Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Pathophysiology of Tetanus
Enviado por
ehmem18Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Pathophysiology of Tetanus
Enviado por
ehmem18Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Michael Erick Virtucio Jean Paola Yap
Section4-D Group 9-b
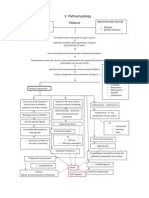
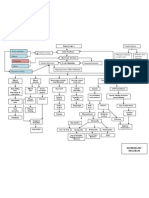
Pathophysiology of Tetanus
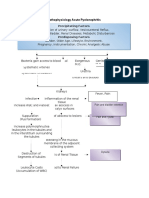
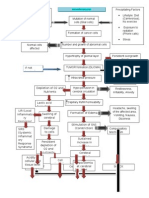
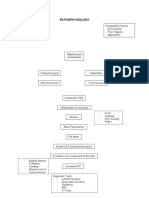
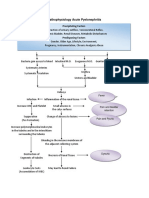
Precipitating Factors: Work (Farming) Exposure to bacteria (wounds/lacerations) No previous history of tetanus immunization
Clostridium tetani bacteria containing virulence plasmids enter wound
Toxins produced by growing cells Spores germinate under anaerobic conditions
Vegetative growth
Spore
Cell lysis occurs Release of bacterial endotoxins into surrounding
Tetanolysin
Tetanospasmin (potent neurotoxin)
Potentiating of infection Toxin circulated around the body through bloodstream and lymphatic system Enter Central Nervous System (CNS) along peripheral nerves
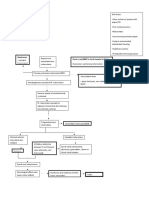
Release of biochemical mediators of inflammatory response (histamine, bradykinin)
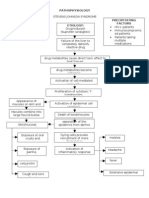
Michael Erick Virtucio Jean Paola Yap
Section4-D Group 9-b
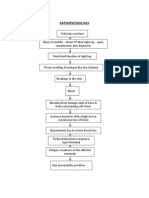
Inflammatory response initiated
Toxin not able to pass through blood-brain barrier
Increased capillary permeability Increased blood flow
WBCs such as neutrophils and monocytes enter Phagocytosis and removal of debris occur
Toxin makes its way to spinal cord
Toxin enters the CNS Toxin taken up by neuromuscular junction Crosses to synaptic cleft Irreversibly binds to gangliosides at presynaptic inhibitory motor nerve endings
Swellin
Rednes Phagocytes release endogenous pyrogens
Stimulation of hypothalamus to increase body temperature Fever
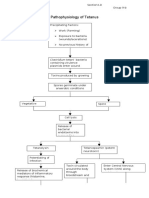
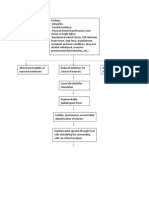
Taken up by preganglionic neuron axon through endocytosis Blocks the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters (glycine and GABA) Excitatory activities unregulated Generalized tonic muscle spasms occur
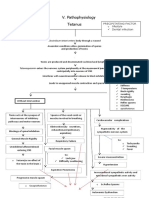
Pain
Pharynx
Cranial
Facial
Masseter
Glottis Respiratory muscles
Aspiration of oral secretions
Rapid firing of impulses
Pneumonia
Irritability of neurons Restless ness
Risus sardonicu s (fixed smile and elevated eyebrows )
Lockjaw
Failure to speak or cry
GI (laryn x, abdo minal wall)
Chest wall muscle Chest wall rigidity
Diaphrag m
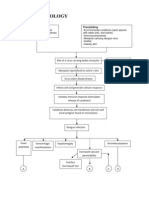
Michael Erick Virtucio Jean Paola Yap
Section4-D Group 9-b
Headache Asphyxiation
Hypoxemia
Cardiac Arrest
DEATH
Respiratory failure
Treatment 1. HTIG (Human tetanus Immunoglobulin): 3000-6000 units/IM 2. ATS (Anti tetanus Serum): 5000-10000 units/ IV IM 3. Antibiotics: Inj. Penicillin G 200000/kg in 4 divided Doses for 2 weeks 4. Sedation: Inj. Diazapam 0.1 0.2 mg/kg/ 4 hourly Inj. Medazolam 1mg/ kg 5. Neuromuscular Blocking Agents: Inj. Pancuronium Bromide IV Infusion. Atracurium Besylate 6. Supportive Care:
Isolation, Avoid Stimulation Vital monitoring( Respiratory Rate, SPO2) Oral Suctioning Keep Nil Per Oral, Feed after 5 days Place Nasogastri tube, Hydration Intake of 3500-4000 Calories and at least 150g of protein
Você também pode gostar
- B. Schematic Pathophysiology TETANUS-a Disease Condition Caused by Clostridium TetaniDocumento3 páginasB. Schematic Pathophysiology TETANUS-a Disease Condition Caused by Clostridium TetaniStephanie Ann L. Torrecampo83% (6)
- Pathophysiology of TetanusDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of TetanusChristopher John Aguelo100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of TB MeningitisDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of TB Meningitisreanzz100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Stevens Johnson Syndrome SJSDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of Stevens Johnson Syndrome SJSDavid Villanueva50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of TetanusDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of TetanusAnitha SuprionoAinda não há avaliações
- Tetanus Case StudyDocumento57 páginasTetanus Case StudyXy-Za Roy Marie100% (15)
- Rabies PreventionDocumento3 páginasRabies PreventionFrinkaWijaya100% (1)
- DengueDocumento4 páginasDengueKathleen DimacaliAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology DengueDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology DengueKevin50% (2)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocumento2 páginasPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverMaynelle Caspe100% (2)
- Electrical Burn PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaElectrical Burn PathophysiologydanicaAinda não há avaliações
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramDocumento4 páginasDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramCyrus De Asis67% (3)
- Pathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisAnonymous 75TDy2y100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CVD InfarctDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of CVD InfarctIris Caberte86% (7)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Meningioma (Edited Version)Documento2 páginasPa Tho Physiology of Meningioma (Edited Version)Niño Villamarin75% (8)
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of AppendicitisAbbie Tantengco100% (3)
- Rabies PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaRabies PathophysiologyMichael Urrutia100% (1)
- Fracture PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaFracture PathophysiologyIrene Joy Gomez100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseLeLi CortezAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology of LeptospirosisDocumento1 páginaPhysiology of LeptospirosisYum C80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Tetanus: Clostridium Tetani BacteriaDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Tetanus: Clostridium Tetani BacteriaSlepy chng100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Brain TumorsDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Brain TumorsNavjot Brar92% (13)
- Pathophysiology (Glioma)Documento2 páginasPathophysiology (Glioma)peterjong100% (2)
- Diphtheria Schematic Diagram (Pathophysiology0Documento3 páginasDiphtheria Schematic Diagram (Pathophysiology0Kathlene Boleche100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Documento2 páginasPathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Rodel Yacas100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverShiella Heart Malana100% (1)
- DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT SubjectiveDocumento1 páginaDIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT Subjectivemawel100% (1)
- Pathophysiology LeptospirosisDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology Leptospirosisjeoffrey_castro100% (3)
- Pathophysiology - AppendicitisDocumento5 páginasPathophysiology - AppendicitisAzielle Joyce RosquetaAinda não há avaliações
- Book-Based: Pathophysiology of Allergic RhinitisDocumento2 páginasBook-Based: Pathophysiology of Allergic RhinitisJeraldine Corpuz PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseIJ Ayop86% (7)
- Appendicitis Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocumento1 páginaAppendicitis Pathophysiology - Schematic Diagrambayu jaya adigunaAinda não há avaliações
- Schematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Giving BirthDocumento2 páginasSchematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Giving BirtharianeAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study AppendicitisDocumento6 páginasCase Study AppendicitisPrincess Camille ArceoAinda não há avaliações
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Bacterial Meningitis 2Documento2 páginasPATHOPHYSIOLOGY Bacterial Meningitis 2Luis Leh100% (2)
- Pathophysiology - PyelonephritisDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology - PyelonephritisFrancis Kevin Sagudo92% (13)
- Myasthenia-Gravis Concept MapDocumento1 páginaMyasthenia-Gravis Concept MapAngelo Dela Cruz VillaromanAinda não há avaliações
- NCP (Age)Documento5 páginasNCP (Age)justinmhayAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocumento1 páginaDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramChristelle GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic FeverDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Rheumatic FeverGehlatin Tumanan100% (2)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF BUERGER DiseaseDocumento1 páginaPATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF BUERGER DiseaseJedson Vizcayno100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Potts DiseaseDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Potts DiseaseJoanna Marie M. dela Cruz100% (5)
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888Ainda não há avaliações
- Seizure PathophysiologyDocumento2 páginasSeizure Pathophysiologyqwertyuiop60% (10)
- Rabies Case StudyDocumento6 páginasRabies Case StudySheryll Almira HilarioAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Gastric Cancer Precipitating Factors: - Predisposing FactorsDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Gastric Cancer Precipitating Factors: - Predisposing FactorsJu Lie AnnAinda não há avaliações
- CASE STUDY 2011-CellulitisDocumento34 páginasCASE STUDY 2011-Cellulitiscyrilcarinan75% (4)
- Chickenpox 1Documento7 páginasChickenpox 1Nica Joy CandelarioAinda não há avaliações
- Management of TetanusDocumento7 páginasManagement of TetanusamutiarAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of TetanospasminDocumento23 páginasEffect of Tetanospasminaparna ranjith markoseAinda não há avaliações
- Tetanus ADocumento3 páginasTetanus ASadaqat KhanAinda não há avaliações
- TetanusDocumento4 páginasTetanusAjay Pal NattAinda não há avaliações
- Tetanus As A Childhood Disease Common in Children Under Age 5Documento12 páginasTetanus As A Childhood Disease Common in Children Under Age 5Adediran DolapoAinda não há avaliações
- !tetanus MDocumento12 páginas!tetanus MInam KhanAinda não há avaliações
- K6 - Tetanus PEDIATRICDocumento23 páginasK6 - Tetanus PEDIATRICbanuperiahAinda não há avaliações
- Management of Patients With Neurologic DisordersDocumento9 páginasManagement of Patients With Neurologic DisordersJames Felix Gallano GalesAinda não há avaliações
- 351255266-Tetanus Id enDocumento14 páginas351255266-Tetanus Id enRezki IndriyantiyusufAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of TetanospasminDocumento23 páginasEffect of Tetanospasminaparna ranjith markoseAinda não há avaliações
- TetanusDocumento37 páginasTetanusMuwanga faizoAinda não há avaliações
- Tetanus: Eu MBCHB 3 DR D M KillingoDocumento44 páginasTetanus: Eu MBCHB 3 DR D M KillingoArjay VisitacionAinda não há avaliações
- EN 14103 - ThermoDocumento4 páginasEN 14103 - ThermoLuciana TrisnaAinda não há avaliações
- 螳螂拳七長八短 - Tanglangquan Qi Chang Ba Duan - Tanglangquan's Seven Long & Eight Short - Lessons Learned in the World of Martial ArtsDocumento2 páginas螳螂拳七長八短 - Tanglangquan Qi Chang Ba Duan - Tanglangquan's Seven Long & Eight Short - Lessons Learned in the World of Martial ArtsGianfranco MuntoniAinda não há avaliações
- Speaking With Confidence: Chapter Objectives: Chapter OutlineDocumento12 páginasSpeaking With Confidence: Chapter Objectives: Chapter OutlinehassanAinda não há avaliações
- Project Risk Management in Hydropower Plant Projects A Case Study From The State-Owned Electricity Company of IndonesiaDocumento16 páginasProject Risk Management in Hydropower Plant Projects A Case Study From The State-Owned Electricity Company of IndonesiaJoli SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 10Documento9 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 10christian josh magtarayoAinda não há avaliações
- Colorado Wing - Sep 2012Documento32 páginasColorado Wing - Sep 2012CAP History LibraryAinda não há avaliações
- Ebp Cedera Kepala - The Effect of Giving Oxygenation With Simple Oxygen Mask andDocumento6 páginasEbp Cedera Kepala - The Effect of Giving Oxygenation With Simple Oxygen Mask andNindy kusuma wardaniAinda não há avaliações
- Operating Manual For Kipor Mobile Gic-Pg Kipor Quick Guide OmDocumento8 páginasOperating Manual For Kipor Mobile Gic-Pg Kipor Quick Guide OmIan CutinAinda não há avaliações
- Scorpio PDFDocumento3 páginasScorpio PDFnimi2364010Ainda não há avaliações
- Atomic Structure RevisionDocumento4 páginasAtomic Structure RevisioncvAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulics - MKM - DLX - Parts - Catalogue MAR 14 PDFDocumento33 páginasHydraulics - MKM - DLX - Parts - Catalogue MAR 14 PDFRS Rajib sarkerAinda não há avaliações
- Craig - 4353 TX CobraDocumento3 páginasCraig - 4353 TX CobraJorge ContrerasAinda não há avaliações
- STAT 713 Mathematical Statistics Ii: Lecture NotesDocumento152 páginasSTAT 713 Mathematical Statistics Ii: Lecture NotesLiban Ali MohamudAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture On Metallurgical BalancesDocumento14 páginasLecture On Metallurgical BalancesVladimir LopezAinda não há avaliações
- DEMU COUP - Leviat - 17 1 EDocumento28 páginasDEMU COUP - Leviat - 17 1 EJianhua WuAinda não há avaliações
- Cross Border Pack 2 SumDocumento35 páginasCross Border Pack 2 SumYến Như100% (1)
- Raw Material Chemical AnalysisDocumento41 páginasRaw Material Chemical AnalysisVinod Kumar VermaAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Elements of Firearms TrainingDocumento6 páginas12 Elements of Firearms TraininglildigitAinda não há avaliações
- Aeration PaperDocumento11 páginasAeration PapersehonoAinda não há avaliações
- Gexcon DDT Scotts PresentationDocumento33 páginasGexcon DDT Scotts PresentationMochamad SafarudinAinda não há avaliações
- TM 55 1520 400 14 PDFDocumento227 páginasTM 55 1520 400 14 PDFOskar DirlewangerAinda não há avaliações
- 02-779 Requirements For 90-10 Copper - Nickel - Alloy Part-3 TubingDocumento47 páginas02-779 Requirements For 90-10 Copper - Nickel - Alloy Part-3 TubingHattar MAinda não há avaliações
- DVH-P4950 P4050Documento111 páginasDVH-P4950 P4050roto44100% (1)
- Hydrostatics-Assignment 3: MPI td9Documento2 páginasHydrostatics-Assignment 3: MPI td9whoeverAinda não há avaliações
- MKRS Training ProfileDocumento10 páginasMKRS Training ProfileZafri MKRS100% (1)
- User'S Design Requirements For Single Chamber Pressure VesselsDocumento8 páginasUser'S Design Requirements For Single Chamber Pressure VesselspjsanchezmAinda não há avaliações
- The Beginningof The Church.R.E.brownDocumento4 páginasThe Beginningof The Church.R.E.brownnoquierodarinforAinda não há avaliações
- Elementary Graph Theory: Robin Truax March 2020Documento15 páginasElementary Graph Theory: Robin Truax March 2020Jefferson WidodoAinda não há avaliações
- Pid 14 MT23 160412Documento20 páginasPid 14 MT23 160412Amol ChavanAinda não há avaliações
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseNo EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (69)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessAinda não há avaliações
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincNo EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (137)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNo Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceNo EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (517)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNo EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeAinda não há avaliações
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseNo EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (52)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldNo EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (597)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainNo EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (65)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesNo EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (397)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNo EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (393)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNo EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceNo EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (18)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomNo EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (216)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorNo EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (137)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainNo EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (111)
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationNo EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (37)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedNo EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (11)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemNo EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (115)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildNo EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (44)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionNo EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (812)