Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
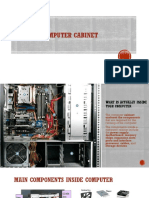
Computer Hardware Components
Enviado por
computerwizDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Computer Hardware Components
Enviado por
computerwizDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Rafay Sheikh
02/08/11
CPU/Microprocessor:
A CPU preforms calculations, does comparisons, and controls the other parts of the computer system. The microprocessor (CPU) is the heart of any computer, whether it is a desktop machine, a server or a laptop. A microprocessor (CPU) is a complete computation engine that is made-up on a single chip. The CPU is placed on the motherboard since the motherboard and is usually located near or under the heat-sink fan.
Ram/Memory:
The Ram temporarily stores data while you are working with it. Random access memory (RAM) is the best known form of computer memory. RAM is "random access memory" because you can access any memory cell directly if you know the row and column that intersect at that cell. Similar to the microprocessor (CPU), a memory chip is an integrated circuit (IC) made of millions of transistors and capacitors. In the most common form of computer memory, dynamic random access memory (DRAM), a transistor and a capacitor are paired to create a memory cell, which represents a single bit of data. The capacitor holds the bit of information as 0 or 1. The transistor acts as a switch that lets the control motherboard on the memory chip read the capacitor or change its state.
ROM:
Read-only memory (ROM), also known as firmware, is an integrated circuit programmed with specific data when it is manufactured. There are five basic ROM types:
ROM PROM EPROM EEPROM Flash memory
Each of the 5 types has their own unique characteristics, but they are all types of memory with two things in common. The Data stored in these chips is non-volatile -- it is not lost when power is removed. And the Data stored in these chips is either fixed or requires a special operation to change (unlike RAM, which can be changed as easily as it is read). This means that removing the power source from the chip will not cause it to lose any data.
BIOS:
Basic input/output system is a common Flash Memory of computers, it is also known as the BIOS. On almost every computer available, the BIOS makes sure all the other chips, hard drives, ports and CPU function together. Basically, it means your computer is ready to be used Computer contain a microprocessor as its central processing unit (CPU). The microprocessor is the hardware component. To get its work done, the microprocessor executes a set of instructions known as software. It turns out that the BIOS is the third type of software your computer needs to operate successfully. The two most other and familiar softwares are: The Operating System - The operating system provides a set of services for the applications running on your computer, and it also provides the fundamental user interface for your computer.
Rafay Sheikh
02/08/11
The Applications - Applications are pieces of software that are programmed to perform specific tasks.
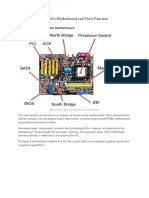
Motherboard:
The Motherboard is one piece of equipment that links everything together. A motherboard allows all the parts of your computer to receive power and communicate with one another. Motherboards affect a computer's capabilities and performance. The motherboard's main job is to hold the computer's microprocessor chip and let everything else connect to it. Everything that runs the computer or enhances its performance is either part of the motherboard or plugs into it the computer in any form. Some FORM FACTORS of a Motherboard include:
Socket for the Microprocessor: decides what kind of Central Processing Unit (CPU) the motherboard uses. Chipset: is part of the motherboard's logic system and is usually made of two parts -the North-side Bridge and the South-side Bridge. These two "bridges" connect the CPU to other parts of the computer. These are placed on the motherboard but are also connected to many components and hardware. (BIOS) Chip- Basic Input/output System: controls the most basic functions of the computer and performs a self-test every time you turn it on. Real time clock Chip: is a battery-operated chip that maintains basic settings and the system time and date. This is located on the motherboard. Buses: are a channels or path between the components in a computer. The idea of a bus is simple -- it lets you connect components to the computer's processor. Some of the components that you might want to connect include hard drives, memory (RAM), sound cards, and graphic cards. These are placed throughout the motherboards. (PCI) Peripheral Component Interconnect: can link up to five external components. Each of the five connectors for an external component can be replaced with two fixed devices on the motherboard. Also, you can have more than one PCI. The PCI bridge chip regulates the speed of the PCI bus independently of the CPU's speed. Only one PCI is located on the motherboard on a computer.
Power Supply:
A power supply basically converts the standard electrical power in to a form the computer can use. One of the most important hardware/component a computer requires is the power supply.
Rafay Sheikh
02/08/11
Without it, a computer would not work. The power supply converts the alternating current (AC) line from your home to the direct current (DC) needed by the personal computer. In a (PC), the power supply is the metal box usually found in a corner of the case. The power supply is visible from the back of many systems because it contains the power-cord receptacle and the cooling fan. Power supplies, often referred to as "switching power supplies", use switcher technology to convert the AC input to lower DC voltages. The typical voltages supplied are:
3.3 volts 5 volts 12 volts
When you push the power button it sends a 5-volt signal to the power supply to tell it when to turn on. The power supply also has a circuit that supplies 5 volts, called VSB for "standby voltage" even when it is officially "off", so that the button will work.
(CMOS)Complementary Metal-oxide Semiconductor:
The CMOS and CMOS battery allow a computer to store information even when the computer powers down. The battery provides continuous power. That battery serves two purposes: to feed the configuration memory (also called CMOS) and to feed the real time clock of the computer.
Hard Drive:
Hard disks change digital information into relatively permanent form. They give computers the ability to remember things when the power goes out. Data is stored onto the disk in the form of files. A file is simply a named collection of bytes. When a program running on the computer requests a file, the hard disk saves its bytes and sends them to the CPU one at a time. There are two ways to measure the performance of a hard disk:
Data rate - The data rate is the number of bytes per second that the drive can deliver to the CPU. Seek time - The seek time is the amount of time between when the CPU requests a file and when the first byte of the file is sent to the CPU.
Memory Cache:
Computers have both L1 and L2 caches, and many now also have L3 cache. Caching is an important computer process that appears on every computer in a variety of forms. There are memory caches, hardware and software disk caches, page caches and more. Virtual memory is also a form of caching. Virtual memory is a common part of most operating systems on desktop
Rafay Sheikh
02/08/11
computers. With virtual memory, what the computer can do is look at RAM for areas that have not been used recently and copy them onto the hard disk. This frees up space in RAM to load the new application. Memory cache is very important in terms of the computers performance.
Graphic Card:
Graphic Cards allow resolution settings, a screen displays over a million pixels, and the computer has to decide what to do with everyone in order to create an image. To do this, it needs a translator; something to take binary data from the CPU and turn it into a picture you can see. A graphics card's job is complex. The CPU, works in combination with software applications, sends information about the image to the graphics card. The graphics card decides how to use the pixels on the screen to create the image. It then sends that information to the monitor through a cable. Creating an image out of binary data is a demanding process. Without a graphics card to perform the necessary calculations, the workload would be too much for the computer to handle. The graphic card is placed on the motherboard, and is usually located behind the VGA or HDMI ports for direct interaction. The graphics card does this task using four main components:
A motherboard connection for data and power A processor to decide what to do with each pixel on the screen Memory to hold info about each pixel and to temporarily store completed pictures A monitor connection so you can see the final result
Sound Card:
Computers communicate digitally, using electrical instincts that represent 0s and 1s. Like a graphics card, a sound card translates between a computer's digital information and the outside world's analog information. They are located on the motherboard and are linked with buses because other components require their assistance. The most basic sound card is a printed circuit board that uses four components to translate analog and digital information:
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) A digital-to-analog converter (DAC) An ISA or PCI interface to connect the card to the motherboard Input and output connections for a microphone and speakers
Instead of separate ADCs and DACs, some sound cards use a coder/decoder chip, also called a CODEC, which performs both functions.
Optical Drive:
In computing, an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disk drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves near the light series as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from discs. Compact discs, DVDs, HD DVDs and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives. They are very commonly used in computers to read software and consumer media distributed in disc form, and to record discs for archival and data exchange.
Rafay Sheikh
02/08/11
Raid Array Controller:
Disk array controller is a device which manages the physical disk drives and presents them to the computer as logical units. It almost always traps hardware RAID, thus it is sometimes referred to as RAID controller. It also often provides additional disk cache. Disk array controller provides front-end interfaces and back-end interfaces. Back-end interface communicates with controlled disks. Front-end interface communicates with a computer's host adapter
External Bus Controllers:
FireWire: FireWire is a way to connect different pieces of equipment so they can easily and quickly share information. FireWire is mainly used to:
Fast transfer of data Ability to put lots of devices on the bus Ease of use Hot-pluggable ability Provision of power through the cable Plug-and-play performance Low cabling cost Low implementation cost
These also apply for USB and flash drives as they are the same!
(USB) Universal Serial Bus: The Universal Serial Bus gives you a single, standardized, easy-touse way to connect up to 127 devices to a computer. Many output devices can work with USBs:
Printers/Routers/Wireless Adapters Mouse/Keyboard/Speakers
Você também pode gostar
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12Ainda não há avaliações
- Parts of A Motherboard and Their FunctionDocumento7 páginasParts of A Motherboard and Their FunctionLanie MagannonAinda não há avaliações
- Parts of A Motherboard and Their FunctionDocumento12 páginasParts of A Motherboard and Their FunctionChristine Prestado100% (2)
- Parts of A Motherboard and Their FunctionDocumento9 páginasParts of A Motherboard and Their FunctionAjoyAinda não há avaliações
- Computer HardwareDocumento12 páginasComputer HardwareAce BorresAinda não há avaliações
- The MotherboardDocumento6 páginasThe MotherboardAko Si Dies ÜAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryDocumento11 páginasLab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryasavariAinda não há avaliações
- The Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocumento6 páginasThe Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsCavs Nek100% (1)
- MotherboardDocumento15 páginasMotherboardFredrick MugoAinda não há avaliações
- Parts of A MotherboardDocumento9 páginasParts of A Motherboardraze techAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter TwoDocumento36 páginasChapter TwoyonasAinda não há avaliações
- Lab ManualDocumento24 páginasLab ManualAhmar KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Motherboard Components and FunctionsDocumento4 páginasMotherboard Components and FunctionsCheryl Dumaguit BelaloAinda não há avaliações
- TO Computers: Neo BaDocumento186 páginasTO Computers: Neo BaNaïGa UmutesiAinda não há avaliações
- CHM LabDocumento85 páginasCHM LabSwarnim ShuklaAinda não há avaliações
- BIOS InstallationDocumento5 páginasBIOS InstallationArif ShaikhAinda não há avaliações
- The Computer System UnitDocumento18 páginasThe Computer System UnitJohn Alfredo Koykoy VicioAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento5 páginasChapter 1nashwah mahomedAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No.4Documento12 páginasExperiment No.4Kshitij DudheAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 (The Visible PC)Documento9 páginasChapter 3 (The Visible PC)Rifat HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Computer ComponentsDocumento3 páginasComputer ComponentsRobson MutsomekwaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment CS by ABRARDocumento9 páginasAssignment CS by ABRARThe King studioAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Notes 2Documento6 páginasBasic Notes 2jivan jyotAinda não há avaliações
- Processors (CPU) : Internal System Unit ComponentsDocumento5 páginasProcessors (CPU) : Internal System Unit ComponentsAnonymous ZzYOKUcOAinda não há avaliações
- Comfiguração Da BIOS-SETUPDocumento44 páginasComfiguração Da BIOS-SETUPEliasAinda não há avaliações
- Computer SystemDocumento10 páginasComputer Systemdhirendra lamsalAinda não há avaliações
- Tle ASSIGNMENTDocumento3 páginasTle ASSIGNMENTmax magsinoAinda não há avaliações
- A+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationDocumento40 páginasA+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationLindasharon AwourAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsDocumento29 páginasComputer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsRajendra PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Prashanti Institute of Technology & ScienceDocumento18 páginasPrashanti Institute of Technology & Sciencezalanipulkit0% (1)
- System Unit: Computer Hardware Servicing ReviewerDocumento4 páginasSystem Unit: Computer Hardware Servicing ReviewerGenevev ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocumento39 páginasUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Hardware Refers To The Physical Machine That Make Up The Computer Installation. These Are TheDocumento5 páginasComputer Hardware Refers To The Physical Machine That Make Up The Computer Installation. These Are Thekariukipoly0% (1)
- COMPUTER CollegeDocumento26 páginasCOMPUTER CollegeHyper RiderAinda não há avaliações
- The Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocumento9 páginasThe Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsJosekutty N Joseph75% (4)
- Components of CPU and Their Function: United International UniversityDocumento13 páginasComponents of CPU and Their Function: United International UniversityNaureen Jahan MouAinda não há avaliações
- External Hard Drive Mac External Hard Drive Network & Tablet Hard Drive Internal Drive Solid State Drive (SSD)Documento5 páginasExternal Hard Drive Mac External Hard Drive Network & Tablet Hard Drive Internal Drive Solid State Drive (SSD)Hasibul AlamAinda não há avaliações
- CMN Lab Expt-1Documento3 páginasCMN Lab Expt-1Aaryan SinghAinda não há avaliações
- A Digital Computer System (DCS) : HardwareDocumento36 páginasA Digital Computer System (DCS) : HardwareMădălin NiculescuAinda não há avaliações
- Architecture of A Computer SystemDocumento6 páginasArchitecture of A Computer SystemJohn VibarAinda não há avaliações
- ReportDocumento8 páginasReportapi-3734554100% (1)
- Basic Computer Hardware MaintenanceDocumento35 páginasBasic Computer Hardware Maintenanceshanea bucknor89% (9)
- Installation and Maintenance 1Documento4 páginasInstallation and Maintenance 1West100% (1)
- Sitti Analyn P. Omar Dcmt-1 Batch-2Documento15 páginasSitti Analyn P. Omar Dcmt-1 Batch-2Maher ArakamaAinda não há avaliações
- Computer System ComponentsDocumento11 páginasComputer System ComponentsNoone F. moonAinda não há avaliações
- CHT Practical 1 KUKDocumento3 páginasCHT Practical 1 KUKDhruv SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersDocumento12 páginasComputer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersRohan DhawaAinda não há avaliações
- System Unit Components: AssignmentDocumento8 páginasSystem Unit Components: AssignmentNhil Cabillon Quieta100% (1)
- 1 Hardware Components WorksheetDocumento9 páginas1 Hardware Components Worksheetapi-267772822Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 - The Components of The System Unit - ReviewDocumento2 páginasChapter 4 - The Components of The System Unit - ReviewYūkiHaseAinda não há avaliações
- ComputerDocumento13 páginasComputeryicho864Ainda não há avaliações
- 2.10 Inside A Computer Cabinet: 2.10.1 MotherboardDocumento3 páginas2.10 Inside A Computer Cabinet: 2.10.1 MotherboardAashish KandelAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Computing Lab: Assignment On Assignment NameDocumento7 páginasIntroduction To Computing Lab: Assignment On Assignment NameHamza KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Module IDocumento55 páginasModule IHrushikesh DanduAinda não há avaliações
- Parts of A MotherboardDocumento5 páginasParts of A MotherboardKeil Yow Yow YowAinda não há avaliações
- Inside A Computer CabinetDocumento14 páginasInside A Computer CabinetJavid HamdardAinda não há avaliações
- Lec02 - Components of ComputersDocumento17 páginasLec02 - Components of ComputersBilal ImranAinda não há avaliações
- Motherboard ElementsDocumento2 páginasMotherboard ElementsMithz SuneAinda não há avaliações
- Installing Windows On The MinnowBoardDocumento6 páginasInstalling Windows On The MinnowBoardalcuin99Ainda não há avaliações
- B08DC9ZWQXDocumento551 páginasB08DC9ZWQXanisAinda não há avaliações
- Danger Object FilingDocumento4 páginasDanger Object FilinghectorjazzAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Mips DatapathDocumento55 páginas6 Mips Datapath1352 : NEEBESH PADHYAinda não há avaliações
- IMS Status CodeDocumento5 páginasIMS Status Codedirceu_bimontiAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle Tips and Techniques 132894Documento48 páginasOracle Tips and Techniques 132894Tarun KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Swati GuptaDocumento22 páginasSwati GuptamanuAinda não há avaliações
- UI PathDocumento22 páginasUI PathPreethiAinda não há avaliações
- SAP - CDS - PLANVIZ - Safeguard Performance of ABAP CDS Views - Part 3 Rules For Good Performance of CDS ViewsDocumento13 páginasSAP - CDS - PLANVIZ - Safeguard Performance of ABAP CDS Views - Part 3 Rules For Good Performance of CDS ViewsfiotuiAinda não há avaliações
- Learning To Hash For Indexing Big Data - A SurveyDocumento22 páginasLearning To Hash For Indexing Big Data - A SurveyAndrás NagyAinda não há avaliações
- ORACLE PLSQL Interview Questions You'Ll Most Likely Be Asked by Vibrant PublishersDocumento8 páginasORACLE PLSQL Interview Questions You'Ll Most Likely Be Asked by Vibrant PublishersRaghavendra KamurthiAinda não há avaliações
- Event LogDocumento107 páginasEvent LogCB ProductionsAinda não há avaliações
- AlienVault USM 4.8 5.x System Backup RestoreDocumento11 páginasAlienVault USM 4.8 5.x System Backup RestorepaulohrodriguesAinda não há avaliações
- KX-NS1000: PC Programming ManualDocumento792 páginasKX-NS1000: PC Programming ManualChandra TioAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Book MaterialDocumento69 páginasComputer Book MaterialAqib Asad100% (1)
- A New Approach For Measuring Latency and Bandwidth in Wireless Ad Hoc NetworkDocumento8 páginasA New Approach For Measuring Latency and Bandwidth in Wireless Ad Hoc NetworkJohn TimothyAinda não há avaliações
- HL7 Ref Guide2.5.1Documento20 páginasHL7 Ref Guide2.5.1scribd9177100% (1)
- CT Phone Interview Guide: Tableau Developers: August 2015 December 2015Documento6 páginasCT Phone Interview Guide: Tableau Developers: August 2015 December 2015savan kalakarAinda não há avaliações
- Using Sub Queries in MySQL (Part 2)Documento20 páginasUsing Sub Queries in MySQL (Part 2)api-3747861Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 9 - LAB - Database SecurityDocumento8 páginasChapter 9 - LAB - Database SecurityThy TrânAinda não há avaliações
- AIX Operating System Hardening Procedures & Security GuideDocumento15 páginasAIX Operating System Hardening Procedures & Security GuideAnuragBoraAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle Database 12c High Availability New Features - D79794GC10 - 1080544 - USDocumento4 páginasOracle Database 12c High Availability New Features - D79794GC10 - 1080544 - USJinendraabhiAinda não há avaliações
- Kubernetes - CKA - 0800 - Networking-V1.2Documento211 páginasKubernetes - CKA - 0800 - Networking-V1.2Ayushi DubeyAinda não há avaliações
- Classful IP Addressing (Cont.) : Address Prefix Address SuffixDocumento25 páginasClassful IP Addressing (Cont.) : Address Prefix Address SuffixGetachew ShambelAinda não há avaliações
- Getting StartedDocumento1 páginaGetting StartedMakni YassineAinda não há avaliações
- FTBLauncher LogDocumento6 páginasFTBLauncher LogJose RafaelAinda não há avaliações
- DS8000 PDFDocumento682 páginasDS8000 PDFChidanand BandihalAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Internet Programming: 5ECTS, 2lec, 2labDocumento18 páginasIntroduction To Internet Programming: 5ECTS, 2lec, 2labrobel ragoAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Anchored Datatype in PL - SQL - RebellionRiderDocumento2 páginas4 Anchored Datatype in PL - SQL - RebellionRiderkunche gangadhara raoAinda não há avaliações
- RHCSA Part 1 Sander Van VugtDocumento59 páginasRHCSA Part 1 Sander Van VugtVynlovanthAinda não há avaliações