Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NCP Psyche2
Enviado por
Nica RTDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NCP Psyche2
Enviado por
Nica RTDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
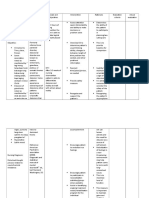
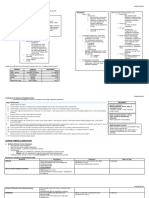
DEPRESSION Nursing Diagnosis Risk for suicide related to feeling of worthlessness Background Knowledge Depression is a state of low mood
and aversion to activity that can affect a person's thoughts, behaviour, feelings and physical well-being. Depressed people may feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, or restless. They may lose interest in activities that once were pleasurable, experience loss of appetite or overeating, or problems concentrating, remembering details or making decisions; and may contemplate or attempt suicide. Insomnia, excessive sleeping, fatigue, loss of energy, or aches, pains or digestive problems that are resistant to treatment may be present. Planning Goal: After 3 days of nursing intervention, the patient will not harm his/her self. Objectives: After rendering nursing interventions patient will: >seek out staff when feeling urge to harm self >make short-term contract with the nurse not to harm self Intervention 1 Ask client directly, have you ever thought about killing yourself>, If so, what do you plan to do?, during therapeutic communication. 2 Create a safe environment for the client. Remove all potentially harmful objects from clients access. 3 formulate a short term verbal contract with the client that he or she will not harm self during specific time period. 4 secure promise from client that he/she will seek out a staff member or support person if thoughts of suicide emerge. 5 Encourage client to express angry feelings within appropriate limits. Rationale >the risk of suicide is greatly increased if the client has developed a plan and particularly if means exist for the client to execute plan. >client safety is a nursing priority. Evaluation >Client verbalizes no thoughts of suicide. >Client commits no acts of self harm. >Client is able to verbalize names of resources outside the hospital from which she may request help in feeling of suicidal.
>this will provide some relief to the client.
>this may provide assistance before the client experiences a crisi situation.
>If the anger was verbalized in a nonthreatening environment, the client may be able to resolve these feelings, regardless of the discomfort involved.
MANIC DISORDER Nursing Diagnosis Risk for injury related to extreme hyperactivity Background Knowledge Mania can be experienced at the same time as depression, in a mixed episode. Dysphoric mania is primarily manic and agitated depression is primarily depressed. This has caused speculation amongst doctors that mania and depression are two independent axes in a bipolar spectrum, rather than opposites. Planning Goal: After 3 days of nursing intervention, the patient will experience no physical injury. Objectives: After rendering nursing interventions patient will: >no longer exhibit potentially injurious movements Intervention 1 Reduce environmental stimuli. Rationale >In hyperactive state, client is extremely distractible, responses even the slightest stimuli are exaggerated. >Milieu unit may be too distracting. >Client feels more secure in one-two relationship. Evaluation >Client is no longer exhibiting signs of physical agitation. >Client exhibits no evidence of physical injury obtained while experiencing hyperactive behavior.
2 Assign to quiet unit, if possible. 3 Limit group activities. Help client try to establish one or two close relationships. 4 Remove hazardous objects and substances from clients environment. 5 Stay with the client and provide rest periods throughout the day. 6 Provide physical activities as a substitute for purposeless hyperactivity.
>Clients rationality is impaired, so client may harm self inadvertently.
>to offer support and provide feeling of security. >Provide a safe and effective means of relieving pent-up tension.
SCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Social Interaction related to absence of available significant others or peers as evidenced by dysfunctional interaction with peers, family, and others Background Knowledge Schizophrenia is an extremely complex mental disorder: in fact it is probably many illnesses masquerading as one. A biochemical imbalance in the brain is believed to cause symptoms. Recent research reveals that schizophrenia may be a result of faulty neuronal development in the fetal brain, which develops into full-blown illness in late adolescence or early adulthood. Planning Goal: After 3 days of nursing intervention, the patient will be able to demonstrate attempts to communicate. Objectives: After rendering nursing interventions patient will: >verbalize to express honest feelings in relation to loss of prior level of functioning Intervention 1 Spend time with client. This may mean just sitting in silence for a while. 2 Develop a therapeutic nurse-client relationship through frequent, brief contacts and an accepting attitude. Show unconditional positive regard. 3 Provide positive reinforcement for client's voluntary interactions with others. 4 Teach assertiveness techniques. Interactions with others may be negatively affected by client's use of passive or aggressive behaviors. Rationale >Your presence may help improve client's perception of self as a worthwhile person. Evaluation > Client demonstrates willingness and desire to socialize with others. >Client voluntarily attends group activities. >Your presence, acceptance, and conveyance of positive regard enhance the client's feelings of self-worth. >Client approaches others in appropriate manner for oneto-one interaction
>Positive reinforcement enhances self-esteem and encourages repetition of desirable behaviors. >Knowledge of assertive techniques could improve client's relationships with others
ANTISOCIAL Nursing Diagnosis Impaired social interaction related to disturbed brain development Background Knowledge Antisocial Personality Disorder is a condition characterized by persistent disregard for, and violation of, the rights of others that begins in childhood or early adolescence and continues into adulthood. Deceit and manipulation are central features of this disorder. For this diagnosis to be given, the individual must be at least 18, and must have had some symptoms of Conduct Disorder (i.e., delinquency) before age 15. This disorder is only diagnosed when these behaviors become persistent and very disabling or distressing. Planning Long term goal: After 6 days of nursing intervention client will be able to demonstrate successful interactions with family members and staffs in educational setting. Objectives: After rendering nursing care client will: >Successfully complete tasks or assignments with assistance >Demonstrate acceptable social skills while interacting with staff or family Intervention 1 Identify the factors that aggravate and alleviate the clients performance. Rationale >The external stimuli that exacerbate the clients problems can be identified and minimized. >The clients ability to deal with external stimulation is impaired >The client must hear instructions as a first step toward compliance. Evaluation >The client was able to demonstrate willingness and desire to socialize with some educational staff but not with all staff.
2 Provide an environment as free from distractions as possible. 3 Engage the clients attention before giving instructions. (calling his/her name, having an eye contact) 4 Give instructions slowly, using simple language and concrete directions. 5 Provide positive feedback for completion of each step or task.
>The clients ability to comprehend instruction is impaired. >The clients opportunity for successful experiences is increased by treating each step/task as an opportunity for success. >The clients restless energy can be given an acceptable outlet, so that he/she can attend to future task more effectively. >This approach called shaping is a behavioral procedure in which
6 Allow breaks during which the client can move around.
7 Give the client positive
feedback for performing behaviors that comes close to task achievement.
successive approximations of a desired behavior are positively reinforced. >Increase logical thought and decrease tangentiality.
8 Assist the client to verbalize by asking sequencing questions to keep on the topic (what happens next?).
OCPD Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Você também pode gostar
- NCPDocumento8 páginasNCPTrixia Diaz67% (3)
- NCPDocumento1 páginaNCPNneka Andrea Datiles0% (2)
- PTSD NCPDocumento2 páginasPTSD NCPDanielle Quemuel Viray0% (1)
- N C PDocumento3 páginasN C PTrixia Diaz100% (1)
- NCP FinalDocumento22 páginasNCP FinalAlmira Ahamad100% (1)
- NCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardDocumento9 páginasNCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardMary Margarett BoadoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Bipolar DisorderDocumento1 páginaNCP For Bipolar DisorderJohn Carlo Santos100% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan 1 Risk For Violence, Self DirectedDocumento9 páginasNursing Care Plan 1 Risk For Violence, Self Directeddbryant010193% (14)
- ND - Risk For SuicideDocumento3 páginasND - Risk For SuicideHu Dawi100% (1)
- NCP - Suicidal TendencyDocumento2 páginasNCP - Suicidal Tendencyяoxel яayмoи eитяeиa100% (5)
- Bipolar NCPDocumento4 páginasBipolar NCPcandy19agustin100% (1)
- NCP SchizophreniaDocumento7 páginasNCP SchizophreniaSteffi Raye Madrid50% (2)
- Disturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Documento3 páginasDisturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Charles Mallari ValdezAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaDocumento14 páginasNursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaMary Luz De GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Schizophrenia NCPDocumento2 páginasSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (2)
- NCP For SchizoDocumento5 páginasNCP For SchizoRichelene Mae Canja100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob80% (5)
- Bipolar NCPDocumento2 páginasBipolar NCPweehdinga89% (9)
- Disturbed Sleep Pattern in Bipolar ClientDocumento2 páginasDisturbed Sleep Pattern in Bipolar ClientJermaine Anne MadayagAinda não há avaliações
- Bipolar Disorders Care Plan Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 páginasBipolar Disorders Care Plan Nursing Care PlanAnne de Vera0% (1)
- Goals for Patient CareDocumento1 páginaGoals for Patient CareJoan ParlanAinda não há avaliações
- SCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 páginaSCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Care Planrinkai130% (1)
- ND - Disturbed Thought ProcessDocumento2 páginasND - Disturbed Thought ProcessHu DawiAinda não há avaliações
- Care Plan 27Documento10 páginasCare Plan 27Oroma TobiasAinda não há avaliações
- Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDocumento16 páginasUndifferentiated SchizophreniavinalonAinda não há avaliações
- NCP PsychDocumento2 páginasNCP PsychJray Inocencio50% (4)
- Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDocumento196 páginasUndifferentiated Schizophreniakathcute150% (1)
- NCP (Psychiatric)Documento6 páginasNCP (Psychiatric)Erl Joy Montaño Cañete100% (1)
- Submitted By: Charisa S. Simbajon BSN IvDocumento8 páginasSubmitted By: Charisa S. Simbajon BSN IvCharisa Simbajon100% (1)
- NCP Disturbed Thought Process Related To SchizophreniaDocumento6 páginasNCP Disturbed Thought Process Related To Schizophrenianaishel0% (1)
- BPD NCP 1Documento4 páginasBPD NCP 1Jordz PlaciAinda não há avaliações
- Bipolar NCPDocumento2 páginasBipolar NCPGenevieve VLs100% (1)
- Schizophrenia Symptoms, Nursing Diagnoses, Interventions and OutcomesDocumento9 páginasSchizophrenia Symptoms, Nursing Diagnoses, Interventions and Outcomesاسيرالاحزان100% (1)
- NCP Assessment Diagnosis Planning Short-Term GoalDocumento4 páginasNCP Assessment Diagnosis Planning Short-Term GoalJessieRamosAnicetoAinda não há avaliações
- Scizophrenia NCP1Documento13 páginasScizophrenia NCP1Kholid Abu Mohammad AlfaizinAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento2 páginasNCPJoshua DecenaAinda não há avaliações
- Dementia NCPDocumento3 páginasDementia NCPDonnalyn MillaresAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor ActivityDocumento3 páginasNCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor Activitydana75% (4)
- NCP - BipolarDocumento2 páginasNCP - BipolarSasha FongAinda não há avaliações
- Schizophrenia Care Plan RNDocumento8 páginasSchizophrenia Care Plan RNlisa75% (4)
- NCP DisturbedThoughtProcessesDocumento1 páginaNCP DisturbedThoughtProcessesJoan KarlaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For DepressionDocumento7 páginasNursing Care Plan For DepressionCatherineAinda não há avaliações
- NursingDx ImpairedVerbalComm SchizophreniaDocumento8 páginasNursingDx ImpairedVerbalComm Schizophreniajmanipon_1100% (1)
- Everyone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDocumento4 páginasEveryone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDanica Kate GalleonAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento6 páginasNursing Care PlanNeza AgdalesAinda não há avaliações
- Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDocumento26 páginasUndifferentiated SchizophreniaVictor Shon100% (1)
- 4 NCP SchizophreniaDocumento9 páginas4 NCP SchizophreniaHazel Banday100% (4)
- SchizophreniaDocumento3 páginasSchizophreniaPete Cobra Cobraiti100% (1)
- Case Study SchizophreniaDocumento3 páginasCase Study SchizophreniaCHRISANTO ARZANANAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For ViolenceDocumento5 páginasRisk For Violencemikaela_pascuaAinda não há avaliações
- Psyche NotesDocumento41 páginasPsyche Notesjadagayle 825Ainda não há avaliações
- Mental Defense MechanismsDocumento26 páginasMental Defense MechanismsMutegeki AdolfAinda não há avaliações
- S E L F - P E R C E P T I O N - S E L F - C O N C E P T P A T T E R A. 1Documento4 páginasS E L F - P E R C E P T I O N - S E L F - C O N C E P T P A T T E R A. 1Diana TardecillaAinda não há avaliações
- Defining Psychological Interventions and Their EffectivenessDocumento26 páginasDefining Psychological Interventions and Their EffectivenessJay Mark Cabrera100% (1)
- Additional Nursing Care Plans - SchizophreniaDocumento26 páginasAdditional Nursing Care Plans - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob100% (4)
- Psych - Nursing InterventionsDocumento23 páginasPsych - Nursing Interventionsmarie100% (19)
- NCPDocumento3 páginasNCPLuiji Amor TiamzonAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Mental Health NursingDocumento27 páginasPrinciples of Mental Health Nursingkanwaljeet kaurAinda não há avaliações
- Abella Pmhn-Case-Study-2-3Documento4 páginasAbella Pmhn-Case-Study-2-3Erma AbellaAinda não há avaliações
- Crisis Intervention: Psychiatric Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocumento13 páginasCrisis Intervention: Psychiatric Nursing Nursing Care PlanKatherine 'Chingboo' Leonico Laud100% (4)
- Git PDFDocumento73 páginasGit PDFNica RTAinda não há avaliações
- Benign Lesions of The Ovary NotesDocumento5 páginasBenign Lesions of The Ovary Notesmkct111Ainda não há avaliações
- Neoplastic Diseases of The Ovary PDFDocumento5 páginasNeoplastic Diseases of The Ovary PDFNica RTAinda não há avaliações
- INTEGMED1Documento17 páginasINTEGMED1Nica RTAinda não há avaliações
- Primary Cutaneous B-Cell Lymphomas Classification and TreatmentDocumento10 páginasPrimary Cutaneous B-Cell Lymphomas Classification and TreatmentNica RTAinda não há avaliações
- CVS Drugs PDFDocumento199 páginasCVS Drugs PDFNica RTAinda não há avaliações
- NCP AutismDocumento4 páginasNCP AutismNica RT67% (3)
- Chapter 1Documento6 páginasChapter 1Nica RTAinda não há avaliações
- Case AnalysisDocumento5 páginasCase AnalysisNica RTAinda não há avaliações
- Major Functions of SupervisionDocumento17 páginasMajor Functions of SupervisionEdelle BaritAinda não há avaliações
- Damon - Infancy To AdelocanceDocumento25 páginasDamon - Infancy To AdelocanceRamani ChandranAinda não há avaliações
- Circle Time WorkshopDocumento18 páginasCircle Time WorkshopShafquat Zaman SolonAinda não há avaliações
- LeadershipDocumento54 páginasLeadershiphansdeep479Ainda não há avaliações
- Castaneda NotesDocumento10 páginasCastaneda NotesannoyingsporeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Case Incident SolutionsDocumento7 páginasChapter 4 Case Incident SolutionsZiaul Onim67% (3)
- Egan, Santos, & BloomDocumento6 páginasEgan, Santos, & Bloomkumargaurav_19852671Ainda não há avaliações
- Need For A Philosophy of Education in 21st Century SchoolsDocumento28 páginasNeed For A Philosophy of Education in 21st Century SchoolsAlok MathurAinda não há avaliações
- Our Return On InvestmentDocumento2 páginasOur Return On Investmentvidelicet00100% (1)
- Action Research Paper Educ 2061Documento7 páginasAction Research Paper Educ 2061api-438417920Ainda não há avaliações
- Epicurus and HappinessDocumento4 páginasEpicurus and HappinessJack CarneyAinda não há avaliações
- 10 5465@amd 2019 0075Documento14 páginas10 5465@amd 2019 0075habib diopAinda não há avaliações
- Alpert & Haber 1960 Anxiety in Academic Achievement Situations.Documento9 páginasAlpert & Haber 1960 Anxiety in Academic Achievement Situations.hoorie50% (2)
- HIV/AIDS Education GuideDocumento12 páginasHIV/AIDS Education GuideDutch EarthAinda não há avaliações
- PBMDocumento4 páginasPBMAshu PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Envy Manifestations and Personality DisordersDocumento7 páginasEnvy Manifestations and Personality DisordersDan Rosca100% (1)
- Merging The Instructional Design Process WithDocumento233 páginasMerging The Instructional Design Process Withangkasa putraAinda não há avaliações
- Student Driver ArticleDocumento2 páginasStudent Driver Articleapi-588922852Ainda não há avaliações
- DSM VDocumento9 páginasDSM VAddie Espiritu100% (4)
- Comprehensive Sexuality Education Learning Area: Personality Development Grade 11 - 12Documento9 páginasComprehensive Sexuality Education Learning Area: Personality Development Grade 11 - 12Jerick SubadAinda não há avaliações
- HRM (Career Planning)Documento21 páginasHRM (Career Planning)pradeep3673Ainda não há avaliações
- Case Study Microsoft-1Documento15 páginasCase Study Microsoft-1cyrus1502Ainda não há avaliações
- Motivation in Language Learning: Factors and TheoriesDocumento6 páginasMotivation in Language Learning: Factors and TheoriesEkin Erin100% (2)
- 10 03 10 Equus AnalysisDocumento5 páginas10 03 10 Equus AnalysisSusan RoweAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Drawing. Bringing Art Into Art Therapy PDFDocumento16 páginasWhat Is Drawing. Bringing Art Into Art Therapy PDFTía MonguiAinda não há avaliações
- Reet 2021 Psychology Book PDFDocumento62 páginasReet 2021 Psychology Book PDFSaista KhanamAinda não há avaliações
- HEALTH6 Q2 Mod1 TheHealthySchoolandCommunityEnvironments V4Documento18 páginasHEALTH6 Q2 Mod1 TheHealthySchoolandCommunityEnvironments V4Huawei GlobeAinda não há avaliações
- Volleyball Lesson With TechnologyDocumento8 páginasVolleyball Lesson With Technologyapi-302055683Ainda não há avaliações
- Enhancing Word Recognition in English PupilsDocumento7 páginasEnhancing Word Recognition in English PupilsJomar BauzonAinda não há avaliações
- Bcom Notes 1Documento15 páginasBcom Notes 1abimartAinda não há avaliações