Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Derivative Exercises Graphs and Tables
Enviado por
Sherrell Blankenship-BrownDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Derivative Exercises Graphs and Tables
Enviado por
Sherrell Blankenship-BrownDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Intro to Calculus: Derivative exercises
Use the graphs of f ( x ) and g ( x ) shown here to
evaluate the following. The graph of f ( x ) passes
through the points (-1.5, -2), (-0.5, 2), and (0.5, 3).
[1] f ( 1)
[4]
[6]
d
f ( g ( x ) )
dx
x =2
[10]
d x3
dx g ( x )
[7]
d
g ( f ( x ) )
dx
x =3
[11]
x =2
d f ( x)
dx g ( x )
[8]
d
f ( x ) g ( x )
dx
x =3
x =3
d f ( 2x)
dx g ( 3 x )
d g ( x)
dx f ( x )
[5]
d
f ( x 2 + 1)
dx
x =1
[12]
d
x f ( x )
dx
x =1
[2] g ( 1) [3]
[9]
d
x g ( 3 x 4 )
dx
x =1
x =1
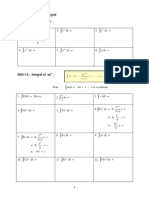
dd[13 - 22] Consider the values in the following table and compute the derivative values.
x
f ( x)
2
4
3
5
4
7
6
11
10
16
f ( x)
-1
g ( x)
-2
-5
-7
-8
-3
g( x )
-2
-3
-4
[13] h ( x ) = f ( 3 x 1) ; find h (1)
[15] k ( x ) = f ( x ) g ( x ) ; find k ( 6 )
[17] n ( x ) =
g ( x)
; find n ( 3)
f ( x)
[14] j ( x ) = f ( x 2 + 1) ; find
[16] m ( x ) = x 4 g ( x ) ; find
[18] p ( x ) =
f ( x ) ; find
dj
dx
dp
dx
x =3
dr
dx
x =6
[20] r ( x ) = ( f ( x ) ) ; find
[21] s ( x ) = f ( g ( x ) ) ; find s ( 3)
1
dv
[22] v ( x ) =
; find
f ( 2x)
dx
x =3
dm
dx x=2
[19] q ( x ) = g ( f ( x ) ) ; find q ( 2 )
x =3
x =3
[23 - 32] Compute the derivative for each function.
[23] f ( x ) = x 2 + 4
[25] f ( x ) =
( 4x + 3 )
1
2x 3
( 2 x + 1)
f ( x) =
2
( x + 1)
[31]
1
x x
5
[26] f ( x ) = ( 2 x + 1) ( 3 x 2 )
[27] f ( x ) = ( x 2 + 1) ( x 1 )
[29] f ( x ) =
[24] f ( x ) =
[28] f ( x ) = 3 5 x + 2
[30] f ( x ) =
3x + 5
( 2x + 1)
[32] f ( x ) = ( 3 x 2 x 3) 3
Você também pode gostar
- Work From Home Policy LeadsquaredDocumento5 páginasWork From Home Policy LeadsquaredAnthonyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2.3 - Relation and FunctionDocumento12 páginasChapter 2.3 - Relation and FunctionPoeil Sergio MoldezAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus Early Transcendentals Solutions Manual Chapter 04Documento28 páginasCalculus Early Transcendentals Solutions Manual Chapter 04Jonathan Martinez Cuesi100% (1)
- The Practice of TratakaDocumento7 páginasThe Practice of TratakaNRV APPASAMY100% (2)
- Impact of K-Pop Music On The Academic PDocumento29 páginasImpact of K-Pop Music On The Academic Pdave tayron paggao100% (1)
- Basics of Excellence Service in The Hotel, Restaurant, and Catering IndustryDocumento43 páginasBasics of Excellence Service in The Hotel, Restaurant, and Catering IndustryTrinitaaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Literary TheoryDocumento3 páginasIntroduction To Literary TheoryAnil Pinto100% (4)
- Fox Hunting - The Art of Dating and SeductionDocumento93 páginasFox Hunting - The Art of Dating and SeductionEdward Ashley Latimore100% (1)
- USAF Electronic Warfare (1945-5)Documento295 páginasUSAF Electronic Warfare (1945-5)CAP History LibraryAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis SPM Additional MathematicsDocumento170 páginasAnalysis SPM Additional MathematicsChun Kit60% (5)
- 354 33 Powerpoint-Slides CH4Documento52 páginas354 33 Powerpoint-Slides CH4Saravanan JayabalanAinda não há avaliações
- Holiday Assignment FunctionsDocumento31 páginasHoliday Assignment FunctionsGaurav YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1.2 - 1.3 - Evaluating Functions & Operations On FunctionsDocumento16 páginasLesson 1.2 - 1.3 - Evaluating Functions & Operations On Functionskate deguzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Thermodynamics Work and Heat Transfer 4th Edition by GFC Rogers Yon Mayhew 0582045665 PDFDocumento5 páginasEngineering Thermodynamics Work and Heat Transfer 4th Edition by GFC Rogers Yon Mayhew 0582045665 PDFFahad HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 4 Operations On FunctionsDocumento17 páginasLesson 4 Operations On FunctionsCelestine LunaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 4 Operations On FunctionsDocumento17 páginasLesson 4 Operations On FunctionsCelestine LunaAinda não há avaliações
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageAinda não há avaliações
- Universidad de La Frontera: Ingenier Ia Inform Atica Christian Ponce, Mathias MollerDocumento7 páginasUniversidad de La Frontera: Ingenier Ia Inform Atica Christian Ponce, Mathias MollerMaria Jose Zamorano Sepulveda100% (1)
- MSM 131 Tutorial Sheet 2Documento3 páginasMSM 131 Tutorial Sheet 2Kingsley MweembaAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 5A: Dy DX 2 1Documento11 páginasExercise 5A: Dy DX 2 1kamaldinho11Ainda não há avaliações
- TABELA de Diretivas de Derivadas e IntegraisDocumento1 páginaTABELA de Diretivas de Derivadas e IntegraispablomuroAinda não há avaliações
- MATHEMATICS FUNCTIONS PART 1Documento7 páginasMATHEMATICS FUNCTIONS PART 1mohit24031986Ainda não há avaliações
- Ejercicios: Calcule La Derivada de Las Siguientes FuncionesDocumento3 páginasEjercicios: Calcule La Derivada de Las Siguientes FuncionesAntonio BustosAinda não há avaliações
- Sia3e SSM 08Documento60 páginasSia3e SSM 08brianAinda não há avaliações
- Beginning Calculus Ex1Documento3 páginasBeginning Calculus Ex1Manjula ManoharanAinda não há avaliações
- 1.0 Review of FunctionsDocumento5 páginas1.0 Review of FunctionsAlvin Louie DiataAinda não há avaliações
- Ejercicios Derivadas Modulo IDocumento11 páginasEjercicios Derivadas Modulo IJuan RojasAinda não há avaliações
- Differentiation Formulas TrigonometryDocumento1 páginaDifferentiation Formulas TrigonometryaokaoaAinda não há avaliações
- Functio NS: Type of Relation 1.2 Functions 1.4 Inverse FunctionDocumento4 páginasFunctio NS: Type of Relation 1.2 Functions 1.4 Inverse FunctionTiffany HeiwAinda não há avaliações
- Ejercicios de Derivadas ResueltosDocumento4 páginasEjercicios de Derivadas Resueltoslb24-0197Ainda não há avaliações
- Máximos y mínimos absolutos de funcionesDocumento1 páginaMáximos y mínimos absolutos de funcionesMiguel WalkerAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Problems On Functions (Maths)Documento8 páginasPractice Problems On Functions (Maths)Shlok SahAinda não há avaliações
- Solution TutorialDocumento4 páginasSolution TutorialShabriYunusAinda não há avaliações
- Math 176 Worksheet 1 2011Documento2 páginasMath 176 Worksheet 1 2011Greg Levy LevyAinda não há avaliações
- CalculuswithGeometry PDFDocumento931 páginasCalculuswithGeometry PDFbogoeskiAinda não há avaliações
- Taller Derivada Por DefinicionDocumento9 páginasTaller Derivada Por DefinicionAntonio DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Derivadas CGT Sección 6560 Utp HHBL 2019Documento3 páginasDerivadas CGT Sección 6560 Utp HHBL 2019Peter huamanñahui ortegaAinda não há avaliações
- Differentiation & Functions Worked ExamplesDocumento5 páginasDifferentiation & Functions Worked ExamplesGraham MooreAinda não há avaliações
- 8704Documento4 páginas8704M GAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz # 01 Application of Function in Real LifeDocumento3 páginasQuiz # 01 Application of Function in Real LifeAngelo Rey NavaAinda não há avaliações
- Math problems and solutionsDocumento3 páginasMath problems and solutionspcgpauloAinda não há avaliações
- C D I 2 L E - D: X X X F X X X X FDocumento0 páginaC D I 2 L E - D: X X X F X X X X Fglobaltech164768Ainda não há avaliações
- Form 4: Chapter 1 (Functions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocumento4 páginasForm 4: Chapter 1 (Functions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsLuculus LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Tarea-3 Analisis MatematicoDocumento1 páginaTarea-3 Analisis MatematicoAlonZo Maz NahAinda não há avaliações
- MAT108 Assignment On Additional Method For DerivativeDocumento3 páginasMAT108 Assignment On Additional Method For DerivativeKuhleAinda não há avaliações
- Ej Cálculo de Derivadas - SolDocumento14 páginasEj Cálculo de Derivadas - SolDaniel Gutiérrez LópezAinda não há avaliações
- MatematicasDocumento9 páginasMatematicasYoel Lopez MejiasAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Technical Mathematics 5th Edition Washington Solutions ManualDocumento38 páginasIntroduction To Technical Mathematics 5th Edition Washington Solutions Manualleo6exthomas100% (8)
- Introduction To Technical Mathematics 5Th Edition Washington Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento33 páginasIntroduction To Technical Mathematics 5Th Edition Washington Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFStacyGonzalezyoar100% (8)
- Evaluating Functions and DerivativesDocumento5 páginasEvaluating Functions and DerivativesJAVID LeonisAinda não há avaliações
- Tarea 2-Monar Valle Carla Ivana-1cDocumento13 páginasTarea 2-Monar Valle Carla Ivana-1civana monarAinda não há avaliações
- HK2 2022Documento5 páginasHK2 2022lasma.dundureAinda não há avaliações
- SS17 124 Derivative WSDocumento5 páginasSS17 124 Derivative WSPhillip BaikAinda não há avaliações
- Math 150 Homework SolutionsDocumento7 páginasMath 150 Homework SolutionsHa NoiAinda não há avaliações
- 14 IntegrationDocumento22 páginas14 IntegrationSeanAinda não há avaliações
- MAT 270 - Derivative Practice II Find The Derivative of The Following Functions. 1. 4 3 XDocumento6 páginasMAT 270 - Derivative Practice II Find The Derivative of The Following Functions. 1. 4 3 XChathura PriyankaAinda não há avaliações
- F: (X, Y) - (4 X Y-3 y 2) : F: Proc (X, Y) Options Operator, Arrow 4 X Y-3 y 2 End ProcDocumento8 páginasF: (X, Y) - (4 X Y-3 y 2) : F: Proc (X, Y) Options Operator, Arrow 4 X Y-3 y 2 End Procrick_markerAinda não há avaliações
- Math 140 Final RevisionDocumento78 páginasMath 140 Final RevisionطاهرالياسرAinda não há avaliações
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico, Industrial y de Servicios N° 137Documento19 páginasCentro de Bachillerato Tecnológico, Industrial y de Servicios N° 137Melissa Janeth Muñoz EscobarAinda não há avaliações
- Week 1 Learning Task 1: Evaluate The Following Polynomials in Your Answer SheetDocumento12 páginasWeek 1 Learning Task 1: Evaluate The Following Polynomials in Your Answer SheetlouiseAinda não há avaliações
- HK5 Assigment 5Documento3 páginasHK5 Assigment 5lasma.dundureAinda não há avaliações
- Skill 1: Indefinite Integral: Skill 1.1: Integrals of XDocumento15 páginasSkill 1: Indefinite Integral: Skill 1.1: Integrals of XHari TharanAinda não há avaliações
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocumento10 páginasAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremAinda não há avaliações
- Exerciæii: X F F (X)Documento1 páginaExerciæii: X F F (X)Rosescu Alin-ConstantinAinda não há avaliações
- Kunci PTS Genap/Kls X/3.1 Mat Wajib XDocumento2 páginasKunci PTS Genap/Kls X/3.1 Mat Wajib XMazeeda Putri JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Local Media22262561799390700Documento2 páginasLocal Media22262561799390700hence manelsAinda não há avaliações
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- Standard:: SS2H1 The Student Will Read About and Describe The Lives of Historical Figures in Georgia HistoryDocumento4 páginasStandard:: SS2H1 The Student Will Read About and Describe The Lives of Historical Figures in Georgia Historyjeffmiller1977Ainda não há avaliações
- Curriculum Evaluation ModelsDocumento2 páginasCurriculum Evaluation ModelsIrem biçerAinda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary and grammar practice for future technologyDocumento4 páginasVocabulary and grammar practice for future technologyRosa MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Reasoning Olympiads Mind Map Class 3Documento7 páginasReasoning Olympiads Mind Map Class 3vikasAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1&2 Exercise Ce StatisticDocumento19 páginasChapter 1&2 Exercise Ce StatisticSky FireAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of PWM Nonlinearity in Non-Inverting Buck-Boost Power ConvertersDocumento7 páginasAnalysis of PWM Nonlinearity in Non-Inverting Buck-Boost Power ConvertershamidmollaniaAinda não há avaliações
- Wjec A Level Maths SpecificationDocumento50 páginasWjec A Level Maths SpecificationastargroupAinda não há avaliações
- EssayDocumento2 páginasEssaySantoshKumarPatraAinda não há avaliações
- Importance of AC & Design for Minimizing Use in Offices & MallsDocumento2 páginasImportance of AC & Design for Minimizing Use in Offices & MallsRitz BernalAinda não há avaliações
- Quality Policy Nestle PDFDocumento6 páginasQuality Policy Nestle PDFJonathan KacouAinda não há avaliações
- University of Leicester - Involving Your AudienceDocumento4 páginasUniversity of Leicester - Involving Your Audiencevalentina zabalaAinda não há avaliações
- A105972 PDFDocumento42 páginasA105972 PDFKelvin XuAinda não há avaliações
- Implementing IPC Java User Exit To Enable Calculation of EMIDocumento27 páginasImplementing IPC Java User Exit To Enable Calculation of EMIArun SinghAinda não há avaliações
- 7949 37085 3 PBDocumento11 páginas7949 37085 3 PBAman ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Guia de Manejo Sdra 2019Documento27 páginasGuia de Manejo Sdra 2019Jorge VidalAinda não há avaliações
- IT Workload Types: Static, Periodic, Once-in-a-lifetime, Unpredictable, Continuously ChangingDocumento3 páginasIT Workload Types: Static, Periodic, Once-in-a-lifetime, Unpredictable, Continuously ChangingAnand KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Fractions, Decimals and Percent Conversion GuideDocumento84 páginasFractions, Decimals and Percent Conversion GuideSassie LadyAinda não há avaliações
- Data Pre Processing in WEKADocumento5 páginasData Pre Processing in WEKAPrashant SunejaAinda não há avaliações
- Qdoc - Tips Select Readings 2nd Pre IntermediateDocumento178 páginasQdoc - Tips Select Readings 2nd Pre IntermediateFarzana BatoolAinda não há avaliações
- AgendaDocumento72 páginasAgendaThusitha WickramasingheAinda não há avaliações
- 5E Lesson Plan ScienceDocumento8 páginas5E Lesson Plan ScienceHanema MENORAinda não há avaliações