Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
The 7 S Model by Mckinsey
Enviado por
Prema Nanda HottaDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
The 7 S Model by Mckinsey
Enviado por
Prema Nanda HottaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
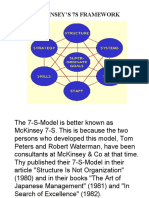
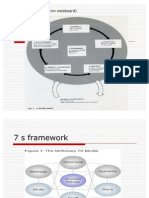
The 7-S-Model
The 7-S-Model is better known as McKinsey 7-S. This is because the two persons who developed this model, Tom Peters and Robert Waterman, have been consultants at McKinsey & Co at that time. Thy published their 7-S-Model in their article Structure Is Not Organization (1980) and in their books The Art of Japanese Management (1981) and In Search of Excellence (1982). The model starts on the premise that an organization is not just Structure, but consists of seven elements:
Those seven elements are distinguished in so called hard Ss and soft Ss. The hard elements (green circles) are feasible and easy to identify. They can be found in strategy statements, corporate plans, organizational charts and other documentations. The four soft Ss however, are hardly feasible. They are difficult to describe since capabilities, values and elements of corporate culture are continuously developing and changing. They are highly determined by the people at work in the organization. Therefore it is much more difficult to plan or to influence the characteristics of the soft elements. Although the soft factors are below the surface, they can have a great impact of the hard Structures, Strategies and Systems of the organization.
Description The Hard Ss Strategy Structure Systems
Actions a company plans in response to or anticipation of changes in its external environment. Basis for specialization and co-ordination influenced primarily by strategy and by organization size and diversity. Formal and informal procedures that support the strategy and structure. (Systems are more powerful than they are given credit)
The Soft Ss Style / Culture The culture of the organization, consisting of two components: Organizational Culture: The dominant values and beliefs, and norms, which develop over time and become relatively enduring features of organizational life. Management Style: More a matter of what managers do than what they say; How do a companys managers spend their time? What are they focusing attention on? Symbolism the creation and maintenance (or sometimes deconstruction) of meaning is a fundamental responsibility of managers. Staff The people/human resource management processes used to develop managers, socialization processes, ways of shaping basic values of management cadre, ways of introducing young recruits to the company, ways of helping to manage the careers of employees Skills The distinctive competences what the company does best, ways of expanding or shifting competences Shared Values / Super-ordinate Goals Guiding concepts, fundamental ideas around which a business is built must be simple, usually stated at abstract level, have great meaning inside the organization even though outsiders may not see or understand them.
Effective organizations achieve a fit between these seven elements. This criterion is the origin of the other name of the model: Diagnostic Model for Organizational Effectiveness. If one element changes then this will affect all the others. For example, a change in HR-systems like internal career plans and management training will have an impact on organizational culture (management style) and thus will affect structures, processes, and finally characteristic competences of the organization. In change processes, many organizations focus their efforts on the hard Ss, Strategy, Structure and Systems. They care less for the soft Ss, Skills, Staff, Style and Shared Values. Peters and Waterman in In Search of Excellence commented however, that most successful companies work hard at these soft Ss. The soft factors can make or break a successful change process, since new structures and strategies are difficult to build upon inappropriate cultures and values. These problems often come up in the dissatisfying results of spectacular mega-mergers. The lack of success and synergies in such mergers is often based in a clash of completely different
cultures, values, and styles, which make it difficult to establish effective common systems and structures. The 7-S Model is a valuable tool to initiate change processes and to give them direction. A helpful application is to determine the current state of each element and to compare this with the ideal state. Based in this it is possible to develop action plans to achieve the intended state.
Você também pode gostar
- The 7 S Model by MckinseyDocumento3 páginasThe 7 S Model by MckinseyMuthyala NagarajuAinda não há avaliações
- MC Kinsey 7s ModelDocumento16 páginasMC Kinsey 7s ModelTanvi DeshmukhAinda não há avaliações
- 7 - S FrameworkDocumento23 páginas7 - S FrameworkRitika AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- MC Kinsey 7S Model Its Implementation in InfosysDocumento24 páginasMC Kinsey 7S Model Its Implementation in InfosysAbdul Halim JoharAinda não há avaliações
- McKinsey 7S ModelDocumento6 páginasMcKinsey 7S ModelNikhil Manocha100% (1)
- MC Kinsey ModelDocumento9 páginasMC Kinsey ModelJuhika SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- 7S FrameworkDocumento10 páginas7S FrameworkAshwini SudheerAinda não há avaliações
- 7s of MckinseyDocumento2 páginas7s of MckinseyNIKKI KUMARIAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Implementation The 7S FrameworkDocumento16 páginasStrategy Implementation The 7S FrameworkVignesh StrykerAinda não há avaliações
- McKinsey 7SDocumento14 páginasMcKinsey 7SVijay HalalliAinda não há avaliações
- 7S Model Of: MckinseyDocumento23 páginas7S Model Of: MckinseyShuchi Prashant SinghAinda não há avaliações
- McKinseys 7S ModelDocumento14 páginasMcKinseys 7S ModelRahul IyerAinda não há avaliações
- MC Kinsey 7 S Model: Hard Elements Soft ElementsDocumento3 páginasMC Kinsey 7 S Model: Hard Elements Soft Elementssmrita jainAinda não há avaliações
- 7s Mckinsey FrameworkDocumento4 páginas7s Mckinsey FrameworkBeenay MaharjanAinda não há avaliações
- The Mckinsey 7 S FrameworkDocumento3 páginasThe Mckinsey 7 S Frameworkshaafi hamzAinda não há avaliações
- McKinsey 7-S FrameworkDocumento4 páginasMcKinsey 7-S FrameworkSOHEB TADVIAinda não há avaliações
- 3 - The McKinsey 7SDocumento6 páginas3 - The McKinsey 7SAlex SimmonsAinda não há avaliações
- AmulDocumento9 páginasAmulAshik NavasAinda não há avaliações
- Small Unit Supervision (McKinsey 7S Model)Documento4 páginasSmall Unit Supervision (McKinsey 7S Model)PEMS Ivan Theodore P LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Seven "S" Model: Nirma University Institute of Law 2 SemesterDocumento18 páginasSeven "S" Model: Nirma University Institute of Law 2 SemesterMishika Shah100% (1)
- McKinsey 7 S ModelDocumento14 páginasMcKinsey 7 S Modelpara0044Ainda não há avaliações
- What Is 7-S Model?: Organizational ChangeDocumento2 páginasWhat Is 7-S Model?: Organizational Changesahilchopra17Ainda não há avaliações
- WK 11 Internal AnalysisDocumento2 páginasWK 11 Internal AnalysisJoshua AnnanAinda não há avaliações
- MC KinseyDocumento12 páginasMC KinseyRishipal ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- MC KinseyDocumento12 páginasMC KinseyArpita BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Change ModelDocumento35 páginasChange ModelAslam HussainAinda não há avaliações
- The McKinsey 7S Framework - Strategy Skills From MindToolsDocumento7 páginasThe McKinsey 7S Framework - Strategy Skills From MindToolstani100% (1)
- The Mckinsey 7-S Framework: Ensuring That All Parts of Your Organization Work in HarmonyDocumento6 páginasThe Mckinsey 7-S Framework: Ensuring That All Parts of Your Organization Work in HarmonychanukyaAinda não há avaliações
- The McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento6 páginasThe McKinsey 7S FrameworkMathan Raj75% (4)
- Strategic ImplementationDocumento8 páginasStrategic ImplementationAnjali KedareAinda não há avaliações
- McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento9 páginasMcKinsey 7S FrameworkCzarPaguioAinda não há avaliações
- The McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento7 páginasThe McKinsey 7S FrameworkShruti VinyasAinda não há avaliações
- McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento7 páginasMcKinsey 7S FrameworkRara AlonzoAinda não há avaliações
- MC Kinsey'S 7S Framework: Seminar Report ONDocumento14 páginasMC Kinsey'S 7S Framework: Seminar Report ONRanjithAinda não há avaliações
- MC Kinsey 7Documento15 páginasMC Kinsey 7Anjani PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- 04 McKinsey 7SDocumento7 páginas04 McKinsey 7Ssunshine4u5Ainda não há avaliações
- 202003291621085882smitasingh McKinsey 7s ModelDocumento6 páginas202003291621085882smitasingh McKinsey 7s ModelJanice MkhizeAinda não há avaliações
- 7s FrameworkDocumento5 páginas7s Frameworknhthang_hdn0% (1)
- SM II-handout 05-Mckinsey 7s ModelDocumento6 páginasSM II-handout 05-Mckinsey 7s ModelAkshay sachanAinda não há avaliações
- MC Kinsey 7-S FrameworkDocumento26 páginasMC Kinsey 7-S FrameworkCraig WilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- PPM-Notes-Unit II-Evolution of Management ThoughtDocumento23 páginasPPM-Notes-Unit II-Evolution of Management ThoughtNilabjo Kanti PaulAinda não há avaliações
- The McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento17 páginasThe McKinsey 7S FrameworkDanna Denise MalotoAinda não há avaliações
- McKinsey 7S Framework of Nestle LTD ScribdDocumento2 páginasMcKinsey 7S Framework of Nestle LTD Scribdsreeya50% (6)
- McKinsey 7 S FrameworkDocumento6 páginasMcKinsey 7 S FrameworkDeepank GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- MC Kinsey 7S Model & Its Implementation in InfosysDocumento24 páginasMC Kinsey 7S Model & Its Implementation in Infosysram gopal90% (21)
- 7s of MescomDocumento5 páginas7s of MescomkunikithAinda não há avaliações
- What Is McKinsey 7S ModelDocumento4 páginasWhat Is McKinsey 7S Modelpolobook3782Ainda não há avaliações
- Mckinsey's 7-S FramewrokDocumento4 páginasMckinsey's 7-S FramewrokMonirul AlamAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of 7s Framework - MergedDocumento9 páginasAnalysis of 7s Framework - MergedPravin Bang100% (1)
- Mckinsey'S 7S ModelDocumento4 páginasMckinsey'S 7S ModelVshare IseindiaAinda não há avaliações
- Part A: 1. Industry ProfileDocumento67 páginasPart A: 1. Industry ProfileSandeep BelurAinda não há avaliações
- Inplant TrainingDocumento67 páginasInplant TrainingVenu SAinda não há avaliações
- The McKinsey 7S Framework - Strategy Skills FromDocumento7 páginasThe McKinsey 7S Framework - Strategy Skills Frommanish PatidarAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Mckinsey 7S ModelDocumento5 páginasWhat Is Mckinsey 7S ModelPrashant Rampuria100% (2)
- The Seven Elements: Hard Elements Soft ElementsDocumento5 páginasThe Seven Elements: Hard Elements Soft ElementsVineet KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Breaking the Leadership Mold: An Executive's Guide to Achieving Organizational ExcellenceNo EverandBreaking the Leadership Mold: An Executive's Guide to Achieving Organizational ExcellenceAinda não há avaliações
- Company Management…Policies, Procedures, PracticesNo EverandCompany Management…Policies, Procedures, PracticesAinda não há avaliações
- Twenty-Two Ways to Develop Leadership in Staff ManagersNo EverandTwenty-Two Ways to Develop Leadership in Staff ManagersAinda não há avaliações
- Track Rollers and SproketsDocumento158 páginasTrack Rollers and SproketsPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- Business Etiquettes: The Secret Behind SuccessDocumento70 páginasBusiness Etiquettes: The Secret Behind SuccessPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- Ladder of Loyalty: Source: Christopher, Payne & Ballantyne, Relationship MarketingDocumento9 páginasLadder of Loyalty: Source: Christopher, Payne & Ballantyne, Relationship MarketingPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- Track Rollers and SproketsDocumento158 páginasTrack Rollers and SproketsPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- Interpersonal SkillsDocumento22 páginasInterpersonal SkillsPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- 5SDocumento30 páginas5SPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Habbits of Highly Ineffective ManagersDocumento19 páginas7 Habbits of Highly Ineffective ManagersPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People: By: Amal - Fatema - Ashraf - AmrDocumento10 páginasThe Seven Habits of Highly Effective People: By: Amal - Fatema - Ashraf - AmrPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- KaizenDocumento15 páginasKaizenPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Habbits of Highly Ineffective ManagersDocumento19 páginas7 Habbits of Highly Ineffective ManagersPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- Kra Kpa Kai SheetDocumento4 páginasKra Kpa Kai SheetVikram Khatri100% (1)
- PP PP PPPP PPDocumento38 páginasPP PP PPPP PPPrema Nanda Hotta100% (2)
- IR PresentationDocumento40 páginasIR PresentationPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) : Northern State University 12 June, 2007Documento71 páginasCustomer Relationship Management (CRM) : Northern State University 12 June, 2007Manish SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Team Building ListeningDocumento139 páginasTeam Building ListeningPrema Nanda HottaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan ArraysDocumento11 páginasLesson Plan ArraysErika MytnikAinda não há avaliações
- GES 301 NewDocumento144 páginasGES 301 NewOyeniyi Oyeladun IfeoluwaAinda não há avaliações
- Field Study Memorandum of Agreement CTP TEMPLATEDocumento2 páginasField Study Memorandum of Agreement CTP TEMPLATEJhodie Anne Isorena100% (1)
- Unit 4 Part 1 Proposal MemoDocumento3 páginasUnit 4 Part 1 Proposal MemoMarshall VilandAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 1 Eng FORM 5Documento4 páginasUNIT 1 Eng FORM 5leonal neevedthanAinda não há avaliações
- College of Teacher Education: Delivery PlanDocumento2 páginasCollege of Teacher Education: Delivery PlanGeraldz Brenzon AgustinAinda não há avaliações
- Building Your Career PortfolioDocumento17 páginasBuilding Your Career Portfoliobudak mataAinda não há avaliações
- Post PositivismDocumento2 páginasPost PositivismNahian SalsabeelAinda não há avaliações
- Case Coach (HBS)Documento19 páginasCase Coach (HBS)amdatabase100% (2)
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics Module 8Documento2 páginasUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics Module 8Joyce CasemAinda não há avaliações
- Content and Contextu Al Analysis of Selecte D Primary SourcesDocumento27 páginasContent and Contextu Al Analysis of Selecte D Primary SourcesKitAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Mission and VissionDocumento14 páginas01 Mission and VissionOmkar RanadeAinda não há avaliações
- Avd1x16 RD-WR PauDocumento4 páginasAvd1x16 RD-WR Pau---acrAinda não há avaliações
- GapInc Case StudyDocumento10 páginasGapInc Case Study018ASHWINI KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- B.Ed. Syllabus Final 15.06.2016-8-7-16Documento209 páginasB.Ed. Syllabus Final 15.06.2016-8-7-16manish.cdmaAinda não há avaliações
- Leadership and Character DevelopmentDocumento36 páginasLeadership and Character DevelopmentAnne Janelle GuanAinda não há avaliações
- Distance Learning TheoryDocumento18 páginasDistance Learning TheoryMaryroseAinda não há avaliações
- Hypnosis, Reporting Bias, and Suggested Negative HallucinationsDocumento8 páginasHypnosis, Reporting Bias, and Suggested Negative HallucinationsMarco DomizioAinda não há avaliações
- Yubal, CogPsych - Obstacles & Aids To Problem SolvingDocumento16 páginasYubal, CogPsych - Obstacles & Aids To Problem SolvingJake CuencaAinda não há avaliações
- Learning To Generate Move-by-Move Commentary For Chess Games From Large-Scale Social Forum DataDocumento11 páginasLearning To Generate Move-by-Move Commentary For Chess Games From Large-Scale Social Forum DataPascua JarisonAinda não há avaliações
- Spiral ModelDocumento3 páginasSpiral ModelIndra Arif RamadhanAinda não há avaliações
- Reference LetterDocumento3 páginasReference LetterPrabhu KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Plan: Learning Outcome Topic Week No. Learnig ActivitiesDocumento2 páginasLearning Plan: Learning Outcome Topic Week No. Learnig ActivitiesJereek EspirituAinda não há avaliações
- Cur DevDocumento23 páginasCur DevKa JoannehAinda não há avaliações
- Don't Think of An Elephant - Know Your Values and Frame The Debate - George LakoffDocumento142 páginasDon't Think of An Elephant - Know Your Values and Frame The Debate - George LakoffBreno ModestoAinda não há avaliações
- Okun y Kantrowitz - Cap4 - Stage1Documento15 páginasOkun y Kantrowitz - Cap4 - Stage1AntoniettaAinda não há avaliações
- About Knowledge Based PayDocumento1 páginaAbout Knowledge Based PaySimant NayakAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 1 - GALERA, TrinaDocumento1 páginaActivity 1 - GALERA, Trinatrina mari cassandra GALERAAinda não há avaliações
- National Education PolicyDocumento34 páginasNational Education Policysona100% (1)
- Hand Out in RealismDocumento2 páginasHand Out in RealismRea Mae SandovalAinda não há avaliações