Meenal Jain MPT (Ortho and Manual)Documento18 páginasInfection: Meenal Jain MPT (Ortho and Manual)Rahul YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Why Do We Fall Ill NotesDocumento6 páginasWhy Do We Fall Ill NotessrianshAinda não há avaliações
- The Big Book of Infectious Disease Trivia: Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about the World's Worst Pandemics, Epidemics and DiseasesNo EverandThe Big Book of Infectious Disease Trivia: Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about the World's Worst Pandemics, Epidemics and DiseasesAinda não há avaliações
- Immune System CombinedDocumento26 páginasImmune System Combinedlyndabravo27Ainda não há avaliações
- Infection and Its Mode of TransmissionDocumento33 páginasInfection and Its Mode of TransmissionAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- 12 Biology Notes Ch08 Human Health and DiseaseDocumento4 páginas12 Biology Notes Ch08 Human Health and DiseaseWali Pramod100% (1)
- TP 1Documento8 páginasTP 1nitesh tirkeyAinda não há avaliações
- BIO 156 Chapter 15 Powerpoint PP07Documento26 páginasBIO 156 Chapter 15 Powerpoint PP07DrPearcyAinda não há avaliações
- Cause of DiseaseDocumento29 páginasCause of DiseaseTariku olanaAinda não há avaliações
- Disease NotesDocumento7 páginasDisease NotesMaira CanashinAinda não há avaliações
- Mapeh ReviewerDocumento12 páginasMapeh ReviewerShane Marie TabulaAinda não há avaliações
- IX Bio Ch4 Ill KeylearningsDocumento4 páginasIX Bio Ch4 Ill KeylearningsPriya DharshniniAinda não há avaliações
- What Are Pathogens?: VirusesDocumento6 páginasWhat Are Pathogens?: VirusesAqiba Tus Sahar100% (1)
- Notes of CH 13 Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9Th Science: Topics in The ChapterDocumento7 páginasNotes of CH 13 Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9Th Science: Topics in The ChaptermallikaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-8 Human Health and DiseasesDocumento10 páginasChapter-8 Human Health and DiseasesbpmbhamoraAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Ged 104 Global Migration BDocumento16 páginas10 Ged 104 Global Migration Brommel benamirAinda não há avaliações
- Health, Common Diseases in Human and Immunity PYQ Part 1Documento33 páginasHealth, Common Diseases in Human and Immunity PYQ Part 1ANKITA GAYENAinda não há avaliações
- Why Do We Fall Ill 2Documento3 páginasWhy Do We Fall Ill 2Shreyashkar JhaAinda não há avaliações
- HIV - AIDS - Training ModulesDocumento193 páginasHIV - AIDS - Training ModulesJohn Chezter V. CarlitAinda não há avaliações
- Diseases Caused by PathogensDocumento2 páginasDiseases Caused by PathogensbrajanosmaniAinda não há avaliações
- INFECTION AND INFECTIOUS PROCESS Lecture 3Documento28 páginasINFECTION AND INFECTIOUS PROCESS Lecture 3Hassan Kafi AliAinda não há avaliações
- 65 Topper 21 101 1 1 9 Why Do We Fall Ill Up201506181308 1434613126 7974Documento5 páginas65 Topper 21 101 1 1 9 Why Do We Fall Ill Up201506181308 1434613126 7974MUZEER PASHAAinda não há avaliações
- Health and DiseaseDocumento3 páginasHealth and DiseaseMehbub LaskarAinda não há avaliações
- HealthDocumento10 páginasHealthAthul ShajiAinda não há avaliações
- Human Health and DiseaseDocumento54 páginasHuman Health and DiseaseTirth TupeAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 12. INFECTIOUS DISEASES NotesDocumento22 páginasUNIT 12. INFECTIOUS DISEASES NotescyumadripAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Notes-Why Do We Fall IllDocumento3 páginas2nd Notes-Why Do We Fall IllLAKSH MITTALAinda não há avaliações
- Emerging Re-Emerging Infectious DiseaseDocumento57 páginasEmerging Re-Emerging Infectious DiseaseshaheenamasoodigmailcomAinda não há avaliações
- Final Hand in 1Documento14 páginasFinal Hand in 1lauraAinda não há avaliações
- Emerging Re-Emerging Infectious Disease 2022Documento57 páginasEmerging Re-Emerging Infectious Disease 2022marioAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 01: Modern Technologies That Help in The Control of DiseasesDocumento17 páginasLesson 01: Modern Technologies That Help in The Control of Diseasesjayar0824Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Infectious Diseases Lec1 2024Documento30 páginasIntroduction To Infectious Diseases Lec1 2024Dictor Omar Botan kheyreAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter10 Pathogens and ImmunityDocumento22 páginasChapter10 Pathogens and ImmunityHiba MoussaliAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter10 Pathogens and ImmunityDocumento22 páginasChapter10 Pathogens and ImmunityHiba MoussaliAinda não há avaliações
- Health and DiseaseDocumento1 páginaHealth and DiseaseKaranGargAinda não há avaliações
- Summary Sheet - Food TestsDocumento1 páginaSummary Sheet - Food Testsrobgardner1Ainda não há avaliações
- Summary Sheet - Cell MembranesDocumento1 páginaSummary Sheet - Cell Membranesrobgardner1Ainda não há avaliações
- Exchange Surfaces Summary SheetDocumento1 páginaExchange Surfaces Summary Sheetrobgardner1Ainda não há avaliações
- Breathing Summary SheetDocumento1 páginaBreathing Summary Sheetrobgardner1Ainda não há avaliações
- Biological Molecules - SugarsDocumento1 páginaBiological Molecules - Sugarsrobgardner1Ainda não há avaliações
- Biological Molecules - ProteinsDocumento1 páginaBiological Molecules - Proteinsrobgardner1Ainda não há avaliações
- Pre and Post Questionnaire MALARIADocumento4 páginasPre and Post Questionnaire MALARIANani Hardianti100% (1)
- Guideline On Provisional Certifiaction As Primary Care Provider For FCM ResidentsDocumento2 páginasGuideline On Provisional Certifiaction As Primary Care Provider For FCM ResidentsJames Lagamayo JavierAinda não há avaliações
- Health Care Delivery System 1Documento21 páginasHealth Care Delivery System 1Carson BirthAinda não há avaliações
- Afalanga CVDocumento17 páginasAfalanga CVBagasAinda não há avaliações
- Zhang Et Al., 2020Documento2 páginasZhang Et Al., 2020camil fernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Translation of Evidence Into Nursing PracticeDocumento8 páginasTranslation of Evidence Into Nursing PracticeNica C. MatsusakiAinda não há avaliações
- My New ThesisDocumento7 páginasMy New ThesisAlla Yeswanth Dilip KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Related ProblemsDocumento25 páginasDrug Related ProblemsChristine GanAinda não há avaliações
- NCP of Fever and HypertensionDocumento2 páginasNCP of Fever and HypertensionDayan CabrigaAinda não há avaliações
- Trametes Versicolor (Turkey Tail) For Breast and Other CancersDocumento3 páginasTrametes Versicolor (Turkey Tail) For Breast and Other Cancerssuperdave147Ainda não há avaliações
- Anees, Prijecth SjebevwhDocumento3 páginasAnees, Prijecth SjebevwhAkAinda não há avaliações
- Hospital Case Study FlexsimDocumento2 páginasHospital Case Study FlexsimMano KanthanathanAinda não há avaliações
- Prevalence and Recurrence Rate of Perianal Abscess - A Population-Based Study, Sweden 1997 - 2009Documento5 páginasPrevalence and Recurrence Rate of Perianal Abscess - A Population-Based Study, Sweden 1997 - 2009Ridha Aswina DalimuntheAinda não há avaliações
- Tri Immunophasic Periodontal TherapyDocumento9 páginasTri Immunophasic Periodontal TherapySireesha SadasivanAinda não há avaliações
- 1975 Jan-Feb #62Documento28 páginas1975 Jan-Feb #62Merlin ChowkwanyunAinda não há avaliações
- Research ArticleDocumento9 páginasResearch ArticlebejarhasanAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Glucose MonitoringDocumento4 páginasBlood Glucose MonitoringAman ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Hunting For Disease XDocumento9 páginasHunting For Disease XPeter GoodsallAinda não há avaliações
- 2009-2010 Annual ReportDocumento20 páginas2009-2010 Annual ReportgenesisworldmissionAinda não há avaliações
- Major Internship DTR SeptoctoberDocumento1 páginaMajor Internship DTR SeptoctoberGeraldineMoletaGabutinAinda não há avaliações
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocumento7 páginasPostpartum HemorrhageRivano Frits Henry PandalekeAinda não há avaliações
- CER77 KneePain FinalReport 20121015 PDFDocumento655 páginasCER77 KneePain FinalReport 20121015 PDFIdaamsiyati0% (1)
- Birth Defects: Genetic CounselorDocumento4 páginasBirth Defects: Genetic CounselorTessa Safitri KotoAinda não há avaliações
- Annotated Bibliography and SynthesisDocumento6 páginasAnnotated Bibliography and SynthesismperezveAinda não há avaliações
- Reading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdDocumento3 páginasReading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdPalupi Salwa BerliantiAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Mental Disorder: Presented By: Priyanka Kumari M.Sc. NursingDocumento50 páginasOrganic Mental Disorder: Presented By: Priyanka Kumari M.Sc. NursingHardeep KaurAinda não há avaliações
- Suspected Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting Form: CdscoDocumento2 páginasSuspected Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting Form: CdscoNaveen Kumar G TAinda não há avaliações
- A Carbohydrate-Restrictive Strategy Is Safer and As Efficient As Intensive Insulin Therapy in Critically Ill PatientsDocumento6 páginasA Carbohydrate-Restrictive Strategy Is Safer and As Efficient As Intensive Insulin Therapy in Critically Ill PatientsTeresaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Abuse in PregnancyDocumento91 páginasDrug Abuse in PregnancyCrystal Gayle Nario Sabado100% (1)
- 2005 PDFDocumento436 páginas2005 PDFAbdulazizAinda não há avaliações