Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Scale
Enviado por
Mark ProchaskaDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Scale
Enviado por
Mark ProchaskaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
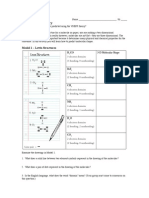
Physics POGIL: Scale In this POGIL we will look at how the volume and surface area of an object changes
as we increase its dimensions. How surface area and volume change relative to each other affects the properties of the object and has implications for biological systems, construction, the development of scale models, and a multitude of other applications. Scaling Dimensions, Surface Area, and Volume When we talk about an object being scaled up in size, we mean that each dimension (length, width, and height) is changed by a certain factor. For example, the rectangular prism below has dimensions of 1 cm 4 cm 2 cm. 1 cm 2 cm 4 cm If we scale the prism by a factor of 3, its new dimensions are 3 cm 12 cm 6 cm.
3 cm 6 cm 12 cm Notice that this scales up the surface area of the prism as well as its volume. 1. In the chart below, fill in the volume and surface area of each of the rectangular prisms in the example above. Include the appropriate units in the column headings. prism dimensions 1 cm 4 cm 2 cm 3 cm 12 cm 6 cm volume (units: ) surface area (units: )
2. In the example above, we scaled up the rectangular prism by a factor of 3. (a) By what factor did the volume change?
(b) By what factor did the surface area change?
3. Now consider a cube 1 cm on a side. Suppose we scale up the cube by factors of 2, 3, and 4. A diagram of each cube is shown below.
cube #1 1 cm on a side
cube #2 scaled by a factor of 2
cube #3 scaled by a factor of 3
cube #4 scaled by a factor of 4
(a) In the chart below, fill in the length of a side, the surface area, and the volume of each cube. cube #1 #2 #3 #4 length of a side (units: cm) 1 surface area (units: ) volume (units: )
(b) In the chart below, fill in the factors by which the surface area and volume change relative to cube #1 as each cube is scaled up. cube #2 #3 #4 4. As an object is scaled up in size, which increases faster: linear dimension or surface area? Justify your answer. factor by which surface area changed factor by which volume changed
5. As an object is scaled up in size, which increases faster: surface area or volume? Justify your answer.
Effects of Scaling As objects are scaled up in size, the difference in the changes in linear dimension, surface area, and volume relative to each other will affect the properties of those objects. This is true when the properties are dependent on surface area or volume. 6. Imagine we are baking a loaf of bread in a 10 cm 30 cm 20 cm pan. Baking the bread requires an input of 1000 J of heat energy into the dough in 30 minutes. We now wish to bake a loaf that is scaled up by a factor of 2. (a) Comparing the bigger loaf of bread to the original, will the surface area change by a factor less than 2, equal to 2, or greater than 2?
(b) Comparing the bigger loaf of bread to the original, will the volume change by a factor less than 2, equal to 2, or greater than 2?
(c) Comparing the bigger loaf of bread to the original, will the time required to bake the bread be less than 30 minutes, equal to 30 minutes, or greater than 30 minutes? Justify your answer.
(d) Will the amount of energy needed to bake the bigger loaf be less than 2000 J (twice the energy required to bake the original loaf), equal to 2000 J, or greater than 2000 J? Justify your answer.
7. Imagine we are waiting for a large pile of snow to melt in the warm spring sun. We may end up waiting all day if we don't use concepts of scaling to help us. So let's take the pile of snow and divide it up into 100 smaller snowballs. (a) By dividing the pile into smaller snowballs, has the total volume of snow increased, decreased, or remain unchanged?
(b) By dividing the pile into smaller snowballs, has the total surface area of snow increased, decreased, or remain unchanged?
(c) Explain why the snow melts faster by dividing it up into smaller snowballs.
8. As an object is scaled up, why does the surface area increase faster than the linear dimensions?
9. As an object is scaled up, why does the volume increase faster than the surface area?
10. Why do the properties of objects often change as they are scaled up?
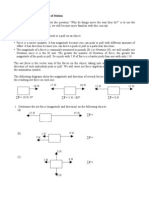
Problems 11. Consider a sphere having a radius of 1 cm. Suppose we scale up the sphere by factors of 2, 3, and 4. A diagram of each sphere is shown below. sphere #1 1 cm radius
sphere #2 scaled by a factor of 2
sphere #3 scaled by a factor of 3
sphere #4 scaled by a factor of 4
(a) In the chart below, fill in the radius, the surface area, and the volume of each sphere. sphere #1 #2 #3 #4 radius (units: cm) 1 surface area (units: ) volume (units: )
(b) In the chart below, fill in the factors by which the surface area and volume change relative to sphere #1 as each sphere is scaled up. sphere #2 #3 #4 (c) Party balloons are made from latex. Suppose a balloon that holds 4000 cm3 of air requires 1200 cm2 of latex. If we want to scale down the size of the balloon so that it holds half as much air, will the amount of latex required for such a balloon be more than 600 cm2, less than 600 cm2, or equal to 600 cm2? factor by which surface area changed factor by which volume changed
Você também pode gostar
- AccelerationDocumento2 páginasAccelerationMark Prochaska0% (1)
- VectorsDocumento2 páginasVectorsMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- 21 Evolution and Selection-SDocumento6 páginas21 Evolution and Selection-SSSSSSSSSSS100% (1)
- Accuracy and Precision Mini LabDocumento6 páginasAccuracy and Precision Mini LabAlistair Morgan100% (1)
- POGIL: Force: Physics First NameDocumento2 páginasPOGIL: Force: Physics First NameMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL TemplateDocumento3 páginasPOGIL Templateurbaitissciencelab3474Ainda não há avaliações
- Action and ReactionDocumento2 páginasAction and ReactionMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL - ThermodynamicsDocumento4 páginasPOGIL - ThermodynamicsMar0% (1)
- Working and PowerDocumento4 páginasWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Heating and Phase ChangesDocumento4 páginasHeating and Phase ChangesMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Vector ComponentsDocumento4 páginasVector ComponentsMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- CP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Documento4 páginasCP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Anthony ButlerAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific Inquiry Methods and ModelsDocumento4 páginasScientific Inquiry Methods and ModelsKavita SadanaAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSDocumento3 páginasPOGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSSharmet SolarzAinda não há avaliações
- Designing POGIL ActivitiesDocumento6 páginasDesigning POGIL ActivitiesCogut Macan DudutzAinda não há avaliações
- CH 01 Matter MeasurementDocumento16 páginasCH 01 Matter Measurementxiaoming zhuAinda não há avaliações
- Temperature and HeatingDocumento4 páginasTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Significant Figures in DataDocumento5 páginasSignificant Figures in DataJSmithChemteachAinda não há avaliações
- Pogil Iinqury-Based Equilibrium ActivityDocumento7 páginasPogil Iinqury-Based Equilibrium Activityapi-252514594Ainda não há avaliações
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDocumento3 páginasPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- GB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015Documento2 páginasGB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015api-261277442Ainda não há avaliações
- POGIL - KinematicsDocumento4 páginasPOGIL - KinematicsmagiclcjAinda não há avaliações
- Pogil - Changes of PhaseDocumento4 páginasPogil - Changes of Phaseapi-293306937Ainda não há avaliações
- Phase Change POGILDocumento4 páginasPhase Change POGILSarah UsmanAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Science Workbook - HeredityDocumento27 páginas7 Science Workbook - HeredityJorge SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Pogil Describing MotionDocumento2 páginasPogil Describing Motionapi-259781257100% (1)
- G Science PDFDocumento177 páginasG Science PDFTaslima TabassumAinda não há avaliações
- Accuracy and Precision POGILDocumento10 páginasAccuracy and Precision POGILmijaggiAinda não há avaliações
- 20 Work, Equilibrium and Free Energy - SDocumento7 páginas20 Work, Equilibrium and Free Energy - SLeia Jones0% (1)
- Selection and Speciation POGILDocumento3 páginasSelection and Speciation POGILCody PalmerAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL Molecular GeometryDocumento3 páginasPOGIL Molecular Geometryliza120750% (2)
- Universal GravitationDocumento3 páginasUniversal GravitationMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- 3 - Determining Activity SeriesDocumento5 páginas3 - Determining Activity Seriescarter0% (2)
- POGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumDocumento5 páginasPOGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumsydAinda não há avaliações
- RC Circuit POGIL 2020Documento8 páginasRC Circuit POGIL 2020fnoschese-1Ainda não há avaliações
- AccelerationDocumento4 páginasAccelerationMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Phase-Changes OriginalDocumento4 páginasPhase-Changes Originalapi-293306937Ainda não há avaliações
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDocumento7 páginasBalancing Chemical EquationsSharmet SolarzAinda não há avaliações
- Electric ForceDocumento4 páginasElectric ForceMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Temperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingDocumento3 páginasTemperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Day 36 Coulombic Attraction and Periodic Trends POGIL PDFDocumento10 páginasDay 36 Coulombic Attraction and Periodic Trends POGIL PDFCoy Romo [STUDENT]Ainda não há avaliações
- Reflection Refraction Diffraction of WavesDocumento1 páginaReflection Refraction Diffraction of WavesVictoria KairooAinda não há avaliações
- Pogil Theories of UniverseDocumento3 páginasPogil Theories of UniverseChell Queentana FundaAinda não há avaliações
- Pogil Fission and FusionDocumento5 páginasPogil Fission and FusionPhạm Bùi Quốc Quyền100% (1)
- AtwoodDocumento3 páginasAtwoodBahril IlmiwanAinda não há avaliações
- Relativistic EnergyDocumento4 páginasRelativistic EnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- 7.05 POGIL Molfgarity KeyDocumento8 páginas7.05 POGIL Molfgarity KeyXazerco LaxAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL Classification of Matter (In Class Activity)Documento9 páginasPOGIL Classification of Matter (In Class Activity)Mauricio MolkoAinda não há avaliações
- Voltage and ResistanceDocumento4 páginasVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Dimensional Analysis Lab - Making FudgeDocumento2 páginasDimensional Analysis Lab - Making FudgeDavid BergeAinda não há avaliações
- EnergyDocumento3 páginasEnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Speed and VelocityDocumento4 páginasSpeed and VelocityMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristics of Life QuizDocumento2 páginasCharacteristics of Life QuizRuth Danielle GasconAinda não há avaliações
- Ap Chemistry Lab RubricDocumento3 páginasAp Chemistry Lab Rubricapi-258145192Ainda não há avaliações
- Balancing Equations Worksheet 1Documento5 páginasBalancing Equations Worksheet 1Kizzy-Anne BoatswainAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL - Heat Transfer ModesDocumento4 páginasPOGIL - Heat Transfer ModesDon SekarAinda não há avaliações
- SURFACE AREA & VOLUME Session 2Documento20 páginasSURFACE AREA & VOLUME Session 2jordanstevenson784Ainda não há avaliações
- Math 5 Q4 Module 2Documento19 páginasMath 5 Q4 Module 2Sarah l. EbdaneAinda não há avaliações
- Measure Lengths and Areas with PrecisionDocumento22 páginasMeasure Lengths and Areas with PrecisionGaurav ShekharAinda não há avaliações
- Time DilationDocumento3 páginasTime DilationMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic ForcesDocumento3 páginasMagnetic ForcesMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Work and PowerDocumento3 páginasWork and PowerMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Voltage and ResistanceDocumento4 páginasVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL: Length ContractionDocumento3 páginasPOGIL: Length ContractionMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Nuclear Fission and FusionDocumento4 páginasNuclear Fission and FusionMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Relativistic EnergyDocumento4 páginasRelativistic EnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDocumento3 páginasPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Vector ComponentsDocumento4 páginasVector ComponentsMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Second LawDocumento3 páginasNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Free Body DiagramsDocumento4 páginasFree Body DiagramsMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Third LawDocumento3 páginasNewton's Third LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's First LawDocumento3 páginasNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Motion in Two Dimensions 2Documento3 páginasMotion in Two Dimensions 2Mark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Motion in Two Dimensions 1Documento4 páginasMotion in Two Dimensions 1Mark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Electric ForcesDocumento4 páginasElectric ForcesMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyDocumento3 páginasMass Defect and Binding EnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Atomic NucleiDocumento4 páginasAtomic NucleiMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Electric CurrentDocumento2 páginasElectric CurrentMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetic InductionDocumento4 páginasElectromagnetic InductionMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- EnergyDocumento3 páginasEnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Electric PowerDocumento4 páginasElectric PowerMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Work and PowerDocumento4 páginasWork and PowerMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Working and PowerDocumento4 páginasWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- WavesDocumento4 páginasWavesMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Universal GravitationDocumento3 páginasUniversal GravitationMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- VelocityDocumento4 páginasVelocityMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Temperature and HeatingDocumento4 páginasTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Che F241 1180Documento3 páginasChe F241 1180Govind ManglaniAinda não há avaliações
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Chapter 2 QuestionsDocumento19 páginasAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Chapter 2 QuestionsAhmed ZiadAinda não há avaliações
- Astm e 518Documento5 páginasAstm e 518Pao Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Liquid - Liquid ExtractionDocumento9 páginasLiquid - Liquid ExtractionMoeAinda não há avaliações
- Glass Manufacturing ProcessDocumento2 páginasGlass Manufacturing ProcessNur Aulia S100% (2)
- Module 6Documento104 páginasModule 6rabih87Ainda não há avaliações
- Bradford Method Protein Assay GuideDocumento3 páginasBradford Method Protein Assay GuideDoreliaAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 2Documento8 páginasPaper 2Prateek MalhotraAinda não há avaliações
- GEAS 1 - Chemistry - 2Documento4 páginasGEAS 1 - Chemistry - 2Leoneil Angelo AbreuAinda não há avaliações
- Stirling EngineDocumento14 páginasStirling EngineShivakumar Ainapur100% (1)
- Galvanic and Corrosion Compatibility Dissimilar Metal Corrosion GuideDocumento21 páginasGalvanic and Corrosion Compatibility Dissimilar Metal Corrosion Guidehitesh_tilalaAinda não há avaliações
- Visible Particles Regulatory and Compendial RequirementsDocumento31 páginasVisible Particles Regulatory and Compendial Requirementsdavincicode888Ainda não há avaliações
- LirioDocumento220 páginasLirioAntonio MeseguerAinda não há avaliações
- Statistical Treatment of Some Properties of Beans: Chemistry 3225 K. PierceDocumento2 páginasStatistical Treatment of Some Properties of Beans: Chemistry 3225 K. Piercespiff spacemanAinda não há avaliações
- Phono Par PDFDocumento8 páginasPhono Par PDFvranceanu.ovidiu-1Ainda não há avaliações
- How To Conduct Bunker Survey - Marine Surveyor InformationDocumento1 páginaHow To Conduct Bunker Survey - Marine Surveyor InformationgustavoseseAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet 2 - TLC - Updated Summer 2021Documento4 páginasWorksheet 2 - TLC - Updated Summer 2021Bria PopeAinda não há avaliações
- Fuels Classification and PropertiesDocumento57 páginasFuels Classification and PropertiesChinmay LearningAinda não há avaliações
- Powder Coating at HomeDocumento9 páginasPowder Coating at Homepakde jongko100% (1)
- C78IA009EN A ViscoQC Yield PointDocumento2 páginasC78IA009EN A ViscoQC Yield Pointjomoro29Ainda não há avaliações
- Ginger CandyDocumento8 páginasGinger CandyRizka Arifani Kromodimedjo100% (2)
- Applications of Polymer Gels in Tissue Engineering, Drug Delivery and MoreDocumento18 páginasApplications of Polymer Gels in Tissue Engineering, Drug Delivery and MorePathik ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Agfa formulas guide photographers through chemical processesDocumento32 páginasAgfa formulas guide photographers through chemical processesRaimundo Civera Redondo100% (1)
- Indian Standard - Code of Safety For MethanolDocumento22 páginasIndian Standard - Code of Safety For Methanolvaibhav_nautiyalAinda não há avaliações
- Synthesis of Magnetic Graphene Oxide From Oil Palm Leaves For Removal of Lead Ions From WaterDocumento7 páginasSynthesis of Magnetic Graphene Oxide From Oil Palm Leaves For Removal of Lead Ions From Water阿尔坎塔拉约翰·肯尼斯Ainda não há avaliações
- Starline VALVESDocumento16 páginasStarline VALVESmanmohansingh1999Ainda não há avaliações
- U1 MAgneticPropDocumento19 páginasU1 MAgneticPropAbinash PandaAinda não há avaliações
- Stainless Steel 422 Round BarDocumento2 páginasStainless Steel 422 Round BarArun KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Aggregate Impact Value TestDocumento6 páginasAggregate Impact Value Testnadz_fynazAinda não há avaliações