Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Intranet: Computer Network Internet Protocol Network Operating System
Enviado por
MANAPDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Intranet: Computer Network Internet Protocol Network Operating System
Enviado por
MANAPDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
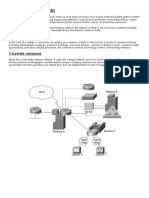
INTRANET
An intranet is a private computer network that uses Internet Protocol technology to securely share any part of an organization's information or network operating system within that organization. The term is used in contrast to internet, a network between organizations, and instead refers to a network within an organization. Sometimes the term refers only to the organization's internal website, but may be a more extensive part of the organization's information technology infrastructure. It may host multiple private websites and constitute an important component and focal point of internal communication and collaboration. Any of the well known Internet protocols may be found in an intranet, such as HTTP (web services), SMTP (e-mail), and FTP (file transfer protocol). Internet technologies are often deployed to provide modern interfaces to legacy information systems hosting corporate data. An intranet can be understood as a private analog of the Internet, or as a private extension of the Internet confined to an organization. The first intranet websites and home pages began to appear in organizations in 1996-1997. Although not officially noted, the term intranet first became common-place among early adopters, such as universities and technology corporations, in 1992. Intranets have also contrasted with extranets. While intranets are generally restricted to employees of the organization, extranets may also be accessed by customers, suppliers, or other approved parties.[1] Extranets extend a private network onto the Internet with special provisions for authentication, authorization and accounting (AAA protocol). Intranets may provide a gateway to the Internet by means of a network gateway with a firewall, shielding the intranet from unauthorized external access. The gateway often also implements userauthentication, encryption of messages, and often virtual private network (VPN) connectivity for off-site employees to access company information, computing resources and internal communication.
EXTRANET
An extranet is a computer network that allows controlled access from the outside, for specific business or educational purposes. An extranet can be viewed as an extension of a company's
intranetthat is extended to users outside the company, usually partners, vendors, and suppliers. It has also been described as a "state of mind" in which the Internet is perceived as a way to do business with a selected set of other companies (business-to-business, B2B), in isolation from all other Internet users. In contrast, business-to-consumer (B2C) models involve known servers of one or more companies, communicating with previously unknown consumer users. An extranet is like a DMZ in that it provides access to needed services for channel partners, without granting access to an organization's entire network.
INETRNET
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) to serve billions of users worldwide. It is a network of networks that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks, of local to global scope, that are linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range ofinformation resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents of the World Wide Web (WWW) and the infrastructure to support electronic mail. I
SP (Internet Service Provider)
An Internet service provider (ISP) is a company that provides access to the Internet. Access ISPs connect customers to the Internet using copper, wireless or fiber connections. Hosting ISPs lease server space for smaller businesses and host other people servers (colocation). Transit ISPs provide large tubes for connecting hosting ISPs to access ISPs.
Você também pode gostar
- Computer Networking Beginners Guide: An Introduction on Wireless Technology and Systems Security to Pass CCNA Exam, With a Hint of Linux Programming and Command LineNo EverandComputer Networking Beginners Guide: An Introduction on Wireless Technology and Systems Security to Pass CCNA Exam, With a Hint of Linux Programming and Command LineAinda não há avaliações
- Intranet Network OverviewDocumento1 páginaIntranet Network OverviewDiksha GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Working of InternetDocumento7 páginasWorking of InternetSaba JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Types of NetworksDocumento14 páginasTypes of Networksm0rph1sAinda não há avaliações
- Computer NetworkDocumento2 páginasComputer NetworkMadison SmithAinda não há avaliações
- E BusinessDocumento29 páginasE BusinessTuryamureeba JuliusAinda não há avaliações
- The IntranetDocumento3 páginasThe IntranetM-soft solutionsAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Network LayerDocumento33 páginasChapter 3 Network LayerFiromsa DineAinda não há avaliações
- Networks Seminar ReportDocumento22 páginasNetworks Seminar ReportHarshaAchyutuni100% (1)
- Intranet, Extranet, Internet, Wan Lan, ManDocumento4 páginasIntranet, Extranet, Internet, Wan Lan, Manmaaheen100% (2)
- Seminar Report on Computer Networking: Distributed ComputingDocumento44 páginasSeminar Report on Computer Networking: Distributed ComputingShubham KhotkarAinda não há avaliações
- Internet Vs IntranetDocumento11 páginasInternet Vs IntranetSvb CharyAinda não há avaliações
- Internet Intranet and ExtranetDocumento3 páginasInternet Intranet and ExtranetANUJ GIRIAinda não há avaliações
- Internet 03Documento13 páginasInternet 03Mano KaranAinda não há avaliações
- Internet: Network of Networks That Consists of Millions of Private, Public, Academic, BusinessDocumento16 páginasInternet: Network of Networks That Consists of Millions of Private, Public, Academic, BusinessVaishak KoovodeAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT-3: Telecommunication and NetworksDocumento13 páginasUNIT-3: Telecommunication and NetworksSameer YadavAinda não há avaliações
- The SPB College of Business Administration: Use of Internet in Various FieldDocumento13 páginasThe SPB College of Business Administration: Use of Internet in Various FieldhemalpandyaAinda não há avaliações
- Internet: Difference Between Extranet, Internet and Intranet?Documento5 páginasInternet: Difference Between Extranet, Internet and Intranet?Rinku SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is The Need of Develop An Intranet Based System When Internet Based System Is Possible? Explain With An Example. Answer 1Documento4 páginasWhat Is The Need of Develop An Intranet Based System When Internet Based System Is Possible? Explain With An Example. Answer 1001nileshkAinda não há avaliações
- E BUSINESS NOTESDocumento10 páginasE BUSINESS NOTESvandanaAinda não há avaliações
- The Differences Between Intranets, Extranets and the InternetDocumento2 páginasThe Differences Between Intranets, Extranets and the Internetvijayab7Ainda não há avaliações
- Internet HandoutDocumento66 páginasInternet HandoutImrana mannirAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Network DiagramDocumento7 páginasWhat Is Network DiagramOundo SamAinda não há avaliações
- ERM Definition and ExamplesDocumento12 páginasERM Definition and ExamplesZain Ul AbdeenAinda não há avaliações
- Web Technologies: 1. InternetDocumento9 páginasWeb Technologies: 1. InternetJayakrishnan B NairAinda não há avaliações
- 50023iiird Semester Addon Course ExaminationDocumento13 páginas50023iiird Semester Addon Course ExaminationVinayaka McAinda não há avaliações
- IT NotesDocumento32 páginasIT Notesdordelderek the lastAinda não há avaliações
- Intranet Basics: Benefits, Uses and How It WorksDocumento15 páginasIntranet Basics: Benefits, Uses and How It WorksUrja JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Adamu Abubakar Abdulrazak AssignDocumento4 páginasAdamu Abubakar Abdulrazak AssignAbdullahi AwwalAinda não há avaliações
- Basics of Internet, Intranet and ExtranetDocumento31 páginasBasics of Internet, Intranet and ExtranetankitpareekAinda não há avaliações
- E CommerceDocumento2 páginasE CommerceLavi KukretiAinda não há avaliações
- CONTENTS FOR E-CommerceDocumento5 páginasCONTENTS FOR E-CommerceThe PaletteAinda não há avaliações
- Internet, Intranet and Extranets: Presentation ByDocumento25 páginasInternet, Intranet and Extranets: Presentation BysurbhibarveAinda não há avaliações
- IntranetDocumento6 páginasIntranetMayank MittalAinda não há avaliações
- ExtranetDocumento2 páginasExtranetHeavenStudio TimisoaraAinda não há avaliações
- Network TypesDocumento1 páginaNetwork Typesthe.elysian.shop2022Ainda não há avaliações
- To Intranet: Presented by - Isha Javed. MBA (G) Semester-1, Section-A. Enrollment No. 68Documento6 páginasTo Intranet: Presented by - Isha Javed. MBA (G) Semester-1, Section-A. Enrollment No. 68Kunal ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Internet Technologies OverviewDocumento29 páginasInternet Technologies OverviewAditi KuteAinda não há avaliações
- 1 4907038154730504391 PDFDocumento116 páginas1 4907038154730504391 PDFWILLIAM FERNANDO OCAMPO GUERREROAinda não há avaliações
- Internetintranetandextranet 121207230205 Phpapp01Documento12 páginasInternetintranetandextranet 121207230205 Phpapp01api-231294003Ainda não há avaliações
- Principles of E-Commerce - Unit 2Documento18 páginasPrinciples of E-Commerce - Unit 2Xcill EnzeAinda não há avaliações
- Internet, Intranet and ExtranetDocumento9 páginasInternet, Intranet and ExtranetRicHArdAinda não há avaliações
- Internet, Intranet and ExtranetDocumento11 páginasInternet, Intranet and Extranetktkalai selviAinda não há avaliações
- Internet, Intranet, ExtranetDocumento14 páginasInternet, Intranet, Extranetmotz100% (8)
- Teleconferences: Uses of The IntranetDocumento14 páginasTeleconferences: Uses of The IntranetAniket SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Abubakar Hudu AssignmentDocumento4 páginasAbubakar Hudu AssignmentAbdullahi AwwalAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment CISDocumento7 páginasAssignment CISTashfeen AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Internet, Intranet and ExtranetDocumento12 páginasInternet, Intranet and ExtranetJehra Mae Sevillano ÜAinda não há avaliações
- Internet, Intranet, ExtranetDocumento35 páginasInternet, Intranet, ExtranetFarah Atika Ar Azmi100% (1)
- Internet Technology -Unit 1Documento22 páginasInternet Technology -Unit 1durgagarg10051998Ainda não há avaliações
- Internet, Intranets and ExtranetsDocumento20 páginasInternet, Intranets and ExtranetsPRAO6005100% (7)
- Module 3newDocumento46 páginasModule 3newAditi KuteAinda não há avaliações
- Types of NetworksDocumento2 páginasTypes of NetworksTsarina Von HAinda não há avaliações
- Notes ItDocumento18 páginasNotes ItkunwarjeetAinda não há avaliações
- CSC 325 Exam Question Marking SchemeDocumento11 páginasCSC 325 Exam Question Marking SchemeFaisal AliAinda não há avaliações
- Extranet: Computer NetworkDocumento4 páginasExtranet: Computer NetworkkhawasikarAinda não há avaliações
- Network Types, Components & ClassificationsDocumento24 páginasNetwork Types, Components & ClassificationsAli AmarAinda não há avaliações
- Iotunit#1Documento128 páginasIotunit#1Sharad PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Computer 7th ClassDocumento16 páginasIntroduction To Computer 7th ClassMoazzam Irfan IrfanAinda não há avaliações
- Intranet, Extranet, InternetDocumento1 páginaIntranet, Extranet, InternetPritisikha BordoloiAinda não há avaliações
- TrussesDocumento10 páginasTrussesMANAPAinda não há avaliações
- Influence LineDocumento5 páginasInfluence LineMANAPAinda não há avaliações
- Shear Force and Bending Moment Full ReportDocumento8 páginasShear Force and Bending Moment Full ReportMANAPAinda não há avaliações
- CableDocumento7 páginasCableMANAPAinda não há avaliações
- TITLE: Torsion TestDocumento8 páginasTITLE: Torsion TestMANAPAinda não há avaliações
- Answers To The Given Assignment Using The Group Creativity and Innovativeness. TheDocumento7 páginasAnswers To The Given Assignment Using The Group Creativity and Innovativeness. TheMANAPAinda não há avaliações
- Means Are Guided and Given To The Students. However The Answers To TheDocumento8 páginasMeans Are Guided and Given To The Students. However The Answers To TheMANAPAinda não há avaliações
- Intranet: Computer Network Internet Protocol Network Operating SystemDocumento3 páginasIntranet: Computer Network Internet Protocol Network Operating SystemMANAPAinda não há avaliações
- BKPDocumento38 páginasBKPabhiramAinda não há avaliações
- STP Part2 - CheatSheet ATech (Waqas Karim)Documento1 páginaSTP Part2 - CheatSheet ATech (Waqas Karim)Waqas KarimAinda não há avaliações
- How To Set Up Stream Media Server Via iVMS-4200Documento12 páginasHow To Set Up Stream Media Server Via iVMS-4200mifereAinda não há avaliações
- Chap. 4: SubnettingDocumento56 páginasChap. 4: SubnettingNdiz The bestAinda não há avaliações
- Cloud Service Mock Exam: Right or WrongDocumento11 páginasCloud Service Mock Exam: Right or WrongAbdessamad Elamriche100% (1)
- System Networking PDFDocumento432 páginasSystem Networking PDFEmmanuel Rodriguez100% (1)
- Nokia TrainingDocumento47 páginasNokia TrainingJoonAinda não há avaliações
- Ankit Baijal - L 1 Support ErDocumento5 páginasAnkit Baijal - L 1 Support ErmaneetduttaAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Simulation and Design of UniversityDocumento6 páginas2 Simulation and Design of UniversityNaveenAinda não há avaliações
- Lab1 HPDocumento9 páginasLab1 HPVictor Hugo Garay SaezAinda não há avaliações
- IMS Basic Signaling Procedure SIP IMS ProceduresDocumento66 páginasIMS Basic Signaling Procedure SIP IMS ProceduresRanjeet SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Site Configuration Manual RMSDocumento29 páginasSite Configuration Manual RMSMuhammad Ali100% (2)
- Evaluación de Habilidades Prácticas de PT (PTSA) RespuestasDocumento10 páginasEvaluación de Habilidades Prácticas de PT (PTSA) Respuestasandresgo123Ainda não há avaliações
- Opening Firewall Ports: Amazon - EC2Documento4 páginasOpening Firewall Ports: Amazon - EC2Nikhitha ThotaAinda não há avaliações
- JhulDocumento5 páginasJhul037 Muhammad SupriyadiAinda não há avaliações
- Prosafe VPN Firewall Fvs318V3 Reference Manual: 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, Ca 95134 UsaDocumento184 páginasProsafe VPN Firewall Fvs318V3 Reference Manual: 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, Ca 95134 UsahernanAinda não há avaliações
- Case Studies Network Gokulatheerthan MDocumento15 páginasCase Studies Network Gokulatheerthan Mmonya1911Ainda não há avaliações
- FOS v6.4.0b RNDocumento58 páginasFOS v6.4.0b RNPraveen KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Hybrid Deployment in Office 365 - Checklist and Pre Requirements - Part 3 of 3Documento7 páginasHybrid Deployment in Office 365 - Checklist and Pre Requirements - Part 3 of 3Eyal DoronAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco Flex VPNDocumento93 páginasCisco Flex VPNdwarez100% (2)
- Jupiter Rising: A Decade of Clos Topologies and Centralized Control in Google's Datacenter NetworkDocumento10 páginasJupiter Rising: A Decade of Clos Topologies and Centralized Control in Google's Datacenter Networkthsilva85Ainda não há avaliações
- GSO SCADA/EMS Requirements for Large Scale Solar PlantsDocumento22 páginasGSO SCADA/EMS Requirements for Large Scale Solar PlantsSube OhAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment: Network TopologiesDocumento17 páginasAssignment: Network TopologiesFatima TariqAinda não há avaliações
- VMCI Sockets Programming Guide - ws8 - Esx5 - Vmci - Sockets PDFDocumento32 páginasVMCI Sockets Programming Guide - ws8 - Esx5 - Vmci - Sockets PDFPeterVUSAAinda não há avaliações
- 3GPP TS 23.402Documento291 páginas3GPP TS 23.402holapaquitoAinda não há avaliações
- 1.azure Load Balancer PDFDocumento4 páginas1.azure Load Balancer PDFSarath KumarAinda não há avaliações
- BT-PON BT-711XR XPON ONU ONT DatasheetDocumento5 páginasBT-PON BT-711XR XPON ONU ONT Datasheetnayux ruizAinda não há avaliações
- Mellanox Onyx User Manual Rev. 3.8.2204 - 03 - 27 - 2021Documento1.242 páginasMellanox Onyx User Manual Rev. 3.8.2204 - 03 - 27 - 2021Emil BerdugoAinda não há avaliações
- Final Ccna NotesDocumento48 páginasFinal Ccna NotesthejunaidAinda não há avaliações
- Network Programming LabDocumento152 páginasNetwork Programming Labraghunath9Ainda não há avaliações