Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Insulin algorithm for type 1 diabetes in children and adults
Enviado por
praful.mehta0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
123 visualizações1 páginaINSULIN ALGORITHM FOR TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS1 ABBREVIATIONS: Basal: Glargine or Detemir Bolus (Prandial): Reg: Regular Insulin (peak action 3-4 hrs) RAI: Rapid Acting Insulin = Aspart, Glulisine, or Lispro (peak action 1-1 1 / 2 hrs) TDI: Total daily insulin dosage in
Descrição original:
Título original
Treatment Algorithm for Type-1 Diabetes
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoINSULIN ALGORITHM FOR TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS1 ABBREVIATIONS: Basal: Glargine or Detemir Bolus (Prandial): Reg: Regular Insulin (peak action 3-4 hrs) RAI: Rapid Acting Insulin = Aspart, Glulisine, or Lispro (peak action 1-1 1 / 2 hrs) TDI: Total daily insulin dosage in
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
123 visualizações1 páginaInsulin algorithm for type 1 diabetes in children and adults
Enviado por
praful.mehtaINSULIN ALGORITHM FOR TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS1 ABBREVIATIONS: Basal: Glargine or Detemir Bolus (Prandial): Reg: Regular Insulin (peak action 3-4 hrs) RAI: Rapid Acting Insulin = Aspart, Glulisine, or Lispro (peak action 1-1 1 / 2 hrs) TDI: Total daily insulin dosage in
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
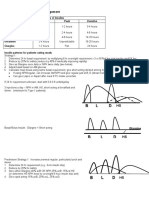
INSULIN ALGORITHM FOR TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS1
ABBREVIATIONS: Glycemic Goals2,3 Revised 1-27-10
Individualize goal based on
Basal: Glargine or Detemir patient risk factors
Bolus (Prandial): A1c 6% <7% <8%
Reg: Regular Insulin (peak action 3-4 hrs) FPG 110 120 140 mg/dL
RAI: Rapid Acting Insulin = Aspart, Glulisine, or 2h PP 130 180 180 mg/dL
Lispro (peak action 1-1 ½ hrs)
PPG: Post-Prandial Glucose
SMBG: Self-monitored blood glucose3
TDI: Total daily insulin dosage in units Intensive Insulin Therapy (IIT)
Physiologic Insulin - 1:1 basal:bolus ratio SQ
Basal: Glargine QD or Detemir QD-BID6,9
Split-Mix Insulin Therapies4 Bolus: RAI (or Reg) before each meal: If meal skipped, skip dose.
1. Two shots: NPH + Reg or RAI
2:1 ratio AM; 1:1 ratio PM Premeal insulin dose includes:
2. Three shots: AM: NPH + Reg or RAI 1. Insulin to cover carbohydrate ingested7; 1 unit RAI covers Pramlintide1,9
PM: Reg or RAI 500/TDI grams carbohydrate from meal Consider as
HS: NPH 2. Additional insulin to correct for high SMBG; 1 unit RAI lowers PG by adjunct therapy to
2/3 TDI ÷ as 2/3 AM NPH + 1/3 as Reg or RAI approximately 1800/TDI mg/dL. (Reg lowers PG by ~1500/TDI)
OR insulin in patients
1/3 TDI ÷ as ½ PM Reg or RAI + ½ NPH at HS
3. Two shots: Premix 3. Consider adjustment for exercise8 unable to stabilize
PPG.
2/3 AM + 1/3 PM
Total Daily Insulin5: 0.3-0.5 units/kg/day and titrate to glycemic
5
Total Daily Insulin : 0.3-0.5 units/kg/day, and titrate targets
to glycemic targets
See web site
Follow A1c Every 3-6 months and Adjust Regimen to Maintain Glycemic Targets (http://www.texasdiabetescouncil.org)
for latest version and disclaimer.
1
Consider referring all type 1 patients to pediatric/adult endocrinologist/comprehensive diabetes specialty team, and consider continuous glucose monitoring. If insulin
pump therapy is considered-refer to Certified Pump Trainer.
2
Intensify management if: Absent/stable cardiovascular disease, mild-moderate microvascular complications, intact hypoglycemia awareness, infrequent hypoglycemic episodes,
recently diagnosed diabetes. Less intensive management if: Evidence of advanced or poorly controlled cardiovascular and/or microvascular complications, hypoglycemia
unawareness, vulnerable patient (ie, impaired cognition, dementia, fall history). SEE “A1c Goal” treatment strategy for further explanation. A1c is referenced to a non-diabetic
range of 4-6% using a DCCT-based assay. ADA Clinical Practice Recommendations. Diabetes Care 2009;32(suppl 1):S19-20.
3
Modern glucose meters give values corrected to plasma glucose.
4
Most type 1 patients need IIT to attain glycemic targets; IIT may be by SQ multiple injection or by SQ continuous insulin pump.
5
Dosages may differ in children and adolescents.
6
Twice daily dosing may be required at low basal insulin doses.
7
Strongly recommend referral to Registered/Licensed Dietitian or Certified Diabetes Educator with experience in diabetes nutrition counseling.
8
Consider decreasing 1 unit for every 30 minutes of vigorous physical activity.
9
IMPORTANT: See package insert for dosing.
Você também pode gostar
- Type 1 Diabetes Treatment AlgorithmDocumento1 páginaType 1 Diabetes Treatment AlgorithmChristopher BeckerAinda não há avaliações
- Standards of Care 2021 Figure 9.2Documento2 páginasStandards of Care 2021 Figure 9.2Ariel GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- InsulinaDocumento1 páginaInsulinaRICARDO DEL ANGEL HERNANDEZAinda não há avaliações
- INSULINDocumento6 páginasINSULINmilaAinda não há avaliações
- Slide Clinical Use of Insulin Therapy (ADA)Documento36 páginasSlide Clinical Use of Insulin Therapy (ADA)Dian SobaAinda não há avaliações
- Fit-Diploma 3-2-2024Documento57 páginasFit-Diploma 3-2-2024light tweenAinda não há avaliações
- Insulin IssuesDocumento6 páginasInsulin Issuesdoctorzo0% (1)
- Simplify Insulin Therapy With IDegAsp Co-Formulation - 2022 UpdtDocumento21 páginasSimplify Insulin Therapy With IDegAsp Co-Formulation - 2022 UpdtTataAinda não há avaliações
- Basal Bolus InsulinDMT22009Documento92 páginasBasal Bolus InsulinDMT22009scribdAinda não há avaliações
- Insulin Initiation PPT - PPTX 2Documento53 páginasInsulin Initiation PPT - PPTX 2Meno Ali100% (1)
- Update Management DMDocumento27 páginasUpdate Management DMnando8396Ainda não há avaliações
- Thera L15 PracticalDocumento21 páginasThera L15 PracticalFatmaAinda não há avaliações
- RTD NovoMix 2017Documento56 páginasRTD NovoMix 2017bayu permasuthaAinda não há avaliações
- Insulin Initiation and MonitoringDocumento35 páginasInsulin Initiation and Monitoringeka prasepti darusmanAinda não há avaliações
- Dr.Rihab Pediatrics 02.Pediatric DM Part TwoDocumento7 páginasDr.Rihab Pediatrics 02.Pediatric DM Part TwoMujtaba JawadAinda não há avaliações
- How Early Should Basal Insulin Be Used in Management of T2DM-intention BaruDocumento36 páginasHow Early Should Basal Insulin Be Used in Management of T2DM-intention BaruRuri harmawantiAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer For Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocumento4 páginasReviewer For Nutrition and Diet TherapyDa MiAinda não há avaliações
- CCO Diabetes South Downloadable 2Documento43 páginasCCO Diabetes South Downloadable 2Carlos VásquezAinda não há avaliações
- Insulin Algorithm For Type 2 Diabetes in Children and AdultsDocumento6 páginasInsulin Algorithm For Type 2 Diabetes in Children and AdultsOlesiaAinda não há avaliações
- Glycemic ControlDocumento2 páginasGlycemic ControlHildaAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Pancreatitis: J. Urquiza Z. M.C. F.CDocumento42 páginasDiabetes Pancreatitis: J. Urquiza Z. M.C. F.CgianmarcoAinda não há avaliações
- DM OHA and InsulinDocumento33 páginasDM OHA and InsulinPraba NanthanAinda não há avaliações
- Interactive Patient Case Management #1Documento33 páginasInteractive Patient Case Management #1Luzman HizrianAinda não há avaliações
- Management of Diabetic Cats With Long Acting InsulinDocumento16 páginasManagement of Diabetic Cats With Long Acting Insulindia_dianneAinda não há avaliações
- Insulin Protocols for Diabetic PatientsDocumento16 páginasInsulin Protocols for Diabetic PatientsSitti Mardiya SariolAinda não há avaliações
- Insulin Case Studies AACE 5-20-05Documento56 páginasInsulin Case Studies AACE 5-20-05Leanne Shepherd100% (2)
- 6403 Advanced Insulin Management FinalDocumento3 páginas6403 Advanced Insulin Management FinalAmada Flores RubioAinda não há avaliações
- Glycemic ManagementDocumento39 páginasGlycemic ManagementZayar HmunAinda não há avaliações
- Avandia RosiglitazoneDocumento1 páginaAvandia RosiglitazoneCassieAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Pancreatitis: J. Urquiza Z. M.C. F.CDocumento36 páginasDiabetes Pancreatitis: J. Urquiza Z. M.C. F.CJuan Enrique EspinozaAinda não há avaliações
- Updated Diabetes Guidelines - DR NandaDocumento19 páginasUpdated Diabetes Guidelines - DR NandaMonish Sudhakar100% (1)
- DM GuideDocumento6 páginasDM GuideMaryNguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Underrecognized Cause of Cryptogenic CirrhosisDocumento6 páginasNonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Underrecognized Cause of Cryptogenic CirrhosisJulio AvalosAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 7 - Inpatient Management of Diabetes and HyperglycemiaDocumento6 páginasCHAPTER 7 - Inpatient Management of Diabetes and HyperglycemiaenesAinda não há avaliações
- Topic: DM Section: 4 Group NamesDocumento8 páginasTopic: DM Section: 4 Group NamesTurkish DizilerAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Mellitus: Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento58 páginasDiabetes Mellitus: Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentAgatha NightrayAinda não há avaliações
- Treating Diabetes: Dr. S. P. Mathew M. D. (Med) Ashok HospitalDocumento57 páginasTreating Diabetes: Dr. S. P. Mathew M. D. (Med) Ashok HospitalMathew S Peedikayil100% (1)
- Diabetes SobrebasalizaciónDocumento7 páginasDiabetes SobrebasalizaciónComisión Académica FCM - UNAHAinda não há avaliações
- The Role of Rapid Insulin Analogue in Diabetes Management Focused On Glulisine Clinical EvidenceDocumento34 páginasThe Role of Rapid Insulin Analogue in Diabetes Management Focused On Glulisine Clinical EvidenceAnonymous iIwZjFpbVAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Cheat SheetDocumento2 páginasDiabetes Cheat Sheetmanuel iglesiasAinda não há avaliações
- Penggunaan Insulin Pada Diabetes Tipe 2Documento47 páginasPenggunaan Insulin Pada Diabetes Tipe 2pebbyfebrianAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes-Oral Monotherapy and Combination TherapyDocumento18 páginasDiabetes-Oral Monotherapy and Combination TherapyBhoomi GoyaniAinda não há avaliações
- The Effect of Glimepiride On Glycemic Control and Fasting Insulin LevelsDocumento3 páginasThe Effect of Glimepiride On Glycemic Control and Fasting Insulin Levelszahrosofi ahmadahAinda não há avaliações
- 0003-1488-Javma 22 09 0402Documento9 páginas0003-1488-Javma 22 09 0402Vicentiu PredescuAinda não há avaliações
- 2011 - Practical Guide Insulin TherapyDocumento6 páginas2011 - Practical Guide Insulin Therapytheva_thy100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Diabetes Mellitus: Glucose RegulationDocumento33 páginasPharmacology of Diabetes Mellitus: Glucose RegulationAbdullah RawashdehAinda não há avaliações
- DM Medical Nutritional TherapyDocumento5 páginasDM Medical Nutritional TherapyNeil AlviarAinda não há avaliações
- Obesity Muhammad Fajri Labdul 821417146 C-S1 2017Documento20 páginasObesity Muhammad Fajri Labdul 821417146 C-S1 2017Putry ReginaAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Treatment: Dr. Chavan P.R. Pharm DDocumento73 páginasDiabetes Treatment: Dr. Chavan P.R. Pharm DAvel ChandAinda não há avaliações
- Skugor TreatmentofdiabetesmellitusDocumento5 páginasSkugor TreatmentofdiabetesmellitusyomiboyAinda não há avaliações
- The Essential Role of Insulin in Diabetes ManagementDocumento9 páginasThe Essential Role of Insulin in Diabetes ManagementAbdul SamadAinda não há avaliações
- Insulin GNTDocumento41 páginasInsulin GNTV Narayan Rao TummalaAinda não há avaliações
- The Dose. Proceedings of The American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine Forum, May 2006 Kentucky, USADocumento3 páginasThe Dose. Proceedings of The American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine Forum, May 2006 Kentucky, USADaniel KissAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition Risk Assessment and ManagementDocumento3 páginasNutrition Risk Assessment and ManagementSitty Aizah MangotaraAinda não há avaliações
- Adjustment: Allow Several Days Between Dose Titrations: Usual Maintenance Dose: 1-4 MGDocumento2 páginasAdjustment: Allow Several Days Between Dose Titrations: Usual Maintenance Dose: 1-4 MGYunita Cahya AwalyaniAinda não há avaliações
- GNUR 237 Nutrition Exam Study GuideDocumento17 páginasGNUR 237 Nutrition Exam Study GuideMeghan Elizabeth100% (1)
- GDM Screening Test and ManagementDocumento5 páginasGDM Screening Test and ManagementTan Yuet YangAinda não há avaliações
- Correcting A High Blood Glucose LevelDocumento5 páginasCorrecting A High Blood Glucose LevelAnnisa Fitri LidiaAinda não há avaliações
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocumento1 páginaNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsCassieAinda não há avaliações
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesNo EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- 5th Circuit Court of Appeals Petition For Review of Occupational Safety and Health Administration Emergency Temporary StandardDocumento22 páginas5th Circuit Court of Appeals Petition For Review of Occupational Safety and Health Administration Emergency Temporary StandardJillian SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Boron DeficiencyDocumento2 páginasBoron DeficiencyManu MandaAinda não há avaliações
- Heart Rate Analysis (R)Documento72 páginasHeart Rate Analysis (R)Raja LakshmiAinda não há avaliações
- Sex Linked Practice Problems TCDocumento17 páginasSex Linked Practice Problems TCanon_11091143Ainda não há avaliações
- Psik Soal UtsDocumento1 páginaPsik Soal UtsNaurahSalsabil / 20Ainda não há avaliações
- Label Nama Obat Di Rak ObatDocumento8 páginasLabel Nama Obat Di Rak ObatDyah SariAinda não há avaliações
- When I hear the noiseDocumento2 páginasWhen I hear the noiseh00nguy0n-18Ainda não há avaliações
- Duodenal Epithelial Polyps: A Clinicopathologic ReviewDocumento16 páginasDuodenal Epithelial Polyps: A Clinicopathologic ReviewsilvanaAinda não há avaliações
- Treating A Bartholins Cyst or Abscess Patient InformationDocumento6 páginasTreating A Bartholins Cyst or Abscess Patient InformationRezaFArthaAinda não há avaliações
- 2.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Part IIDocumento183 páginas2.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Part IIBharat ThapaAinda não há avaliações
- Essay and Outline FaiqaDocumento3 páginasEssay and Outline FaiqaFaiqa Himma EmaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Yr. 1 Microbiology. LECDocumento22 páginasYr. 1 Microbiology. LECrex367100% (1)
- Pathology Test LUMHSDocumento2 páginasPathology Test LUMHSDr-Irfan HabibAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy For A Pediatric Electrical BurnDocumento3 páginasHyperbaric Oxygen Therapy For A Pediatric Electrical Burnsarah iriamanaAinda não há avaliações
- BioPsych Lecture Notes CH 7Documento6 páginasBioPsych Lecture Notes CH 7Generic_Persona100% (1)
- Drug-Induced Blood Disorders: Aplastic Anemia and AgranulocytosisDocumento29 páginasDrug-Induced Blood Disorders: Aplastic Anemia and AgranulocytosispaymanmatinAinda não há avaliações
- Chelating Therapy: Azeem ImamDocumento14 páginasChelating Therapy: Azeem Imamazeem imamAinda não há avaliações
- Societe Belge de Biochimie Et de Biologie Moleculaire Belgische Vereniging Voor Biochemie en Moleculaire BiologieDocumento30 páginasSociete Belge de Biochimie Et de Biologie Moleculaire Belgische Vereniging Voor Biochemie en Moleculaire BiologieAmirAinda não há avaliações
- Hemoglobin (Mass - Volume) in BloodDocumento5 páginasHemoglobin (Mass - Volume) in BloodUci Rahmawati UtamiAinda não há avaliações
- CH 7 MseDocumento20 páginasCH 7 MseIyanna BaylonAinda não há avaliações
- First Aid - CPR - AED Participant's ManualDocumento196 páginasFirst Aid - CPR - AED Participant's Manualadamiam100% (2)
- IEN 420: Environmental & Safety Engineering Spring 2021-2022Documento34 páginasIEN 420: Environmental & Safety Engineering Spring 2021-2022Moh HAinda não há avaliações
- Durward CVVHDocumento10 páginasDurward CVVHblakewilAinda não há avaliações
- Nurs 501 Public Health Nursing IDocumento140 páginasNurs 501 Public Health Nursing Iprincesssilver419Ainda não há avaliações
- Rapid SurveyDocumento11 páginasRapid SurveyPeterson SihotangAinda não há avaliações
- Novel Alzheimer's Drug Targets Multiple PathwaysDocumento4 páginasNovel Alzheimer's Drug Targets Multiple PathwaysIndra HedarAinda não há avaliações
- Operative DentistryDocumento51 páginasOperative Dentistryqra_beliebersAinda não há avaliações
- Fallen Angels - Walter Dean MyersDocumento815 páginasFallen Angels - Walter Dean MyersTache_Georgescu60% (5)
- Manual On The Management of Brown Root Rot DiseaseDocumento43 páginasManual On The Management of Brown Root Rot DiseaseTang TreyAinda não há avaliações
- Management and prevention of head injuryDocumento6 páginasManagement and prevention of head injuryAndreas LaseAinda não há avaliações