Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Mobile Charger
Enviado por
api-3747180Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Mobile Charger
Enviado por
api-3747180Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CCI IRRC UCIU
T II TD E IADS E A S
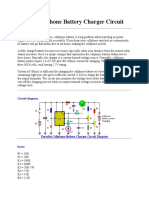
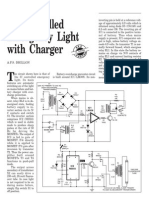
MOBILE CELLPHONE CHARGER SAN
I THE
O
D. MOHAN KUMAR cells gives sufficient
current (1.8A) to LED Status for Different Charging Conditions
C
harging of the cellphone battery is charge the battery con- Load across the output Output frequency (at pin 3) LED1
a big problem while travelling as nected across the out-
power supply source is not gener- put terminals. The cir- No battery connected 765 kHz On
cuit also monitors the Charging battery 4.5 Hz Blinks
ally accessible. If you keep your cellphone
switched on continuously, its battery will voltage level of the bat- Fully charged battery 0 Off
go flat within five to six hours, making tery. It automatically
the cellphone useless. A fully charged bat- cuts off the charging process when its out- to take output pin 3 high. When the battery
tery becomes necessary especially when put terminal voltage increases above the is fully charged, the output terminal voltage
your distance from the nearest relay sta- predetermined voltage level. increases the voltage at pin 2 of IC1 above
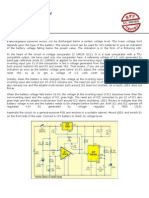
tion increases. Here’s a simple charger that Timer IC NE555 is used to charge and the trigger point threshold. This switches off
replenishes the cellphone battery within monitor the voltage level in the battery. the flip-flop and the output goes low to
two to three hours. Control voltage pin 5 of IC1 is provided terminate the charging process. Threshold
Basically, the charger is a current-lim- with a reference voltage of 5.6V by zener pin 6 of IC1 is referenced at 2/3Vcc set by
VR1. Transistor T1 is used to enhance the
charging current. Value of R3 is critical in
providing the required current for charging.
With the given value of 39-ohm the charg-
ing current is around 180 mA.
The circuit can be constructed on a
small general-purpose PCB. For calibration
of cut-off voltage level, use a variable DC
power source. Connect the output termi-
nals of the circuit to the variable power
supply set at 7V. Adjust VR1 in the middle
position and slowly adjust VR2 until LED1
goes off, indicating low output. LED1
should turn on when the voltage of the
variable power supply reduces below 5V.
Enclose the circuit in a small plastic case
and use suitable connector for connecting
ited voltage source. Generally, cellphone diode ZD1. Threshold pin 6 is supplied to the cellphone battery.
battery packs require 3.6-6V DC and 180- with a voltage set by VR1 and trigger pin Note. At EFY lab, the circuit was tested
200mA current for charging. These usually 2 is supplied with a voltage set by VR2. with a Motorola make cellphone battery
contain three NiCd cells, each having 1.2V When the discharged cellphone battery rated at 3.6V, 320 mAH. In place of 5.6V
rating. Current of 100mA is sufficient for is connected to the circuit, the voltage given zener, a 3.3V zener diode was used. The
charging the cellphone battery at a slow to trigger pin 2 of IC1 is below 1/3Vcc and charging current measured was about 200
rate. A 12V battery containing eight pen hence the flip-flop in the IC is switched on mA.The status of LED1 is shown in the table.
ELECTRONICS FOR YOU MARCH 2004
Você também pode gostar
- Mobile Phone Battery Charger: Circuit IdeasDocumento1 páginaMobile Phone Battery Charger: Circuit IdeasKuntaweeAinda não há avaliações
- Circuit Diagram of Mobile Phone Battery Charger TestedDocumento3 páginasCircuit Diagram of Mobile Phone Battery Charger TestedMashood NasirAinda não há avaliações
- Add A Composite Video Input To A TVDocumento6 páginasAdd A Composite Video Input To A TVEnya Andrea Ribba HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile ChargerDocumento1 páginaMobile ChargerVaz Patrick100% (1)
- Auto Emergency LightDocumento1 páginaAuto Emergency LightAsad AbbasAinda não há avaliações
- Qa 00187 Mobile Charger CircuitDocumento3 páginasQa 00187 Mobile Charger CircuitShivam JainAinda não há avaliações
- Lead-Acid Battery Charger With Voltage AnalyzerDocumento2 páginasLead-Acid Battery Charger With Voltage AnalyzerhyperseraphimAinda não há avaliações
- Charger For Mobile PhonesDocumento2 páginasCharger For Mobile PhonessivaganeshanAinda não há avaliações
- Qa 00187 Mobile - Charger - CircuitDocumento3 páginasQa 00187 Mobile - Charger - CircuitShayan FarrukhAinda não há avaliações
- Constant-Current Batter Char Er: IdeasDocumento54 páginasConstant-Current Batter Char Er: IdeasKliffy Fernandes100% (1)
- Mini UPS System PDFDocumento1 páginaMini UPS System PDFShrivlsi RamAinda não há avaliações
- Project Report of Visitor Counter CircuitDocumento13 páginasProject Report of Visitor Counter Circuitshital shermaleAinda não há avaliações
- Counting Device Circuit Diagram and ComponentsDocumento13 páginasCounting Device Circuit Diagram and ComponentsMuhammad Rizwan Haider Durrani50% (2)
- Low-Power Voltage DoublerDocumento1 páginaLow-Power Voltage Doublerxcfmhg hAinda não há avaliações
- Solar Battery Charging Indicator CircuitDocumento2 páginasSolar Battery Charging Indicator CircuitRakeshAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile Cellphone Battery ChargerDocumento2 páginasMobile Cellphone Battery ChargerWahyu NovendiAinda não há avaliações
- Automatic Phase ChangerDocumento2 páginasAutomatic Phase Changervinay reddy100% (3)
- Deep Sea Electronics Battery Charger ManualDocumento2 páginasDeep Sea Electronics Battery Charger Manualabduallah muhammadAinda não há avaliações
- Const CT Battery ChargerDocumento2 páginasConst CT Battery Chargervinay_98493722556954Ainda não há avaliações
- Tda 4605Documento21 páginasTda 4605Salim SaeidyAinda não há avaliações
- Over Voltage Protection Circuit For Automotive Load DumpDocumento6 páginasOver Voltage Protection Circuit For Automotive Load Dumplennon rAinda não há avaliações
- Infrared Remote Switch ReportDocumento3 páginasInfrared Remote Switch ReportsivamskrAinda não há avaliações
- Automatic Evening LampDocumento4 páginasAutomatic Evening LampRamkrishna ChoudhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Automatyczna Ładowarka Akumulatorów Ołowiowych: Kity AVTDocumento8 páginasAutomatyczna Ładowarka Akumulatorów Ołowiowych: Kity AVTadyhansoloAinda não há avaliações
- Efy 2009Documento8 páginasEfy 2009Vipin Chalakutty CAinda não há avaliações
- Water Level Cum Motor ProtectorDocumento1 páginaWater Level Cum Motor Protectorj_alagesan1990Ainda não há avaliações
- Load Detecting Power Supply: 1.0 Design SpecificationsDocumento17 páginasLoad Detecting Power Supply: 1.0 Design SpecificationsLucre SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Power-Supply Failure Alarm Circuit Generates Warning Tone for Over a MinuteDocumento1 páginaPower-Supply Failure Alarm Circuit Generates Warning Tone for Over a MinutesakthiAinda não há avaliações
- 0-30V 1a PDFDocumento1 página0-30V 1a PDFVas VvasAinda não há avaliações
- E3 Charger Manual-New PDFDocumento2 páginasE3 Charger Manual-New PDFअभिजीत कुमारAinda não há avaliações
- Potencia PDFDocumento109 páginasPotencia PDFdavidAinda não há avaliações
- IC Controlled Emergency Light With Charger: Ircuit IdeasDocumento1 páginaIC Controlled Emergency Light With Charger: Ircuit Ideasindracahayaku100% (2)
- ShangHai Consonance Elec CN3165 - C559035Documento12 páginasShangHai Consonance Elec CN3165 - C559035Yosef GordonAinda não há avaliações
- Smart Phone Light PDFDocumento2 páginasSmart Phone Light PDFPavan Kumar ThopaAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Workshop Project ReportDocumento5 páginasElectronic Workshop Project ReportAbubakr AtiqueAinda não há avaliações
- NE555 Based Low Voltage Battery Cutoff CircuitDocumento10 páginasNE555 Based Low Voltage Battery Cutoff Circuitjohn george doeAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Power Electronics Notes 2.1 To 2.3 PDFDocumento8 páginasBasic Power Electronics Notes 2.1 To 2.3 PDFEscape From EngineeringAinda não há avaliações
- E430 Instruction Manual EN V5.0Documento2 páginasE430 Instruction Manual EN V5.0Jan waAinda não há avaliações
- An Imprint of IC IC 555 Timer in The Contemporary World He ContemporaryDocumento4 páginasAn Imprint of IC IC 555 Timer in The Contemporary World He ContemporaryChinnapogula dineshAinda não há avaliações
- ELECTRONOTES.comDocumento8 páginasELECTRONOTES.comJairus TanAinda não há avaliações
- T.D.A 4605-3Documento20 páginasT.D.A 4605-3Jose M PeresAinda não há avaliações
- Light Dependent Resistor LM339 Automatic Lightdark Indicator BC 547Documento3 páginasLight Dependent Resistor LM339 Automatic Lightdark Indicator BC 547yeateshwarriorAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile Battery Charging Circuit Using Timer 555Documento2 páginasMobile Battery Charging Circuit Using Timer 555ujjwalgupta4Ainda não há avaliações
- Microcontroller-Based Single-Phase Automatic Voltage RegulatorDocumento5 páginasMicrocontroller-Based Single-Phase Automatic Voltage RegulatorFuh ValleryAinda não há avaliações
- Battery-Low Indicator: Raj K. GorkhaliDocumento1 páginaBattery-Low Indicator: Raj K. GorkhaliÁsgeirr Ánsgar Ósgar CanuroAinda não há avaliações
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsNo EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Ainda não há avaliações
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Nota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (3)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsNo EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5)
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Ainda não há avaliações
- Ultersonice RederDocumento5 páginasUltersonice Rederapi-3747180100% (1)
- BC548 - Datashet PDFDocumento2 páginasBC548 - Datashet PDFBraian KonzgenAinda não há avaliações
- Ul Sonic RederDocumento2 páginasUl Sonic Rederapi-3747180Ainda não há avaliações
- Tda 2320Documento5 páginasTda 2320api-3747180Ainda não há avaliações
- Tda 7513Documento58 páginasTda 7513api-3747180100% (1)
- Ba 4911Documento3 páginasBa 4911api-3747180Ainda não há avaliações
- DIGITAL SPEEDOMETER - Measures Speed in Kmph Using Infrared LED & PhototransistorDocumento2 páginasDIGITAL SPEEDOMETER - Measures Speed in Kmph Using Infrared LED & PhototransistorSrikanth ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- LM4766Documento19 páginasLM4766api-3747180Ainda não há avaliações
- CI 06 Mar05Documento1 páginaCI 06 Mar05api-3747180Ainda não há avaliações
- LM4700Documento19 páginasLM4700api-3747180Ainda não há avaliações
- Over Under VoltDocumento1 páginaOver Under Voltapi-3747180100% (1)
- CA3162, CA3162A: Features DescriptionDocumento7 páginasCA3162, CA3162A: Features Descriptionapi-3747180100% (2)
- Emergency LightDocumento1 páginaEmergency Lightapi-3747180100% (1)
- Fire AlarmDocumento1 páginaFire Alarmapi-3747180Ainda não há avaliações
- Ding-Dong Bell PDFDocumento1 páginaDing-Dong Bell PDFShrivlsi RamAinda não há avaliações
- Mje 13007Documento10 páginasMje 13007arao_filhoAinda não há avaliações
- Ca 3161Documento4 páginasCa 3161api-3747180Ainda não há avaliações
- BCR 8 CMDocumento5 páginasBCR 8 CMapi-3747180Ainda não há avaliações
- Parts List Volt MeterDocumento1 páginaParts List Volt Meterapi-3747180100% (1)
- A 3715 AbstractDocumento5 páginasA 3715 Abstractapi-3747180100% (1)
- Design of Deep FoundationDocumento23 páginasDesign of Deep FoundationAnand KumarAinda não há avaliações
- PMP Fluid Power Urun KataloguDocumento94 páginasPMP Fluid Power Urun KataloguSreedhar PAinda não há avaliações
- dcP-9055CDN DCP-9270CDN MFC-9460CDN MFC-9465CDN MFC-9560CDW MFC-9970CDW PDFDocumento42 páginasdcP-9055CDN DCP-9270CDN MFC-9460CDN MFC-9465CDN MFC-9560CDW MFC-9970CDW PDFStefanGarnetAinda não há avaliações
- LED Signalling Handbook CatalogueDocumento31 páginasLED Signalling Handbook CatalogueSteven David Bates100% (1)
- Lac 5045spe Manual Eng 2013Documento31 páginasLac 5045spe Manual Eng 2013Angela0% (1)
- SA GuascorDocumento52 páginasSA GuascorcihanAinda não há avaliações
- Shining A Light On Coiled Tubing PDFDocumento10 páginasShining A Light On Coiled Tubing PDFGade JyAinda não há avaliações
- Ce Project 1: Presenter NameDocumento9 páginasCe Project 1: Presenter NameJayron John Puguon AquinoAinda não há avaliações
- Formula Sheet, Physics 1P22/1P92Documento2 páginasFormula Sheet, Physics 1P22/1P92Roy VeseyAinda não há avaliações
- Asme ViiiDocumento88 páginasAsme ViiiAnonymous jtbdj73W100% (15)
- WEG w22 Three Phase Electric MotorDocumento44 páginasWEG w22 Three Phase Electric MotorMATIAS GODOYAinda não há avaliações
- Accelerator Pedal Position SensorDocumento4 páginasAccelerator Pedal Position SensorRicka AndriamadyAinda não há avaliações
- LCD Module Repair Guide 240209Documento21 páginasLCD Module Repair Guide 240209ledu035Ainda não há avaliações
- Emissions Data For Cat EngineDocumento4 páginasEmissions Data For Cat EngineRajan SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12Documento10 páginasChapter 12Mary IdrusAinda não há avaliações
- CB Materials Handling Brochure-May2010Documento12 páginasCB Materials Handling Brochure-May2010Guglielmo CancelliAinda não há avaliações
- Europass CV DMDocumento2 páginasEuropass CV DMerdhirajmandalAinda não há avaliações
- KPM On Load Tap Changer Analyzer: FunctionalityDocumento1 páginaKPM On Load Tap Changer Analyzer: FunctionalityVikaas JainAinda não há avaliações
- Rethinking Barometric LegsDocumento25 páginasRethinking Barometric LegsLeomar Pcheco100% (1)
- Contactor FinderDocumento10 páginasContactor FinderEfrain Valiente RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- Operation Manual BLR-CX: Attention!Documento16 páginasOperation Manual BLR-CX: Attention!Pandu BirumakovelaAinda não há avaliações
- HP LP BYPASS SYSTEM ADVANTAGESDocumento3 páginasHP LP BYPASS SYSTEM ADVANTAGESkaruna346Ainda não há avaliações
- Water Hammer Arrestor (Handbook JR Smith) PDFDocumento22 páginasWater Hammer Arrestor (Handbook JR Smith) PDFLubyanka100% (1)
- Design of Welded StructuresDocumento842 páginasDesign of Welded StructuresRancor8297% (39)
- D Regulators enDocumento52 páginasD Regulators enmasakpAinda não há avaliações
- Ho-SolarToday-April13 - v2Documento4 páginasHo-SolarToday-April13 - v2Danny Sánchez YánezAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Cooling Water Temperature On MEEDocumento8 páginasEffect of Cooling Water Temperature On MEEkishna009Ainda não há avaliações
- @perkins: 400 Series 404C-22GDocumento2 páginas@perkins: 400 Series 404C-22GNibrasAinda não há avaliações
- CIFA Concrete PumpDocumento12 páginasCIFA Concrete PumpVipulAinda não há avaliações
- Strama PaperDocumento28 páginasStrama PaperHiezll Wynn R. Rivera100% (1)