Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
10MotionalEmf Inductance Transformers SY2011
Enviado por
Ginger KevlarDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
10MotionalEmf Inductance Transformers SY2011
Enviado por
Ginger KevlarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Engineering Physics 2 Motional Emf, Electromagnetic Induction, Motors and Generators Topic Outline for week 13 Course Objectives:
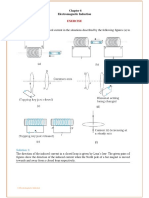
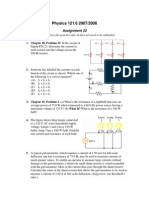
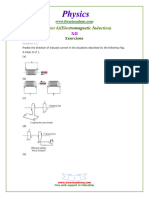
At the end of the week, the student should be able to Cognitive: Define Faradays Law of electromagnetic Induction. State some applications of Faradays Law Affective: Relate the principle of electromagnetic induction to the operation of motors and generators. Psychomotor: Solve some exercises/problems related to the topic Values Integration: Camaraderie Subject Matter: Electromagnetic Induction 1. Faradays Law of Induction 2. Motional emf 3. Lenzs Law 4. Induced emf & Electric Fields 5. Transformers, Generators & Motors Readings: 1. Beiser, A. Schaums Outlines, 2004 pp. 335-337 2. Cutnell & Johnson, Physics, 2007 pp.686-716 3. Serway & Jewett, Physics for Scientist and Engrs., 2008 pp. 968-990 4. Tipler, Physics for Scientist& Engrs., 2004 pp. 927-948 Activity: 1. Motivation: Did you know that a. An induction stove which operates using the electromagnetic induction can cook food without getting hot. b. Trivia: Hes a physicist who invented electric motor, electric generator, & transformer among others. 2. Explore the effects produced by a magnetic field that vary in time. 3. Discuss Lenzs Law 4. Discuss induced emf and electric fields 5. Present various applications 6. Sample Problem: 1. (Read about Faradays Law of Induction and Lenzs Law) A 50-turn rectangular coil of dimensions 5.00 cm x 10.0 com is allowed to fall from a position where B = 0 to a new position where B = 0.5000T and the magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of the coil. Calculate the magnitude of the average emf that is induced in the coil if the displacement occurs in 0.250 s. 2. A flat coil of wire has an area of 0.020 m2 and consists of 50 turns. At to = 0 s, the coil is oriented so the normal to its surface is parallel (o = 0) to a constant magnetic field of magnitude 0.18 T. The coil is then rotated through an angle of = 30.0 in a time of 0.10 s. a. Determine the average induced emf b. What would be the induced emf if the coil were returned to its initial orientation in the same time of 0.10s? Assignment: Group 1,2,3 & 4 for problems 4,3,2 & 1, respectively. -3 1. (Read about Magnetic Flux ) A coil of wire consists of 20 turns, or loops, each of which has an area of 1.5 x 10 2 m . A magnetic field is perpendicular to the surface of each loop at all times, so that = o = 0. At time to = 0s, the magnitude of the field at the location of the coil is Bo = 0.050 T. At a later time t = 0.10s, the magnitude of the field at the coil has increased to B = 0.060 T. a. Find the average emf induced in the coil during this time. b. What would be the value of the average induced emf if the magnitude of the magnetic field decreased from 0.060 T to 0.050 T in 0.10s? 2. (Read about Magnetic Flux ) The magnetic field shown in the figure decreases from 1.0 T to 0.4 T in 1.2 s. A 6.0 cm diameter loop with a resistance of 0.010 W is perpendicular to the field. a. Find the average emf induced in the coil during this time. b. What is the size and direction of the current induced in the loop?
x x x
x x x
x x
x x x
x x x B
3. (Motional Emf) The figure above shows a top view of a bar that can slide without friction. The resistor is 6.00 and a 2.50 T magnetic field is directed perpendicularly downward, into the paper. Let l=1.20 m. a. Calculate the applied force required to move the bar to the right at a constant speed of 2.00 m/s. b. At what rate is energy delivered to the resistor? 4. (Read about emf induced in AC Generator) The coil of the ac generator rotates at a frequency of f =60.0 Hz and -3 2 develops an emf of 120 V (rms). The coil has an area of A = 3.0 x 10 m and consists of N = 500 turns. a. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field in which the coil rotates. b. If the total resistance of the wire is 12, what is the maximum induced current when the output terminals are connected to a low resistance conductor? \Module9Phy271-SY2010-11
Você também pode gostar
- Given On Exams Induction EMF (With Answers)Documento3 páginasGiven On Exams Induction EMF (With Answers)firuze.isgenderli41Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 - ExerciseDocumento17 páginasChapter 6 - ExerciseRizky HermawanAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetic InductionDocumento1 páginaElectromagnetic InductionArijit SahaAinda não há avaliações
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic InductionDocumento20 páginasNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic InductionDileep GAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial QuestionsDocumento20 páginasTutorial Questionsharshiika kathiravanAinda não há avaliações
- Electric Motor LabreportDocumento5 páginasElectric Motor Labreportapi-257066694Ainda não há avaliações
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic InductionDocumento26 páginasNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Inductionjaswanth .sAinda não há avaliações
- Probset 3Documento1 páginaProbset 3SkambalahardarAinda não há avaliações
- Exercises Chapter2-Phy106 - MaxwellDocumento2 páginasExercises Chapter2-Phy106 - MaxwellhwuhwuheAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 30 (1) .MagneticDocumento29 páginasChapter 30 (1) .MagneticOsama HassanAinda não há avaliações
- PHY102: Electricity and Magnetism Homework 4Documento2 páginasPHY102: Electricity and Magnetism Homework 4Gourav GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Chapter 6Documento3 páginasTutorial Chapter 6malzAinda não há avaliações
- 4bexample 30Documento2 páginas4bexample 30Sharath MysoreAinda não há avaliações
- Motors PhysicsDocumento25 páginasMotors PhysicsBilly100% (1)
- Jrs Tutorials: Physics Practice Sheet Electromagnetic InductionDocumento18 páginasJrs Tutorials: Physics Practice Sheet Electromagnetic InductionSumSetAinda não há avaliações
- ExercisesDocumento9 páginasExercisesKriti NarayananAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 2 - SJP SirDocumento2 páginasAssignment 2 - SJP SirrunurmineAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Worksheet 2 For Grade 12Documento2 páginasPhysics Worksheet 2 For Grade 12Daniel GtsadkanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 30 PhysicsDocumento29 páginasChapter 30 Physicseg40340% (1)
- Generator Write UpDocumento14 páginasGenerator Write UpJerome B. PioAinda não há avaliações
- Fisika FaradayDocumento3 páginasFisika FaradaySutirto SuhartoAinda não há avaliações
- Phy 150Documento5 páginasPhy 150AtyA Sßir4hAinda não há avaliações
- Physics XII: Important Questions 2020 NumericalDocumento3 páginasPhysics XII: Important Questions 2020 NumericalShaheer JafriAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 8 Electromagnetic Induction and Induct AnceDocumento20 páginasTopic 8 Electromagnetic Induction and Induct AnceSmk Abdul Rahim Dua100% (1)
- Tutorial 7: Electromagnetic Induction MARCH 2015: Phy 150 (Electricity and Magnetism)Documento3 páginasTutorial 7: Electromagnetic Induction MARCH 2015: Phy 150 (Electricity and Magnetism)NOR SYAZLIANA ROS AZAHARAinda não há avaliações
- EMI and AC TYPE 1Documento19 páginasEMI and AC TYPE 1sanits591Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment Work Class: Xii Subject: Physics (Magnetism and Matter)Documento7 páginasAssignment Work Class: Xii Subject: Physics (Magnetism and Matter)NishantAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento33 páginasChapter 6sanjanaAinda não há avaliações
- Module2 Lesson3Documento5 páginasModule2 Lesson3Jerald AlvaradoAinda não há avaliações
- Faraday's Law of Induction: Lab ReportDocumento8 páginasFaraday's Law of Induction: Lab ReportAymen JavaidAinda não há avaliações
- Faraday's Law of Induction: Lab ReportDocumento8 páginasFaraday's Law of Induction: Lab ReportAymen JavaidAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engg QB Unit II 1302020Documento2 páginasFundamentals of Electrical Engg QB Unit II 1302020ABHI THORATAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet 6@HiLCoEDocumento4 páginasWorksheet 6@HiLCoEAbraham DamtewAinda não há avaliações
- Expected Important Problems XiiDocumento9 páginasExpected Important Problems XiiKandhan KandhanAinda não há avaliações
- NCERT Grade-12 Physics CH 06 Electromagnetic-Induction1Documento15 páginasNCERT Grade-12 Physics CH 06 Electromagnetic-Induction1Raunak KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 22Documento3 páginasAssignment 22Ashish AwasthiAinda não há avaliações
- Ihw 4Documento7 páginasIhw 4LogoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4-MAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT-1Documento3 páginasChapter 4-MAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT-1helixvector45411Ainda não há avaliações
- Em Shock AbsorbersDocumento4 páginasEm Shock AbsorbersIctor PrinceAinda não há avaliações
- Phys 162 Chapter 11-15Documento7 páginasPhys 162 Chapter 11-15Aisha NurymgaliAinda não há avaliações
- Session 1-1Documento40 páginasSession 1-1Youssef El-HendawyAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Physics NcertSolutions Chapter 6 ExercisesDocumento9 páginas12 Physics NcertSolutions Chapter 6 ExercisestheAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Assign 8Documento19 páginasBio Assign 8Gaurav ShekharAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - Electromagnetic FieldDocumento5 páginasChapter 1 - Electromagnetic Fieldhoangkhanhvn8Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento2 páginasChapter 6Monisha RAinda não há avaliações
- Wind Generator by KshitijDocumento11 páginasWind Generator by KshitijKshitij BhakooAinda não há avaliações
- 1.1: Discuss The Effect On The Magnitude of The Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor of Variations inDocumento20 páginas1.1: Discuss The Effect On The Magnitude of The Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor of Variations inYousef YohannaAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 5Documento4 páginasTutorial 5Wan HafizaAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetism STUDocumento19 páginasElectromagnetism STUFirdaus BhathenaAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsDocumento5 páginasMagnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsBug LordAinda não há avaliações
- 12th Class Guess Papers 2024 Phy LongDocumento4 páginas12th Class Guess Papers 2024 Phy Longia3461220020Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento2 páginasAssignment 1Vishal VermaAinda não há avaliações
- 12th Physics Guess Papers +subjective + MCQs by Urdu BooksDocumento26 páginas12th Physics Guess Papers +subjective + MCQs by Urdu BooksshahmeergraphicsserviceAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Electromagnetic InductionDocumento23 páginas6 Electromagnetic Inductionveeru343Ainda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Numerical Problems With SolutionDocumento4 páginasMagnetic Effect of Electric Current Numerical Problems With SolutionAtul Vikash Kumar AnshAinda não há avaliações
- XII Physics Important Topic List 2024Documento2 páginasXII Physics Important Topic List 2024khaanianasAinda não há avaliações
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocumento18 páginasMoving Charges and MagnetismsmsubramaniamAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 10 Physics L1 FeedbackDocumento3 páginasGrade 10 Physics L1 FeedbackYonasAinda não há avaliações
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsNo EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (4)
- MS 005 For DUCT FABRICATION - INSULATION & INSTALLATION REV-1Documento21 páginasMS 005 For DUCT FABRICATION - INSULATION & INSTALLATION REV-1vusal huseynli100% (2)
- Vanilla Farming: The Way Forward: July 2019Documento6 páginasVanilla Farming: The Way Forward: July 2019mituAinda não há avaliações
- SMA - Core 1 - IEC62109-2 - 0 Test ReportDocumento6 páginasSMA - Core 1 - IEC62109-2 - 0 Test ReportFurqan HamidAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-3 DC Machines IMP QuestionsDocumento30 páginasUnit-3 DC Machines IMP Questionskrishna Sai Atla VenkataAinda não há avaliações
- Fractal Audio Footswitch Functions Guide PDFDocumento22 páginasFractal Audio Footswitch Functions Guide PDFerikAinda não há avaliações
- (Q2) Electrochemistry 29th JulyDocumento21 páginas(Q2) Electrochemistry 29th JulySupritam KunduAinda não há avaliações
- Refrigerant Solutions: Refrigerant Retrofit For Existing R22 EquipmentDocumento2 páginasRefrigerant Solutions: Refrigerant Retrofit For Existing R22 EquipmentpriyoAinda não há avaliações
- Driver DST-4812 For 7.2 KG CMDocumento5 páginasDriver DST-4812 For 7.2 KG CMWWW.150775.BUGME.PWAinda não há avaliações
- IJETR022563Documento5 páginasIJETR022563erpublicationAinda não há avaliações
- Genesis of KupferschieferDocumento15 páginasGenesis of KupferschieferMaricela GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical BOQ 07.12.2021 New Boq R4 05-01-2022 Final 16.02.2022Documento92 páginasElectrical BOQ 07.12.2021 New Boq R4 05-01-2022 Final 16.02.2022Upendra ChariAinda não há avaliações
- Module IiDocumento5 páginasModule IiFahmi PrayogiAinda não há avaliações
- LC Magna Leaflet 2019Documento2 páginasLC Magna Leaflet 2019saemiAinda não há avaliações
- Bài 1: Fill in The Blank With Present Simple, Present Continuous or Past SimpleDocumento6 páginasBài 1: Fill in The Blank With Present Simple, Present Continuous or Past SimplePhương Anh Đỗ NgọcAinda não há avaliações
- Planet Earth: Its Propeties To Support LifeDocumento27 páginasPlanet Earth: Its Propeties To Support LifegillianeAinda não há avaliações
- Obs Inf Worksheet 2013Documento2 páginasObs Inf Worksheet 2013api-338002331Ainda não há avaliações
- NHouse SelfBuilder Brochure v2 Jan19 LowresDocumento56 páginasNHouse SelfBuilder Brochure v2 Jan19 LowresAndrew Richard ThompsonAinda não há avaliações
- Zhou 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 252 032144Documento11 páginasZhou 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 252 032144Dante FilhoAinda não há avaliações
- Ar ExportsDocumento1 páginaAr ExportsRais AlamAinda não há avaliações
- Brenda Patton Guided Reflection QuestionsDocumento3 páginasBrenda Patton Guided Reflection QuestionsCameron JanzenAinda não há avaliações
- DHL Product Solutions Portfolio 2017Documento1 páginaDHL Product Solutions Portfolio 2017Hanzla TariqAinda não há avaliações
- Rightship Ship Inspection Questionnaire RISQDocumento177 páginasRightship Ship Inspection Questionnaire RISQИгорь100% (3)
- MFI 2 - Unit 3 - SB - L+SDocumento10 páginasMFI 2 - Unit 3 - SB - L+SHoan HoàngAinda não há avaliações
- Service Manual: RP-6000 MK6 LTD RP-6000 MK6 BDocumento44 páginasService Manual: RP-6000 MK6 LTD RP-6000 MK6 BFivor EdwardsAinda não há avaliações
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography: University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Pharmacy Department of BiochemistryDocumento32 páginasHigh Performance Liquid Chromatography: University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Pharmacy Department of BiochemistryMa. Ellah Patricia M. GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- 510 1453 1 PB Tiang ReklameDocumento6 páginas510 1453 1 PB Tiang ReklameGunaedy UtomoAinda não há avaliações
- Sugar Factory InsulationDocumento29 páginasSugar Factory InsulationZerihun Negash100% (1)
- Course For Loco Inspector Initial (Diesel)Documento239 páginasCourse For Loco Inspector Initial (Diesel)Hanuma Reddy93% (14)
- Question Paper - GIAN - 19 - ModifiedDocumento4 páginasQuestion Paper - GIAN - 19 - Modifiedsayan mukherjeeAinda não há avaliações
- The Modern Day Cult: by Antonio Panebianco, Jason Devine, Will RichardsDocumento11 páginasThe Modern Day Cult: by Antonio Panebianco, Jason Devine, Will RichardsAntonio PanebiancoAinda não há avaliações