Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
1.) Commitments and Contingent Liabilities: Notes To The Accounts - K.S.Oils
Enviado por
Rajat PrasadDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1.) Commitments and Contingent Liabilities: Notes To The Accounts - K.S.Oils
Enviado por
Rajat PrasadDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
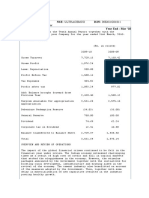
Notes to the Accounts K.S.Oils 1.) Commitments and Contingent Liabilities Rs.
. in Lacs Particulars As on 31st As on 31st March 2010 March 2009
(I) Claims against the company not acknowledged as debts in respect of: (a) Excise and custom duty matters under 48.46 dispute (b) Commercial Taxes matter dispute (c) Income Tax under 237.35 19.11 48.46
32.31 4.35
(II) Estimated amount of contracts remaining to be executed on capital 3694.5 account and not provided for(Net of advances) (III) Bank/ Corporate Guarantee (IV) Export Promotion against Capital Goods. 8012.76 283.24
6575.98
255.26 15.78
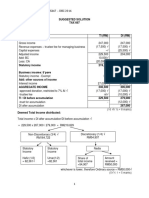
2.) Preferential Issues of Equity Shares and Warrants: In order to meet the fund requirement of the Company for its (i) Expansion of refinery in India along with other allied expenditure (ii) Investment in its overseas subsidiaries for development of Greenfield palm plantations and acquisition of mature palm plantations and/or CPO mills, all in Indonesia. The Company has come out with preferential allotment of Equity Shares and Warrants to the promoters and other foreign Investors during the year at an issue price calculated under SEBI (DIP) Guidelines, 2000 on preferential basis duly approved by Shareholders and Board of Directors of the Company 3.) Share Issue Expenses To be in conformity with Accounting Standards-26 on Intangible Assets and as per provision of Section 78 of Companies Act, 1956, Share issue expenses (Including GDR/ Private Equity issue expenses) amounting to `
380.69 Lacs (Previous year - ` 27.57 Lacs) are charged off against Security Premium Account. 4.) Agricultural Activity During the Financial Year 2008-2009, Government of Madhya Pradesh has allotted a land admeasuring 2,000 hectares to the Company on a license basis for no consideration, for carrying out the agricultural activity for a period of two years; consequently this has not been recognized as a grant. 5.) Borrowing Cost Borrowing cost capitalized during the year from Rs.56.05 lacs in 2007-08 to Rs.382.36 lacs in 2008-09. Observations from Accounting Statements: Shareholders Capital almost remains constant for the past two years. The financial statements of the company and its subsidiary companies are combined on a line-by-line basis by adding together the book values of like items of assets, liabilities, income and expenses, after fully eliminating intra-group balances and intragroup transactions in accordance with Accounting Standard (AS) 21 - Consolidated Financial Statements. Inventories are valued at lower of cost or net realizable value on FIFO basis. Depreciation has been charged on SLM basis for1. Windmill 2. Plant assets (except for oil and refinery plant located at Morena) For all other assets depreciation is provided on WDV basis.
Foreign exchange transactions are recorded at the closing rate prevailing on the date of the respective transactions. Exchange difference arising on foreign exchange transactions settled during the year is recognized in the profit and loss account. Tax expenses are the aggregate of current tax and deferred tax charged or credited in the statement of profit and loss for the period. a. Current Tax- The current charge for income tax is calculated in accordance with the relevant tax regulations applicable to the Company. b. Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT)- In case the company is liable to pay income tax u/s 115JB of income tax Act,1961 (i.e. MAT), the amount of tax paid in excess of normal income tax is recognized as an asset (MAT Credit Entitlement) only if there is convincing evidence for realization of such asset during the specified period. MAT credit entitlement is reviewed at each balance sheet date. c. Deferred Tax- Deferred tax charge or credit reflects the tax effects of timing differences between accounting income and taxable income for the period. The deferred tax charge or credit and the corresponding deferred tax liabilities or assets are recognized using the tax rates that have been enacted or substantively enacted by the balance sheet date. Deferred tax assets are recognized only to the extent there is reasonable certainty that the assets can be realized in future; however, where there is
unabsorbed depreciation or carry forward of losses, deferred tax assets are recognized only if there is virtual certainty of realization of such assets. Unique Features/Highlights of the Sector:
Industry Structure Highly fragmented industry Over 600 oil extraction units, 166 vanaspathi manufacturing units
- only 10 edible oil units and 8 vanaspathi units have national reach Over 50% of the units - sick or under utilised due to surplus capacity Idle capacities among these units due to shortage in feedstock supply Major oil brands - - Sundrop, Dhara, Saffola, Sweekar, Postman
FUTURE Demand Drivers Macroeconomic factors : Population growth, per capita income, purchasing power, oilseeds crop Other factors : Prices - domestic/ international, Availability - oil, oilseeds Influence of branded products - `health message Growing preference for convenience foods. Raw material sourcing : focus on improving yields, getting better quality oilseeds , ensuring regular supplies - through symbiotic relationship with farmer Branding essential for success (Vanaspathi - Dalda, Oils - Sundrop) Better distribution network to improve reach Efficiency in operation - to become price competent and withstand overseas competition Proposed Future trading in edible oils will help curtail price volatility and lend knowledge - based assistance to farmers of eliminate unofficial markets In the next five years, the market for - edible oils will grow by 8% to 12.65 million MT
Key Success Factors
Future
- vanaspathi will grow to 1.5 million MT
Você também pode gostar
- Brookstone Ob-Gyn Associates Case SummaryDocumento2 páginasBrookstone Ob-Gyn Associates Case SummaryRoderick Jackson JrAinda não há avaliações
- Strategic Analysis of Procter and Gamble CompanyDocumento15 páginasStrategic Analysis of Procter and Gamble CompanySunil78% (9)
- Schmidt ADocumento2 páginasSchmidt AAnonymous xlp6qlVJ0% (2)
- Sure Repair LectureDocumento10 páginasSure Repair LectureKaye Villaflor80% (5)
- ACCA p4 2007 Dec QuestionDocumento13 páginasACCA p4 2007 Dec QuestiondhaneshwareeAinda não há avaliações
- 2020 - PFRS For SEs NotesDocumento16 páginas2020 - PFRS For SEs NotesRodelLabor100% (1)
- Financial Management Chapter 2Documento28 páginasFinancial Management Chapter 2beyonce0% (1)
- Accounting Entries For DEPB & Target Plus Scheme PDFDocumento7 páginasAccounting Entries For DEPB & Target Plus Scheme PDFrajdeeppawarAinda não há avaliações
- Organisational Study of Kse Ltdsummer Internship ReportDocumento52 páginasOrganisational Study of Kse Ltdsummer Internship ReportHIJAS HAMSA100% (4)
- Financial Analysis of Berger PaintsDocumento8 páginasFinancial Analysis of Berger PaintsArun PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- TataDocumento56 páginasTataAndreea GeorgianaAinda não há avaliações
- SECTION E - 23 ArchidplyDocumento24 páginasSECTION E - 23 ArchidplyazharAinda não há avaliações
- Ashok Leyland - Financial Analysis 2006-07Documento44 páginasAshok Leyland - Financial Analysis 2006-07Apoorv BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Arl Internship ReportDocumento19 páginasArl Internship ReportChaudhry RashidAinda não há avaliações
- Taxation in Companies-Module IIIDocumento10 páginasTaxation in Companies-Module IIIlathaharihimaAinda não há avaliações
- A) Case 9.1Documento3 páginasA) Case 9.1Satchit VarmaAinda não há avaliações
- Creamline Dairy Products Limited Annual Report 201819Documento160 páginasCreamline Dairy Products Limited Annual Report 201819Tapesh SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines For CADocumento24 páginasGuidelines For CAAnjuElsaAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting StandardDocumento5 páginasAccounting StandardJyoti JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- FIN408 Assignment 1Documento34 páginasFIN408 Assignment 1Ahnaf RaselAinda não há avaliações
- Continous Assignment 2: Mittal School of BusinessDocumento8 páginasContinous Assignment 2: Mittal School of BusinessMd UjaleAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Accounting May 1996 Nov 2010Documento533 páginasAdvanced Accounting May 1996 Nov 2010Rakesh Krishnamoorthy100% (1)
- CA IPCC Company Audit IIDocumento50 páginasCA IPCC Company Audit IIanon_672065362Ainda não há avaliações
- Annual Report 2015-16 JK FennerDocumento68 páginasAnnual Report 2015-16 JK FennerMohan RajAinda não há avaliações
- Analysisoffinancialstatementofasianpaintsltd 130904112245Documento7 páginasAnalysisoffinancialstatementofasianpaintsltd 130904112245Amit PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Tax Aspects of M&ADocumento18 páginasTax Aspects of M&AManeet TutejaAinda não há avaliações
- FAR2 NotesDocumento132 páginasFAR2 NotesCarlito DiamononAinda não há avaliações
- Afsr M1Documento22 páginasAfsr M1Tayyab AliAinda não há avaliações
- Disclosure in Financial StatementsDocumento8 páginasDisclosure in Financial StatementsAnkur ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Adv Aud Final May08Documento16 páginasAdv Aud Final May08Fazi HaiderAinda não há avaliações
- Afr AssignmentDocumento5 páginasAfr Assignmentshahid sjAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting Theory PDFDocumento61 páginasAccounting Theory PDFrabin khatriAinda não há avaliações
- Dividend Distribution PolicyDocumento3 páginasDividend Distribution Policyajaygupta.af3919Ainda não há avaliações
- Versus And: Efore Shim Umar Anerjee AND Apan UkherjeeDocumento6 páginasVersus And: Efore Shim Umar Anerjee AND Apan UkherjeeMRIDUSHI DAMANIAinda não há avaliações
- AnnualReport - 09-10 MRF TYREDocumento88 páginasAnnualReport - 09-10 MRF TYRESanjay ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- 9 Framework For Preparation - Presentation of Financial StatementsDocumento13 páginas9 Framework For Preparation - Presentation of Financial StatementssmartshivenduAinda não há avaliações
- 105 DepaDocumento12 páginas105 DepaLA M AEAinda não há avaliações
- Renuka Sugars PVT LTDDocumento22 páginasRenuka Sugars PVT LTDeasyinformationAinda não há avaliações
- Global Expression of Interest (Eoi) For Implementation of Asset Performance Management Solution in Oil & Gas Facilities Barmer, RajasthanDocumento2 páginasGlobal Expression of Interest (Eoi) For Implementation of Asset Performance Management Solution in Oil & Gas Facilities Barmer, RajasthanTanaya SahaAinda não há avaliações
- 07 BE Week4 Shreyas Roll No 52Documento4 páginas07 BE Week4 Shreyas Roll No 52Shreyas RautAinda não há avaliações
- Set OffDocumento9 páginasSet OffAditya MehtaniAinda não há avaliações
- Taxation Management AssignmentDocumento12 páginasTaxation Management AssignmentJaspreetBajajAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-3: Project SelectionDocumento101 páginasUnit-3: Project SelectionMandeep Singh BhatiaAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting Aspects of MergersDocumento26 páginasAccounting Aspects of MergersInder Preet Singh BadhanAinda não há avaliações
- Fin. Acounting Project 2022Documento14 páginasFin. Acounting Project 2022Sahil ParmarAinda não há avaliações
- Preparation of Consolidated Financial StatementsDocumento3 páginasPreparation of Consolidated Financial Statementsfmsalehin9406Ainda não há avaliações
- Presented By:-Group 10 - Sarvesh Payous Sridivya Kanwaljeet HaritaDocumento14 páginasPresented By:-Group 10 - Sarvesh Payous Sridivya Kanwaljeet HaritaShrey KashyapAinda não há avaliações
- Nishat Mills LTD: Financial DepartmentDocumento6 páginasNishat Mills LTD: Financial DepartmentALI SHER HaidriAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Report Analysis: Date of Submission CDocumento18 páginasFinancial Report Analysis: Date of Submission CVikraman SridharAinda não há avaliações
- 42 As Past QuestionsDocumento61 páginas42 As Past QuestionsAjay RavindranAinda não há avaliações
- Case Studies On Accounting & Auditing Standards: Lucknow Chartered Accountants' SocietyDocumento12 páginasCase Studies On Accounting & Auditing Standards: Lucknow Chartered Accountants' SocietyReema TembhurkarAinda não há avaliações
- Master of Business Administration - MBA Semester 3 Subject Code - MF0012 Subject Name - Taxation Management 4 Credits (Book ID: B1210) Assignment Set-1 (60 Marks)Documento10 páginasMaster of Business Administration - MBA Semester 3 Subject Code - MF0012 Subject Name - Taxation Management 4 Credits (Book ID: B1210) Assignment Set-1 (60 Marks)balakalasAinda não há avaliações
- T3 Ans.. (RA)Documento8 páginasT3 Ans.. (RA)KY LawAinda não há avaliações
- CCI - Guidelines For ValuationDocumento13 páginasCCI - Guidelines For Valuationsujit0577Ainda não há avaliações
- 3-6int 2002 Dec QDocumento9 páginas3-6int 2002 Dec Qadrianlee0107Ainda não há avaliações
- Itc Bhadrachalam Paperboards Limited: Report of The DirectorsDocumento11 páginasItc Bhadrachalam Paperboards Limited: Report of The DirectorsHarish GowdaAinda não há avaliações
- CSM - CHP 12 - Accounting For Income TaxDocumento4 páginasCSM - CHP 12 - Accounting For Income TaxaseppahrudinAinda não há avaliações
- Ultratech Cement Bse: 532538 Nse: Ultracemco Isin: Ine481G01011 Industry: Cement - Major Directors Report Year End: Mar '10Documento7 páginasUltratech Cement Bse: 532538 Nse: Ultracemco Isin: Ine481G01011 Industry: Cement - Major Directors Report Year End: Mar '10Anushree Harshaj GoelAinda não há avaliações
- Corporate Disclosure and Investor ProtectionDocumento26 páginasCorporate Disclosure and Investor ProtectionMatharu Knowlittle100% (1)
- Section e - QuestionsDocumento4 páginasSection e - QuestionsAhmed Raza MirAinda não há avaliações
- ActDocumento436 páginasActRoshan KaharAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting of Life Insurance Companies: Prakash VDocumento4 páginasAccounting of Life Insurance Companies: Prakash VSaurav RaiAinda não há avaliações
- Group 1 Pranav Shukla Kunal Jha Navdeep Sangwan Mansi Bharadwaj Nainika NarulaDocumento42 páginasGroup 1 Pranav Shukla Kunal Jha Navdeep Sangwan Mansi Bharadwaj Nainika NarulaDarek LinonAinda não há avaliações
- A Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific: Fifth EditionNo EverandA Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific: Fifth EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Course OutlineDocumento10 páginasCourse OutlineRajat PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- StratCM Outline (2011-13)Documento1 páginaStratCM Outline (2011-13)Rajat PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- Ops Strat Outline (2011-13)Documento3 páginasOps Strat Outline (2011-13)Rajat PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- ES Outline 2011 - 2013Documento3 páginasES Outline 2011 - 2013Rajat PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- Budget 2011 AnalysisDocumento6 páginasBudget 2011 AnalysisRajat PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- Investopedia Industry Primer HandbookDocumento65 páginasInvestopedia Industry Primer Handbooknkrish1Ainda não há avaliações
- Debt Securities ReviewerDocumento30 páginasDebt Securities Reviewerjhie boterAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 2 3Documento14 páginasChapter 1 2 3Airon BendañaAinda não há avaliações
- Trent Nov07 19Documento9 páginasTrent Nov07 19Ravi KAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 05 The Concept of Leverage and Leverage AnalysisDocumento28 páginasChapter 05 The Concept of Leverage and Leverage AnalysisAGAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer in Intermediate Accounting Mam F Revised 1docxDocumento106 páginasReviewer in Intermediate Accounting Mam F Revised 1docxJessaAinda não há avaliações
- Review JurnalDocumento12 páginasReview JurnalMahatma RamantaraAinda não há avaliações
- MHBAN00496110000230098 NewDocumento2 páginasMHBAN00496110000230098 NewSâñjây BîñdAinda não há avaliações
- Bahri Annual Report 2021Documento98 páginasBahri Annual Report 2021Claudiu BucuricaAinda não há avaliações
- Bcom 3 Sem Corporate Accounting 1 19102078 Oct 2019Documento5 páginasBcom 3 Sem Corporate Accounting 1 19102078 Oct 2019xyxx1221Ainda não há avaliações
- Financial Management Mba (Syllabus)Documento2 páginasFinancial Management Mba (Syllabus)lini liniAinda não há avaliações
- Preparation of Financial StatementsDocumento5 páginasPreparation of Financial StatementsOji ArashibaAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 9 To CHAPTER 15 ANSWERSDocumento38 páginasCHAPTER 9 To CHAPTER 15 ANSWERSryanmartintaanAinda não há avaliações
- Paper Pattern: Do Not Copy The Questions OnDocumento4 páginasPaper Pattern: Do Not Copy The Questions OnMANISHA GARGAinda não há avaliações
- On January 1 2013 Porter Company Purchased An 80 InterestDocumento1 páginaOn January 1 2013 Porter Company Purchased An 80 InterestMuhammad ShahidAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Accounting 2022 NeHu Question PaperDocumento7 páginasFinancial Accounting 2022 NeHu Question PaperSuraj BoseAinda não há avaliações
- Poa T - 6Documento2 páginasPoa T - 6SHEVENA A/P VIJIANAinda não há avaliações
- Maruti Suzuki Annual Report 2020-21-107-108Documento2 páginasMaruti Suzuki Annual Report 2020-21-107-108Atul PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- C Ujeniuc 2Documento17 páginasC Ujeniuc 2cujeniucYAHOO.COMAinda não há avaliações
- Questions To Lecture 7 - IS-LM Model and Aggregate DemandDocumento6 páginasQuestions To Lecture 7 - IS-LM Model and Aggregate DemandMandar Priya Phatak100% (2)
- Proposal To Stage One of Msgr. Ting Anabas' One Act PlaysDocumento2 páginasProposal To Stage One of Msgr. Ting Anabas' One Act PlaysGlaine GemperoaAinda não há avaliações
- Letter-2 Appraisal 19-27 Sep 2019Documento2 páginasLetter-2 Appraisal 19-27 Sep 2019Kiran DandileAinda não há avaliações
- Income Statement (Accrual) PT ManunggalDocumento1 páginaIncome Statement (Accrual) PT ManunggalDelia OktaAinda não há avaliações
- Solution Tax667 - Dec 2016Documento7 páginasSolution Tax667 - Dec 2016Zahiratul QamarinaAinda não há avaliações
- CFA L1 SCHWSR FL Test Ques+Ans - NDocumento52 páginasCFA L1 SCHWSR FL Test Ques+Ans - NAdamAinda não há avaliações
- 3 - BAF - Direct Tax IDocumento3 páginas3 - BAF - Direct Tax Isid pjAinda não há avaliações