Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Microbio Lab 5
Enviado por
api-3743217Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Microbio Lab 5
Enviado por
api-3743217Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
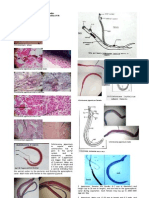
MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY 5 Єtest Susceptibility Testing
USTMED ’07 Sec C – AsM; Photos provided by JV.N. & MeaM.
Procedure
SENSITIVITY TESTING 1. inoculation of the
organism for testing
Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing Using The Kirby-Bauer
using cotton swab
Procedure
by overlapping
streaking using
Kirby Bauer method. The test, introduced by William Kirby and
Mueller Hinton Agar
Alfred Bauer in 1966, consists of exposing a newly-seeded lawn
Plate.
of the bacterium to be tested, growing on a nutrient medium
(Mueller-Hinton agar) to filter paper disks impregnated with
2. Overlaying of Єtest
various antibiotics. The culture is incubated for 16 to 18 hours
strip on the
and then examined for growth. If the organism is inhibited by
previously
one of the antibiotics, there will be a zone of inhibition around
inoculated culture
the disk, representing the area in which the organism was
media
inhibited by that antibiotic.
3. Reading of the strip and recording the results
The diameter of the zone of inhibition around an antibiotic disk
is an indication of the sensitivity of the tested microorganism
to that antibiotic. The diameter of the zone, however, is also
related to the rate of diffusion of the antibiotic in the medium.
This fact must be kept in mind then interpreting the zone of
inhibition of various antibiotics.
MATERIALS:
- culture of the organisms in Mueller-Hinton agar plate
with antibiotic sensitivity discs
- Ruler graduated in millimeters
NOTE:
- The complete procedure is in you(r) lab [lab u 2!
Disk Diffusion Method
Hahaha!] manual.
Procedure
1. Measure the zone of inhibition and record your
1. dip the sterile swab into bacterial suspension
results.
compared to 0.5 MF standard then swab onto the
2. Interpret the results based on the table provided
surface of Mueller Hinton Agar using Overlapping
technique.
2. Allow the organism to be absorbed by the medium.
Place the appropriate antimicrobial (sensitivity) discs
using the dispenser or a sterile forceps. Incubate for
24 hours at 37o
3. Reading and Interpretation of the results. Measure
the diameter of the Zone of Inhibition (area wherein
there is no growth around the discs) using the
millimeter of a ruler. Record your results and
Interpret based on the table provided. Determine if
the Antibiotic (organism) is Sensitive, Intermediate or
Resistant. If there is overlapping in the zone of
inhibition, you can just measure the radius and
multiply the reading by 2 to get the diameter.
E. coli ATCC 25922. The
isolate tested on this Mueller-
Hinton agar plate is
interpreted as susceptible (S)
Єtest – The Problem Solver in Antimicrobial to all antimicrobial agents.
Susceptibility Testing Reading clockwise from the
top, MZ, AN, AM, CZ, CTX,
Etest is an antimicrobial CXM, CF, GM, NN: the three
gradient strip for the discs in the center of the
quantitative determination plate are SXT, FOX and TIM.
of susceptibility or
resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a
microorganisms. It is a resistant strain. Growth on
robust and simple this Mueller-Hinton agar plate
technique, minimally indicates that the isolate is
affected by laboratory resistant to six of 12
variations and can be used antimicrobial agents and
to test most susceptible to the remaing.
microorganisms. An The isolate is resistant to
accurate and reproducible SXT, GM, ATM, TIM, TIC and
Minimum Inhibitory MMZ. The isolate is
Concentration (MIC) is susceptible to CIP, AN, NN,
generated for reliable CA, IPM and PIP.
guidance of antimicrobial
therapy. ustmedc3@yahoogroups.com
audrey_cl@yahoo.com
- fin -
Você também pode gostar
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Clin Path Lab 6 Urinalysis Part 2Documento7 páginasClin Path Lab 6 Urinalysis Part 2api-3743217100% (3)
- Microbio Lec 11 - Ecoli, Klebsiella Proteus, Citrobacter AnDocumento3 páginasMicrobio Lec 11 - Ecoli, Klebsiella Proteus, Citrobacter Anapi-374321750% (2)
- Microbio Lec 10 - Enterobacteriaceae Gen, Shigella and SalmoDocumento8 páginasMicrobio Lec 10 - Enterobacteriaceae Gen, Shigella and Salmoapi-3743217100% (7)
- Clin Path Lab 6 UrinalysisDocumento5 páginasClin Path Lab 6 Urinalysisapi-3743217100% (6)
- Microbio Lec 8 - MycobacteriaDocumento6 páginasMicrobio Lec 8 - Mycobacteriaapi-374321750% (2)
- Microbio Lab 9,10,11,12 & ReviewDocumento3 páginasMicrobio Lab 9,10,11,12 & Reviewapi-374321750% (2)
- Microbio Lab 8Documento4 páginasMicrobio Lab 8api-3743217100% (5)
- Microbio Lec 5 - StreptococcusDocumento6 páginasMicrobio Lec 5 - Streptococcusapi-3743217100% (4)
- Microbio Lec 5 - StaphylococcusDocumento6 páginasMicrobio Lec 5 - Staphylococcusapi-3743217100% (2)
- Microbio Lab 6Documento4 páginasMicrobio Lab 6api-374321750% (2)
- Parasitology-Lec 12 TrypanosomesDocumento6 páginasParasitology-Lec 12 Trypanosomesapi-3743217Ainda não há avaliações
- Microbio Lab 7 (Leigh)Documento8 páginasMicrobio Lab 7 (Leigh)api-3743217100% (6)
- Microbio Lec 1 - Bacterial Morphology and Ultra StructureDocumento8 páginasMicrobio Lec 1 - Bacterial Morphology and Ultra Structureapi-3743217100% (3)
- Para Lab 8Documento2 páginasPara Lab 8api-3743217100% (2)
- Para Lab 11Documento3 páginasPara Lab 11api-3743217Ainda não há avaliações
- Parasitology-Lec 10 EntamoebaDocumento7 páginasParasitology-Lec 10 Entamoebaapi-3743217100% (2)
- Parasitology-Lec 13 MalariaDocumento6 páginasParasitology-Lec 13 Malariaapi-3743217Ainda não há avaliações
- Para Lab 4Documento3 páginasPara Lab 4api-3743217Ainda não há avaliações
- Parasitology-Lec 9 CestodesDocumento5 páginasParasitology-Lec 9 Cestodesapi-3743217100% (4)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- RXN For DR - SagamlaDocumento2 páginasRXN For DR - Sagamlayeng botzAinda não há avaliações
- Carte PsihiatrieDocumento9 páginasCarte PsihiatrieInna CazacliuAinda não há avaliações
- Damolo, Jules Aldrich C. October 30, 2021 Bsit 1 Year Block - A Instructor: Jerson CamayDocumento3 páginasDamolo, Jules Aldrich C. October 30, 2021 Bsit 1 Year Block - A Instructor: Jerson CamayAldrich Dos DamoloAinda não há avaliações
- Wikipedia Names ClearDocumento127 páginasWikipedia Names ClearJassim AlblooshiAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 - Vitamine D Treatment Guidelines in India - JClinSciResDocumento10 páginas2018 - Vitamine D Treatment Guidelines in India - JClinSciResnagashayana gAinda não há avaliações
- GMFMscoresheetDocumento6 páginasGMFMscoresheetAbdur RasyidAinda não há avaliações
- 2423 20160427105703 FbcfiDocumento16 páginas2423 20160427105703 FbcfiCorrinne Mah Yoke Yin0% (1)
- Quantitative Analysis of The Lifting Effect Of.10Documento12 páginasQuantitative Analysis of The Lifting Effect Of.10Arcelino FariasAinda não há avaliações
- Fiji Times Jan 7Documento48 páginasFiji Times Jan 7fijitimescanadaAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Generated by Dental Implant Drills During Osteotomy - A Review-SKumarMishraDocumento13 páginasHeat Generated by Dental Implant Drills During Osteotomy - A Review-SKumarMishraanilsamuel0077418Ainda não há avaliações
- Current & Future Status of Herbal MedicinesDocumento4 páginasCurrent & Future Status of Herbal MedicinesimmchrAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map 3 MM (Abdominal Pain)Documento2 páginasConcept Map 3 MM (Abdominal Pain)Matt McKinleyAinda não há avaliações
- Current Issues in Postoperative Pain Management PDFDocumento12 páginasCurrent Issues in Postoperative Pain Management PDFikm fkunissulaAinda não há avaliações
- Johns Hopkins Dean - Reflections On Medical School AdmissionsDocumento4 páginasJohns Hopkins Dean - Reflections On Medical School AdmissionstheintrepiddodgerAinda não há avaliações
- NICU OrganizationDocumento5 páginasNICU Organizationgopscharan100% (1)
- (Godefroy Christian) Super Health PDFDocumento231 páginas(Godefroy Christian) Super Health PDFAlexandre Dantas100% (1)
- 08 Chapter 3 Pyrazole AppDocumento100 páginas08 Chapter 3 Pyrazole AppSaima KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Herbal Supplements-Drug Interactions Lam Huang Hall (CRC 2006) BBS PDFDocumento330 páginasHerbal Supplements-Drug Interactions Lam Huang Hall (CRC 2006) BBS PDFAnonymous m4A4Yuvrwm100% (1)
- 95 Formulation and Evaluation of Diclofenac Sodium Gel by Using Natural PolymerDocumento3 páginas95 Formulation and Evaluation of Diclofenac Sodium Gel by Using Natural PolymerJulian Kayne100% (1)
- Screenshot 2564-04-16 at 09.45.04Documento95 páginasScreenshot 2564-04-16 at 09.45.04Sarunpong ImampaiAinda não há avaliações
- Primary Awards 2012-2014 - CaribbeansDocumento7 páginasPrimary Awards 2012-2014 - CaribbeansGuillaume PrefolAinda não há avaliações
- 40 Sa Hindi - LBDocumento6 páginas40 Sa Hindi - LBIrshad mohammedAinda não há avaliações
- 1358453842.3856hematology Question BankDocumento182 páginas1358453842.3856hematology Question BankKay BristolAinda não há avaliações
- Intrathecal Morphine Single DoseDocumento25 páginasIntrathecal Morphine Single DoseVerghese GeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- Physician To Population Ratios Physician Supply StandardsDocumento5 páginasPhysician To Population Ratios Physician Supply StandardsjackeldescargadorAinda não há avaliações
- Practicing Clinical Instructor (PCI) Evaluation Form: College of NursingDocumento1 páginaPracticing Clinical Instructor (PCI) Evaluation Form: College of NursingJoe RealAinda não há avaliações
- Client Choice Plus Key FactsDocumento4 páginasClient Choice Plus Key Factsjudge101Ainda não há avaliações
- High Power Electrosurgery Review Update 2005Documento33 páginasHigh Power Electrosurgery Review Update 2005Ana ObradovicAinda não há avaliações
- Doctors Order Form D4Documento1 páginaDoctors Order Form D4Marielle ChuaAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar Harga Pengujian Dan Kalibrasi Alat KesehatanDocumento3 páginasDaftar Harga Pengujian Dan Kalibrasi Alat KesehatanVIDYA VIRA PAKSYA PUTRAAinda não há avaliações