Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Stepper Motor
Enviado por
api-265872370 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
384 visualizações4 páginasThe shaft of a stepper motor rotates indiscrete step increments when electrical command pulses are applied to it in the proper sequence. ADVANTAGES The rotation angle of the motor is proportional to the input pulse. Excellent response to starting / stopping / reversing. Very reliable since there are no contact brushes in the motor. Not easy to operate at extremely high speeds.
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThe shaft of a stepper motor rotates indiscrete step increments when electrical command pulses are applied to it in the proper sequence. ADVANTAGES The rotation angle of the motor is proportional to the input pulse. Excellent response to starting / stopping / reversing. Very reliable since there are no contact brushes in the motor. Not easy to operate at extremely high speeds.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
384 visualizações4 páginasStepper Motor
Enviado por
api-26587237The shaft of a stepper motor rotates indiscrete step increments when electrical command pulses are applied to it in the proper sequence. ADVANTAGES The rotation angle of the motor is proportional to the input pulse. Excellent response to starting / stopping / reversing. Very reliable since there are no contact brushes in the motor. Not easy to operate at extremely high speeds.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 4
Stepper Motor
A stepper motor is an electromechanicaldevice which converts
electrical pulses into discrete mechanical movements.
The shaft of a stepper motor rotates indiscrete step increments when
electrical command pulses are applied to it in the proper sequence.
The sequence of the applied pulses is directly related to the direction
of motor shafts rotation. The speed of the motor shafts rotation is
directly related tothe frequency of the input pulses.
ADVANTAGES
The rotation angle of the motor is proportional to the input pulse.
The motor has full torque at standstill
Precise positioning
Excellent response to starting/stopping/reversing.
Very reliable since there are no contact brushes in the motor.
Therefore the life of the motor is simply dependant on the life of the
bearing.
The motors response to digital input pulses provides open-loop
control, making the motor simpler and less costly to control.
It is possible to achieve very low speed synchronous rotation with a
load that is directly coupled to the shaft.
A wide range of rotational speeds can be realized, as the speed is
proportional to the frequency of the input pulses.
Disadvantages
Resonance’s can occur if not properly controlled.
Not easy to operate at extremely high speeds.
Stepper Motor Types
There are three basic stepper motor types. They are
Variable-reluctance
Permanent magnet
Hybrid
Variable-reluctance (VR)
This type of motor consists of a soft iron multi-toothed rotor and a wound
stator. When the stator windings are energized with DC current the poles
become magnetized. Rotation occurs when the rotor teeth are attracted to
the energized stator poles.
Permanent Magnet (PM)
The rotor no longer has teeth as with the VR motor. Instead the rotor is
magnetized with alternating north and south poles situated in a straight line
parallel to the rotor shaft. These magnetized rotor poles provide an
increased magnetic flux intensity and because of this the PM motor exhibits
improved torque characteristics when compared with the VR type.
Hybrid Motor
The hybrid stepper motor is more expensive than the PM stepper
motor but provides better performance with respect to step
resolution, torque and speed.
The hybrid stepper motor combines the best features of both the PM
and VR type stepper motors.
The rotor is multi-toothed like the VR motor and contains an axially
magnetized concentric magnet around its shaft. The teeth on the
rotor provide an even better path, which helps guide the magnetic
flux to preferred locations in the air gap. This further increases the
detent, holding and dynamic torque characteristics of the motor
when compared with both the VR and PM types.
Torque Generation
The torque produced by a stepper motor depends on several factors.
• The step rate
• The drive current in the windings
• The drive design or type
In a stepper motor a torque is developed when the magnetic fluxes of the
rotor and stator are displaced from each other.
The stator is made up of a high permeability magnetic material. The
presence of this high permeability material causes the magnetic flux to be
confined for the most part to the paths defined by the stator structure in
the same fashion that currents are confined to the conductors of an
electronic circuit.
This serves to concentrate the flux at the stator poles. The torque output
produced by the motor is proportional to the intensity of the magnetic flux
generated when the winding is energized.
Stepping Modes (or) Modes of Excitation
The following are the most common drive modes.
Wave Drive (1 phase on)
Full Step Drive (2 phases on)
Half Step Drive (1 & 2 phases on)
Você também pode gostar
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- CircuitAnalysis CK Tse PDFDocumento49 páginasCircuitAnalysis CK Tse PDFcivaasAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Magnet Is Am NotesDocumento18 páginasMagnet Is Am Notesapi-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- Nodal Analysis of Electric CircuitsDocumento5 páginasNodal Analysis of Electric Circuitsapi-26587237100% (3)
- CH 29Documento52 páginasCH 29api-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Node AnalysisDocumento25 páginasNode Analysisapi-26587237100% (1)
- CH 21Documento50 páginasCH 21api-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- CH 26Documento38 páginasCH 26api-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- CH 9Documento40 páginasCH 9api-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- CH 18Documento52 páginasCH 18api-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- CH 25Documento34 páginasCH 25api-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- CH 4Documento36 páginasCH 4api-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- CH 7Documento43 páginasCH 7api-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Controller For Switchede Luctance MotorDocumento74 páginasController For Switchede Luctance MotorakkarapakaanandaAinda não há avaliações
- Modelsim TutDocumento84 páginasModelsim TutcomtectureAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- CH 4 SWProcessesDocumento50 páginasCH 4 SWProcessesapi-3748142Ainda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- An Introduction To Software Engineering: ©ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th Edition. Chapter 1 Slide 1Documento29 páginasAn Introduction To Software Engineering: ©ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th Edition. Chapter 1 Slide 1api-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- Multilevel Modeling and Simulation of A Switched Reluctance MachineDocumento5 páginasMultilevel Modeling and Simulation of A Switched Reluctance Machineapi-26587237Ainda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- AICTE Approved Institutes Dec 19 2012Documento789 páginasAICTE Approved Institutes Dec 19 2012dipakdks420Ainda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Instructions For Vinyl Ester Butt Weld KitsDocumento4 páginasInstructions For Vinyl Ester Butt Weld KitsMukiara LuffyAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- SPI Mold Finish - Practical Approach: ShareDocumento2 páginasSPI Mold Finish - Practical Approach: ShareDavid Lay IIAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Hitachi Ex1201 Parts Sec Wat PDFDocumento82 páginasHitachi Ex1201 Parts Sec Wat PDFBeatriceJessiAinda não há avaliações
- P94 1398Documento2 páginasP94 1398JoseGarzaAinda não há avaliações
- Wacker Neuson Concrete Technology BrochureDocumento17 páginasWacker Neuson Concrete Technology BrochureMuhaiminAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Guide On Internal Audit of Automobile Industry: ISBN: 978-81-8441-853-8Documento205 páginasTechnical Guide On Internal Audit of Automobile Industry: ISBN: 978-81-8441-853-8Dev JainAinda não há avaliações
- Exemptions Granted To Large Taxpayers January, 2010 To September, 2014 PDFDocumento82 páginasExemptions Granted To Large Taxpayers January, 2010 To September, 2014 PDFRashid BumarwaAinda não há avaliações
- RTMST 2013Documento327 páginasRTMST 2013palpandi.mAinda não há avaliações
- Latrine Slabs and SeatsDocumento4 páginasLatrine Slabs and SeatsGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Lab II Manual Cycle 1Documento13 páginasThermal Lab II Manual Cycle 1Rony RkzAinda não há avaliações
- Report On SwitzerlandDocumento21 páginasReport On Switzerlandyrrej odlasAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Service ML 350/370Documento531 páginasService ML 350/370Lex Jang100% (1)
- NR24A-SR Datasheet En-Gb PDFDocumento3 páginasNR24A-SR Datasheet En-Gb PDFWagesusilo23121986_Ainda não há avaliações
- Interconnect Noise Optimization in Nanometer TechnologiesDocumento145 páginasInterconnect Noise Optimization in Nanometer TechnologiesSmile NagsAinda não há avaliações
- Turbo Chargers T3-T4Documento1 páginaTurbo Chargers T3-T4Andries FerreiraAinda não há avaliações
- Selecting Either Layered Manufacturing or CNC Machining To Build Your PrototypeDocumento9 páginasSelecting Either Layered Manufacturing or CNC Machining To Build Your PrototypeMico StanojevicAinda não há avaliações
- Outdoor Off Load Disconnectors 12 420KVEnglishDocumento2 páginasOutdoor Off Load Disconnectors 12 420KVEnglishdip461Ainda não há avaliações
- Biogastrain Produktblad 2005Documento2 páginasBiogastrain Produktblad 2005adamyogiAinda não há avaliações
- FirecelDocumento24 páginasFirecelapi-3803155Ainda não há avaliações
- Proposed External Bathroom For Mr. at Bills of QuantitiesDocumento2 páginasProposed External Bathroom For Mr. at Bills of QuantitiesNadun AthukoralaAinda não há avaliações
- RC Chapter01 2016Documento7 páginasRC Chapter01 2016Luna Latisya0% (1)
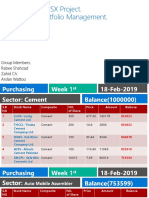
- Investment in PSX Project. Investment Portfolio Management.: Group Members. Rabee Shahzad Zahid Ch. Arslan WattooDocumento50 páginasInvestment in PSX Project. Investment Portfolio Management.: Group Members. Rabee Shahzad Zahid Ch. Arslan WattooAhmad MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Economics of Gas Gathering CashflowDocumento83 páginasEconomics of Gas Gathering CashflowDerrick GloverAinda não há avaliações
- Flow, Slope &pipe Dia. Calculation Using Manning's FormulaDocumento8 páginasFlow, Slope &pipe Dia. Calculation Using Manning's FormulaAhmed KhalifaAinda não há avaliações
- Abedian School of Architecture - CRAB Studio - ArchDailyDocumento7 páginasAbedian School of Architecture - CRAB Studio - ArchDailyAnonymous 1uGSx8bAinda não há avaliações
- PREFACE 1978 Laminar Flow Forced Convection in DuctsDocumento2 páginasPREFACE 1978 Laminar Flow Forced Convection in Ductsakamaka99Ainda não há avaliações
- 1.review of PFD, Pid, PdsDocumento10 páginas1.review of PFD, Pid, PdssuhailfarhaanAinda não há avaliações
- ECSCADA Presentation NRB 120816Documento36 páginasECSCADA Presentation NRB 120816Mohit Sharma100% (1)
- Warmate enDocumento12 páginasWarmate enSonia RainaAinda não há avaliações
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonNo EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...Ainda não há avaliações
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionNo EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (543)