Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Unit 5-Heart Answers
Enviado por
areyouthere92Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Unit 5-Heart Answers
Enviado por
areyouthere92Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1.
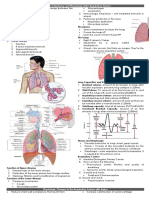
(a) reference to (impulse) conduction between atria and ventricles ; delay at AV node ; allows ventricles to fill before contraction ; (b) distance from one P wave to next (or R to R) is 56 to 58 ; heart rate = 60 50 / 56 to 58 ; = 51.7 (52) to 53.8 (54) beats per minute ;
3
[5]
2.
(a)
A B C D
Epidermis / epidermal cells / piliferous layer / root hair cells ; Cortex ; Endodermis ; Xylem ; [any two correct answers for 1 mark]
(b)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Osmosis ; (across cortex) down water potential gradient ; Symplastic route explained / vacuolar route explained ; Apoplastic route explained ; Reference to plasmodesmata ; Reference to function of endodermis / cell C / Casparian strip (e.g. controlling water uptake) ; Reference to transpiration stream / cohesion tension theory (qualified) ; Reference pores / pits allows water into xylem ; (i) Active transport / uptake ; Energy / ATP, used ; Ions moved, against / up, concentration gradient ; Respiration provides ATP ; Aerobic / oxygen required ; Some uptake without aeration ;
(c)
(ii)
No active transport ; Diffusion only ; Transporters / carriers / ion channels, absent / reduced ; Smaller surface area / with root hairs, larger surface area ; Lack of / fewer, mitochondria ; [accept converse points]
2
[12]
3.
(a) Spontaneous / automatic (contraction) / self-stimulating ; No {nerve impulse / eq} required / no nerve stimulation ;
(b)
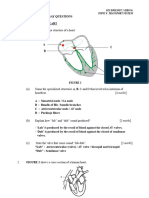
(i) B C (ii) 1. 2. 3. ventricles 4. 5.
A SAN / sino-atrial node / pacemaker ; AVN / atrio-ventricular node ; Bundle of His / Purkyne fibres / Purkinje tissue ; {SAN / A / pacemaker} initiates impulse / eq ; {Impulse / eq} to {AVN / B} then delay ; So atrial {systole / contraction} before ventricular systole /
fill with blood before systole ; {Bundle of His / C} conducts impulse to (base of) ventricles ; Which contract from {apex / eq} upwards ; 3
[8]
4.Question 5 Maximum mark (a) (b) (Ventricular) systole / ventricular contraction; max 1
(As ventricle contracts) pressure increases; From 2.0 - 4.0 kPa / to {14.0 / 15.0} kPa; 2
(c)
X Point when pressure in ventricle first exceeds pressure in atrium; Y Point when pressure in aorta first exceeds pressure in ventricle; [allow marks if X and Y both placed on the X axis at the correct times] 2
(d)
(60 0.8) = 75; Beats per minute / bpm; 2
(e)
(i)
Same pattern as normal ECG; max 2
More than one cycle in the grid; (ii) They may have been {exercising / stressed / eq} / genetic variation / age / fever / body temperature / stimulant / excitement;
(iii)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
Measure (ECG) under physical exercise (treadmill); Blood pressure check; Measure blood cholesterol; Ultrasound; Calculate BMI; MRI; CAT / CT / EBCT; {Ambulatory / 24 hour} monitoring; Coronary {angiography / angiogram}; 2
[12]
5.
(a) 21 190 / 21 000 190; 3 3 = 110.5 cm / 0.11 dm ; (b) (ii) (i) 1. 2. 3. 4. (iii) 1. 2. 3. (c) 2. 3. 4. 1. Vena cava; Right atrium; 2 Force of blood {pushing against / stretching} blood vessel wall; Systolic increases and diastolic decreases; Systolic increases more than diastolic decreases; Reference to manipulated figures; Diastolic pressure does not decrease with light exercise; Cardiac output and heart rate increase; So more blood enters the {arteries / blood vessels}; Per unit time; 2
2 1
Carotid {sinus / artery};
Aorta {arch / sinus};
[10]
6. (ii)
(a)
(i)
650 250 = 400; 2
400 250 100 = 160%; [All points in the context of increased cardiac output] Contractions (of cardiac muscles) are {harder / faster / eq (Cardiac muscle) requires more oxygen; For more (aerobic) respiration / to generate more ATP; (i) skin; (Overall) increase to cardiac muscle and (increase then) decrease to
(b)
Manipulation of figures, e.g. 414% increase and 33.3% fall; (Flow) increase to both as exercise increases from low to medium; (Flow) increase to cardiac muscle but decreases to skin as exercise increase from medium to high; (ii) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. By muscle; More blood flow to skin (from low to medium exercise) allows more heat to be lost; (From medium to high exercise) less blood available to flow to skin / eq; As greater demand by / diversion to (cardiac / skeletal) muscle; 3
[9]
More heat generated (as exercise increases);
7. (b)
(a) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
{Sinoatrial / SA} node / SAN / pacemaker; {(Wave of electrical) impulses / depolarisation} from SA node; Passes over (both) atria / eq; Resulting in atrial {systole / contraction}; Slight delay at AV node; (Impulses) pass along bundle of His; (Up / along) Purkinje fibres / eq; Correct direction of impulse described / ventricles contract from the base up / eq; Resulting in ventricular {systole / contraction};
4
[5]
8. (b)
(a) (ii)
SA node / SAN / sinoatrial node (i) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Bainbridge (reflex) Increased blood pressure (in vena cava / right atrium); Baroreceptors stimulated; {Cardiovascular centre / medulla} initiate impulses in {sympathetic / accelerator} nerve; {Stimulation of SAN increased / eq} / decreased delay at AVN; Heart rate increased / eq; 3 Placed under the skin on the chest wall / eq;
1 1
(c) 2. 3. 4. 5.
1.
Wired to {wall / muscle} of heart / eq; Can detect hearts beat; Generates {impulses / eq}; {Stimulate / eq} (regular) contraction of cardiac muscle / mimics action of SAN (and AVN) / eq; 3
[8]
9.
(a) 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. (b) (ii) (iii)
1.
Ventricle contracts / systole;
Pressure in ventricles increases; Correct reference to pressure changes from graph; Pressure in ventricle exceeds pressure in aorta; Semilunar valve opens; Blood flows into aorta; Blood flows down a pressure gradient / eq; (i) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Sinoatrial (SA) node / pacemaker / SAN; 1 Reference to AV node; Delay at AV node; Reference to bundle of His; Reference to Purkinje fibres; {Electrical activity / impulse} travels from base up through cardiac muscle; Electrical activity / impulse stimulates contraction of cardiac muscle / eq; 3
[9]
4 1
Right atrium;
10.
(a)
(i)
Adnan: 67.1
5
AND James: 45.7; 1 (ii) (iii) 191.3 4 = 47.8; 1 [Allow ecf] 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (b) (Same) age; (Same) {size / weight / mass}; {Duration / type / intensity / frequency} of exercise; Duration of rest period; Same techniques for measuring the heart rate / eq; Standardise lifestyle / medical factors; 2
Regular exercise increases size of heart / more muscle; Greater stroke volume / increase heart force / eq; More blood circulated per beat / increased cardiac output / increased venous return; 2
[6]
11.
(a)
(Rhythmic) expansion / eq ; 2 13 11 ; 2 Heart rate increases ; Stroke volume increases ; Increased force of contraction ; Cardiac output increases ; Reference to increased {oxygen / glucose} demand(by muscles) ; 2 Systolic pressure increases, diastolic pressure decreases ; Increase in systolic pressure is greater than the decrease in diastolic pressure ; No change in diastolic pressure at light level of exercise, (but systolic pressure increases) ; Credit a manipulated, quantitative comparison ; 3
[9]
Of an artery ; (b) (i) = 2 kPa ; (ii) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
(iii)
1. 2. 3. 4.
12.
(a) {Sequence / series / eq} of events each time heart beats ; Atrial systole ; Followed by ventricular systole ;
Then diastole ; (b) (ii) (i) R wave correctly indicated ;
3 1
Allows atria to contract (fully) ; Before ventricles contract ; Correct reference to {atrial emptying / ventricular filling} ;
3
[7]
13.
sinoatrial node / sinuatrial node / SAN / pacemaker; ventricles; IGNORE left / right coronary arteries; capillaries; 4
[4]
14. (ii)
(i)
T wave correctly labelled;
number of complete cardiac cycles = 5; calculation (5 12) / eq; heart rate = 60 (beats per minute); 3
[4]
15. B C (b) 2. 3. 4. (c) 2.
(a)
right ventricle; 3
aorta / aortic arch; (left) atrioventricular valve / mitral valve; 1. sequence of events each time the heart beats / eq;
(starts with) atrial systole; (then) ventricular systole; (then) diastole; 1. 3
ability of heart (muscle) to {contract / beat / pump }; 2
[8]
spontaneously / on its own / without nervous stimulation / eq;
16. (b)
(a)
medulla (oblongata); 1. ref. to increase in rate of (anaerobic / aerobic) respiration;
2.
{increase in carbon dioxide levels / increase in {lactic acid / lactate} + levels / decrease of pH / increase in {hydrogen ions / H } / increase in carbonic acid} in the blood; ref. to chemoreceptors; {aortic / carotid} bodies or ref. to carotid {artery / aorta}; {cardiac / cardiovascular} centre (in medulla); {more / increase in frequency} of impulses along sympathetic nerve; ref. to SAN / sinoatrial node; 4
[5]
3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
17.
(a)
(i)
lack of oxygen / eq;
+
anaerobic respiration (produces lactate); (respiration) produces reduced NAD / NADH H / NAD H2/ reduced co-factors; pyruvate produced by glycolysis; pyruvate converted to lactate (in anaerobic conditions); lactate production oxidises NADH so glycolysis can continue/eq; in anaerobic respiration {glucose / lactate} cannot be fully oxidised / correct reference to Krebs cycle / oxidative phosphorylation / suitable ref. to mitochondria /eq; allows continued production of ATP; (ii) the difference {cannot be explained by chance/is really caused by diving / not some other factor}; the {probability/chance} that the difference could be due to chance/ accident is less than 5% / 0.05 / 1 in 20 / 95% confident that difference is not due to change alone; (iii) correct description of change of lactate in dives of different duration e.g. little change in blood lactate concentration up to six minutes, faster increase in blood lactate concentration after {five / six} minutes / eq / ref. to greater variability of blood lactate in longer dives; in dives of up to {five / six} minutes there is enough oxygen (in the lungs / blood / body) to maintain (largely) aerobic respiration /in a dive of six to twelve minutes (all / most) oxygen gets used up therefore respiration (more / or less) entirely anaerobic / eq;
(b)
heart rate decreases when the seal dives / rises when the seal surfaces; use of figures to emphasise that the HR falls very low from e.g from 130 - 150 beats per minute to 10 - 30; at the surface increases supply of oxygen to remove lactate / to repay oxygen debt; ref. to moving the lactate away from the muscles / to the liver; when submerged little oxygen carried to muscles in blood / eq; correct ref. to cardiovascular centre / correct ref. to nerve action on the SAN / reflex action; ref. to myoglobin; 4 QRS (complex); 2
(c) (ii)
(i)
resulting in contraction of ventricles / ventricular systole; 90 120 bpm; 20 40 bpm; (d) 2
(i) {shock / disruption of control mechanisms / eq} at the sudden change in temperature at the {lower temperature / 25 C}; 35 C is close to normal body temperature (therefore less of a shock than 25 C); reduced (blood) circulation to conserve heat / a thermoregulatory mechanism / vasoconstriction (to surface); ref. to diving reflex / bradycardia; (ii) she hyperventilated / filled her body / lungs / blood with as much oxygen as possible before diving; she {had prepared herself mentally / was afraid / stressed} and this caused the increase in heart beat; ref. to adrenaline / hormone; ref. to autonomic nervous system / sympathetic nervous system; 2
[20]
18.
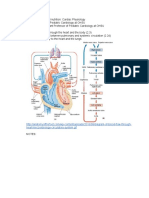
(a) A aorta / aortic arch; B (right) atrioventricular valve / tricuspid valve;
(b) 2. 3. 4. 5.
1.
reference to coronary circulation;
reference to coronary artery / coronary arteries; reference to capillaries (in wall of heart); oxygen {transported / eq} by {red cells / haemoglobin}; oxygen diffuses out of {blood / red cells / capillaries} (to heart muscle); max 3 1. pacemaker / SAN sends {impulse / eq} (to atria);
(c) 2. 3. 4. 5.
{causing/ eq} atria to contract; {impulse / eq} reaches AVN; reference to delay at the AVN; idea that the impulse travels to ventricles via {bundle of His / Purkyne tissue / eq}; 1. increased {demand for / eq} {oxygen / glucose} / increased respiration; max 3
(d) 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
increased heart rate / heart beats faster / eq; increased stroke volume / cardiac output; increased production of carbon dioxide; reference to dilation of blood vessels in muscle; reference to adrenaline; max 3
[11]
19.
(a) Award one mark for each of the following points in context to a maximum of four marks. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (b) wave of excitation sent from SAN; spreads over atria walls; delayed at atrioventricular septum; wave of excitation sent from AVN; passes along bundles of His/purkine fibres; spreading over walls of ventricles; 4
Duration of 1 beat OR 60 / duration; Correct answer, 50 1 Beats min / bpm;
(c)
Award one mark for each of the following points in context to a maximum of two marks. 1. 2. 3. Interval between QRS phases longer (in normal rhythm); Credit correctly manipulated figures; Lower voltage during QRS phase in normal rhythm; 2
(d)
Award one mark for each of the following points in context to a maximum of three marks. 1. 2. 3. Cardiac output could decrease if there was insufficient time to fill the ventricles (between contractions); Cardiac output could increase if ventricles fill sufficiently; The change in cardiac output will depend on whether the decrease in stroke volume is compensated by the increase in heart rate/eq; 3
[11]
11
Você também pode gostar
- 101 Things Everyone Should Know About Science PDFDocumento138 páginas101 Things Everyone Should Know About Science PDFsmeenaAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac CycleDocumento30 páginasCardiac CycleNosh AnbreenAinda não há avaliações
- ASE Reference BookDocumento68 páginasASE Reference BookBeatriz Jáuregui Garrido100% (9)
- Ecg Tutorial PDFDocumento82 páginasEcg Tutorial PDFpacpacpac123Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Physiology NotesDocumento11 páginasCardiac Physiology Notespunter11100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Transport in Mammals - WorksheetDocumento5 páginasChapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Worksheetapi-3728508100% (2)
- Electrocardiography IDocumento19 páginasElectrocardiography IsalochinAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory SystemDocumento22 páginasCirculatory Systemparitosh7_886026Ainda não há avaliações
- Ganong's Review of Medical Physiology - 23rd EdDocumento4 páginasGanong's Review of Medical Physiology - 23rd Edareyouthere92100% (2)
- Cardiovascular DrillsDocumento12 páginasCardiovascular DrillsMaria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia IIAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease 7th Edition by Des JardinsDocumento6 páginasTest Bank For Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease 7th Edition by Des Jardinssamanthaportergxnmjoeftz100% (32)
- Chapter 5 Care of The Clients With Cardiovascular DisordersDocumento226 páginasChapter 5 Care of The Clients With Cardiovascular DisordersDon Felicisimo EbronAinda não há avaliações
- Kanda Sashti Kavacham Lyrics TamilDocumento7 páginasKanda Sashti Kavacham Lyrics Tamilrevathigopinath83% (42)
- Outline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Documento8 páginasOutline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Jhason John J. CabigonAinda não há avaliações
- Pediatrics ECG by DR Ali Bel KheirDocumento9 páginasPediatrics ECG by DR Ali Bel KheirFerasAinda não há avaliações
- Fetal Pig DissectionDocumento14 páginasFetal Pig Dissectionrangerblue86% (7)
- 9 Transport in AnimalssDocumento59 páginas9 Transport in AnimalssFathmath JameelAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific Article For Use With Question 7 - A Red Card For The HeartDocumento13 páginasScientific Article For Use With Question 7 - A Red Card For The HeartAmar MuhammedAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5-Ventilation Breathing AnswersDocumento9 páginasUnit 5-Ventilation Breathing Answersareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Groby Community College 1Documento5 páginasGroby Community College 1Rubban KunaAinda não há avaliações
- Checked - Unit 1 Molecules, Diet, Transport and Health - Exam - MSDocumento16 páginasChecked - Unit 1 Molecules, Diet, Transport and Health - Exam - MSEllane leeAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in Animals 1 MSDocumento7 páginasTransport in Animals 1 MS青木ケイAinda não há avaliações
- Unit5 PRACAnsDocumento9 páginasUnit5 PRACAnsLola ShmeerAinda não há avaliações
- Final Q Bank CVS Upto Cardiac Output (13-01-2017)Documento2 páginasFinal Q Bank CVS Upto Cardiac Output (13-01-2017)faris babuAinda não há avaliações
- Aqa Unit 1 June 2002 MsDocumento6 páginasAqa Unit 1 June 2002 MsYanahan ParamalingamAinda não há avaliações
- 5.2 Heart Questions Mark SchemeDocumento4 páginas5.2 Heart Questions Mark SchemeLesley Boulton100% (2)
- As 04 Transport in Animals Ans - BiologyDocumento7 páginasAs 04 Transport in Animals Ans - BiologyUncleBulgaria100% (1)
- Mark Scheme Transport QuestionsDocumento3 páginasMark Scheme Transport QuestionsJohn OsborneAinda não há avaliações
- Heart and Heart Disease 1 2 Mark SchemeDocumento5 páginasHeart and Heart Disease 1 2 Mark SchemerkblsistemAinda não há avaliações
- Распознавание шоковх аритмий с использованием CNN ENGLDocumento8 páginasРаспознавание шоковх аритмий с использованием CNN ENGLAbduljabbar Salem Ba-MahelAinda não há avaliações
- Vasculopathy Emulation and Its Influence On The Cardiac Output Curve-Franyi Lorena DiazDocumento7 páginasVasculopathy Emulation and Its Influence On The Cardiac Output Curve-Franyi Lorena Diazfranyi lorenaAinda não há avaliações
- Eve 12588Documento7 páginasEve 12588Flavio RibeiroAinda não há avaliações
- Intra Aortic Balloon CounterpulsationDocumento39 páginasIntra Aortic Balloon Counterpulsationmerin sunilAinda não há avaliações
- Heart & Diseases MSDocumento5 páginasHeart & Diseases MSashfairfan30Ainda não há avaliações
- A2 5.1.5 Spec Notes AnswersDocumento3 páginasA2 5.1.5 Spec Notes AnswersjnrjknerAinda não há avaliações
- June 2003 U2bDocumento3 páginasJune 2003 U2bapi-3726022Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 5-Homeostasis AnswersDocumento6 páginasUnit 5-Homeostasis Answersareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 5-Nervous System Brain Retina AnswersDocumento33 páginasUnit 5-Nervous System Brain Retina Answersareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Output HandoutDocumento10 páginasCardiac Output Handoutsac50900Ainda não há avaliações
- ECG EquinoDocumento19 páginasECG EquinoAgro PetAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 9 Ciculatory System II 202001 - Self LearningDocumento5 páginasTutorial 9 Ciculatory System II 202001 - Self LearningChun Chee LeongAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac CycleDocumento29 páginasCardiac CycleRussell Suter100% (1)
- RPT CardioDocumento2 páginasRPT CardioBrad PamnaniAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 8 TRANSPORT SYSTEM Answer SchemeDocumento19 páginasCHAPTER 8 TRANSPORT SYSTEM Answer Schemeipgm-3870Ainda não há avaliações
- Guest Speakers-Cardio NotesDocumento5 páginasGuest Speakers-Cardio NotesKANAK KOKAREAinda não há avaliações
- ECG EKG InterpretationDocumento11 páginasECG EKG InterpretationGunma AkagiAinda não há avaliações
- ECG HRV Assignment 19334107Documento18 páginasECG HRV Assignment 19334107katehughes332Ainda não há avaliações
- Physio 2 - NotesDocumento157 páginasPhysio 2 - NotesSivaranjini BhalaAinda não há avaliações
- WBI05 Energy Exercise and Co-OrdiantionDocumento172 páginasWBI05 Energy Exercise and Co-OrdiantionOxygen CarbonAinda não há avaliações
- Wigger's Diagram WorksheetDocumento6 páginasWigger's Diagram WorksheetYina BambinaAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook Hupperts Notes Pathophysiology and Clinical Pearls For Internal Medicine PDF Full Chapter PDFDocumento67 páginasEbook Hupperts Notes Pathophysiology and Clinical Pearls For Internal Medicine PDF Full Chapter PDFmartha.delancey633100% (26)
- Transport System Question and AnswersDocumento12 páginasTransport System Question and Answerskumara guruparanAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Intracardiac EGMs: A Patient Centered GuideNo EverandUnderstanding Intracardiac EGMs: A Patient Centered GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Kegawatan KVDocumento71 páginasKegawatan KVAsri HartatiAinda não há avaliações
- Nikus2017 PDFDocumento11 páginasNikus2017 PDFAngie AlonsoAinda não há avaliações
- School of Engineering Department of Biomedical Engineering: EENG424L-Medical Instrumentation I LabDocumento8 páginasSchool of Engineering Department of Biomedical Engineering: EENG424L-Medical Instrumentation I LabMahdi BraitehAinda não há avaliações
- Outline The Transmission of The Electrical Impulse Through The HeartDocumento3 páginasOutline The Transmission of The Electrical Impulse Through The HeartHannah JohnstonAinda não há avaliações
- Hupperts Notes Pathophysiology and Clinical Pearls For Internal Medicine Laura Huppert Full ChapterDocumento67 páginasHupperts Notes Pathophysiology and Clinical Pearls For Internal Medicine Laura Huppert Full Chapterannette.reese953100% (6)
- Unit Three: The Heart: Chapter 9: Cardiac Muscle The Heart As A Pump and Function of The Heart ValvesDocumento36 páginasUnit Three: The Heart: Chapter 9: Cardiac Muscle The Heart As A Pump and Function of The Heart ValvesEbaa Moh'd ZayadnehAinda não há avaliações
- Study FastDocumento49 páginasStudy FastmbbsporalekhaAinda não há avaliações
- اسئلة علم الدواءDocumento2 páginasاسئلة علم الدواءMohamedErrmaliAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Cycle Option HDocumento8 páginasCardiac Cycle Option HstorykuAinda não há avaliações
- Temporal Analysis of Ecg Using Labview: Prof. Amruta Mhatre, Prof. Sadhana Pai, Prof. Manita RajputDocumento4 páginasTemporal Analysis of Ecg Using Labview: Prof. Amruta Mhatre, Prof. Sadhana Pai, Prof. Manita RajputSitara KhanAinda não há avaliações
- CardiovascularDocumento6 páginasCardiovascularMabes100% (1)
- Electrocardiography - WikipediaDocumento18 páginasElectrocardiography - WikipediaAkhil WaliaAinda não há avaliações
- CardiovascularDocumento155 páginasCardiovascularEric VeranoAinda não há avaliações
- 29303-Theory Techniques of Counterpulsation Therapy CardiosaveDocumento117 páginas29303-Theory Techniques of Counterpulsation Therapy Cardiosavejuancar90Ainda não há avaliações
- The Heart: Guyton Unit III Ch9 Dr. Ebaa AlzayadnehDocumento16 páginasThe Heart: Guyton Unit III Ch9 Dr. Ebaa AlzayadnehEbaa Moh'd ZayadnehAinda não há avaliações
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 3 - MsDocumento11 páginas3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 3 - MsMaymunah HussainAinda não há avaliações
- 2017 2019 SyllabusDocumento26 páginas2017 2019 Syllabusareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Ca2sampleprojectl12audit TrailDocumento6 páginasCa2sampleprojectl12audit Trailareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Lifestyle Fund ExerciseDocumento2 páginasLifestyle Fund Exerciseareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Rang and Dales - Pharma (6th Ed.)Documento2 páginasRang and Dales - Pharma (6th Ed.)areyouthere92100% (1)
- Portfolio ManagementDocumento9 páginasPortfolio Managementareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Econ 3 June 2011 MSDocumento16 páginasEcon 3 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Edexcel GCE June 2011 Grade BoundriesDocumento14 páginasEdexcel GCE June 2011 Grade Boundriesareyouthere9250% (2)
- Basic EmbryologyDocumento28 páginasBasic EmbryologyTwinkle SalongaAinda não há avaliações
- Econ 4 June 2011 MSDocumento20 páginasEcon 4 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Survive Medical SchoolDocumento24 páginasSurvive Medical Schoolmohd-khairil-anwar-ramli-2048Ainda não há avaliações
- D1 June 2010 MSDocumento14 páginasD1 June 2010 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Econ 4 June 2011 QPDocumento40 páginasEcon 4 June 2011 QPareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- English 1 June 2011 MSDocumento32 páginasEnglish 1 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Econ 2 June 2011 MSDocumento14 páginasEcon 2 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Econ 3 June 2011 QPDocumento28 páginasEcon 3 June 2011 QPareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- English 2 June 2011 QPDocumento21 páginasEnglish 2 June 2011 QPareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Econ 1 June 2011 QPDocumento40 páginasEcon 1 June 2011 QPareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Econ 1 June 2011 MSDocumento23 páginasEcon 1 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- English 1 June 2011 QPDocumento36 páginasEnglish 1 June 2011 QPareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- S3 June 2011 MSDocumento18 páginasS3 June 2011 MSareyouthere92100% (1)
- D2 June 2011 MSDocumento16 páginasD2 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Econ 2 June 2011 QPDocumento36 páginasEcon 2 June 2011 QPareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- English 2 June 2011 QPDocumento28 páginasEnglish 2 June 2011 QPareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- S2 June 2011 MSDocumento12 páginasS2 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- S4 June 2011 MSDocumento12 páginasS4 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- M3 June 2011 MSDocumento12 páginasM3 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- S1 June 2011 MSDocumento14 páginasS1 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- M2 June 2011 MSDocumento12 páginasM2 June 2011 MSareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Rivision QuestionsDocumento38 páginasNursing Rivision Questionssosokhideer100% (1)
- Cardiac Arrythmia For PathophysiologyDocumento47 páginasCardiac Arrythmia For PathophysiologywilzmaxAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Strengthening Sheet CSS-03 Zoology: Based On AIATS-03 TYMDocumento3 páginasConcept Strengthening Sheet CSS-03 Zoology: Based On AIATS-03 TYMSparsh MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- Best Management in Isolated Right Ventricular Hypoplasia With Septal Defects in AdultsDocumento7 páginasBest Management in Isolated Right Ventricular Hypoplasia With Septal Defects in AdultsReinaldi octaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomical Dissection GuideDocumento4 páginasAnatomical Dissection GuideLidy HigueraAinda não há avaliações
- 112 NotesDocumento9 páginas112 NotesDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eAinda não há avaliações
- Class Xi Sample PaperDocumento5 páginasClass Xi Sample PaperSaurav MitraAinda não há avaliações
- Amrita School of Medicine: BSC Cardiovascular TechnologyDocumento47 páginasAmrita School of Medicine: BSC Cardiovascular TechnologySamrat GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- BronchitisDocumento82 páginasBronchitisstrawberry pieAinda não há avaliações
- 1.2 Synthesising The Concept of Circulatory SystemDocumento16 páginas1.2 Synthesising The Concept of Circulatory SystemJuliet LingAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 Molecules, Diet, Transport and HealthDocumento9 páginasUnit 1 Molecules, Diet, Transport and HealthNandiAinda não há avaliações
- Echocardiographic Changes in The Shape and Size of The AorticDocumento8 páginasEchocardiographic Changes in The Shape and Size of The AorticAristoteles Esteban Cine VelazquezAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 7 CH 4.05 The HeartDocumento12 páginasGrade 7 CH 4.05 The HeartMunmun AfnanAinda não há avaliações
- X - em - Lab ManualDocumento16 páginasX - em - Lab Manualrubeel.bcAinda não há avaliações
- 'T Hooft, Time in Powers of TenDocumento230 páginas'T Hooft, Time in Powers of TenEduardo Salgado E.Ainda não há avaliações
- NRSG 238 Fetal CirculationDocumento5 páginasNRSG 238 Fetal CirculationElijah MogoaAinda não há avaliações
- SchistosomiasisDocumento93 páginasSchistosomiasisJordz PlaciAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System ReadingDocumento4 páginasCirculatory System ReadingAlejandro PabonAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No. - Frog Dissection: RubricDocumento9 páginasExperiment No. - Frog Dissection: RubricEloisa Baquista BatengaAinda não há avaliações
- SirkulasiDocumento17 páginasSirkulasiJessica VanyaAinda não há avaliações