Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Em Spectrum
Enviado por
Mark ProchaskaDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Em Spectrum
Enviado por
Mark ProchaskaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Physics POGIL: The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes radio signals, microwaves,
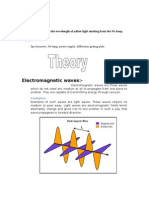
infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. One model of electromagnetic radiation is a propagating wave that is partially electric in nature and partially magnetic in nature. The following diagram is a pictorial description of this model:
electric part of wave
magnetic part of wave
direction of propagation
This type of wave is called an electromagnetic wave. Another model of electromagnetic radiation is a particle called a photon. It is a somewhat strange particle in that the laws of physics tell us that it has no mass and no volume, yet it must exist because we can observe its effects! 1. Scientist often say that light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation have a dual nature. What do you think they mean by this?
2. Are electromagnetic waves transverse or longitudinal? Justify your answer.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum The electromagnetic spectrum is an ordered list of all the types of electromagnetic radiation. All electromagnetic radiation can be described using the wave model or particle model above. The only difference between each type is the wavelength and frequency of the associated electromagnetic wave. The types of radiation and their wavelength ranges are shown in the diagram below.
Physics 100 m 1m 102 m 104 m 106 m 108 m 1010 m 1012 m 1014 m
radio waves
microwaves
infrared
ultraviolet
X-rays
gamma rays
visible light AM radio FM radio, TV
Note that the wavelengths are listed on a logarithmic scale. In other words, each increment on the scale represents an increase in the wavelength by a factor of 10, not an addition of 10 m. Recall that the relationship between frequency and wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is described by the equation = , or = . All electromagnetic radiation propagates at a speed of c = 3x108 m/s (approximately 186,000 miles per second). 3. What is the difference between an X-ray, light, and a radio wave?
4. The Sun is approximately 150 billion meters from the Earth. Approximately how long does it take light to travel from the Sun to the Earth?
5. The Sun also emits infrared. Approximately how long does it take infrared to travel from the Sun to the Earth?
6. Which type of electromagnetic radiation has: (a) the longest wavelength?
(b) the shortest wavelength?
(c) the highest frequency?
Physics (d) the lowest frequency?
(e) the highest period?
(f) the lowest period?
7. What is the approximate range of wavelengths of visible light?
8. What is meant by the statement Light is the only thing we can see?
Electromagnetic Radiation and Energy Electromagnetic radiation carries energy with it over space. The energy of a photon is given by the equation = or =
The constant h is called Plank's constant, equal to 6.63x1034 J-s, a very small number. 9. List the types of electromagnetic radiation in order from lowest energy photons to highest energy photons.
10. The colors of the light spectrum (those wavelengths corresponding to visible light only) from shortest frequency to highest frequency are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet. List the colors of the light spectrum in order from: (a) shortest wavelength to longest wavelength.
(b) lowest energy photons to highest energy photons.
Você também pode gostar
- Work and PowerDocumento3 páginasWork and PowerMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Voltage and ResistanceDocumento4 páginasVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Time DilationDocumento3 páginasTime DilationMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- VectorsDocumento2 páginasVectorsMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Motion in Two Dimensions 1Documento4 páginasMotion in Two Dimensions 1Mark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Relativistic EnergyDocumento4 páginasRelativistic EnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDocumento3 páginasPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Newton's First LawDocumento3 páginasNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Nuclear Fission and FusionDocumento4 páginasNuclear Fission and FusionMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Third LawDocumento3 páginasNewton's Third LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Second LawDocumento3 páginasNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Vector ComponentsDocumento4 páginasVector ComponentsMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetic InductionDocumento4 páginasElectromagnetic InductionMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic ForcesDocumento3 páginasMagnetic ForcesMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Motion in Two Dimensions 2Documento3 páginasMotion in Two Dimensions 2Mark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Work and PowerDocumento4 páginasWork and PowerMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyDocumento3 páginasMass Defect and Binding EnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL: Length ContractionDocumento3 páginasPOGIL: Length ContractionMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- AccelerationDocumento2 páginasAccelerationMark Prochaska0% (1)
- EnergyDocumento3 páginasEnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Electric PowerDocumento4 páginasElectric PowerMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Free Body DiagramsDocumento4 páginasFree Body DiagramsMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Electric ForcesDocumento4 páginasElectric ForcesMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Working and PowerDocumento4 páginasWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Electric CurrentDocumento2 páginasElectric CurrentMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- VelocityDocumento4 páginasVelocityMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Atomic NucleiDocumento4 páginasAtomic NucleiMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Universal GravitationDocumento3 páginasUniversal GravitationMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- WavesDocumento4 páginasWavesMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Temperature and HeatingDocumento4 páginasTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Qwestion ExamDocumento3 páginasQwestion ExamKumbati SupertiksAinda não há avaliações
- Optoelectronics and Photonics Principles and Practices 2nd Edition Kasap Solution ManualDocumento59 páginasOptoelectronics and Photonics Principles and Practices 2nd Edition Kasap Solution Manualryan100% (21)
- SonarDocumento323 páginasSonarDhimas Afihandarin100% (1)
- Vibrations Caused by Pile DrivingDocumento6 páginasVibrations Caused by Pile DrivingDamar WardhanaAinda não há avaliações
- Dewi Kurnia (60400118035) - Jurnal JFT Panjang Gelombang CahayaDocumento13 páginasDewi Kurnia (60400118035) - Jurnal JFT Panjang Gelombang CahayaDewi KurniaAinda não há avaliações
- Grating and Prism Spectrometer ExperimentDocumento6 páginasGrating and Prism Spectrometer ExperimentAakash VermaAinda não há avaliações
- International Physics Olympiad QuestionsDocumento6 páginasInternational Physics Olympiad QuestionspritomAinda não há avaliações
- NSS Phy Curriculum (Notes For Teachers)Documento30 páginasNSS Phy Curriculum (Notes For Teachers)energy0124Ainda não há avaliações
- Design of Laser Based UnderwaterDocumento10 páginasDesign of Laser Based UnderwaterFaiz Haider KhanAinda não há avaliações
- 10 The Wave Nature of Light 3 Speed, Frequency and Wavelength1Documento9 páginas10 The Wave Nature of Light 3 Speed, Frequency and Wavelength1Aaesha Sulaiman Salem Saeed AlshehhiAinda não há avaliações
- Answers To Grade 12U Physics Key Questions Unit 4Documento19 páginasAnswers To Grade 12U Physics Key Questions Unit 4Domenico Barillari86% (7)
- IELTS Reading Practice 62: SOSUS: Listening to the OceanDocumento31 páginasIELTS Reading Practice 62: SOSUS: Listening to the OceanVõ Thành HiệpAinda não há avaliações
- Quantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of Atoms: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento69 páginasQuantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of Atoms: Multiple Choice QuestionsRs Remo KookieAinda não há avaliações
- EC 232 Tutorial 2Documento3 páginasEC 232 Tutorial 2RUSHIL MOTWANIAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Spectroscopy of Biological CellsDocumento57 páginasOptical Spectroscopy of Biological CellsEnzo Victorino Hernandez AgressottAinda não há avaliações
- Che 101 NoteDocumento39 páginasChe 101 Noteadebowalepeace502Ainda não há avaliações
- Session 1Documento26 páginasSession 1Andrea PovedaAinda não há avaliações
- Test Corrections WavesDocumento6 páginasTest Corrections WavesDuane TalleyAinda não há avaliações
- Observation of Unknown SpectrumDocumento3 páginasObservation of Unknown SpectrumOmar HusseinAinda não há avaliações
- Klimov Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactors PDFDocumento417 páginasKlimov Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactors PDFHarry SmartAinda não há avaliações
- Section3 Michelson InterferometerDocumento5 páginasSection3 Michelson InterferometerRoy VeseyAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Physics (BT-201) B.Tech. I Year CO - 01 Unit I - Quantum PhysicsDocumento39 páginasEngineering Physics (BT-201) B.Tech. I Year CO - 01 Unit I - Quantum PhysicsAbhishek ThakralAinda não há avaliações
- Objective:: To Determine The Wavelength of Yellow Light Emitting From The Na-Lamp.Documento14 páginasObjective:: To Determine The Wavelength of Yellow Light Emitting From The Na-Lamp.suleman205Ainda não há avaliações
- Hased Array Ultrasonic Testing, Sectorial ScanDocumento7 páginasHased Array Ultrasonic Testing, Sectorial Scanநந்த குமார் சம்பத் நாகராஜன்100% (1)
- ASNT Level I II III Q&A Ultrasonic Testing PDFDocumento63 páginasASNT Level I II III Q&A Ultrasonic Testing PDFShyam Sundar Gayen83% (35)
- General Physics 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Periodic MotionDocumento31 páginasGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Periodic MotionWendle OrtadoAinda não há avaliações
- Newtons Rings - Experiment N AimsDocumento6 páginasNewtons Rings - Experiment N AimsSammy BennettAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Diagnostics For Soot and Temperature Measurement in Diesel EnginesDocumento35 páginasOptical Diagnostics For Soot and Temperature Measurement in Diesel EnginesRicardo Rabello de CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Igcse 31 PropertiesofwavesDocumento23 páginasIgcse 31 PropertiesofwavesHany ElGezawy100% (1)