Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
En Vista Warehouse Layout
Enviado por
anewemailDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
En Vista Warehouse Layout
Enviado por
anewemailDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
e
e n a b l i n g l o g i s t i c s e x c e l l e n c e
i e
t a
e b
Making Sense of Warehouse Layout Philosophies
Developing a warehouse layout can be a daunting task without understanding the important warehouse layout philosophies. Grasping the knowledge of these philosophies and using techniques based on overall company warehouse and distribution business, operation and product ow will ultimately assist with proper layout design. The greatest potential to optimize your ROI is when the designer completely understands your business. For this to occur, the designer must (1) visit the facility, (2) observe all operations, (3) clearly understand information and product ow, (4) observe product handling methods and equipment, (5) interview personnel, (6) obtain requested data information such as inbound, outbound and inventory characteristics and (7) obtain all the building and equipment layout drawings. Type of SKU Handled Philosophy
Vi e w p o i n t
In the diagram below, A moving items are located closest to the shipping area to decrease the amount of travel distance from pick to ship. The second layout philosophy is based on the type of SKU that will be handled in the operation. Generally there are three product types, (1) pallet load, (2) carton and (3) single item. A pallet load layout is dictated by the function of a pallet load storage method, material handling equipment and inventory. Typically, the facility has a high clear ceiling elevation, adequate oor areas for turning aisles and sufcient dock space for staging loads. Square footage allocation for this type of warehouse is usually 25 percent of the total facility area for shipping and receiving and 75 percent for the storage-pick area.
What are the Philosophies?
SKU Popularity Philosophy: Paretos Law
A ZONE
Fast Movers 20% SKUs 80% Volume
B ZONE
Medium Movers 55% SKUs 95% Volume
C ZONE
Slow Movers 100% SKUs 100% Volume
Simply put, the A storage pick zone is allocated to the fast-moving SKUs. These SKUs are small in number and have a large inventory quantity. The B storage pick zone is allocated to mediummoving SKUs with a medium amount of inventory. The C storage pick zone is allocated to slow moving SKUs. These SKUs are large in number and have a small inventory quantity per SKU.
Shipping Area
Receiving Area
When a warehouse-distribution facility layout is based on SKU popularity, then it is based on Paretos Law. Named after Vilfredo Pareto, an Italian economist, the law states that 20 percent of SKUs represent 80 percent of volume. This law holds true for the ABC SKU velocity theory where Paretos Law represents the A moving items.
A carton pick layout is based on two areas: reserve and pick. The reserve area will handle pallet loads awaiting breakdown and replenishment. This reserve area is based on the same factors as the pallet load layout. Carton pick areas are to be based on the general size of the cartons. Fast moving cartons can be placed in a pallet ow rack with pallet stocking occurring from the rear of the ow rack, or directly off pallets using an order picker. Slow moving cartons can be stocked in high-bay decked racking also by material handling equipment such as orderpickers and space can be saved by housing these slow movers in Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) racking. Typically these buildings have a clear ceiling height of 20 to 30 feet and are square or rectangular facilities. A single item layout is a more specialized facility due to the fact that SKU characteristics are often different. For example, garments on hangers and single piece items that can t into bin boxes will dictate storage mediums such as hanger pick modules or cart-pick modules. An operation of this nature generally requires a separate reserve area and primary pick area. In this design, a clear ceiling height that is appropriate for mezzanine levels should be considered. MHE Travel Distance Philosophy The next layout philosophy is determined by the material handling equipment travel distances. Keeping transportation distance to a minimum between warehouse function is the key to this philosophy because it reduces operating costs and boosts production. Referring back to SKU velocity, when fast moving items are slotted near the shipping area then travel time by order pickers is reduced. More work can be done at greater efciency. Family Group Philosophy When a company requires that SKUs be sorted by item characteristics they are using the family group layout philosophy. This layout requires that the facility and material handling equipment be
designed based on SKUs that have similar dimensions, weight, and components; are location in the same aisle in the retail store; and require the same security level. For example, an auto parts distribution center would designate a certain zone for heavy products such as brakes and a separate zone for smaller items such as spark plugs. This philosophy promotes good wave planning. Storage Method Philosophy The storage method is a key factor in determining the square footage of a building. The type of storage is determined by the number of SKUs, the number of storage units per SKU (pallet loads or cartons), inventory requirements, SKU life-cycle and product rotation. Also, if certain material handling equipment types are a constraint, this will dictate what storage method would be needed. For example if your distribution center only uses narrow aisle reach lifts then this will open the range of using certain aisle widths based on the general area of your facility and specications of the equipment manufacturer. In conclusion, there are many different philosophies and thoughts on how to layout a warehouse. The path you choose to take is ultimately dependant on your business plan and constraints. The proper strategy and know-how must be taken into consideration before jumping into any facility design project.
Brian Ladao is a consultant with enVista. He can be reached at 619-253-0034 or at bladao@envistacorp.com.
enVista 11711 N Meridian Street, Suite 415 Carmel, IN 46032 877-684-7700 www.envistacorp.com
Você também pode gostar
- The Design and Operation of Warehouse: Kristina RimieneDocumento8 páginasThe Design and Operation of Warehouse: Kristina RimieneCosmin Dincă100% (1)
- Colegio de La Purisima Concepcion B.S. Computer Engineering 2012 Team BravoDocumento62 páginasColegio de La Purisima Concepcion B.S. Computer Engineering 2012 Team BravoYokito YamadaAinda não há avaliações
- Storage and WarehousingDocumento82 páginasStorage and WarehousingBrigita Ratri MayangsariAinda não há avaliações
- Warehouse Management System in SAPDocumento10 páginasWarehouse Management System in SAPWaaKaaWAinda não há avaliações
- Brand Strategy - in B2BDocumento6 páginasBrand Strategy - in B2BKrishan SahuAinda não há avaliações
- Warehouse Layout and DesignDocumento7 páginasWarehouse Layout and DesignMani Bhushan Arya0% (1)
- Racking SystemDocumento76 páginasRacking SystemmlogvijayAinda não há avaliações
- alsandy-ENGLISH MARITIEDocumento13 páginasalsandy-ENGLISH MARITIEAl SandyAinda não há avaliações
- Expert Insight: Optimizing Warehouse Facility DesignDocumento4 páginasExpert Insight: Optimizing Warehouse Facility DesignMd Abdullah Al ArmanAinda não há avaliações
- Warehouse DesignDocumento11 páginasWarehouse Designmishal chAinda não há avaliações
- Warehouse DesignDocumento11 páginasWarehouse Designmishal chAinda não há avaliações
- System Directed PutawayDocumento3 páginasSystem Directed PutawayJovan ĆetkovićAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment Chapter 6 "Process Selection and Facility Layout" (Service Layout)Documento5 páginasAssignment Chapter 6 "Process Selection and Facility Layout" (Service Layout)Apricilia PangemananAinda não há avaliações
- Warehouse Essentials: Logistics & SCM Manufacturing SystemsDocumento6 páginasWarehouse Essentials: Logistics & SCM Manufacturing SystemsJon JijongAinda não há avaliações
- Warehouse Operations ThesisDocumento4 páginasWarehouse Operations Thesisruthuithovensiouxfalls100% (2)
- Warehouse Layout and PlanningDocumento12 páginasWarehouse Layout and PlanningJasmine KariukiAinda não há avaliações
- Act1 T3mtiaDocumento8 páginasAct1 T3mtiaisabel martinezAinda não há avaliações
- Operation Management (VW)Documento7 páginasOperation Management (VW)Harshit RajAinda não há avaliações
- Tilt Up Construction GuideDocumento24 páginasTilt Up Construction GuideAmin ZuraiqiAinda não há avaliações
- Distribution Center: Navigation SearchDocumento6 páginasDistribution Center: Navigation SearchsaipuppalaAinda não há avaliações
- Warehouse Management: Enterprise StructureDocumento45 páginasWarehouse Management: Enterprise StructureRakesh Reddy Gopi ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Warehousing Unit - 4Documento42 páginasWarehousing Unit - 4pramav2411Ainda não há avaliações
- SCM Final Project ReportDocumento14 páginasSCM Final Project ReportShaharyar Amin NCBA&EAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of An Efficient Warehouse Layout: Planning and Optimizing Your Warehouse Layout - Supply Chain ImpactDocumento2 páginasPrinciples of An Efficient Warehouse Layout: Planning and Optimizing Your Warehouse Layout - Supply Chain ImpactNtinaGanes0% (1)
- Term PaperDocumento4 páginasTerm PaperPraneeth Akula SonaAinda não há avaliações
- Storage Space UtilizationDocumento4 páginasStorage Space UtilizationSajjad NawazAinda não há avaliações
- Slide 2Documento12 páginasSlide 2Mani Bhushan AryaAinda não há avaliações
- Six Steps To Optimized Order Fulfillment: White PaperDocumento14 páginasSix Steps To Optimized Order Fulfillment: White PaperMA TotalforkliftAinda não há avaliações
- (Production and Operations Management) Chapter 4 SummaryDocumento7 páginas(Production and Operations Management) Chapter 4 Summarytrang.ngo71Ainda não há avaliações
- Colegio de La Purisima Concepcion B.S. Computer Engineering 2012 Team BravoDocumento62 páginasColegio de La Purisima Concepcion B.S. Computer Engineering 2012 Team BravoSO FabAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of An Efficient Warehouse Layout: Inventory Receiving Pick and Pack Processes CrossdockingDocumento2 páginasPrinciples of An Efficient Warehouse Layout: Inventory Receiving Pick and Pack Processes CrossdockingNtinaGanes100% (1)
- Operations Management (UV)Documento7 páginasOperations Management (UV)Harshit RajAinda não há avaliações
- Layout Strategies: de Ocampo, Jenalyn Pineda, Daniela Corpuz, Lindsay Cabrera, PatriciaDocumento33 páginasLayout Strategies: de Ocampo, Jenalyn Pineda, Daniela Corpuz, Lindsay Cabrera, Patriciamelvin cunananAinda não há avaliações
- Supply Chain Management Course TrainingDocumento5 páginasSupply Chain Management Course TrainingPrabhat DubeyAinda não há avaliações
- Lean Management: Warehousing Decisions & LayoutsDocumento55 páginasLean Management: Warehousing Decisions & Layoutsmegaspice100% (5)
- Warehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Documento29 páginasWarehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Muhammad AhsanAinda não há avaliações
- Ankit Singhvi Mahipatraj - GroupAssignment - Group2Documento6 páginasAnkit Singhvi Mahipatraj - GroupAssignment - Group2Ankit SinghviAinda não há avaliações
- Improving Warehouse Efficiency and EffectivenessDocumento3 páginasImproving Warehouse Efficiency and EffectivenessMarika DixonAinda não há avaliações
- Warehouse Layout ThesisDocumento7 páginasWarehouse Layout Thesisjoannapaulsenelgin100% (2)
- Document 4Documento3 páginasDocument 4Samillano Bajala RolenAinda não há avaliações
- Operations Management Answer 1Documento8 páginasOperations Management Answer 1shiv panjnaniAinda não há avaliações
- Berg - 1999 - Models For Warehouse Management Classification and ExamplesDocumento10 páginasBerg - 1999 - Models For Warehouse Management Classification and ExamplesHallan MarquesAinda não há avaliações
- HypermarketDocumento4 páginasHypermarketKenneth RemigioAinda não há avaliações
- Actividadndenaprendizajen9nKATERINEnRAMIREZ 306290d2884dd16Documento7 páginasActividadndenaprendizajen9nKATERINEnRAMIREZ 306290d2884dd16Michael Arevalo DuarteAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Q & ADocumento3 páginas6 Q & ASIVAREDDY PALLETIAinda não há avaliações
- Development of A Design Methodology For Warehousing Systems: Hierarchical FrameworkDocumento6 páginasDevelopment of A Design Methodology For Warehousing Systems: Hierarchical FrameworkGilangRisangAinda não há avaliações
- Research Paper On Warehouse Management SystemDocumento9 páginasResearch Paper On Warehouse Management Systemqosryjvnd100% (1)
- Manual de Logística y Almacenes IDocumento12 páginasManual de Logística y Almacenes IK-PurpleAinda não há avaliações
- Actividad de Aprendizaje 9 Evid. InglesDocumento7 páginasActividad de Aprendizaje 9 Evid. InglesJorge ManjarresAinda não há avaliações
- Setting Up and Designing Your Warehouse LayoutDocumento13 páginasSetting Up and Designing Your Warehouse LayoutSiew Ming SooAinda não há avaliações
- 01 - WM Intro and IM InterfaceDocumento23 páginas01 - WM Intro and IM Interfacekumar_282392851Ainda não há avaliações
- SE Report 2007 09 PDFDocumento62 páginasSE Report 2007 09 PDFtintucinbAinda não há avaliações
- SDMDocumento16 páginasSDMSam LordAinda não há avaliações
- How To Design Your Warehouse in 7 Steps: The Ultimate Guide To The Ideal LayoutDocumento8 páginasHow To Design Your Warehouse in 7 Steps: The Ultimate Guide To The Ideal LayoutEllyella ElormAinda não há avaliações
- Components of On-Demand WarehousingDocumento3 páginasComponents of On-Demand WarehousingMainali GautamAinda não há avaliações
- WarehouseDocumento3 páginasWarehouseAmr M. AbdelhadyAinda não há avaliações
- Warehouse Operations Best 5 PracticesDocumento4 páginasWarehouse Operations Best 5 PracticesJochie Teruel100% (1)
- Assignment 4Documento8 páginasAssignment 4Miracle -Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment 4Documento8 páginasAssignment 4Miracle -Ainda não há avaliações
- Running a Good Business - Book 7: Designing Your Space: Running a Good Business, #7No EverandRunning a Good Business - Book 7: Designing Your Space: Running a Good Business, #7Ainda não há avaliações
- Test 51Documento7 páginasTest 51Nguyễn Hiền Giang AnhAinda não há avaliações
- Jackson V AEGLive - May 10 Transcripts, of Karen Faye-Michael Jackson - Make-up/HairDocumento65 páginasJackson V AEGLive - May 10 Transcripts, of Karen Faye-Michael Jackson - Make-up/HairTeamMichael100% (2)
- Subject Manual Tle 7-8Documento11 páginasSubject Manual Tle 7-8Rhayan Dela Cruz DaquizAinda não há avaliações
- Cable To Metal Surface, Cathodic - CAHAAW3Documento2 páginasCable To Metal Surface, Cathodic - CAHAAW3lhanx2Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 - 2020-CAP Surveys CatalogDocumento356 páginas1 - 2020-CAP Surveys CatalogCristiane AokiAinda não há avaliações
- Deep Hole Drilling Tools: BotekDocumento32 páginasDeep Hole Drilling Tools: BotekDANIEL MANRIQUEZ FAVILAAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco UCS Adapter TroubleshootingDocumento90 páginasCisco UCS Adapter TroubleshootingShahulAinda não há avaliações
- Dwnload Full Principles of Economics 7th Edition Frank Solutions Manual PDFDocumento35 páginasDwnload Full Principles of Economics 7th Edition Frank Solutions Manual PDFmirthafoucault100% (8)
- Meno's Paradox of Inquiry and Socrates' Theory of RecollectionDocumento10 páginasMeno's Paradox of Inquiry and Socrates' Theory of RecollectionPhilip DarbyAinda não há avaliações
- Phytotherapy On CancerDocumento21 páginasPhytotherapy On CancerSiddhendu Bhattacharjee100% (1)
- CL57T V4.0Documento14 páginasCL57T V4.0dimitriAinda não há avaliações
- 2014 - A - Levels Actual Grade A Essay by Harvey LeeDocumento3 páginas2014 - A - Levels Actual Grade A Essay by Harvey Leecherylhzy100% (1)
- Friction: Ultiple Hoice UestionsDocumento5 páginasFriction: Ultiple Hoice Uestionspk2varmaAinda não há avaliações
- In Flight Fuel Management and Declaring MINIMUM MAYDAY FUEL-1.0Documento21 páginasIn Flight Fuel Management and Declaring MINIMUM MAYDAY FUEL-1.0dahiya1988Ainda não há avaliações
- (1921) Manual of Work Garment Manufacture: How To Improve Quality and Reduce CostsDocumento102 páginas(1921) Manual of Work Garment Manufacture: How To Improve Quality and Reduce CostsHerbert Hillary Booker 2nd100% (1)
- Aluminum PorterDocumento2 páginasAluminum PorterAmir ShameemAinda não há avaliações
- WarringFleets Complete PDFDocumento26 páginasWarringFleets Complete PDFlingshu8100% (1)
- World Insurance Report 2017Documento36 páginasWorld Insurance Report 2017deolah06Ainda não há avaliações
- Winter CrocFest 2017 at St. Augustine Alligator Farm - Final ReportDocumento6 páginasWinter CrocFest 2017 at St. Augustine Alligator Farm - Final ReportColette AdamsAinda não há avaliações
- Fast Track Design and Construction of Bridges in IndiaDocumento10 páginasFast Track Design and Construction of Bridges in IndiaSa ReddiAinda não há avaliações
- Heimbach - Keeping Formingfabrics CleanDocumento4 páginasHeimbach - Keeping Formingfabrics CleanTunç TürkAinda não há avaliações
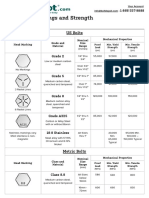
- Bolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartDocumento2 páginasBolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartGregory GaschteffAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Resume For Supply Chain Logistics PersonDocumento2 páginasSample Resume For Supply Chain Logistics PersonAmmar AbbasAinda não há avaliações
- MMS - IMCOST (RANJAN) Managing Early Growth of Business and New Venture ExpansionDocumento13 páginasMMS - IMCOST (RANJAN) Managing Early Growth of Business and New Venture ExpansionDhananjay Parshuram SawantAinda não há avaliações
- Apron CapacityDocumento10 páginasApron CapacityMuchammad Ulil AidiAinda não há avaliações
- Out PDFDocumento211 páginasOut PDFAbraham RojasAinda não há avaliações
- Toeic: Check Your English Vocabulary ForDocumento41 páginasToeic: Check Your English Vocabulary ForEva Ibáñez RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Eloy-Stock English Full PDFDocumento0 páginaEloy-Stock English Full PDFR.s. WartsAinda não há avaliações
- DLP - Light Science 7Documento6 páginasDLP - Light Science 7Samara M. SalacayanAinda não há avaliações