Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Me07401 - Metrology and Quality Control
Enviado por
amsubra8874Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Me07401 - Metrology and Quality Control
Enviado por
amsubra8874Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Govt.
Polytechnic, Mumbai
Rubber Technology
METROLOGY AND QUALITY CONTROL
PROGRAMME : Rubber Technology Compulsory Prerequisite Credit Optional L P Total Examination scheme Theory TH TS PR OR TW Total Course Code
Course Title
ME Metrology and C 4 2 6 80 20 07401 Quality Control 1. Theory papers duration 3 hrs. 2. Theory paper assessment is internal and external. 3. The assessment of practical, oral, term work is internal except mark (*). 4. (*) The assessment is internal and external. 5. C = Compulsory, O = Optional.
25
125
RATIONALE: Metrology is the science of measurement. Technician working in industries should understand various instruments used. The subject impart the necessary knowledge so that student can select & use various instrument used for measurement. ISO 9000 emphasizes on the quality system and total quality management the success of any industry depends on Quality of its product. Technician placed in Quality control or Inspection department has to take various decisions such decision of a acceptance or rejection. Investigating reasons for defects and giving suggestion etc. The subject imparts necessary knowledge so that student can perform the job of quality control supervisor effectively and efficiently. OBJECTIVES: By the end of this course the student will able to: Develop the ability of analysis interpretation and drawing conclusions the data / instrument / graph / chart pertaining to the area of quality control. Develop an ability of problem solving and decision making. Plot and use of quality control charts. Suggest measures to improve the quality of product and reduce cost. To understand the quality system ISO-9000 Understand the salient concept and principles required to develop the ability of using different types of measuring instrument. Understand the principles, construction and use of various measuring instruments. Understand the techniques of handling and maintaining measuring instrument. SECTION - I (P-32, M-40) 1. Measuring Instrument (P-06, M-07) a. Definition, need of inspection, precision, accuracy, sensitivity amplification magnification errors, sources of errors. b. Construction, working and method of use for simple measuring instruments like calipers, surface plate, angle plate, V block different types of micrometer vernier slip gauges. c. Standards of measurements, line and end standard, wavelength std. ME07401 (Provisional) Page 1 of 4
Govt. Polytechnic, Mumbai
Rubber Technology
2. Angular Measurements (P-04, M-06) Angular measurement by instrument such as universal bevel protractor, spirit level, sine bars, censers, angle Decker, autocollimator angle gauges. 3. Limits Fits and Tolerances (P-06, M-09) Limits-fits-gauges definitions-tolerance-fit, deviation, basic shaft, hole. Taylors principle-limit gauges, elementary study of gauge-design (I.S.919-1963) 4. Measurements (P-06, M-09) a. Measurements by comparison: Comparators Mechanical, electrical, electronic, optical and pneumatic. b. Dial indicators, types, construction and working. 5. Testing Methods (P-10, M-09) a. Straightness testing by straight edge spirit level auto-collimator b. Flatness testing by straightness testing techniques and by optical flats. c. Square ness testing by dial indicators. d. Parallelism testing between two axes, two planes one plane stationary other moving axis of rotation and trajectory. e. Roundness testing by dial indicator roundness testing machine. f. Roughness testing-Terminology C.L.A., R.M.S. Values g. Stylus probe instruments. Tomlinsons surface meter. SECTION II (P-32, M-40) 6. Quality Control (P-08, M-07) a. Meaning of quality control difference between quality of design, quality of conformance and quality of performance concept of reliability and maintainability. b. Quality policy, quality of objectives economics of quality, cost and value, quality specification. c. Quality maintenance assurance, quality audit, quality vendor rating, organization set up for quality. d. Inspection and quality control difference between inspection and quality control inspection stations. 7. New trends in Quality Management (P-05, M-07) a. Quality circles-basic concept, purpose and functioning. b. Concept of TQM. c. Concept of KAIZEN d. Concept of POKAYOKE. e. ISO-9000 8. Fundamental of Statistical Quality Control (P-06, M-07) a. Importance of statistics in quality control. b. Frequency distribution mean, medium, mode, range, standard deviation and variance construction and normal distribution curve, interpretation area under the normal. ME07401 (Provisional) Page 2 of 4
Govt. Polytechnic, Mumbai
Rubber Technology
9. Control charts (P-08, M-13) a. Charts for variables-X chart R chart b. Control charts for attributes. P chart C chart c. Process capability of a machine-Statistical limits, tolerance limits, different possibilities, rejection areas, capable-incapable process. 10. Acceptance sampling (P-05, M-06) Q.C. curve, its important characteristics sampling, risks, single-double sampling plans, advantages disadvantages of Sampling. Laboratory Works: Laboratory experience should develop the following skills / abilities:1. A skill in handling different measuring instruments. 2. Ability in planning and setting experiment work to measure the given production job. 3. Ability of selecting measuring instruments. 4. Ability of investigating defects / errors or locating, faults and suggesting remedial measures. 5. Ability of collecting, analyzing and interpretation of data. 6. Ability of problem solving and decision making. 7. Attitude of inquiry. 8. Safety and cost consciousness. 9. Ability of using different control charts. The laboratory work should be supported by frequents visits to industries to get the practical experience. It is desirable that simple production jobs from the industries are included as laboratory exercises. For inspection simple problems from the industries can also be given to the students to find out alternatives. 1. Use of various basic measuring instruments-steel rule, hand calipers, surface plate, angle plate, V-block, radius-feeler-pitch screw gauge, spirit level, combination set, straight edge, universal surface gauge, engineering square. Internal telescopic gauge, vernier calipers, vernier height gauge, internal external micrometer, micrometer depth gauge. 2. Measurement of dimensions of actual components using instrument of experiment No.-1. Measure the dimensions of at least five components by using various instruments. Justify for the difference in readings when it dim is measured by caliper, vernier and micrometer (i.e. the instruments of difference categories) 3. Use of slip gauges- Write the details of slip gauge set observed. Understand the method of wringing. Build a required dimension with the help of available slips. Sketch-the accessories like holder with measuring jaws. Understand its use. Measure unknown gap with slip. 4. Use of Dial Indicator-uses classification as per I.S. specifications. 5. Use of mechanical (any one type) Pneumatic Comparators with the help of slip gauges / ring gauges. Measure the unknown dimensions. 6. Use of sine bar to find unknown angle using slip gauges. Compare this angle with that obtained by bevel protractor. 7. Use of optical profile projector- measure suitable parameters of a small screw check the profile of the component (gear, screw thread) supplied. ME07401 (Provisional) Page 3 of 4
Govt. Polytechnic, Mumbai
Rubber Technology
8. Use of optical flat for flatness testing- check whether the surface of slip gauge is perfectly flat or not note the precautions taken with monochromatic source of light. Sketch the fringe pattern observed. Predict the fringe pattern with convex / concave surface write how this techniques is suitable for parallelism testing screw. 9. Construction of control charts- for variable measurements (X, R chart) Take readings. Draw the control charts on graph. Interpret results. Suggest the options if any. 10. Construction of control charts for Attribute measurements (p. chart) takes readings, show them it on graph. Interpret results and suggest the change to be done if any. 11. Determination of process capability of a machine- (Actual testing of machine or process be done if possible) Give procedure to know process capability of a machine with three sigma and tolerance limits on normal distribution curve. Give different possibilities. Reference Books 1. Engineering Metrology R.K. Jain 2. Metrology and Quality control M.S. Mahajan 3. Hand book of Industrial Metrology ASTME. 4. Metrology Lab manual M. Addith and R. Bahl (T.T.T.I.) 5. Quality planning and analysis Juran 6. Hand book industrial engg. H.B. Maynard 7. Quality Control M.S. Mahajan 8. Total Quality Control Feigenbaum 9. Quality Control TTTI, Madras 10. Quality Control Grant, Leavenworth 11. ISO-9000-Brian Rothery 12. Metrology and Quality Control R.K. Jains
ME07401 (Provisional)
Page 4 of 4
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- CTS FitterDocumento37 páginasCTS Fitterrajum465100% (1)
- Astm E45.18aDocumento20 páginasAstm E45.18aMarconi Cosme100% (6)
- Solar Turbines Technical Training Package Leveling and AlignmentDocumento167 páginasSolar Turbines Technical Training Package Leveling and Alignmentdennis_packiaraj3063100% (20)
- Kristeel CatalogueDocumento52 páginasKristeel CatalogueRam TejaAinda não há avaliações
- Engaging Students: Active Learning Strategies in The College ClassroomDocumento13 páginasEngaging Students: Active Learning Strategies in The College Classroomamsubra8874100% (1)
- Fea BookDocumento155 páginasFea BookLakhan Kumar SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Finite Element Analysis - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDocumento13 páginasFinite Element Analysis - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M77% (30)
- Instrument Calibration ProcedureDocumento16 páginasInstrument Calibration ProcedureMohammad Nurayzat JohariAinda não há avaliações
- Paper Test EquipmentDocumento46 páginasPaper Test Equipmentandhie68Ainda não há avaliações
- Machine Tools Lab Assignment ReportDocumento10 páginasMachine Tools Lab Assignment Reportmohsin931Ainda não há avaliações
- FEA Unit1 - Gaussian Elimination MethodDocumento7 páginasFEA Unit1 - Gaussian Elimination Methodamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Solve The Following System of Three Equations ScilabDocumento7 páginasSolve The Following System of Three Equations Scilabamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Fea 2MDocumento13 páginasFea 2MSubharanjani MathiAinda não há avaliações
- FEA Unit1 - Governing EquationsDocumento8 páginasFEA Unit1 - Governing Equationsamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- 1646 Personal Letter of CancellationDocumento1 página1646 Personal Letter of CancellationRaymond MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Three Dimensional Cutting Force Analysis in End MillingDocumento11 páginasThree Dimensional Cutting Force Analysis in End Millingamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- 1646 Personal Letter of CancellationDocumento1 página1646 Personal Letter of CancellationRaymond MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Pergamon: (Received 6 AugustDocumento24 páginasPergamon: (Received 6 Augustamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Aircraft Production Technology VijayDocumento10 páginasAircraft Production Technology Vijayamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- MillingDocumento12 páginasMillingamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Lamies TheoremDocumento1 páginaLamies Theoremamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Cutting ForceDocumento12 páginasCutting Forceamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 MetrologyDocumento16 páginasUnit 5 MetrologyMuthuvel M100% (2)
- Unit 4 MetrologyDocumento12 páginasUnit 4 MetrologyMuthuvel M89% (9)
- Man Vs Machine: A Consolidated Presentation Submitted at AISSQ-2012 ConferenceDocumento42 páginasMan Vs Machine: A Consolidated Presentation Submitted at AISSQ-2012 Conferenceamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Me6603 Notes Rejinpaul Fea PDFDocumento155 páginasMe6603 Notes Rejinpaul Fea PDFFakkir Mohamed100% (2)
- FeaLect Note5Documento15 páginasFeaLect Note5amsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- FEM Lecture NotesDocumento188 páginasFEM Lecture NotesHenry Martinez CarmonaAinda não há avaliações
- Lect RoboticsDocumento21 páginasLect Roboticsamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Finite Element Methods April May 2007 Question PaperDocumento6 páginasFinite Element Methods April May 2007 Question PaperelimelekAinda não há avaliações
- Easwari Engineering College Question Bank: Finite Element AnalysisDocumento12 páginasEaswari Engineering College Question Bank: Finite Element Analysisamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Fea Class Note1Documento40 páginasFea Class Note1amsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Lect 1roboDocumento129 páginasLect 1roboamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- ME2353 Finite Element Analysis Lecture NotesDocumento34 páginasME2353 Finite Element Analysis Lecture NotesgoldencometAinda não há avaliações
- CFD JnalDocumento12 páginasCFD Jnalamsubra8874Ainda não há avaliações
- Finite Element Methods April May 2007 Question PaperDocumento6 páginasFinite Element Methods April May 2007 Question PaperelimelekAinda não há avaliações
- Caleffi: Valvole Di BilanciamentoDocumento16 páginasCaleffi: Valvole Di BilanciamentoThomas GregantiAinda não há avaliações
- Certificate of Accreditation: Perry Johnson Laboratory Accreditation, IncDocumento11 páginasCertificate of Accreditation: Perry Johnson Laboratory Accreditation, IncJoel MelendezAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Aided Metrology PrinciplesDocumento3 páginasComputer Aided Metrology PrinciplesramptechAinda não há avaliações
- Metrology Lab 1Documento8 páginasMetrology Lab 1Kashif RazaqAinda não há avaliações
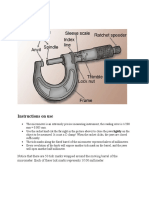
- Instructions On Use: MicrometerDocumento4 páginasInstructions On Use: MicrometerCarlton GrantAinda não há avaliações
- Micrometer WorkheetDocumento9 páginasMicrometer Workheetlonkarsb1979Ainda não há avaliações
- EN ISO 3126 (2005) (E) CodifiedDocumento6 páginasEN ISO 3126 (2005) (E) Codifiedlorenzinho290Ainda não há avaliações
- Sub-Spec 027 - DP Master DS, MT and High Torque PAC: Visual InspectionDocumento3 páginasSub-Spec 027 - DP Master DS, MT and High Torque PAC: Visual InspectionJosue FishAinda não há avaliações
- Tesa Tubular PDFDocumento14 páginasTesa Tubular PDFMarcelo Godinho BatistaAinda não há avaliações
- E 759 - 92 R00 - Rtc1oqDocumento2 páginasE 759 - 92 R00 - Rtc1oqmishil90Ainda não há avaliações
- Verify Test Equipment CalibrationDocumento16 páginasVerify Test Equipment CalibrationAzhar ArisAinda não há avaliações
- Metrology Solved ProblemsDocumento63 páginasMetrology Solved ProblemsKo Qurban Ahmedli :/Ainda não há avaliações
- VTEC Conversion Kit GuideDocumento11 páginasVTEC Conversion Kit GuidesdwsedAinda não há avaliações
- Company Profile: An Iso 9001: 2015 Certified CompanyDocumento50 páginasCompany Profile: An Iso 9001: 2015 Certified CompanySumit SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Calibration Services and CapabilitiesDocumento58 páginasLaboratory Calibration Services and Capabilitiesgopinadh57100% (1)
- Measuring Tools No.C052009Documento291 páginasMeasuring Tools No.C052009Daniela MiguelAinda não há avaliações
- Shinwa (Jet)Documento62 páginasShinwa (Jet)geetha raniAinda não há avaliações
- Apex150 16/18 AWG Female Terminal On 18AWG M1L123A Wire: ESR# AM-030127A Test Request #05-003Documento20 páginasApex150 16/18 AWG Female Terminal On 18AWG M1L123A Wire: ESR# AM-030127A Test Request #05-003Amir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Profile Projector: Dynamics of Machine LaboratoryDocumento4 páginasProfile Projector: Dynamics of Machine LaboratoryAshish VermaAinda não há avaliações
- CBC Machining NC IDocumento79 páginasCBC Machining NC IKaren Mae Altarejos AlocAinda não há avaliações
- Tune Up Engine Konvensional NO Tools Dan Alat UkurDocumento5 páginasTune Up Engine Konvensional NO Tools Dan Alat UkurAlby AchmadAinda não há avaliações
- Lee's Disc Method - PresentationDocumento14 páginasLee's Disc Method - PresentationAmruta DongreAinda não há avaliações
- MM Lab VivaDocumento2 páginasMM Lab VivaRajesh KannanAinda não há avaliações