Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
BE-I (SS) of Computer Science: Applied Mathematics - II
Enviado por
Vismay ParmarTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
BE-I (SS) of Computer Science: Applied Mathematics - II
Enviado por
Vismay ParmarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
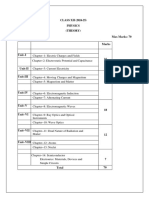
BE-I (SS) of Computer Science
Applied Mathematics II
1. Partial Derivatives Functions of two variables, Limits, continuity and Derivatives Eulers theorem, chain rule Implicit Functions, Differentials Applications of Partial Derivatives : Tangent plane and Normal line Maxima-Minima, Lagrangian Multipliers Jacobians Taylors Expansion Vector Calculus - Del Operator Gradient of scalar function Directional Derivatives Divergence and Curl of a vector field and its applications Laplace Transforms Laplace Transforms of different functions First Shifting Theorem Transform of a derivative Inverse Laplace Transform and its application: Solving ODE Analytical Solid Geometry Reorientation Curvilinear co-ordinates: Polar, Cylindrical & Spherical Cone, Cylinder, Conicoids, Surfaces and Solids of revolution Tangent Plane & Normal Lines to above surfaces (by calculus method) Tracing of Curves Cardioid, Limacon, Lemniscate, Archimedean Spiral and Rose Curve Matrices Revision, Rank of a matrix, Solution of homogeneous & non-homogeneous system of linear equations Eigen values and Eigenvectors of a matrix Caley-Hamilton theorem Special matrices, Hermitian, Skew-Hermitian, Orthogonal and Unitary matrices
2.
3.
4.
5. 6.
Reference Books
1. Calculus & Analytical Geometry by Thomas-Finney 2. Higher Engineering Mathematics by Dr. K. R. Kachot Vizzmay
3. Advanced Engineering Mathematics by Erwin Kreyszig 4. Analytical Solid Geometry by Shantinarayan
Engineering Mechanics
1. Coplanar Force Systems Coplanar forces Resultant of concurrent and non-concurrent forces Operations with couples Graphical methods Equilibrium of Forces Free body diagram Support reactions Equation of statics Graphical methods Forces in members of simple trusses Properties of Lines, Area and Solids Centroid of lines and plane figures Moment of inertia of plane figures Transfer theorem Product of inertia C.G. of rigid bodies Equilibrium on a rough inclined plane The wedge, the screw, the screw jack Simple lifting machines Power transmission in belt drives Gearings Train of wheels Epicyclic gearing Simple Stresses and Strains Hookes law Elastic limit Ultimate stress Factor of safety Lateral strain Poissons ratio Temperature stress Simple shear Proof test Elastic moduli relation Principal stresses
2.
3.
4.
5.
Vizzmay
Strain energy 6. Thin cylindrical and spherical shells Analysis and design 7. Riveted and welded joints Analysis and design 8. Determination of internal forces in beams and shafts Bending / Twisting moment diagram
Reference Books
1. Applied Mechanics by S. B. Junnarkar 2. Mechanics of Structure by H. J. Shah
Applied Physics II
Section I
Quantum Mechanics Review of Schrdinger Equation Step potential function Potential Barrier and Penetration Harmonic Oscillator Allowed and forbidden energy bands Krnig-Penney model The energy band and bond model Drift current Electron effective mass Concept of a hole K-space diagrams of Si and GaAs 2. Statistical Mechanics Statistical distributions (three different kinds) Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution Molecular energies in an ideal gas Bose-Einstein distribution Rayleigh-Jeans formula Plancks radiation law Specific heats of solids Fermi-Dirac distribution Free electrons in a metal The density of states Specific heat of electrons Thermionic emission Vizzmay 1.
The Schottky effect 3. Conductivity of Metals Ohms law and relaxation time of electrons Relaxation and collision time Mean free path Electron scattering and resistivity of metals Superconductivity (incl. BCS theory and cooper pairs) and applications 4. Semiconductors Mechanism of conduction in semiconductors The chemical bond in Si and Ge and its consequences The energy gap The conductivity of intrinsic semiconductors Carrier densities in n- and p-type semiconductors 5. Semiconductors Minority and majority carrier densities in semiconductors Drift current and diffusion current Continuity equation for minority charge carriers
Section II
6. Fiber Optics Principles of fiber Structure and classifications of optical fibers The numerical aperture Fiber optics communication system Advantage of fiber optics communication Applications and Uses 7. Electrostatics and Magnetostatics Polarization, Field of a polarized object Electric Displacement, Linear Dielectrics Vector Potential Field of a magnetized object Auxiliary Field H 8. Maxwells Equations Maxwells equations inside matter Boundary conditions Poyntings theorem Maxwells stress tensor Conservation of momentum 9. Electromagnetic Waves Monochromatic plane waves in vacuum Energy and momentum of electromagnetic waves Vizzmay
Propagation through linear media Electromagnetic waves in conductor The modified wave equation Monochromatic plane waves in conducting media 10. Electron Optics Motion in electric field Force acting on a charged particle The analogy between the motion of charged particle in electromagnetic fields and propagation of light beam in transparent media Centered electron systems The basic equation of electron optics for axially symmetric fields The Helmholtz-Lagrange equation The thin lens Electron multiplier 11. Motion in Magnetic Field Motion in uniform magnetic field Axially symmetric magnetic fields Short coil focusing The electron microscope Focusing in crossed electric and magnetic fields Strong focusing Mass spectroscopy and electromagnetic separation of isotopes
Reference Books
1. Electrical Engineering Materials by A. J. Dekker (Chap. 3, 4, 5) 2. Motion of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields: L. A. Artsimovich & S. Y. Lukyanov (Chap. 10, 11) 3. Concepts of Modern Physics by Arthur Beiser (Chap. 2) 4. Semiconductor Physics and Devices by D. A. Neamen (Chap. 1) 5. Introduction to Electrodynamics by D. J. Griffihs (Ch. 7, 8, 9) 6. Engineering Physics by Gaur & Gupta (Ch. 6)
Electrical Engineering & Machines
Electrical Circuits
1. DC circuits Review of Ohms law Kirchhoffs laws Series and Parallel connections Solution of Simple DC circuits
Vizzmay
2. AC circuits Sinusoidal e.m.f. and currents RMS value, Phasor representation Voltage-current relationship in pure resistor, inductor Resistive, inductive and capacitive circuits and their combinations Power and Power Factor Polyphase System : Voltage and Current relation and power in balanced 3phase system
Electrical Machines
3. DC Characteristics Principle of working Types of generators, Their characteristics and applications DC motors : Principle of working Types of Motors, their characteristics and applications 4. Transformers Review of Faradays law and Lenzs law Self and Mutual Induction Principle of working of transformer EMF equation Uses of Transformers 5. Alternators & Sync. Motors Induction Motor Sync. Motors i. Principle of working ii. Methods of starting V characteristics iii. Applications of Sync. Motors Alternators i. Construction, EMF equation, Regulations ii. OC and SC test iii. Synchronization of Alternators
Reference Books
1. Electrical Engineering by V. N. Mittal 2. Electrical Technology by B. L. Thareja 3. Problems in Electrical Engineering by Parker Smith
Vizzmay
Structured Programming & UNIX
Structured Programming
Fundamentals Programming Higher Level Languages Operating System Compiling Programs 2. Programming in C Language Foundation of programming Variables, Constants, Data types Operators, Expressions and Assignment Statements Control Statements Console Input/output Arrays, Functions, Pointers, Structures Unions and Enumerated Data types File Handling The C Preprocessor Header File and Standard Library Functions 1.
UNIX
1. Introduction History of Unix Types of OS Features of Unix Parts of Unix Unix file system and its physical representation Security and accessibility Commands Administrative Commands Additional Features I/O redirection Piping Shell Scripts
2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
7.
Reference Books
1. Programming in ANSI C by Balagurusamy
Vizzmay
Você também pode gostar
- Solution Manual For Investment Science by David LuenbergerDocumento94 páginasSolution Manual For Investment Science by David Luenbergerkoenajax96% (28)
- Schaum's Outline of Electromagnetics, Fifth EditionNo EverandSchaum's Outline of Electromagnetics, Fifth EditionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- ETO Exam SyllabusDocumento3 páginasETO Exam SyllabusVarun AerosAinda não há avaliações
- Novozhilov Yappa Electrodynamics PDFDocumento362 páginasNovozhilov Yappa Electrodynamics PDFAscanio Barbosa100% (1)
- EASA Part-66 Modules (17 Modules)Documento40 páginasEASA Part-66 Modules (17 Modules)Anthony FratelliAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Engineering Paper - I: SR No Subject BookDocumento15 páginasElectrical Engineering Paper - I: SR No Subject BookVibhuti VyasAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus Followed at Massey UniversityDocumento17 páginasSyllabus Followed at Massey Universityjhon jackAinda não há avaliações
- Hoja de Ruta - MsC. Optics - UCFDocumento36 páginasHoja de Ruta - MsC. Optics - UCFFabricio CascoAinda não há avaliações
- Electro-Magneto-Mechanics: Dr. Kevin Craig Professor of Mechanical Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic InstituteDocumento0 páginaElectro-Magneto-Mechanics: Dr. Kevin Craig Professor of Mechanical Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic InstituteNenad VujosevicAinda não há avaliações
- Al - Hidaayah International School Academic Year 2021 - 22 Mid Term SyllabusDocumento7 páginasAl - Hidaayah International School Academic Year 2021 - 22 Mid Term SyllabusZihad Anwar SharafiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Capsule For NeetDocumento120 páginasPhysics Capsule For Neetharshit pandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Beg 2105 Physical Electronics I - 1 IntroDocumento166 páginasBeg 2105 Physical Electronics I - 1 IntroElias keAinda não há avaliações
- 12th Imp Topics CH WiseDocumento4 páginas12th Imp Topics CH Wiseujjubro1201Ainda não há avaliações
- CLASS XII Physics Syl-Project ReportDocumento7 páginasCLASS XII Physics Syl-Project Report88vhmfwdbbAinda não há avaliações
- A A A A A A A A A A A A A A A A A ADocumento55 páginasA A A A A A A A A A A A A A A A A A0786khanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Computational Chemistry: by Benjamin Lynch and Patton Fast June 14, 2005Documento49 páginasIntroduction To Computational Chemistry: by Benjamin Lynch and Patton Fast June 14, 2005MAVERICK_HUNTER1234936Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics GE 3 & 4 TH Sem PDFDocumento6 páginasPhysics GE 3 & 4 TH Sem PDFSurajit DasAinda não há avaliações
- GRE PhysicsDocumento4 páginasGRE PhysicsHarminder SanghaAinda não há avaliações
- BewakoofDocumento10 páginasBewakoofAkhil AroraAinda não há avaliações
- Electric Circuits Notes, Example EtcDocumento86 páginasElectric Circuits Notes, Example EtcDamodar Reddy MAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus For BITSAT-2019 Part I: Physics: AnnexureDocumento12 páginasSyllabus For BITSAT-2019 Part I: Physics: AnnexureSaurabh YadavAinda não há avaliações
- EC 2006 Sem I & II - Part3Documento2 páginasEC 2006 Sem I & II - Part3Vishnu PrabhakarAinda não há avaliações
- Class 11 Physics SyllabusDocumento7 páginasClass 11 Physics SyllabusShridansh TripathiAinda não há avaliações
- XII Physics Topics of Minimal LearningDocumento1 páginaXII Physics Topics of Minimal Learninggoddhruv17Ainda não há avaliações
- First Year Second Semester: Department of Mechanical Engineering - Course CatalogueDocumento12 páginasFirst Year Second Semester: Department of Mechanical Engineering - Course Cataloguekapun kumar nayakAinda não há avaliações
- EP 311 Physics of Semiconductor Devices: Prof. Dr. Beşire GönülDocumento5 páginasEP 311 Physics of Semiconductor Devices: Prof. Dr. Beşire GönülRagu NathAinda não há avaliações
- 4th Sem ECDocumento54 páginas4th Sem ECAnup BhowmickAinda não há avaliações
- IESL General Qualifying Examination SyllabusDocumento38 páginasIESL General Qualifying Examination SyllabusXiao ShadowlordAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus For BITSAT-2019 Part I: Physics: AnnexureDocumento12 páginasSyllabus For BITSAT-2019 Part I: Physics: AnnexureSunit JalanAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus B.Tech Applied Electronics and Instrumentation PDFDocumento55 páginasSyllabus B.Tech Applied Electronics and Instrumentation PDFShiva KiranAinda não há avaliações
- EM Motion Fundamentals 1 PDFDocumento86 páginasEM Motion Fundamentals 1 PDFSalim AlsenaniAinda não há avaliações
- UEE001 SyllabusDocumento2 páginasUEE001 SyllabusashAinda não há avaliações
- Ems ch1 NTDocumento4 páginasEms ch1 NTAlbert OngAinda não há avaliações
- B - Tech MME 2011 2012Documento38 páginasB - Tech MME 2011 2012Priyanka RamanAinda não há avaliações
- VJTI Syllabus 28-08-2008Documento560 páginasVJTI Syllabus 28-08-2008Abhinav MauryaAinda não há avaliações
- B.Tech 1st SemDocumento15 páginasB.Tech 1st Semmrkhan.04565Ainda não há avaliações
- VTU Syllabus For Computer ScienceDocumento14 páginasVTU Syllabus For Computer Scienceroshanpoudel21Ainda não há avaliações
- BUET EEE Course Catalog 2011-2012Documento27 páginasBUET EEE Course Catalog 2011-2012Shahariar HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Eee - Core Paper 2011Documento56 páginasEee - Core Paper 2011etasureshAinda não há avaliações
- EM 232 Electromechanical Systems: Major Adnan Masood PHD Ee (Uk), Ms Ee (Usa)Documento10 páginasEM 232 Electromechanical Systems: Major Adnan Masood PHD Ee (Uk), Ms Ee (Usa)Abdul Basit ZaideeAinda não há avaliações
- RME SyllabusDocumento2 páginasRME SyllabusMD.Muhiuddin anikAinda não há avaliações
- Part I: Physics: Syllabus For BITSAT-2022Documento15 páginasPart I: Physics: Syllabus For BITSAT-2022Ammar QureshiAinda não há avaliações
- PhysicsDocumento3 páginasPhysicsak86Ainda não há avaliações
- 18EE45Documento2 páginas18EE45vinod kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Section ADocumento6 páginasSection AAmanjot GaurAinda não há avaliações
- BITSAT 2024 SyllabusDocumento11 páginasBITSAT 2024 SyllabusSatvik KambojAinda não há avaliações
- 2007-08 M.sc. ElectronicsDocumento19 páginas2007-08 M.sc. ElectronicsUlhasAinda não há avaliações
- GCSE Electronics - Volume One - Foundations For Electronics: Course Summary SheetDocumento2 páginasGCSE Electronics - Volume One - Foundations For Electronics: Course Summary SheetBilminatorAinda não há avaliações
- 3MGU Btech2010 s1 S2syllabusDocumento21 páginas3MGU Btech2010 s1 S2syllabusAby PanthalanickalAinda não há avaliações
- SRMS ManualDocumento41 páginasSRMS ManualHarshit SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- University Insitute of Engineering Electrical EngineeringDocumento85 páginasUniversity Insitute of Engineering Electrical EngineeringPyrenean IbexAinda não há avaliações
- Michael Bertolli - Striping in CupratesDocumento22 páginasMichael Bertolli - Striping in CupratesSaqqerAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus For BITSAT-2023: Part I: PhysicsDocumento11 páginasSyllabus For BITSAT-2023: Part I: Physicsjake nallaAinda não há avaliações
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part A: Gravitational, Electric, and Magnetic FieldsNo EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part A: Gravitational, Electric, and Magnetic FieldsAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Electromagnetics: From Biomedical Sciences to Wireless CommunicationNo EverandPractical Electromagnetics: From Biomedical Sciences to Wireless CommunicationAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Positioning Equations: Theory and ApplicationsNo EverandMagnetic Positioning Equations: Theory and ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Rotational Spectra and Molecular Structure: Physical Chemistry: A Series of MonographsNo EverandRotational Spectra and Molecular Structure: Physical Chemistry: A Series of MonographsAinda não há avaliações
- Transient Phenomena in Electrical Power Systems: Problems and IllustrationsNo EverandTransient Phenomena in Electrical Power Systems: Problems and IllustrationsNota: 1.5 de 5 estrelas1.5/5 (3)
- Fundamental Principles of Modern Theoretical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyNo EverandFundamental Principles of Modern Theoretical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyAinda não há avaliações
- Newvhdl Syllabus (It&Cse)Documento2 páginasNewvhdl Syllabus (It&Cse)Mude Kishore NaikAinda não há avaliações
- Improving of Transient Stability of Power Systems Using UPFCDocumento6 páginasImproving of Transient Stability of Power Systems Using UPFCTana AzeezAinda não há avaliações
- Agfa CR 10XDocumento4 páginasAgfa CR 10Xwisateru Inti niagaAinda não há avaliações
- Cable Size Calculations SpreadsheetDocumento4 páginasCable Size Calculations Spreadsheetbhavin24uAinda não há avaliações
- Plate - 3 (FLOT)Documento2 páginasPlate - 3 (FLOT)patrick dgAinda não há avaliações
- PB152 - CJ60 GongDocumento2 páginasPB152 - CJ60 GongJibjab7Ainda não há avaliações
- Me (3) - 2Documento16 páginasMe (3) - 2aviralAinda não há avaliações
- Final Thesis Owura Kofi AmoabengDocumento84 páginasFinal Thesis Owura Kofi AmoabengKunal AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- PTP Symmetric Om FNLDocumento8 páginasPTP Symmetric Om FNLn888nAinda não há avaliações
- PC - Section 1.3 - Worksheet PDFDocumento2 páginasPC - Section 1.3 - Worksheet PDFAnabbAinda não há avaliações
- LCS21 - 35 - Polar PlotsDocumento14 páginasLCS21 - 35 - Polar Plotsgosek16375Ainda não há avaliações
- EJ Mini Lesson #7Documento3 páginasEJ Mini Lesson #7ArmandoAinda não há avaliações
- Petrom OMV Norm DEF 2001 Rom Eng Rev.2 2009-06-01Documento61 páginasPetrom OMV Norm DEF 2001 Rom Eng Rev.2 2009-06-01luciandu100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions (The Answers Are Provided After The Last Question.)Documento6 páginasMultiple Choice Questions (The Answers Are Provided After The Last Question.)VijendraAinda não há avaliações
- Design Principles of Rigid and Flexible PavementsDocumento66 páginasDesign Principles of Rigid and Flexible PavementsWycliffe otienoAinda não há avaliações
- QPT Charts BarDocumento8 páginasQPT Charts BarKacak BergayaAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Papers ScienceDocumento199 páginasSample Papers SciencerkkanodiaAinda não há avaliações
- Groundwater Flow-Chapter3FYDocumento73 páginasGroundwater Flow-Chapter3FYTemesgen workiyeAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Water Supply System-High Rise BLDGDocumento108 páginasDesign of Water Supply System-High Rise BLDGcris bunagAinda não há avaliações
- Lec1 PDFDocumento12 páginasLec1 PDFtogarsAinda não há avaliações
- 86-Article Text-596-1-10-20211030Documento7 páginas86-Article Text-596-1-10-20211030adel bbAinda não há avaliações
- Template Question BankDocumento11 páginasTemplate Question Bankeshwar_worldAinda não há avaliações
- Estimating QuotientsDocumento7 páginasEstimating Quotientssheila mae neri100% (1)
- Caterpillar Product Line 13Documento7 páginasCaterpillar Product Line 13GenneraalAinda não há avaliações
- Gantt ChartDocumento4 páginasGantt ChartSyed FaridAinda não há avaliações
- Homeassignment 4 (1) (1) - 2Documento3 páginasHomeassignment 4 (1) (1) - 2hellokaun1072Ainda não há avaliações
- Open Source Software Development and Lotka's Law: Bibliometric Patterns in ProgrammingDocumento10 páginasOpen Source Software Development and Lotka's Law: Bibliometric Patterns in ProgrammingAttya ShahidAinda não há avaliações
- 4$20 Triangles$20 ProofsDocumento23 páginas4$20 Triangles$20 ProofsBaskaran SeetharamanAinda não há avaliações
- GB-T 5137.1-2002 Test Methods of Safety Glazing Materials Used On Road Vehicles Part1 Mechanical Properties TestsDocumento14 páginasGB-T 5137.1-2002 Test Methods of Safety Glazing Materials Used On Road Vehicles Part1 Mechanical Properties TestsRandyzhuAinda não há avaliações