Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Case: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing Inference
Enviado por
Lovelyn GanirTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Case: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing Inference
Enviado por
Lovelyn GanirDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
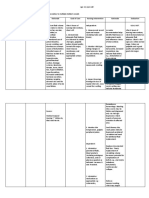
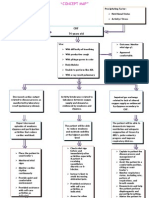
CASE: LIVER CIRRHOSIS
ASSESSMENT:
Subjective: “Wala akong ganang kumain” as verbalized by the patient.
Objective:
Weak in appearance
Refusal to eat
Weight loss
Low serum protein levels
NURSING DIAGNOSIS:
Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements, related to anorexia and
possible alcohol abuse manifested by weight loss and low serum protein levels.
NURSING INFERENCE:
Cirrhosis of the liver is a chronic disease that causes cell destruction and fibrosis
(scarring) of hepatic tissues. Fibrosis alters normal liver structure and vasculature,
impairing blood and lymph flow and resulting in hepatic insufficiency and hypertension
in the portal vein. Complications include hyponatremia, water retention, bleeding
esophageal varices, coagulopathy, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and hepatic
encephalopathy.
NURSING GOAL:
After of rendering nursing intervention, the patient will gain 1 lb (0.45 kg) per
week without evidence of increased fluid retention and serum albumin levels will return
to normal range.
NURSING INTERVENTION RATIONALE
1. Assist in oral hygiene before meals. A clean mouth enhances appetite.
2. Discuss eating habits including food To appeal the client likes and
preferences. dislikes.
3. Serve favorite foods that are not To stimulate the appetite.
contraindicated.
4. Prevent or minimize unpleasant May have negative effect on
odors during meal time. appetite.
5. Serve foods that are attractive and To stimulate the appetite.
palatable.
6. Recommend small, frequent meals. Poor tolerance to larger meals may
be due to increased intra abdominal
pressure/ascites.
7. Restrict intake of caffeine, gas- Aids in reducing gastric irritation
producing or spicy and excessively and abdominal discomfort that may
hot or cold foods. impair oral intake/digestion.
8. Provide assistance with activities as Conserving energy reduces
needed. Promote undisturbed rest metabolic demands on the liver and
periods, especially before meals. promotes cellular regeneration.
EVALUATION:
After of rendering nursing intervention, the patient will gain 1 lb (0.45 kg) per
week without evidence of increased fluid retention and serum albumin levels will return
to normal range.
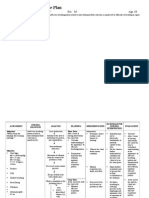
CASE: LIVER CIRRHOSIS
ASSESSMENT:
Subjective: “I feel that my tummy is getting bigger” as verbalized by the patient.
Objective:
Weight gain
Altered electrolyte levels
Edema
V/S taken as follows:
T: 37.0 °C
P: 92 bpm
R: 20 cpm
BP: 120/80 mmHg
NUSING DIAGNOSIS:
Excess fluid volume related to electrolyte imbalance and hypoalbuminemia as
manifested by ascites and peripheral edema.
NURSING INFERENCE:
Chronic liver disease develops cardiovascular abnormalities due to an increased
cardiac output and decreased peripheral vascular resistance, possibly resulting from the
release of vasodilators.
NURSING GOAL:
After 3 days of applying appropriate nursing interventions, the patient`s
abdominal girth will decrease by 1 to 2 cm per day and peripheral edema will decrease.
NURSING INTERVENTION RATIONALE
1. Measure intake and output, weight Reflects circulating volume status.
daily and note weight gain more Positive balance/weight gain after
than 0.5 kg/day. reflects continuing fluid retention.
2. Restrict sodium and fluids as Sodium may be restricted to
ordered. minimize fluid retention in
extravascular spaces. Fluid
restriction may be necessary to
prevent dilutional hyponatremia.
3. Monitor blood pressure. BP elevation usually associated
with fluid volume excess but may
not occur because of fluid shifts out
of the vascular space.
4. Compare current weight with To evaluate degree of excess.
admission and/or previously stated
weight.
5. Measure abdominal girth for To evaluate severity of fluid
changes that may indicate retention/edema.
increasing fluid retention/edema.
6. Weigh daily or on a regular Provides comparative baseline.
schedule.
7. Encourage bed rest when ascites is May promote recumbency-induced
present. diuresis.
8. Administer medications as ordered To control edema and ascites.
such as diuretics.
9. Monitor electrolytes. To correct further imbalances.
10. Assist with Paracentesis procedure. Done to remove ascites fluid.
EVALUATION:
After 3 days of applying appropriate nursing interventions, the patient`s
abdominal girth decreased by 1 to 2 cm per day and peripheral edema decreased. The
goal was completely met.
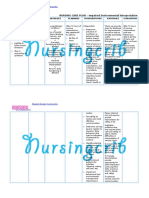
CASE: LIVER CIRRHOSIS
ASSESSMENT:
Subjective: “Ina-antok ako palagi, hindi ako makapag-isip ng maayos” as
verbalized by the patient.
Objective:
Changes of the behavior
Asterexis
Impaired thinking
Lethargy
NURSING DIAGNOSIS:
Disturbed thought processes, related to effects of high ammonia levels as
manifested by lethargy.
NURSING INFERENCE:
Cirrhosis of the liver is a chronic disease that causes cell destruction and fibrosis
(scarring) of hepatic tissues. Fibrosis alters normal liver structure and vasculature,
impairing blood and lymph flow and resulting in hepatic insufficiency and hypertension
in the portal vein. Complications include hyponatremia, water retention, bleeding
esophageal varices, coagulopathy, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and hepatic
encephalopathy.
NURSING GOAL:
After 8-10 hours of rendering nursing intervention, the patient will be alert and
oriented and serum ammonia levels are within normal range.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE
1. Restrict dietary protein as Reduces source of ammonia
prescribed for transient period. (protein foods).
2. Give frequent, small feedings of Promotes consumption of adequate
carbohydrates. carbohydrates for energy
requirements and spares protein
from breakdown for energy.
3. Protect from infection. Minimizes risk for further increase in
metabolic requirements.
4. Keep environment warm and draft- Minimizes shivering, which would
free. increase metabolic requirements.
5. Awaken at intervals (every 2-4 h) to Provides stimulation to the patient
assess cognitive status. and opportunity for observing the
patient`s level of consciousness.
6. Encourage patient and family to Promoting activities such as
participate in therapeutic strategies listening to music, relaxation
to enhance coping with episodes of techniques or preillness coping
mental deterioration. strategies can reduce anxiety.
7. Encourage patient and family to Actively listening demonstrates
discuss feeling of fear, caring and concern.
powerlessness or emotional
distress related to patient`s mental
deterioration.
EVALUATION:
After 8 hours of rendering nursing intervention, the patient will be alert and
oriented and serum ammonia levels are within normal range.
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION:
Liver biopsy – detects destruction and fibrosis of hepatic tissue.
Liver scan – shows abdominal thickening and a liver mass.
CT scan – determines the size of the liver and its irregular nodular surface.
Esophagoscopy – to determine esophageal varices.
Paracentesis – to examine ascetic fluid for cell, protein, and bacterial counts.
PTC – differentiates extrahepatic from intrahepatic obstructive jaundice.
Laparoscopy and liver biopsy – permit direct visualization of the liver.
Serum liver function test – results are elevated
MEDICATIONS:
1)Lactulose.
2) Spironolactone for patients with ascites.
3) Lasix.
Você também pode gostar
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocumento7 páginasNCP Liver CirrhosisIris Jimenez-BuanAinda não há avaliações
- Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento1 páginaDeficient Fluid VolumeSheila ErpeloAinda não há avaliações
- Liver NCPDocumento5 páginasLiver NCPMerrill HansAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocumento3 páginasNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- NCPDocumento3 páginasNCPJezza RequilmeAinda não há avaliações
- NCP HemothoraxDocumento3 páginasNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Aminogen Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasAminogen Drug Studymilesmin100% (1)
- Critical Thinking ExerciseDocumento1 páginaCritical Thinking ExerciseMaye ArugayAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveDocumento3 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveMaverick LimAinda não há avaliações
- NCP HemoDocumento2 páginasNCP HemoJigs HechAinda não há avaliações
- Daily NCPDocumento5 páginasDaily NCPKuennie SabalAinda não há avaliações
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocumento3 páginasSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocumento2 páginasRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeDocumento4 páginasNCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeryanAinda não há avaliações
- Gender Dysphoria NCPDocumento1 páginaGender Dysphoria NCPSeann LorescoAinda não há avaliações
- Body Weakness NCPDocumento1 páginaBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassRheegell Ellar-Fuertes100% (3)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasNCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionYasminGianneDeOcampoBarizoAinda não há avaliações
- BSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitDocumento12 páginasBSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitJane DuropanAinda não há avaliações
- NCP FVDDocumento2 páginasNCP FVDMarlon AnryAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Diagnosis: Acute ConfusionDocumento4 páginasNursing Diagnosis: Acute Confusionasmika danaAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento2 páginasImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- NCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDocumento5 páginasNCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirementsrusnani100% (1)
- NCPDocumento4 páginasNCPDaniel Garraton0% (1)
- NCP About Fluid IntakeDocumento5 páginasNCP About Fluid IntakeWild Rose100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP For Liver CirrhosisDocumento25 páginasNCP For Liver CirrhosisWendy Escalante100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaDocumento2 páginasNursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaAbdallah AlasalAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotDocumento3 páginasNCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotMikko Enoc100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento13 páginasNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocumento4 páginasNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- NCP PancreatitisDocumento2 páginasNCP PancreatitisJeanelle Generoso100% (1)
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Documento2 páginasCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento11 páginasNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan ADocumento6 páginasNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattAinda não há avaliações
- Deficit)Documento2 páginasDeficit)Lee DeeAinda não há avaliações
- NCP DMDocumento6 páginasNCP DMstara123Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPderic100% (2)
- Concept Map - Abby !Documento2 páginasConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocumento3 páginasLiver Cirrhosis NCPSharmaine MadlaAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocumento3 páginasFluid Volume Excess NCPAfia TawiahAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasNursing Diagnosis Rationale Interventions Rationale EvaluationJobie CasipongAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 páginasNCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceAngelyn ArdinesAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocumento5 páginasNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- NCP AneurysmDocumento4 páginasNCP AneurysmJanielle Christine Monsalud100% (1)
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocumento2 páginasNCP Liver Cirrhosismarlx5100% (3)
- NCP For Ruptured AppendicitisDocumento2 páginasNCP For Ruptured AppendicitisJansen Arquilita RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- NCP 2Documento2 páginasNCP 2Neil Abraham Mendoza Lalap100% (2)
- NCP 2 Addison's DiseaseDocumento4 páginasNCP 2 Addison's DiseaseRenee RoSeAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For SVTDocumento6 páginasNCP For SVTRen VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDocumento1 páginaActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 páginasRisk For Decreased Cardiac OutputSid Artemis FriasAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento5 páginasRisk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionElle Oranza100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: DiagnosisDocumento11 páginasNursing Care Plan: DiagnosisCharmaine100% (1)
- Aguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningDocumento9 páginasAguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningSophia Kaye AguinaldoAinda não há avaliações
- المستندDocumento18 páginasالمستندAndrew MidaAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocumento23 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentWendy EscalanteAinda não há avaliações
- Liver Cirrhosis Case PresDocumento77 páginasLiver Cirrhosis Case Presmarlx580% (5)
- Case 034: ConstipationDocumento7 páginasCase 034: ConstipationZauza100% (1)
- BloomDocumento17 páginasBloomLovelyn GanirAinda não há avaliações
- Formulas On Drug CalculationsDocumento2 páginasFormulas On Drug CalculationsLovelyn GanirAinda não há avaliações
- Bryan Miles - Integration Met PDFDocumento10 páginasBryan Miles - Integration Met PDFjenjavierAinda não há avaliações
- Intake and Output MonitoringDocumento3 páginasIntake and Output MonitoringMarco Alabanza100% (2)
- Pest ManagementDocumento5 páginasPest ManagementLovelyn GanirAinda não há avaliações
- Intake and Output MonitoringDocumento3 páginasIntake and Output MonitoringMarco Alabanza100% (2)
- Leopold' ManeuversDocumento3 páginasLeopold' Maneuversjava_biscocho122995% (22)
- Logic/A Brief Introduction: The Categorical SyllogismDocumento4 páginasLogic/A Brief Introduction: The Categorical SyllogismLovelyn GanirAinda não há avaliações
- Liver CirrhosisDocumento7 páginasLiver CirrhosisLovelyn GanirAinda não há avaliações
- Top Richest Person in The World 2010Documento7 páginasTop Richest Person in The World 2010Lovelyn GanirAinda não há avaliações
- 1.9 Drug Abuse Prevention and EducationDocumento8 páginas1.9 Drug Abuse Prevention and EducationRiamie Cortes100% (1)
- Microbiology 1.6 Gram Positive Bacilli - Dr. Sia-CuncoDocumento7 páginasMicrobiology 1.6 Gram Positive Bacilli - Dr. Sia-CuncoRyn ShadowAinda não há avaliações
- 2023 Surgery Viva ReleaseDocumento5 páginas2023 Surgery Viva ReleaseduncanAinda não há avaliações
- HeadachehelpsheetDocumento1 páginaHeadachehelpsheetapi-219567017Ainda não há avaliações
- Huether: Understanding Pathophysiology, 6th EditionDocumento4 páginasHuether: Understanding Pathophysiology, 6th EditionTecsh DeckgirlAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory MedicationsDocumento18 páginasRespiratory Medicationsapi-338095748Ainda não há avaliações
- Phosphate BinderDocumento51 páginasPhosphate BinderbedestySAinda não há avaliações
- 112-2 - Heather Bruce - Chapter 3 of Cold DamagesDocumento14 páginas112-2 - Heather Bruce - Chapter 3 of Cold Damagesmudrahora100% (1)
- Hanks, J. R., & Hanks, L. M. (1948) - The Physically Handicapped in Certain Non-Occidental Societies PDFDocumento10 páginasHanks, J. R., & Hanks, L. M. (1948) - The Physically Handicapped in Certain Non-Occidental Societies PDFjuanitoendaraAinda não há avaliações
- Laporan Asuhan Keperawatan Bahasa InggrisDocumento8 páginasLaporan Asuhan Keperawatan Bahasa InggrisBagus Wijanarko100% (1)
- Symptoms of Low PotassiumDocumento3 páginasSymptoms of Low PotassiumCharlene Mae Calanoy100% (1)
- California Gold Rush TextDocumento105 páginasCalifornia Gold Rush TexttombrodbeckAinda não há avaliações
- Thesis ProposalDocumento3 páginasThesis ProposalMelissa SerranoAinda não há avaliações
- Health and MedicineDocumento2 páginasHealth and MedicineLaura Marcela Cristancho TovarAinda não há avaliações
- MCRP 3-35.2A Small Unit Leader's Guide To Mountain Operations (Jun 2000)Documento95 páginasMCRP 3-35.2A Small Unit Leader's Guide To Mountain Operations (Jun 2000)Sven WeißenbergerAinda não há avaliações
- Unit12 English 2Documento11 páginasUnit12 English 2Nana ArangoAinda não há avaliações
- 1IPR F300 RE V12.0 MSiteDocumento6 páginas1IPR F300 RE V12.0 MSiteSANDIP N KAPADIA100% (1)
- Compartment SyndromeDocumento15 páginasCompartment SyndromeBoneMonkey888100% (1)
- Impact of Clinical Appraisal and Therapeutic Talk On OCD Patients: A Case StudyDocumento5 páginasImpact of Clinical Appraisal and Therapeutic Talk On OCD Patients: A Case StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- What Is LordosisDocumento10 páginasWhat Is LordosisNisa ShaqiriAinda não há avaliações
- Spritual Health Life: 1. Gyan Mudra (Mudra of Knowledge)Documento10 páginasSpritual Health Life: 1. Gyan Mudra (Mudra of Knowledge)chachu123100% (2)
- Scrub TyphusDocumento4 páginasScrub TyphusVijaya Aditya TadepalliAinda não há avaliações
- Question Excerpt From 96Documento5 páginasQuestion Excerpt From 96Lorainne FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition Study GuideDocumento3 páginasNutrition Study GuidedianaAZPAinda não há avaliações
- Abdominal Compartment SyndromeDocumento24 páginasAbdominal Compartment SyndromePrateek Vaswani100% (1)
- Sea RemediesDocumento2 páginasSea Remedieskaravi schiniasAinda não há avaliações
- Dischage RevisionDocumento44 páginasDischage RevisionRaidis PangilinanAinda não há avaliações
- Medication - ALT-Template Polythene GlycolDocumento1 páginaMedication - ALT-Template Polythene GlycolNancyAmissahAinda não há avaliações
- Homoeopathy For Every Home: Health Is Wealth Health For AllDocumento8 páginasHomoeopathy For Every Home: Health Is Wealth Health For AllSwetha YarlagaddaAinda não há avaliações
- Gedesnii TugjrelDocumento40 páginasGedesnii TugjrelSaibo BoldsaikhanAinda não há avaliações