Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
LTM Laplace Transform 2011a MK
Enviado por
Nguyen Manh LongDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
LTM Laplace Transform 2011a MK
Enviado por
Nguyen Manh LongDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Nguyn Cng Phng g y g g
Electric Circuit Theory Electric Circuit Theory
The Laplace Transform
Contents
1. Basic Elements Of Electrical Circuits
2. Basic Laws
3. Electrical Circuit Analysis
4. Circuit Theorems
5. Active Circuits
6. Capacitor And Inductor
7. First Order Circuits
8 S d O d Ci it 8. Second Order Circuits
9. Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis
10. AC Power Analysis
11 Three phase Circuits 11. Three-phase Circuits
12. Magnetically Coupled Circuits
13. Frequency Response
14. The Laplace Transform 14. The Laplace Transform
15. Two-port Networks
The Laplace Transform
2
The Laplace Transform
f(t) = 0
(integrodifferential)
i(t), v(t), Circuit
Laplace Transform Inverse Transform Laplace Transform Inverse Transform
F(s) = 0
(algebraic)
I(s), V(s),
The Laplace Transform
3
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
4
Definition
( ) f t
t 0
| |
0
( ) ( ) ( )
st
F s L f t f t e dt
= =
}
s j o e = +
0
( )
t
f t e dt
o
<
}
| |
1
1
1
1
( ) ( ) ( )
2
j
st
j
f t L F s F s e ds
j
o
o
t
+
= =
}
The Laplace Transform
5
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
6
Two Important Singularity Functions (1)
( ) u t
1
0 0
( )
1 0
t
u t
t
<
=
>
t 0
1 0 t >
( ) u t a
1
0 t a <
t 0
1
a
0
( )
1
t a
u t a
t a
<
=
>
The Laplace Transform
7
Two Important Singularity Functions (2)
Ex. 1
Determine the Laplace transform for the waveform?
( ) u t
1
0
( ) ( )
st
F s u t e dt
=
}
t 0
0
}
0
1
st
e dt
=
}
0
1
st
e
s
=
1
s
=
The Laplace Transform
8
Two Important Singularity Functions (3)
Ex. 2
Determine the Laplace transform for the waveform?
0
( ) ( )
st
F s u t a e dt
=
}
( ) u t a
1
0
}
0
0 1
a
st
a
dt e dt
= +
} }
t 0
a
1
st
a
e
s
=
as
e
s
=
The Laplace Transform
9
Two Important Singularity Functions (4)
Ex. 3
Determine the Laplace transform for the waveform?
1
0
( ) [ ( ) ( )]
st
F s u t u t a e dt
=
}
t 0
1
a
0
}
0
1
( )
st
u t e dt
s
=
}
( ) u t
1
0
( )
st
st
e
u t a e dt
s
=
}
t 0
1 1
( )
as as
e e
F s
= =
t
( ) u t a
0
The Laplace Transform
10
( )
s s s
1
a
Two Important Singularity Functions (5)
( ) t o
( ) 0 0 t t o = =
t 0
( ) 0 0
( ) 1 0
t t
t dt
c
c
o
o c
=
= >
}
( ) t a o
( ) 0 t a t a o = =
t 0
a
( )
( ) 1 0
a
a
t a dt
c
c
o c
+
= >
}
2 1 2
( )
( ) ( )
t f a t a t
f t t a dt o
< <
=
}
The Laplace Transform
11
1
1 2
( ) ( )
0 ,
t
f t t a dt
a t a t
o
< >
}
Two Important Singularity Functions (6)
Ex. 4
Determine the Laplace transform of an impulse function?
0
( ) ( )
st
F s t a e dt o
=
}
2
1
1 2
1 2
( )
( ) ( )
0 ,
t
t
f a t a t
f t t a dt
a t a t
o
< <
=
< >
}
( )
as
F s e
=
1
1 2
0 , a t a t < >
The Laplace Transform
12
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
13
Transform Pairs (1)
Ex. 1
Find the Laplace transform of f(t) = t?
0
( )
st
F s te dt
=
}
1
Let & &
st st st
u t dv e dt du dt v e dt e
= = = = =
}
s
}
2
0
0
0
1
( ) 0
st st
st
t e e
F s e dt
s s s s
= + = =
}
The Laplace Transform
14
Transform Pairs (2)
Ex. 2
Find the Laplace transform of f(t) =cost?
0
( ) cos
st
F s te dt e
=
}
0
2
j t j t
st
e e
e dt
e e
+
=
}
( ) ( ) s j t s j t e e + ( ) ( )
0
2
s j t s j t
e e
dt
e e +
+
=
}
1 1 1 | | 1 1 1
2 s j s j e e
| |
= +
|
+
\ .
s
The Laplace Transform
15
2 2
s
s e
=
+
Transform Pairs (3)
f(t)
( ) t o ( ) u t
1
at
e
1
t
1
at
te
1
sinat cosat
F(s)
1
1
s
1
s a +
2
1
s
2
1
( ) s a +
2 2
a
s a +
2 2
s
s a +
The Laplace Transform
16
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
17
Properties of the Transform (1)
Property f(t) F(s)
( ) Af ( ) AF
1. Magnitude scaling
2. Addition/subtraction
3 Time scaling
( ) Af t ( ) AF s
1 2
( ) ( ) f t f t
1 2
( ) ( ) F s F s
( ) f at
1 s
F
| |
|
3. Time scaling
4. Time shifting
5 F hif i
( ) f at
F
a a
|
\ .
( ) ( ), 0 f t a u t a a >
( )
as
e F s
( )
at
f ( ) F
( ) ( ), 0 f t u t a a >
[ ( )]
as
e L f t a
+
5. Frequency shifting
6. Differentiation
7. Multiplication by t
( )
at
e f t
( ) F s a +
( ) /
n n
d f t dt
1 2 1 1
( ) (0) (0) ... (0)
n n n o n
s F s s f s f s f
( )
n
t f t
( 1) ( ) /
n n n
d F s ds
8. Division by t
9. Integration
( ) ( )
( ) / f t t ( )
s
F d
}
0
( )
t
f d
}
( ) / F s s
The Laplace Transform
18
10. Convolution
1 2 1 2
0
( ) * ( ) ( ) ( )
t
f t f t f f t d =
} 1 2
( ) ( ) F s F s
Properties of the Transform (2)
Ex. 1
Find the Laplace transform of
10
( ) 5 cos 20 ?
t
f t e t
= +
1 2 1 2
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) f t f t F s F s
10
( ) [5] [ ] [cos 20 ]
t
F s L L e L t
= +
( ) ( ) Af t AF s
[5] 5 [1] L L =
1
5
[5] L
s
=
1
[1] L
s
=
s
10
1
[ ]
10
t
L e
s
=
+10 s +
2 2 2
[cos 20 ]
20 400
s s
L t
s s
= =
+ +
3
The Laplace Transform
19
3
2 2
5 1 5 2400 4000
( )
10 400 ( 10)( 400)
s s s
F s
s s s s s s
+ +
= + =
+ + + +
Properties of the Transform (3)
Ex. 2
Find the Laplace transform of the waveform?
5
t 0
1 2 3
5
( ) 5 ( 1) 5 ( 2) f t u t u t =
t 0
1 2 3
2
2
5
( ) 5 5 ( )
s s
s s
e e
F s e e
= =
5
( ) 5 5 ( ) F s e e
s s s
The Laplace Transform
20
t 0
1 2 3
Properties of the Transform (4)
Ex. 3
Find the Laplace transform of the waveform?
5
t 0
1 2 3
( ) ( 5 10)[ ( 1) ( 2)] f t t u t u t = +
5 ( 1) 10 ( 1) tu t u t = + +
5
5 ( 2) 10 ( 2) tu t u t +
5 ( 1) 5( 1 1) ( 1) tu t t u t = +
5( 1) ( 1) 5 ( 1) t u t u t =
t 0
5
1 2 3
5( 1) ( 1) 5 ( 1) t u t u t =
5 ( 2) 5( 2 2) ( 2) tu t t u t = +
5( 2) ( 2) 10 ( 2) t u t u t = +
1
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) 5( 1) ( 1) 5 ( 1)
10 ( 1)
5( 2) ( 2) 10 ( 2)
f t t u t u t
u t
= +
+
t 0
1 2 3
The Laplace Transform
21
5( 2) ( 2) 10 ( 2)
10 ( 2)
t u t u t
u t
+ +
Properties of the Transform (5)
Ex. 3
Find the Laplace transform of the waveform?
5
t 0
1 2 3
( ) ( 5 10)[ ( 1) ( 2)] f t t u t u t = +
5( 1) ( 1) 5 ( 1) t u t u t = +
5
10 ( 1)
5( 2) ( 2) 10 ( 2)
10 ( 2)
u t
t u t u t
t
+
+ +
t 0
5
1 2 3
10 ( 2) u t
5( 1) ( 1) 5 ( 1)
5( 2) ( 2)
t u t u t
t u t
= + +
+
1
5( 2) ( 2) t u t +
2
2 2
5
( ) 5 5
s s
s
e e
F s e
s s s
= + +
The Laplace Transform
22
t 0
1 2 3
2
5
(1 )
s
s
e
s e
s
=
Properties of the Transform (6)
Ex. 4
Find the Laplace transform of the waveform?
5
t 0
1 2 3
The Laplace Transform
23
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
24
The Laplace Transform
f(t) = 0
(integrodifferential)
i(t), v(t), Circuit
Laplace Transform Inverse Transform Laplace Transform Inverse Transform
F(s) = 0
(algebraic)
I(s), V(s),
The Laplace Transform
25
Inverse Transform (1)
1
1 1 0
( ) ...
( )
m m
m m
P s a s a s a s a
F s
+ + + +
= =
1
1 1 0
( )
( ) ...
n n
n n
F s
Q s b s b s b s b
= =
+ + + +
1 2
Simple poles : ( )
n
K K K
F s + + +
1 2
1 2
Simple poles : ( ) ...
n
n
F s
s p s p s p
= + + +
+ + +
1
( )
Complex- conjugate poles : ( )
( )( )( )
P s
F s
Q j j | |
=
+ + +
1
*
1 1
( )( )( )
...
Q s s j s j
K K
s j s j
o | o |
o | o |
+ + +
= + +
+ + +
1
1 1
( )
Multiple poles : ( )
( )( )
n
P s
F s
Q s s p
K K K
=
+
The Laplace Transform
26
11 12 1
2
1 1
... ...
( ) ( ) ( )
n
n
K K K
s p s p s p
= + + + +
+ + +
Inverse Transform (2)
( ) P s K K K
1 2
1 2
( )
Simple poles : ( ) ...
( )
n
n
P s K K K
F s
Q s s p s p s p
= = + + +
+ + +
( )
( ) 0 ... 0 0 ... 0
( )
i
i i
s p
P s
s p K
Q s
=
+ = + + + + + +
1
i
p t
i
i
K
L K e
s p
(
=
(
+
i
s p +
1 2
1 2
( ) ...
n
p t p t p t
f t K e K e K e
= + + +
The Laplace Transform
27
1 2
( ) ...
n
f t K e K e K e + + +
Inverse Transform (3)
Ex. 1
Find the inverse Laplace transform of
2
25 300 640
( )
( )( )
s s
F s
+ +
= p ( )
( 4)( 8) s s s + +
1 2 3
( )
( ) ; ( ) 0 ... 0 0 ... 0
4 8 ( )
i i
K K K P s
F s s p K
s s s Q s
= + + + = + + + + + +
+ + 4 8 ( )
i
s p
s s s Q s
=
+ +
2 2
25 300 640 25 300 640 640
( ) 20
s s s s
K sF s s
+ + + +
= = = = =
1
0
0 0
( ) 20
( 4)( 8) ( 4)( 8) 4 8
s
s s
K sF s s
s s s s s
=
= =
= = = = =
+ + + +
2 2
25 300 640 25 300 640 s s s s + + + +
2
4
4 4
2
25 300 640 25 300 640
( 4) ( ) ( 4)
( 4)( 8) ( 8)
25( 4) 300( 4) 640
10
s
s s
s s s s
K s F s s
s s s s s
=
= =
+ + + +
= + = + = =
+ + +
+ +
= =
The Laplace Transform
28
10
( 4)( 4 8)
= =
+
Inverse Transform (4)
Ex. 1
Find the inverse Laplace transform of
2
25 300 640
( )
( )( )
s s
F s
+ +
= p ( )
( 4)( 8) s s s + +
1 2 3
( )
( ) ; ( ) 0 ... 0 0 ... 0
4 8 ( )
i i
K K K P s
F s s p K
s s s Q s
= + + + = + + + + + +
+ +
1 2
20; 10 K K = =
2 2
25 300 640 25 300 640
( 8) ( ) ( 8)
s s s s
K s F s s
+ + + +
+ +
4 8 ( )
i
s p
s s s Q s
=
+ +
3
8
8 8
2
( 8) ( ) ( 8)
( 4)( 8) ( 4)
25( 8) 300( 8) 640
5
s
s s
K s F s s
s s s s s
=
= =
= + = + = =
+ + +
+ +
= =
( 8)( 8 4) +
20 10 5
( ) F s = +
4 8
( ) 20 10 5
t t
f t e e
+
The Laplace Transform
29
( )
4 8
F s
s s s
= +
+ +
( ) 20 10 5 f t e e = +
Inverse Transform (5)
Ex. 2
Find the inverse Laplace transform of
100( 6)
( )
( )( )
s
F s
+
= p ( )
( 1)( 3) s s + +
The Laplace Transform
30
Inverse Transform (6)
*
1 1 1
( )
Complex- conjugate poles : ( ) ...
P s K K
F s = = + +
1
p j g p ( )
( )( )( ) Q s s j s j s j s j o | o | o | o | + + + + + +
1 1
( )
( )
( )
P s
s j K K
Q s
o | + = = u
( )
s j
Q s
o | = +
*
1 1
K K = u
K K u
j j
K e K e
u u
u
1
( )
K
F s =
1
K
s j
u
o |
+
+
1 1
... ...
j j
K e K e
s j s j s j
u
o | o | o |
+ = + +
+ + + + +
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1 1 1
( ) ... ...
j j t j j t t j t j t
f t K e e K e e K e e e
u o | u o | o | u | u + + +
( = + + = + +
1 1 1
( ) f
cos sin
j
e j
|
| | = +
| |
1
( ) cos( ) sin( ) cos( ) sin( ) ...
t
f t K e t j t t j t
o
| u | u | u | u
= + + + + + +
The Laplace Transform
31
| |
1
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) f j j | | | |
1
2 cos( ) ...
t
K e t
o
| u
= + +
Inverse Transform (7)
Ex. 3
Find the inverse Laplace transform of
2
2
4 76
( )
( )( )
s s
F s
+
= p
2
( )
( 2)( 6 25) s s s + + +
1 2 3
( )
3 4 3 4 2
K K K
F s
s j s j s
= + +
+ + + +
1 1
( )
( ) ; ( ) 2 cos( ) ...
( )
t
s j
P s
K s j f t K e t
Q s
o
o |
o | | u
= +
= + = + +
3 4 3 4 2 s j s j s + + + +
( )
s j
Q
o | = +
2 2
3
2 2
2
2
4 76 4 76
( 2) 8
( 2)( 6 25) 6 25
s
s
s s s s
K s
s s s s s
=
=
| | + +
= + = =
|
+ + + + +
\ .
2
2
s
s
=
=
\ .
2
1
2
3 4
4 76
( 3 4) 6 8 10
( 2)( 6 25)
s j
s s
K s j j
s s s
= +
+
= + = =
+ + +
o
53.1
The Laplace Transform
32
3 s j
3 o 2 3 o 2
( ) 2 10 cos(4 53.1 ) 8 20 cos(4 53.1 ) 8
t t t t
f t e t e e t e
= =
Inverse Transform (8)
Ex. 4
Find the inverse Laplace transform of
2
5( 2)
( )
( 4 )
s
F s
+
= p
2
( )
( 4 5) s s s + +
The Laplace Transform
33
Inverse Transform (9)
1 11 12 1
2
( )
Multiple poles : ( ) ... ...
( )( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
n
n n
P s K K K
F s
Q s s p s p s p s p
= = + + + +
+ + + +
1 1 1 1
( )( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Q s s p s p s p s p + + + +
1
1 1
( ) ( )
n
n
s p
s p F s K
=
+ =
1
1 1 1
[( ) ( )]
n
n
s p
d
s p F s K
ds
=
+ =
2
1 1 2
2
[( ) ( )] (2!)
n
n
s p
d
s p F s K
ds
+ =
1
s p =
1 1
1
[( ) ( )]
( )!
n j
n
j
n j
d
K s p F s
n j ds
= +
The Laplace Transform
34
1
( )!
j
s p
n j ds
=
Inverse Transform (10)
Ex. 5
Find the inverse Laplace transform of
2
2
10 34 27
( )
( 3)
s s
F s
+ +
= p
2
( )
( 3) s s +
11 12 2
1 1
2
1
( ) ; [( ) ( )]
3 ( 3) ( )!
n j
n
j
n j
K K K d
F s K s p F s
s s s n j ds
= + + = +
+ +
2 2
2 2
12
2
3
3 3
10 34 27 10 34 27
( 3) ( ) ( 3) 5
( 3)
s
s s s s
K s F s s
s s s
=
+ + + +
= + = + = =
+
1
3 ( 3) ( )!
s p
s s s n j ds
=
+ +
3 3
( )
s s = =
2
2
11
3
3
10 34 27
[( 3) ( )]
s
s
d d s s
K s F s
ds ds s
=
=
| | + +
= + = =
|
\ .
2
2
3
(20 34) (10 34 27)
7
s
s s s s
s
=
+ + +
= =
2
10 34 27 + +
The Laplace Transform
35
2
2
2
0
0
10 34 27
( ) 3
( 3)
s
s
s s
K sF s s
s s
=
=
+ +
= = =
+
Inverse Transform (11)
Ex. 5
Find the inverse Laplace transform of
2
2
10 34 27
( )
( 3)
s s
F s
+ +
= p
2
( )
( 3) s s +
11 12 2
1 1
2
1
( ) ; [( ) ( )]
3 ( 3) ( )!
n j
n
j
n j
K K K d
F s K s p F s
s s s n j ds
= + + = +
+ +
11 12 2
7; 5; 3 K K K = = =
1
3 ( 3) ( )!
s p
s s s n j ds
=
+ +
2
7 5 3
( ) F s = +
11 12 2
; ;
2
( )
3 ( 3)
s
s s s
+ +
3 3
( ) 7 5 3
t t
f t e te
= +
The Laplace Transform
36
( ) 7 5 3 f t e te = +
Inverse Transform (12)
Ex. 6
Find the inverse Laplace transform of
2
5( 3)
( )
( 1)( 2)
s
F s
+
= p
2
( )
( 1)( 2) s s + +
The Laplace Transform
37
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
38
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems (1)
Initial value theorem: lim ( ) lim ( ) f t sF s
0
Initial value theorem: lim ( ) lim ( )
t s
f t sF s
=
0
Final value theorem: lim ( ) lim ( )
t s
f t sF s
=
The Laplace Transform
39
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems (2)
Ex.
Find the initial and final values of
2
5( 1)
( )
( 2 2)
s
F s
+
=
2
( )
( 2 2) s s s + +
2
5( 1)
(0) lim ( ) lim 0
2 2
s s
s
f sF s
s s
+
= = =
+ + 2 2
s s
s s
+ +
2
0 0
5( 1)
( ) lim ( ) lim 2.5
2 2
s s
s
f sF s
s s
+
= = =
+ +
The Laplace Transform
40
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
41
Ex.
Find the current i(t)?
t = 0
+
200O
100mH
Method 1
Laplace Circuit Solutions (1)
100mH
1V
( ) i t
1
L R
di
v v e L Ri
dt
+ = + =
0
n
di
L Ri
t
i K
o
0
t t
LK RK
o o
0 L R o +
0
n
n
L Ri
dt
+ =
t
n
i Ke
o
= 0
t t
LK e RKe
o o
o + =
0 L R o + =
3
200
2000
100 10
R
L
o
= = =
2000t
n
i Ke
=
1
0.005A
200
f
e
i
R
= = =
2000
0.005
t
f n
i i i Ke
= + = +
2000 0
(0) 0.005 0.005 0 0.005 i Ke K K
= + = + = =
The Laplace Transform
42
2000
( ) 0.005(1 ) A
t
i t e
=
Laplace Circuit Solutions (2)
f(t) = 0
(integrodifferential)
i(t), v(t), Circuit
Laplace Transform Inverse Transform Laplace Transform Inverse Transform
F(s) = 0
(algebraic)
I(s), V(s),
The Laplace Transform
43
Laplace Circuit Solutions (3)
Ex.
Find the current i(t)?
t = 0
+
200O
100mH
Method 2
100mH
1V
( ) i t
0.1 200 1
L R
di
v v e i
dt
+ = + =
di di
( (
0.1 200 [1] 0.1 [200 ]
di di
L i L L L i
dt dt
( (
+ = = +
( (
1
[1] L =
s
[200 ] 200 ( ) L i I s =
1 2 1 1
( )
( ) (0) (0) (0)
n
n n n o n
d f t
s F s s f s f s f
( ) (0) (0) ... (0)
n
s F s s f s f s f
dt
0.1 0.1[ ( ) (0)] 0.1 ( )
di
L sI s i sI s
dt
(
= =
(
The Laplace Transform
44
dt
1
0.1 ( ) 200 ( ) sI s I s
s
+ =
Laplace Circuit Solutions (4)
Ex.
Find the current i(t)?
t = 0
+
200O
100mH
Method 2
100mH
1V
( ) i t
0.1 200 1
L R
di
v v e i
dt
+ = + =
1
0 1 ( ) 200 ( ) I I 0.1 ( ) 200 ( ) sI s I s
s
+ =
1 2
1 10
( )
(0 1 200) ( 2000) 2000
K K
I s
s s s s s s
= = = +
+ + + (0.1 200) ( 2000) 2000 s s s s s s + + +
1
0
10
0.005
2000
s
K
s
=
= =
+
0 s
0 005 0 005
2
2000
10
0.005
s
K
s
=
= =
The Laplace Transform
45
0.005 0.005
( )
2000
I s
s s
=
+
2000
( ) 0.005(1 ) A
t
i t e
=
f(t) = 0
(integrodifferential)
i(t), v(t), Circuit
Laplace Transform Inverse Transform Circuit Element Models Laplace Transform Inverse Transform Circuit Element Models
F(s) = 0
(algebraic)
I(s), V(s),
Circuit
in s-domain
The Laplace Transform
46
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
47
Circuit Element Models (1)
( ) i t ( ) I s
R ( ) v t
( ) i t
+
R ( ) V s
( ) I s
+
( )
( )
v Ri =
( ) ( ) Af t AF s
( ) ( ) V s RI s =
The Laplace Transform
48
Circuit Element Models (2)
( ) i t ( ) I s
L
( ) v t
+
sL
( ) V s
+
( ) v t
(0) i
( ) V s
(0) Li
di di
v L
dt
=
( )
[ ( ) (0)]
df t
A A sF s f
( ) [ ( ) (0)]
( ) (0)
V s L sI s i
sLI s Li
=
=
The Laplace Transform
49
[ ( ) (0)] A A sF s f
dt
( ) (0) sLI s Li =
Circuit Element Models (3)
( ) i t ( ) I s
C
( ) v t
+
1
sC
( ) V s
+
( ) v t
( ) V s
+
(0) v
s
0
1
( ) (0)
t
v i x dx v
C
= +
}
C
0
( )
( )
t
F s
f d
s
}
1 (0)
( ) ( )
v
V s I s
sC s
= +
(0) v
The Laplace Transform
50
(0)
(0)
v
v
s
Circuit Element Models (4)
(0) (0) Li Mi +
2 2 1
(0) (0) L i Mi +
L L
+ M
( ) v t
+
( ) v t
L L
+
sM
( ) V s
+
( ) V s
+
1 1 2
(0) (0) Li Mi +
2 2 1
(0) (0) L i Mi +
1
(0) i
2
(0) i
( ) i t
1
L
2
L
( ) i t
2
( ) v t
1
( ) v t
( ) I s
1
sL
2
sL
( ) I s
2
( ) V s
1
( ) V s
1 2
( ) ( )
( )
di t di t
v t L M = + ( ) ( ) (0) ( ) (0) V s sL I s Li sMI s Mi = +
1
( ) i t
2
( ) i t
1
( ) I s
2
( ) I s
1 1
( ) v t L M
dt dt
= +
1 1 1 1 1 2 2
( ) ( ) (0) ( ) (0) V s sL I s Li sMI s Mi = +
2 1
( ) ( )
( )
di t di t
v t L M = + ( ) ( ) (0) ( ) (0) V s sL I s L i sMI s Mi = +
The Laplace Transform
51
2 2
( ) v t L M
dt dt
= +
2 2 2 2 2 1 1
( ) ( ) (0) ( ) (0) V s sL I s L i sMI s Mi = +
Circuit Element Models (5)
( ) i t ( ) I s
R ( ) v t
( )
+
R ( ) V s
( )
+
( ) i t ( ) I s
L
( ) i t
+
sL
( ) I s
+
( ) v t
(0) i
( ) V s
+
(0) Li
The Laplace Transform
52
Circuit Element Models (6)
( ) i t ( ) I s
C
( ) v t
+
1
sC
( ) V s
+
+
(0) v
s
+ M + +
sM
+ +
1 1 2
(0) (0) Li Mi +
2 2 1
(0) (0) L i Mi +
1
L
2
L
+
2
( ) v t
+
1
( ) v t
1
sL
2
sL
+
s
2
( ) V s
+
1
( ) V s
The Laplace Transform
53
1
( ) i t
2
( ) i t
1
( ) I s
2
( ) I s
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
54
Analysis Techniques (1)
1 2
KVL/KCL: ( ) ( ) ... ( ) 0
n
x t x t x t + + + =
1 2
( ) ( ) ( )
n
1 2
KVL/KCL: ( ) ( ) ... ( ) 0
n
X s X s X s + + + =
i(t), v(t), Circuit
Inverse Transform Circuit Element Models
DC circuit analysis techniques
(KVL KCL nodal analysis
Circuit
(KVL, KCL, nodal analysis,
mesh analysis, source
transformation, superposition,
Thevenin/Norton equivalent, )
The Laplace Transform
55
I(s), V(s),
Circuit
in s-domain
Analysis Techniques (2)
Ex. 1
Find the current i(t)?
t = 0
+
200O
100mH
100mH
1V
( ) i t
200
(0) 0 i =
1
200 ( ) 0.1 ( ) 0.1 (0) 200 ( ) 0.1 ( ) I s sI s i I s sI s
s
+ = = +
+
200
0.1s
s
1 2
1 10
( )
(0.1 200) ( 2000) 2000
K K
I s
s s s s s s
= = = +
+ + +
1
s
( ) I s
+
0.1 (0) i
1
0
10
0.005
2000
s
K
s
=
= =
+
0 005 0 005
2
2000
10
0.005
s
K
s
=
= =
2000
The Laplace Transform
56
0.005 0.005
( )
2000
I s
s s
=
+
2000
( ) 0.005(1 ) A
t
i t e
=
Analysis Techniques (3)
t 0
Ex. 1
Find the current i(t)?
t = 0
+
200O
100mH
2000
( ) 0.005(1 ) A
t
i t e
=
1. Solve for initial capacitor
voltages & inductor currents
2. Draw an s-domain circuit
Inverse Transform
1V
( ) i t
3. Use one of DC circuit
analysis techniques to solve
for voltages or/and currents
in s-domain
(0) 0 i =
Inverse Transform
Circuit Element Models
200
in s domain
4. Find the inverse Laplace
transform to convert them
back to the time domain
+
0.1s
1
0.1 (0) 0 i =
1
200 ( ) 0.1 ( ) I s sI s
s
+ =
10
( )
( 2000)
I s
s s
=
+
The Laplace Transform
57
s
( ) I s
+
0.1 (0) 0 i
s ( 2000) s s +
Analysis Techniques (4)
Ex. 2
Find the voltage v(t)?
t = 0
10kO
+
4
6
4
1
10
1 5
25 10
( ) // ( )
1
2
10
s
V s R J s
sC s
(
= =
(
+
+
(0) 0 v =
2
5 A
t
e
25 F
v
+
6
10
25 10 s
10k
5
A
2 s +
+
( ) V s
4
1 2
4 10
( 2)( 4) 2 4
K K
s s s s
= = +
+ + + +
1. Solve for initial capacitor voltages &
i d t t
6
1
25 10 s
( 2)( 4) 2 4 s s s s + + + +
4
4
1
2
4 10
2 10
4
s
K
s
=
= =
+
inductor currents
2. Draw an s-domain circuit
3. Use one of DC circuit analysis
techniques to solve for voltages or/and
currents in s-domain
4
4
2
4
4 10
2 10
2
s
K
s
=
= =
+
The Laplace Transform
58
currents in s-domain
4. Find the inverse Laplace transform to
convert them back to the time domain
4 2 4
( ) 2 10 ( ) V
t t
v t e e
=
0
Analysis Techniques (5)
Ex. 3
Find the current i(t)?
( ) i t
+
( ) I s
+
+
4O
0 t =
8O
+
12
8
(0) 1A
8
i = = L
( ) v t
+
(0) i
sL
( ) V s
+
+
2H
8V
( ) i t
12V
12
2
( )
2 4
s
I s
s
+
=
+
(0) Li
+
4
2
2
( ) I s
+
12
1. Solve for initial capacitor voltages &
i d t t
1 2
6
( 2) 2
s K K
s s s s
+
= = +
+ +
2s
( ) I s
12
s
inductor currents
2. Draw an s-domain circuit
3. Use one of DC circuit analysis
techniques to solve for voltages or/and
currents in s-domain
1
0
6
3
2
s
s
K
s
=
+
= =
+
6
2
( ) 3 2 A
t
i t e
=
The Laplace Transform
59
currents in s-domain
4. Find the inverse Laplace transform to
convert them back to the time domain
2
2
6
2
s
s
K
s
=
+
= =
0
Analysis Techniques (6)
Ex. 4
Find the voltage v(t)?
+
4O
0 t =
8O
+
+
( ) i t
+
1
( ) I s
+
12 8
1
( )
s s
V s
(0) 8 V v =
2F
8V
( ) v t
12V
C
( ) v t
+
sC
( ) V s
+
+
( )
1
2
4
2
s s
V s
s
s
=
+
1 2
0.5 K K
+
4
1
8
s
( ) V
+
12
+
(0) v
s
1. Solve for initial capacitor voltages &
i d t t
1 2
0.5
( 0.125) 0.125
K K
s s s s
= = +
+ +
1
0.5
4 K = =
2s
( ) V s
12
s
inductor currents
2. Draw an s-domain circuit
3. Use one of DC circuit analysis
techniques to solve for voltages or/and
currents in s-domain
1
0
0.125
s
s
=
+
2
0 125
0.5
4 K
s
= =
The Laplace Transform
60
currents in s-domain
4. Find the inverse Laplace transform to
convert them back to the time domain
0.125 s
s
=
0.125
( ) 4(1 ) V
t
v t e
=
Analysis Techniques (7)
Ex. 5
Write the mesh equations in the s-domain?
1
C
1
R
2
R
2
L
+
1
( ) e t
2
( ) e t
3
L
C
3
(0) i
2
(0) i
+
+
1
(0) v
(0) v
L
( ) v t
( ) i t
+
sL
( ) V s
( ) I s
+
(0) Li
3
C
3
(0) v
1
R
2
R
2
sL
1
(0) v
s
+
( ) v t
(0) i
( ) V s
+
(0) Li
+
1
1
sC
3
sL
2 2
(0) L i
+
( ) i t ( ) I s
1
( ) E s
2
( ) E s
3 3
(0) L i
3
(0) v
+
C
( ) v t
+
1
sC
( ) V s
+
+
(0) v
The Laplace Transform
61
3
1
sC
s
+
s
Analysis Techniques (8)
Ex. 5
Write the mesh equations in the s-domain?
1
C
1
R
2
R
2
L
+
1
( ) e t
2
( ) e t
3
L
C
3
(0) i
2
(0) i
+
+
1
(0) v
(0) v
1
1
1
: ( )
1
A
A R I s
sC
| |
+ +
|
\ .
| |
3
C
3
(0) v
3
3
1 3
1
[ ( ) ( )]
(0) (0)
( ) (0)
A B
sL I s I s
sC
v v
E s L i
| |
+ + =
|
\ .
= +
1
R
2
R
2
sL
1
(0) v
s
+ 1 3 3
( ) (0) E s L i
s s
= +
+
1
1
sC
3
sL
2 2
(0) L i
+
( )
2 2
: ( )
B
B R sL I s + +
( )
A
I s
( )
B
I s
1
( ) E s
2
( ) E s
3 3
(0) L i
3
(0) v
+
3
3
1
[ ( ) ( )]
(0)
B A
sL I s I s
sC
| |
+ + =
|
\ .
The Laplace Transform
62
3
1
sC
s
3
3 3 2 2 2
(0)
(0) (0) ( )
v
L i L i E s
s
=
Analysis Techniques (9)
Ex. 6
Write the node equations in the s-domain?
+
2
C
2
(0) v
1
L
1
(0) i
2
(0) i
2
L
3
(0) v
3
C
+
1
( ) j t 1
R
3
R
3
3
( ) j t
The Laplace Transform
63
Analysis Techniques (10)
Ex. 7
Solve for v(t) ?
8O
1F
(0) 0; (0) 0;
L C
i v = =
+
1H
2O
1F
+
( ) v t
15
( )
5 ( )
: 0
1
2
a
a
V s
V s
s
a
s s
+ =
+
5 ( ) A u t
15 ( ) V u t
s
2
3 2
10 35 15
( )
2
a
s s
V s
s s s
+ +
=
+ +
8
s
1
s
a
2 s s s + +
2
3 2
( ) 10 35 15
( ) 2 2
1
2 2 1
2
a
V s s s s
V s
s s s s
+ +
= =
+ + +
+
5
s
15
s
2
+
( ) V s
2 2 1
2
s s s s
s
+ + +
+
11 12
10( 3) s K K +
= = +
The Laplace Transform
64
s
2 2
( 1) 1 ( 1) s s s
+
+ + +
Analysis Techniques (11)
Solve for v(t) ?
8
1
a
Method 1
Ex. 7
+
5
15
s
2
s
+
( ) V s
11 12
2 2
10( 3)
( )
( 1) 1 ( 1)
s K K
V s
s s s
+
= = +
+ + +
2
12
2
1
1
10( 3)
( 1) 10( 3) 20
( 1)
s
s
s
K s s
s
=
=
+
= + = + =
+
s
s
( )
2
11
2
1
1
10( 3)
( 1) 10 3 10
( 1)
s
s
d s d
K s s
ds s ds
=
=
( +
= + = + =
(
+
1 s
2
10 20
( ) ( ) 10(2 1) V
1 ( 1)
t
V s v t t e
= + = +
+ +
The Laplace Transform
65
2
1 ( 1) s s + +
Analysis Techniques (12)
Solve for v(t) ?
8
1
a
Method 2
Ex. 7
+
5
15
s
2
s
+
( ) V s
( )
A
I s
Suppose the current source flows via the inductor.
5 1 15
( ) 2 ( )
A A
s I s I s
s s s
( | |
+ + =
|
(
\ .
s
s
2
3
( ) 5
( 1)
A
s
I s
s
+
=
+
2
3
( ) 10
( 1)
s
V s
s
+
=
+
The Laplace Transform
66
( 1) s +
Analysis Techniques (13)
Solve for v(t) ?
8
1
a
Method 3
Ex. 7
1
2
| |
|
+
5
15
s
2
s
+
( ) V s
5
2
1
2
5 10( 0.5)
( )
1
( 1)
2
ab
s
s
s
s
V s
s s
s
s
| |
+
|
+
\ .
= =
+
+ +
s
s
s
5
10( 0.5) 2 10
( )
s s
V s
+
= =
8
s
1
s
a
5
2 2
( )
1
( 1) ( 1)
2
s
V s
s s
s
= =
+ +
+
5
s
2
+
5 ( )
s
V s
The Laplace Transform
67
s
b
Analysis Techniques (14)
Solve for v(t) ?
8
1
a
Method 3
Ex. 7
15
+
5
15
s
2
s
+
( ) V s
15
2
15
15
( )
1
( 1)
2
C
s
s
I s
s
s
s
= =
+
+ +
s
s
15
8
s
1
s
a
15
2
15
( ) 2
( 1)
s
V s
s
=
+
+
15
s
2
+
15 ( )
s
V s
The Laplace Transform
68
Analysis Techniques (15)
Solve for v(t) ?
8
1
a
Method 3
Ex. 7
+
5
15
s
2
s
+
( ) V s 8
s
1
s
a
s
s
5
2
10
( )
( 1)
s
s
V s
s
=
+
5
s
2
+
5 ( )
s
V s
s
b
a
15 15 ( ) ( ) ( )
s s
V s V s V s = +
15
2
15
( ) 2
( 1)
V s =
+
8
s
2
1
s
+
15 ( ) V s
2 2
10 30
( 1) ( 1)
10( 3)
s
s s
s
= +
+ +
+
The Laplace Transform
69
2
( 1)
s
s +
+
15
s
2
15 ( )
s
V s
2
( )
( 1) s
=
+
Analysis Techniques (16)
Solve for v(t) ?
8
1
a
Method 4
Ex. 7
+
5
15
s
2
s
+
( ) V s
( ) Z s s =
s
s
2
5 15 3
( ) 5
s
E s s
s s s
+
| |
= + =
|
\ .
( ) Z s
1
s
2
3
5
3
( ) 5
1
( 1)
2
s
s
s
I s
s
s
+
+
= =
+
+ +
+
( ) E s
( )
2
+
( ) V s
s
2 2
3 3
( ) 2 5 10
( 1) ( 1)
s s
V s
s s
+ +
= =
+ +
The Laplace Transform
70
( 1) ( 1) s s + +
Analysis Techniques (17)
Solve for v(t) ?
8
1
a
Method 5
Ex. 7
+
5
15
s
2
s
+
( ) V s
8
s
1
s
a
1
s
s
( ) Z
( )
eq
Z s
1
( )
eq
Z s s
s
= +
+
( )
eq
E s
( )
eq
Z s
2
+
( ) V s
8
1
+
a
( )
eq
+
8
s
1
s
( )
eq
E s
5 15
( )
eq
E s s
s s
=
3
( ) 5
s
E
+
( )
( ) 2
2 ( )
eq
E s
V s
Z s
=
+
The Laplace Transform
71
+
5
s
15
s
( ) 5
eq
E s
s
=
2
2 ( )
3
10
( 1)
eq
Z s
s
s
+
+
=
+
0.5
x
v
Analysis Techniques (18)
Ex. 8
Solve for i(t) ?
2 ( ) A u t
x
2O
2O
1 2 ( ) A u t
x
v
+
2O
2O
2O
1
1
F
6
i
(0) 0; (0) 0
C L
v i = =
| |
6
( ) 2 ( ) ( ) ( 2) ( ) 0
x A c A
V s I s I s s I s
s
| |
+ + + + =
|
\ .
1H
( ) 0 5 ( ) I s V s =
s
\ .
| |
6
( ) 2 ( ) 0.5 ( ) ( 2) ( ) 0
x A x A
V s I s V s s I s
s
| |
+ + + + =
|
\ .
( ) 0.5 ( )
c x
I s V s
2 4
( ) 2 ( ) 2 ( )
x A A
V s I s I s
s s
(
= =
(
4 6 4
( | | (
2
( )
x
V s
+
2
2
2
6
s
( ) I s
( )
A
I s
4 6 4
2 ( ) 2 ( ) 0.5 2 ( )
( 2) ( ) 0
A A A
A
I s I s I s
s s s
s I s
( | | (
+ + +
`
|
( (
\ .
)
+ + =
The Laplace Transform
72
2
s
s
( )
A
8 12
( ) ( )
( 2)( 6)
A
s
I s I s
s s s
+
= =
+ +
0.5
x
v
Analysis Techniques (19)
Ex. 8
Solve for i(t) ?
2 ( ) A u t
x
2O
2O
1 2 ( ) A u t
x
v
+
2O
2O
2O
1
1
F
6
i
1 2 3
8 12
( )
( 2)( 6) 2 6
s K K K
I s
s s s s s s
+
= = + +
+ + + +
1H
( ) 0 5 ( ) I s V s =
1
0
8 12
1
( 2)( 6)
s
s
K
s s
=
+
= =
+ +
8 12
( ) 0.5 ( )
c x
I s V s
2
2
8 12
0.5
( 6)
s
s
K
s s
=
+
= =
+
8 12
2
( )
x
V s
+
2
2
2
6
s
( ) I s
3
6
8 12
1.5
( 2)
s
s
K
s s
=
+
= =
+
2 6
( ) 1 0 5 1 5 A
t t
The Laplace Transform
73
2
s
s
2 6
( ) 1 0.5 1.5 A
t t
i t e e
= +
Analysis Techniques (20)
Ex. 9
Find the current i(t)?
0 t =
2
2
15
2
16 5 s
+
+
8
(0) 1A
8
i = =
+
4O
2H
8V
( ) i t
8O
+
5sin3 V t
2
2
16.5
9
( )
2 4 ( 2)( 9)
s
s
I s
s s s
+
+
= =
+ + +
*
1 2 2
K K K
= + +
5sin3 V t
2 3 3 s s j s j
+ +
+ +
2
1
2
16.5
1.58
9
s
K
s
+
= =
+
+
4
2s
2
( ) I s
+
15
2
9
s
s
=
+
2
2
3
16.5
0.35
( 2)( 3)
s j
s
K
s s j
=
+
= =
+ +
o
146.3
2s
( )
2
9 s +
The Laplace Transform
74
3 s j =
2 o
( ) 1.58 0.70cos(3 146.3 ) A
t
i t e t
= +
Analysis Techniques (21)
i(t), v(t), Circuit
Inverse Transform Circuit Element Models
DC circuit analysis techniques
(KVL, KCL, nodal analysis,
h l i
I(s) V(s)
Circuit
mesh analysis, source
transformation, superposition,
Thevenin/Norton equivalent, )
I(s), V(s),
in s-domain
The Laplace Transform
75
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
76
Convolution Integral (1)
1 2 1 2 1 2
0 0
( ) ( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
t t
f t f t f t f t f d f f t d = = =
} }
2
( ) f t
t 0
1
( ) f t
t 0
1
( ) f
1
( ) f
1
( ) f t
2
( ) f t
( ) f
The Laplace Transform
77
0
0
1
( ) f
2
( ) f
Convolution Integral (2)
Ex. 1
Find the convolution of the two signal?
1
1
( ) f t
t 0
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f t
1 2 1 2 1 2
0 0
( ) ( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
t t
f t f t f t f t f d f f t d = = =
} }
t 0
2
( ) f t
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f
1
1
( ) f t
2
2
( ) f
1
0
1 2 3 4
0
1 2 3 4
1
( ) f t
1 2
0 1: 1; 0 t f f < < = =
The Laplace Transform
78
1 2
( ) * ( ) 0 f t f t =
Convolution Integral (3)
Ex. 1
Find the convolution of the two signal?
1
1
( ) f t
t 0
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f t
1 2 1 2 1 2
0 0
( ) ( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
t t
f t f t f t f t f d f f t d = = =
} }
t 0
2
( ) f t
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f
1
1
( ) f t
0
1 2 3 4
1 2
0 1: ( ) * ( ) 0 t f t f t < < =
1 2
1 2 : 1; 2 t f f < < = =
The Laplace Transform
79
1 2 1 2
1
1 1
( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 2 2 2( 1)
t t
t
f t f t f t f d d t
=
= = = =
} }
Convolution Integral (4)
Ex. 1
Find the convolution of the two signal?
1
1
( ) f t
t 0
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f t
1 2 1 2 1 2
0 0
( ) ( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
t t
f t f t f t f t f d f f t d = = =
} }
t 0
2
( ) f t
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f
1
1
( ) f t
0
1 2 3 4
1 2
0 1: ( ) * ( ) 0 t f t f t < < =
1 2
1 2 : ( ) * ( ) 2( 1) t f t f t t < < =
1 2
2 3: 1; 2 t f f < < = =
1 2
( ) ( ) ( ) f f
The Laplace Transform
80
1 2 1 2
1
1 1
( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 2 2 2
t t
t
t
t t
f t f t f t f d d
=
= = = =
} }
Convolution Integral (5)
Ex. 1
Find the convolution of the two signal?
1
1
( ) f t
t 0
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f t
1 2 1 2 1 2
0 0
( ) ( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
t t
f t f t f t f t f d f f t d = = =
} }
t 0
2
( ) f t
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f
1
1
( ) f t
0
1 2 3 4
1 2
0 1: ( ) * ( ) 0 t f t f t < < =
1 2
1 2 : ( ) * ( ) 2( 1) t f t f t t < < =
1 2
3 4 : 1; 2 t f f < < = =
1 2
( ) ( ) ( ) f f
1 2
2 3: ( ) * ( ) 2 t f t f t < < =
The Laplace Transform
81
3 3
3
1 2 1 2
1
1 1
( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 2 2 8 2
t
t t
f t f t f t f d d t
=
= = = =
} }
Convolution Integral (6)
Ex. 1
Find the convolution of the two signal?
1
1
( ) f t
t 0
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f t
1 2 1 2 1 2
0 0
( ) ( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
t t
f t f t f t f t f d f f t d = = =
} }
t 0
2
( ) f t
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f
1
1
( ) f t
0
1 2 3 4
1 2
0 1: ( ) * ( ) 0 t f t f t < < =
1 2
1 2 : ( ) * ( ) 2( 1) t f t f t t < < =
1 2
4 : 1; 0 t f f > = =
1 2
( ) ( ) ( ) f f
1 2
2 3: ( ) * ( ) 2 t f t f t < < =
1 2
3 4 : ( ) * ( ) 8 2 t f t f t t < < =
The Laplace Transform
82
1 2
( ) * ( ) 0 f t f t =
Convolution Integral (7)
Ex. 1
Find the convolution of the two signal?
1
1
( ) f t
t 0
1 2 3 4
2
2
( ) f t
1 2 1 2 1 2
0 0
( ) ( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
t t
f t f t f t f t f d f f t d = = =
} }
t 0
2
( ) f t
1 2 3 4 1 2
0 1: ( ) * ( ) 0 t f t f t < < =
1 2
1 2 : ( ) * ( ) 2( 1) t f t f t t < < =
1 2
2 3: ( ) * ( ) 2 t f t f t < < =
3 4 ( ) * ( ) 8 2 f f
2
1 2
( ) * ( ) f t f t
1 2
4 : ( ) * ( ) 0 t f t f t > =
1 2
3 4 : ( ) * ( ) 8 2 t f t f t t < < =
t 0
1 2 3 4
The Laplace Transform
83
t 0
1 2 3 4
Convolution Integral (8)
Ex. 2
Find the convolution of the two signal?
1
( ) w t
t 0
1 2 3 4
1 2 1 2 1 2
0 0
( ) ( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
t t
f t f t f t f t f d f f t d = = =
} }
2
2
t
Method 1
t 0
2
t
e
1 2 3 4
2
2e
( ) w t
Method 1
t 0
1 2 3 4
t t =
}
t 0
1 2 3 4
2
( )
0 0
0 2 : ( ) 2 1 2 2(1 )
t t
t t t
t f t e d e e
=
=
< < = = =
}
2 2
( ) 2 t t t
=
}
t 0
1 2 3 4
The Laplace Transform
84
2 2
( ) 2
0 0
2 : ( ) 2 1 2 2( 1)
t t t
t f t e d e e e
=
> = = =
}
Convolution Integral (9)
Ex. 2
Find the convolution of the two signal?
1
( ) w t
t 0
1 2 3 4
1 2 1 2 1 2
0 0
( ) ( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
t t
f t f t f t f t f d f f t d = = =
} }
2
2
t
Method 2
t 0
2
t
e
1 2 3 4
2
2
t
e
( ) w
Method 2
t 0
1 2 3 4
t t =
}
t 0
1 2 3 4
2
0 0
0 2 : ( ) 1 2 2 2(1 )
t t
t
t f t e d e e
=
=
< < = = =
}
2
t t
t
=
}
t 0
1 2 3 4
The Laplace Transform
85
2
2 2
2 : ( ) 1 2 2 2( 1)
t t
t
t t
t f t e d e e e
=
> = = =
}
Convolution Integral (10)
Property f(t) F(s)
( ) Af ( ) AF
1. Magnitude scaling
2. Addition/subtraction
3 Time scaling
( ) Af t ( ) AF s
1 2
( ) ( ) f t f t
1 2
( ) ( ) F s F s
( ) f at
1 s
F
| |
|
3. Time scaling
4. Time shifting
5 F hif i
( ) f at
F
a a
|
\ .
( ) ( ), 0 f t a u t a a >
( )
as
e F s
( )
at
f ( ) F
( ) ( ), 0 f t u t a a >
[ ( )]
as
e L f t a
+
5. Frequency shifting
6. Differentiation
7. Multiplication by t
( )
at
e f t
( ) F s a +
( ) /
n n
d f t dt
1 2 1 1
( ) (0) (0) ... (0)
n n n o n
s F s s f s f s f
( )
n
t f t
( 1) ( ) /
n n n
d F s ds
8. Division by t
9. Integration
( ) ( )
( ) / f t t ( )
s
F d
}
0
( )
t
f d
}
( ) / F s s
The Laplace Transform
86
10. Convolution
1 2 1 2
0
( ) * ( ) ( ) ( )
t
f t f t f f t d =
} 1 2
( ) ( ) F s F s
Convolution Integral (11)
Ex. 3
Find v
o
(t)?
+
+
1O
i
v
5
t
( )
i
v t
1O
0.2F
( )
o
v t
t 0
i
5
t
e
1 2 3 4
1
t 0
1 2 3 4
1
( ) 5 5 5
0.2
( ) ( )
1
( ) 1 5 1
1
0.2
C
o i
C
Z s
s
V s V s
R Z s s s s
s
= = =
+ + + +
+
0.2s
Method 1:
5
( ) ( ) 6.25( ) V
t t
o o
V s v t e e
=
Method 2: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) * ( )
o i o i
V s H s V s v t h t v t = =
5
5
( ) ( ) 5
5
t
H s h t e
s
= =
+
5( ) 5 4 5 4
( ) ( ) ( ) 5 5 25 6 25
t t t
t
t t t
v t h t v d e e d e d e
=
+ +
} } }
The Laplace Transform
87
( )
0
0 0 0
5
( ) ( ) ( ) 5 5 25 6.25
6.25( ) V
o i
t t
v t h t v d e e d e d e
e e
=
= = = =
=
} } }
The Laplace Transform
Definition
Two Important Singularity Functions
Transform Pairs
Properties of the Transform
Inverse Transform
Initial-Value & Final-Value Theorems
Laplace Circuit Solutions
Circuit Element Models Circuit Element Models
Analysis Techniques
Convolution Integral Convolution Integral
Transfer Function
The Laplace Transform
88
Transfer Function (1)
( )
in
I s
( )
out
I s
+
( )
in
V s
+
( )
out
V s ( ) H s
( )
( )
Out s
H s = ( )
( )
H s
In s
=
If ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 ( ) ( ) in t t In s H s Out s o = = =
The Laplace Transform
89
Transfer Function (2)
Linear
b d
+ +
( ) ( ) t
Ex. 1
Find the transfer function h(t) of the filter?
bandpass
filter
( )
i
v t ( )
o
v t
( ) 10 ( )
i
v t u t =
10
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
o i
V s H s V s H s
s
= =
s
1
( ) ( )
10
o
H s sV s =
10
1 ( )
( )
o
dv t
h t =
The Laplace Transform
90
( )
10
h t
dt
Transfer Function (3)
Ex. 2
Find the transfer function H(s)?
+
++
( )
i
v t
1O
0.2F
( )
o
v t
1
( ) 5
0.2
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
C
i i i i
Z s
s
V s V s V s V s H s V s = = = = ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1
( ) 5
1
0.2
o i i i i
C
V s V s V s V s H s V s
R Z s s
s
+ +
+
( ) 5
( )
( ) 5
o
i
V s
H s
V s s
= =
+
The Laplace Transform
91
Transfer Function (4)
A circuit is stable if : lim ( ) finite
x
h t
=
je
1 2
( )
( )
( )( )...( )
n
N s
H s
s p s p s p
=
+ + +
1 2 n
1 2
1 2
( ) ( ... ) ( )
n
p t p t p t
h t k e k e k e u t
= + + +
o
1 2
( ) ( ... ) ( )
n
h t k e k e k e u t + + +
Acircuit is stable when all the poles of its transfer function H(s)
The Laplace Transform
92
A circuit is stable when all the poles of its transfer function H(s)
lie in the left half of the s-plane
Transfer Function (5)
Ex. 3
An active filter has the transfer function
( )
k
H s =
An active filter has the transfer function
2
( )
(4 ) 1
H s
s k s + +
For what values of k is the filter stable?
i i i bl h ll h l f i f
je
A circuit is stable when all the poles of its transfer
function H(s) lie in the left half of the s-plane
2
1,2
(4 ) (4 ) 4
2
k k
p
=
oo
4 0 k >
k
The Laplace Transform
93
4 k <
Transfer Function (6)
Ex. 4
+
+
Given the transfer function
5
( ) H s =
+
( )
i
v t
1O
C
( )
o
v t
1
Given the transfer function ( )
5
H s
s +
Find C?
1
( ) 1
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1
( ) 1
1
C
o i i i
C
Z s
sC
V s V s V s V s
R Z s Cs
sC
= = =
+ +
+
+
+
( ) V
1
sC
( ) 1 5
( )
( ) 1 5 5
o
V s
H s
V s Cs Cs
= = =
+ +
( )
i
V s
1
1
sC
( )
o
V s
( ) 1 5 5
i
V s Cs Cs + +
5 1 C =
The Laplace Transform
94
0.2F C =
Você também pode gostar
- Laplace Transform Example SolutionDocumento105 páginasLaplace Transform Example SolutionJed Efraim Espanillo100% (4)
- Turkle Sherry What Does Simulation Want PDFDocumento11 páginasTurkle Sherry What Does Simulation Want PDFmonterojuAinda não há avaliações
- RCE Unpacking Ebook (Translated by LithiumLi) - UnprotectedDocumento2.342 páginasRCE Unpacking Ebook (Translated by LithiumLi) - Unprotecteddryten7507Ainda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transforms1Documento110 páginasLaplace Transforms1nileshsawAinda não há avaliações
- LAPLACE TRANSFORM MASTERYDocumento74 páginasLAPLACE TRANSFORM MASTERYRenaltha Puja BagaskaraAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace TransformDocumento28 páginasLaplace Transformsjo05Ainda não há avaliações
- 6 LTMDocumento32 páginas6 LTMyjartesnAinda não há avaliações
- LaplaceDocumento19 páginasLaplaceBlackArmy88Ainda não há avaliações
- Transform A Dala PlaceDocumento28 páginasTransform A Dala PlaceGino MasciottiAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transform by Engr. VergaraDocumento88 páginasLaplace Transform by Engr. VergaraSharmaine TanAinda não há avaliações
- Free Ebooks DownloadDocumento31 páginasFree Ebooks DownloadedholecomAinda não há avaliações
- 03 - The Laplace TransformDocumento54 páginas03 - The Laplace TransformHandi RizkinugrahaAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transforms ExplainedDocumento3 páginasLaplace Transforms Explainedhfaith13Ainda não há avaliações
- Laplace TransformationDocumento7 páginasLaplace TransformationnualdinAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace BookDocumento51 páginasLaplace BookAjankya SinghaniaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit IDocumento15 páginasUnit IDominic SavioAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace 01Documento36 páginasLaplace 01Trung Nam NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Ee602 Circuit AnalysisDocumento77 páginasEe602 Circuit AnalysisArryshah Dahmia100% (1)
- 4 Laplace TransformsDocumento32 páginas4 Laplace TransformsinaazsAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transform GuideDocumento10 páginasLaplace Transform Guideariana_kardiamouAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transforms and ApplicationsDocumento23 páginasLaplace Transforms and ApplicationsEECS7Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit-VII Laplace Transforms: Properties of Laplace Transforms: L. Linearity Property: IfDocumento21 páginasUnit-VII Laplace Transforms: Properties of Laplace Transforms: L. Linearity Property: IfRanjan NayakAinda não há avaliações
- EM806 PDocumento12 páginasEM806 PHolysterBob GasconAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace TransformDocumento98 páginasLaplace TransformMihail ColunAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Madeling and Block DiagramaaDocumento93 páginasMathematical Madeling and Block Diagramaaabdul.azeezAinda não há avaliações
- LAPLACE TRANSFORM CIRCUIT ANALYSISDocumento56 páginasLAPLACE TRANSFORM CIRCUIT ANALYSISSando CrisiasaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 4Documento22 páginasChapter 7 4Muhd RzwanAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Shifting Theorem LAPLACE TRANSFORMSDocumento42 páginas1st Shifting Theorem LAPLACE TRANSFORMSPlaiboiAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No.7: X (T) T 2u (T) H (T) e 2tu (T)Documento4 páginasExperiment No.7: X (T) T 2u (T) H (T) e 2tu (T)meghasingh_09Ainda não há avaliações
- Step Functions and Laplace Transforms of Piecewise Continuous FunctionsDocumento20 páginasStep Functions and Laplace Transforms of Piecewise Continuous FunctionsLemuel C. FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Models of Control SystemsDocumento32 páginasMathematical Models of Control SystemsLai Yon PengAinda não há avaliações
- 05 LaplaceTableDocumento2 páginas05 LaplaceTableAmo Amor AmornAinda não há avaliações
- Yeek01 2014 I.A-I.EDocumento77 páginasYeek01 2014 I.A-I.ELeungSiuYapAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5-Laplace TransformDocumento27 páginasChapter 5-Laplace TransformKhairul AmirinAinda não há avaliações
- EEE202 Lec13Documento17 páginasEEE202 Lec13Osama HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transforms - GATE Study Material in PDFDocumento6 páginasLaplace Transforms - GATE Study Material in PDFPraveen Agrawal100% (1)
- Circuit Analysis in S-DomainDocumento22 páginasCircuit Analysis in S-Domainshreyas_stinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Sample Answe Questions Questions Er Hints: Cs / Acs W14 Lect 2012Documento57 páginasSample Sample Answe Questions Questions Er Hints: Cs / Acs W14 Lect 2012Timothy AshleyAinda não há avaliações
- LaplaceDocumento77 páginasLaplaceSyaa MalyqaAinda não há avaliações
- Modeling: ∞ −st 1 s 1 s n n! s −at 1 s+a ω s +ω s s +ωDocumento4 páginasModeling: ∞ −st 1 s 1 s n n! s −at 1 s+a ω s +ω s s +ωjameelahmadAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 - FormulasDocumento3 páginasUnit 5 - FormulasAdhi ThyanAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Unit 3 MCQDocumento4 páginasMaths Unit 3 MCQAmit AmitAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transforms: Gilles Cazelais May 2006Documento53 páginasLaplace Transforms: Gilles Cazelais May 2006Aadii AliAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 Lapalce TransformDocumento21 páginasChapter 5 Lapalce TransformAnonymous ma0HXq2iXAinda não há avaliações
- Transformasi Laplace: Ade Elbani Dept. of Electrical Engineering Tanjungpura UniversityDocumento7 páginasTransformasi Laplace: Ade Elbani Dept. of Electrical Engineering Tanjungpura UniversityHenky Vasko ManaluAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transforms ExplainedDocumento65 páginasLaplace Transforms ExplainedvaibhavAinda não há avaliações
- Elementary Laplace Transform Formulas and PropertiesDocumento2 páginasElementary Laplace Transform Formulas and PropertiesMuhammad Asraf Afiffiq SapieeAinda não há avaliações
- Bab V Transformasi Laplace: DT T F e T F LDocumento14 páginasBab V Transformasi Laplace: DT T F e T F LKisworo DiniantoroAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transforms : F (S) e F (T) DTDocumento3 páginasLaplace Transforms : F (S) e F (T) DTAniket SankpalAinda não há avaliações
- Consys PDFDocumento44 páginasConsys PDFRosemarie Taniza VenturaAinda não há avaliações
- Application of Laplace TransformDocumento35 páginasApplication of Laplace TransformSingappuli100% (1)
- Tables of Coulomb Wave Functions: Whittaker FunctionsNo EverandTables of Coulomb Wave Functions: Whittaker FunctionsAinda não há avaliações
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentNo EverandMathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentAinda não há avaliações
- Tables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesNo EverandTables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- Transmutation and Operator Differential EquationsNo EverandTransmutation and Operator Differential EquationsAinda não há avaliações
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27Ainda não há avaliações
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99Ainda não há avaliações
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Ainda não há avaliações
- 8:30am (Invited) FA1Documento2 páginas8:30am (Invited) FA1Nguyen Manh LongAinda não há avaliações
- A New Design of 3-DOF Flexure-Mechanism Positioner With Electromagnetic TechnologyDocumento6 páginasA New Design of 3-DOF Flexure-Mechanism Positioner With Electromagnetic TechnologyNguyen Manh LongAinda não há avaliações
- Biomechanics ChapterDocumento20 páginasBiomechanics Chapterttouman100% (2)
- An Introduction To MEMSDocumento56 páginasAn Introduction To MEMSAhmed AliAinda não há avaliações
- Biomechanics ChapterDocumento20 páginasBiomechanics Chapterttouman100% (2)
- MaterialDocumento12 páginasMaterialNguyen Manh LongAinda não há avaliações
- Ac Servo Motor Principal PDFDocumento26 páginasAc Servo Motor Principal PDFAman Deep86% (7)
- BS 5896 2010Documento33 páginasBS 5896 2010shashiresh50% (2)
- Msds Thinner 21-06Documento8 páginasMsds Thinner 21-06ridhowibiiAinda não há avaliações
- Method Statement For Cable & TerminationDocumento6 páginasMethod Statement For Cable & TerminationRajuAinda não há avaliações
- Template Icme 13 PosterDocumento1 páginaTemplate Icme 13 PosterZulma Xiomara Rueda GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Scrap NFL PanipatDocumento9 páginasScrap NFL PanipatJitenderSinghAinda não há avaliações
- Unit V DSS Development: Arun Mishra 9893686820Documento17 páginasUnit V DSS Development: Arun Mishra 9893686820Arun MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Ref Paper 2Documento4 páginasRef Paper 2Subhanjali MyneniAinda não há avaliações
- E12817 GT AC5300 Manual EnglishDocumento152 páginasE12817 GT AC5300 Manual Englishlegato1984Ainda não há avaliações
- RefrigerationDocumento11 páginasRefrigerationBroAmirAinda não há avaliações
- OkDocumento29 páginasOkgouthamlabsAinda não há avaliações
- HT Series: 73-136Kw I Up To 12 Mppts Three PhaseDocumento2 páginasHT Series: 73-136Kw I Up To 12 Mppts Three PhasesyamprasadAinda não há avaliações
- Questionnaire For Future BLICZerDocumento1 páginaQuestionnaire For Future BLICZerAlejandra GheorghiuAinda não há avaliações
- Raft Foundations - Design & Analysis With A Practical Approach PDFDocumento140 páginasRaft Foundations - Design & Analysis With A Practical Approach PDFemmanuel83% (6)
- ESG Service Information: BackgroundDocumento6 páginasESG Service Information: BackgroundAbdulSattarAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle Database Question Bank 1Documento5 páginasOracle Database Question Bank 1subbaraomca2010Ainda não há avaliações
- DIMENSIONAL TOLERANCES FOR COLD CLOSE RADIUS PIPE BENDINGDocumento11 páginasDIMENSIONAL TOLERANCES FOR COLD CLOSE RADIUS PIPE BENDINGpuwarin najaAinda não há avaliações
- Design Rules CMOS Transistor LayoutDocumento7 páginasDesign Rules CMOS Transistor LayoututpalwxyzAinda não há avaliações
- Guide: Royal Lepage Estate Realty BrandDocumento17 páginasGuide: Royal Lepage Estate Realty BrandNazek Al-SaighAinda não há avaliações
- The Five Generations of Computers: AssignmentDocumento10 páginasThe Five Generations of Computers: Assignmentjismon_kjAinda não há avaliações
- INFRARED BASED VISITOR COUNTER TECHNOLOGYDocumento21 páginasINFRARED BASED VISITOR COUNTER TECHNOLOGYRahul KumarAinda não há avaliações
- SI Units in Geotechnical EngineeringDocumento7 páginasSI Units in Geotechnical EngineeringfaroeldrAinda não há avaliações
- Rob Thomas Digital Booklet - Cradle SongDocumento15 páginasRob Thomas Digital Booklet - Cradle SongAgnieszka ŁukowskaAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On BAJAJDocumento19 páginasPresentation On BAJAJVaibhav AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of A440 Steel Joints Connected With A325 Bolts PublicatDocumento52 páginasStrength of A440 Steel Joints Connected With A325 Bolts Publicathal9000_mark1Ainda não há avaliações
- CNC Meldas 60-60sDocumento300 páginasCNC Meldas 60-60schidambaram kasiAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Burial Optic Fiber Cable Specification - KSD2019 PDFDocumento5 páginasDirect Burial Optic Fiber Cable Specification - KSD2019 PDFjerjyAinda não há avaliações
- Process Thermodynamic Steam Trap PDFDocumento9 páginasProcess Thermodynamic Steam Trap PDFhirenkumar patelAinda não há avaliações


























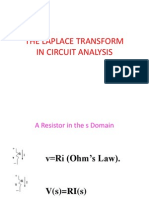



























![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)






































