Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
M 315
Enviado por
Epic WinDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
M 315
Enviado por
Epic WinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MISN-0-315
ANOMALOUS ZEEMAN EFFECT AND THE LANDE g-FACTOR
ANOMALOUS ZEEMAN EFFECT AND THE LANDE g-FACTOR by J. H. Hetherington 1. Study Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Acknowledgments. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
D1
D2
off
on
Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MI
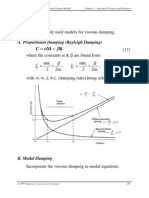
ID Sheet: MISN-0-315 THIS IS A DEVELOPMENTAL-STAGE PUBLICATION OF PROJECT PHYSNET The goal of our project is to assist a network of educators and scientists in transferring physics from one person to another. We support manuscript processing and distribution, along with communication and information systems. We also work with employers to identify basic scientic skills as well as physics topics that are needed in science and technology. A number of our publications are aimed at assisting users in acquiring such skills. Our publications are designed: (i) to be updated quickly in response to eld tests and new scientic developments; (ii) to be used in both classroom and professional settings; (iii) to show the prerequisite dependencies existing among the various chunks of physics knowledge and skill, as a guide both to mental organization and to use of the materials; and (iv) to be adapted quickly to specic user needs ranging from single-skill instruction to complete custom textbooks. New authors, reviewers and eld testers are welcome. PROJECT STAFF Andrew Schnepp Eugene Kales Peter Signell Webmaster Graphics Project Director
Title: Anomalous Zeeman Eect and the Land g-Factor e Author: J. H. Hetherington, Michigan State University Version: 2/1/2000 Length: 1 hr; 8 pages Input Skills: 1. Vocabulary: angular momentum quantization, Bohr magneton, energy level splitting, (MISN-0-251); total angular momentum (MISN-0-244); atomic transition (MISN-0-215). 2. Determine the energy of a magnetic dipole in a magnetic eld (MISN-0-251). 3. Be familiar with electron spin and spectroscopic notation (MISN0-244). Output Skills (Knowledge): K1. Derive the Land g-factor. e K2. Compare the anomalous Zeeman eect to the normal Zeeman effect. Output Skills (Problem Solving): S1. Given a particular transition in terms of spectroscopic notation, determine the number of Zeeman components and their splittings in a weak magnetic eld. External Resources (Required): 1. R. T. Weidner and R. L. Sells, Elementary Modern Physics, alt. 2nd ed., Allyn and Bacon, (1973). For access, see this modules Local Guide. 2. H. Semat and J. R. Albright, Introduction to Atomic and Nuclear Physics, 5th ed., Holt, Rinehart, Winston (1972). For access, see this modules Local Guide. Evaluation: Stage B0
ADVISORY COMMITTEE D. Alan Bromley E. Leonard Jossem A. A. Strassenburg Yale University The Ohio State University S. U. N. Y., Stony Brook
Views expressed in a module are those of the module author(s) and are not necessarily those of other project participants. c 2001, Peter Signell for Project PHYSNET, Physics-Astronomy Bldg., Mich. State Univ., E. Lansing, MI 48824; (517) 355-3784. For our liberal use policies see: http://www.physnet.org/home/modules/license.html.
MISN-0-315
MISN-0-315
LG-1
ANOMALOUS ZEEMAN EFFECT AND THE LANDE g-FACTOR by J. H. Hetherington 1. Study Program
1. Work Problems 7-32 and 7-33 in WSM.1 2. Read supplementary material (Sec. 9-16) from SA.2 This may help you work Problem 7-32 above. 3. Read SA, Section 8-16. 4. Determine the Zeeman splitting of the 21 P1 11 S0 line in He and the 23 P1 1 S0 line in He. 5. Determine the splitting in the 33 D2 33 P1 line in Ca. 6. Determine the splitting in the 32 D3/2 32 P1/2 line of Na.
LOCAL GUIDE
The readings for this unit are on reserve for you in the Physics-Astronomy Library, Room 230 in the Physics-Astronomy Building. Ask for them as The readings for CBI Unit 315. Do not ask for them by book title.
Acknowledgments
Preparation of this module was supported in part by the National Science Foundation, Division of Science Education Development and Research, through Grant #SED 74-20088 to Michigan State University.
1 R. T. Weidner and R. L. Sells, Elementary Modern Physics 3rd ed., (Allyn and Bacon, Boston: 1980. For access, see this modules Local Guide. 2 H. Semat and J. R. Albright, Introduction to Atomic and Nuclear Physics, 5th ed. (Holt, Rinehart, Winston, New York, 1972. For access, see this modules Local Guide.
MISN-0-315
PS-1
MISN-0-315
ME-1
PROBLEM SUPPLEMENT
Note: The problem below also occurs on this modules Model Exam. 1. Determine the number of Zeeman components and splittings in the 32 P3/2 32 S1/2 line of Na in a weak magnetic eld of magnitude B.
MODEL EXAM
1. See Output Skills K1-K2 in this modules ID Sheet. 2. Determine the number of Zeeman components and splittings in the 32 P3/2 32 S1/2 line of Na in a weak magnetic eld of magnitude B.
Brief Answers: 1. There are 6 components of the original line, 0 : 1 = 0 + 1 2 = 0 3 5 3 = 0 + 3 5 4 = 0 3 1 5 = 0 + 3 6 = 0 where = eB/4m; e is the charge of an electron and m is the mass of an electron.
Brief Answers: 1. See this modules text. 2. See this modules Problem Supplement, problem 1.
Você também pode gostar
- Electricity and Magnetism: Electromagnetic WavesDocumento4 páginasElectricity and Magnetism: Electromagnetic WavesEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Math Physics: Fourier Integrals: Part 1Documento4 páginasMath Physics: Fourier Integrals: Part 1Epic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Classical Mechanics: Vector AnalysisDocumento4 páginasClassical Mechanics: Vector AnalysisEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- The Gravitational Field: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocumento6 páginasThe Gravitational Field: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Time-Independent Perturbations: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocumento4 páginasTime-Independent Perturbations: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Electricity and Magnetism: Review of Vector AnalysisDocumento4 páginasElectricity and Magnetism: Review of Vector AnalysisEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Relativistic Energy and Momentum: DerivationDocumento4 páginasRelativistic Energy and Momentum: DerivationEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Classical Mechanics: Calculus of VariationsDocumento4 páginasClassical Mechanics: Calculus of VariationsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Math Physics: Integral Calculus For VectorsDocumento4 páginasMath Physics: Integral Calculus For VectorsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Pumping: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocumento4 páginasOptical Pumping: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Relativity: Einstein'S Field EquationsDocumento4 páginasRelativity: Einstein'S Field EquationsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Classical Mechanics: Rigid Bodies The Inertia TensorDocumento4 páginasClassical Mechanics: Rigid Bodies The Inertia TensorEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Transitions and Spectral Analysis: Two Slit Images (Two Lines)Documento4 páginasTransitions and Spectral Analysis: Two Slit Images (Two Lines)Epic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Special Relativity: The Michelson-Morley Experiment: FlashlightDocumento4 páginasSpecial Relativity: The Michelson-Morley Experiment: FlashlightEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- The Numerov Algorithm For Magnetic Field TrajectoriesDocumento4 páginasThe Numerov Algorithm For Magnetic Field Trajectoriesp_k_soni_iit_physicsAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Fields in Bulk Matter: Magnets: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocumento4 páginasMagnetic Fields in Bulk Matter: Magnets: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Electron Spin: MISN-0-244Documento4 páginasElectron Spin: MISN-0-244Epic WinAinda não há avaliações
- MYP3 Scope and Sequence DownloadDocumento4 páginasMYP3 Scope and Sequence DownloadJerry LouAinda não há avaliações
- Classical Mechanics: Newtonian Mechanics - Single ParticleDocumento8 páginasClassical Mechanics: Newtonian Mechanics - Single Particlep_k_soni_iit_physicsAinda não há avaliações
- Foucault'S Pendulum: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocumento4 páginasFoucault'S Pendulum: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Coursefile - Jan2020 - PH0011 - Eng - Physics - CSE - Tanushree BasakDocumento11 páginasCoursefile - Jan2020 - PH0011 - Eng - Physics - CSE - Tanushree BasakLana RoseAinda não há avaliações
- Harmonic Perturbations: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocumento4 páginasHarmonic Perturbations: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Electricity and Magnetism: Maxwell'S EquationsDocumento4 páginasElectricity and Magnetism: Maxwell'S EquationsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Relativity: Introduction To General RelativityDocumento4 páginasRelativity: Introduction To General RelativityEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Derivation of The Lorentz Transformation: DerivingDocumento4 páginasDerivation of The Lorentz Transformation: DerivingEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Relativity: Weak-Field Approximation and Gravitational WavesDocumento4 páginasRelativity: Weak-Field Approximation and Gravitational WavesEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Electricity and Magnetism: Dielectrics Displacement VectorDocumento4 páginasElectricity and Magnetism: Dielectrics Displacement VectorEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- The Spectrum of Sodium: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocumento6 páginasThe Spectrum of Sodium: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Ocean County Grade 2 Science CurriculumDocumento39 páginasOcean County Grade 2 Science CurriculumAli khan7Ainda não há avaliações
- Relativity: Relativistic Kinematics and Einsteinian OpticsDocumento4 páginasRelativity: Relativistic Kinematics and Einsteinian OpticsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Msu NSCL ThesisDocumento4 páginasMsu NSCL Thesispbfbkxgld100% (1)
- Modelling Microstructures With OOF2: Andrew C.E. ReidDocumento13 páginasModelling Microstructures With OOF2: Andrew C.E. ReidKaram JaradatAinda não há avaliações
- Classical Mechanics: Matrices and TransformationsDocumento5 páginasClassical Mechanics: Matrices and TransformationsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Punjab Technical University: Scheme & Syllabus of B. Tech. 1 & 2 Semester Batch-2011Documento42 páginasPunjab Technical University: Scheme & Syllabus of B. Tech. 1 & 2 Semester Batch-2011Pankaj SainiAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Course Code: Course Name: Credit Hours: Contact Hours: Prerequisite: Mode of TeachingDocumento5 páginasLesson Plan: Course Code: Course Name: Credit Hours: Contact Hours: Prerequisite: Mode of TeachingMusaab MahmoodAinda não há avaliações
- M 530Documento4 páginasM 530Epic WinAinda não há avaliações
- General Physics SylabusDocumento5 páginasGeneral Physics SylabusTadesse AbateAinda não há avaliações
- M 254Documento4 páginasM 254Epic WinAinda não há avaliações
- ZeroDocumento18 páginasZeroSherlcok HolmesAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture PlanDocumento3 páginasLecture PlanvinitarohitAinda não há avaliações
- M.SC - Physics (MSP) Ay2021 2022Documento62 páginasM.SC - Physics (MSP) Ay2021 2022ultimate starkAinda não há avaliações
- B.Tech Winter Elective Course on Bio-PhysicsDocumento7 páginasB.Tech Winter Elective Course on Bio-PhysicsArijeet SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Scheme & Syllabus 2017-18Documento72 páginasScheme & Syllabus 2017-18Ritik GandhiAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier Analysis and Wave Packets: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocumento4 páginasFourier Analysis and Wave Packets: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- B Tech 1st Year-10-11-2015Documento44 páginasB Tech 1st Year-10-11-2015navneetsherry21Ainda não há avaliações
- As Physics Coursework Quality of Measurement ExamplesDocumento8 páginasAs Physics Coursework Quality of Measurement Examplesf0jimub1lef2100% (1)
- PHYFUN1 SyllabusDocumento6 páginasPHYFUN1 SyllabusBrian SoanAinda não há avaliações
- Phy 210-Physics 1 SyllabusDocumento2 páginasPhy 210-Physics 1 SyllabusHarold TaylorAinda não há avaliações
- Physics - Semester 1: Course-Level SyllabusDocumento3 páginasPhysics - Semester 1: Course-Level Syllabusanon-579447Ainda não há avaliações
- Cse All SemDocumento131 páginasCse All Semarpankruze007Ainda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics 100 Semester 1 2014 Bentley Campus INTDocumento10 páginasEngineering Mechanics 100 Semester 1 2014 Bentley Campus INTJeff JabeAinda não há avaliações
- (Major American Universities Ph.D. Qualifying Questions and Solutions) Yung-Kuo Lim-Problems and Solutions on Electromagnetism_ Major American University Ph.D. Qualifying Questions and Solutions-WorldDocumento677 páginas(Major American Universities Ph.D. Qualifying Questions and Solutions) Yung-Kuo Lim-Problems and Solutions on Electromagnetism_ Major American University Ph.D. Qualifying Questions and Solutions-Worldimran khan100% (1)
- Atomic Structure Myp Unit PlanDocumento9 páginasAtomic Structure Myp Unit Planapi-352917620Ainda não há avaliações
- B.Tech - 1st Semester - Syllabus - 2023-24Documento2 páginasB.Tech - 1st Semester - Syllabus - 2023-24kumarjaawAinda não há avaliações
- Formal Structure of QM (Ii) : Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocumento5 páginasFormal Structure of QM (Ii) : Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Antony Course File TemplateDocumento65 páginasAntony Course File TemplateKumari PanimalarAinda não há avaliações
- Core Curriculum Requirements 2014Documento3 páginasCore Curriculum Requirements 2014Dennis TerceroAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Science Engineering Syallabus Kuk Univ.Documento131 páginasComputer Science Engineering Syallabus Kuk Univ.Er Saurabh Sharma100% (1)
- Solar Energy Technology Education: Portland State UniversityDocumento19 páginasSolar Energy Technology Education: Portland State UniversityTeju TejaswiniAinda não há avaliações
- Warning Signs of A Possible Collapse of Contemporary MathematicsDocumento12 páginasWarning Signs of A Possible Collapse of Contemporary MathematicsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- OutlineDocumento7 páginasOutlineEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- InequalitiesDocumento192 páginasInequalitiesEpic Win100% (2)
- Mathematics and The Mind: Nelson/papers - HTMLDocumento6 páginasMathematics and The Mind: Nelson/papers - HTMLEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- RomeDocumento7 páginasRomeEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- IstDocumento34 páginasIstEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Ram RecDocumento8 páginasRam RecEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- New 18Documento5 páginasNew 18Epic WinAinda não há avaliações
- The Mystery of Stochastic MechanicsDocumento18 páginasThe Mystery of Stochastic MechanicsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- HopeDocumento4 páginasHopeEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Syntax and Semantics: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLDocumento7 páginasSyntax and Semantics: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Nelson BibDocumento5 páginasNelson BibEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Zhang TDocumento4 páginasZhang TEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Hilbert's Mistake: Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton UniversityDocumento27 páginasHilbert's Mistake: Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton UniversityEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- FogDocumento5 páginasFogEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Edward NelsonDocumento1 páginaEdward NelsonEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Intuitionism: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLDocumento20 páginasUnderstanding Intuitionism: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- EDocumento9 páginasEEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- FaithDocumento8 páginasFaithceceph354Ainda não há avaliações
- ElemDocumento101 páginasElemEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Set TheoryDocumento26 páginasInternal Set TheoryEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Zhang QDocumento15 páginasZhang QEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- WeinerDocumento6 páginasWeinerEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- WoolfDocumento9 páginasWoolfEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- J. P. MayDocumento17 páginasJ. P. MayEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Probability Theory: 1 Heuristic IntroductionDocumento17 páginasProbability Theory: 1 Heuristic IntroductionEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- WalijiDocumento6 páginasWalijiEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- J-Spectra For A Quotient Group J of G. That Context Gives An Interesting SituationDocumento9 páginasJ-Spectra For A Quotient Group J of G. That Context Gives An Interesting SituationEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- WaddleDocumento10 páginasWaddleEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- VParticipantsDocumento1 páginaVParticipantsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- 15 SphereDocumento17 páginas15 Sphereaustinfru7Ainda não há avaliações
- CH08 PDFDocumento25 páginasCH08 PDFpestaAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Quantum Physics lecture handoutDocumento5 páginasAdvanced Quantum Physics lecture handoutPhyo ThihaAinda não há avaliações
- (Lecture Notes in Physics 631) Claus Kiefer (auth.), Domenico J. W. Giulini, Claus Kiefer, Claus Lämmerzahl (eds.)-Quantum Gravity_ From Theory to Experimental Search-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.pdfDocumento394 páginas(Lecture Notes in Physics 631) Claus Kiefer (auth.), Domenico J. W. Giulini, Claus Kiefer, Claus Lämmerzahl (eds.)-Quantum Gravity_ From Theory to Experimental Search-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.pdfBriptu Andri JauhariAinda não há avaliações
- A Survey of Geometric Algebra and Geometric CalculusDocumento33 páginasA Survey of Geometric Algebra and Geometric CalculusRodrigo Rafael Gomes100% (1)
- Reciprocity Principle and The Lorentz Transformations: Additional Information On J. Math. PhysDocumento8 páginasReciprocity Principle and The Lorentz Transformations: Additional Information On J. Math. PhysPericoAinda não há avaliações
- 17.pertemuan 13 Triple Integral-883-900Documento18 páginas17.pertemuan 13 Triple Integral-883-900yoventa vernas veroAinda não há avaliações
- HTTP WWW - Feynmanlectures.caltech - Edu II 19.HTMLDocumento2 páginasHTTP WWW - Feynmanlectures.caltech - Edu II 19.HTML88915334Ainda não há avaliações
- On Fractional (P, Q) - Calculus: Research Open AccessDocumento18 páginasOn Fractional (P, Q) - Calculus: Research Open AccessBoutiara AbdellatifAinda não há avaliações
- Indrani Bose - Spin Gap Antiferromagnets: Materials and PhenomenaDocumento9 páginasIndrani Bose - Spin Gap Antiferromagnets: Materials and PhenomenaPo48HSDAinda não há avaliações
- 2-DOF System AnalysisDocumento41 páginas2-DOF System AnalysisManavAinda não há avaliações
- B-Spline - Chapter 4 PDFDocumento24 páginasB-Spline - Chapter 4 PDFMarius DiaconuAinda não há avaliações
- EmtDocumento13 páginasEmtAnonymous VASS3z0wTHAinda não há avaliações
- Quantum Numbers: N, L, M, and SDocumento9 páginasQuantum Numbers: N, L, M, and Seminent career academyAinda não há avaliações
- ENGR 376 Dynamics Notes StudentDocumento133 páginasENGR 376 Dynamics Notes StudentMatthew EellsAinda não há avaliações
- Surface IntegralsDocumento33 páginasSurface IntegralsAfwanilhuda NstAinda não há avaliações
- MMathPhys Handbook 2020-2021Documento44 páginasMMathPhys Handbook 2020-2021hemantchaudhari56Ainda não há avaliações
- Implicit Differentiation: Lesson 6.4Documento11 páginasImplicit Differentiation: Lesson 6.4Noli NogaAinda não há avaliações
- Beet3383 Lab1 (B082110143 B082110014 B082110053)Documento7 páginasBeet3383 Lab1 (B082110143 B082110014 B082110053)Siti Sarah binti nazarruddinAinda não há avaliações
- U X, U Y, V X and V y U X V y and V X U Y: Unit Ii - Analytical Functions Part - ADocumento13 páginasU X, U Y, V X and V y U X V y and V X U Y: Unit Ii - Analytical Functions Part - ACurious ManAinda não há avaliações
- Strauss PDEs Section 1.1 Exercise 1Documento37 páginasStrauss PDEs Section 1.1 Exercise 1maria100% (2)
- Cinvestav Research ProgramsDocumento8 páginasCinvestav Research ProgramsMartín ReynosoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapt 07 Lect03Documento5 páginasChapt 07 Lect03Shanmukha SundaramAinda não há avaliações
- Physicists Provide Support For Retrocausal Quantum Theory, in Which The Future Influences The PastDocumento4 páginasPhysicists Provide Support For Retrocausal Quantum Theory, in Which The Future Influences The PastCraig HoughtonAinda não há avaliações
- 599 - PR 04 - Lagrangian Density For Schrodinger Equation FieldsDocumento1 página599 - PR 04 - Lagrangian Density For Schrodinger Equation FieldsBradley NartowtAinda não há avaliações
- M 3 Assignment VDocumento4 páginasM 3 Assignment Vrs VivoAinda não há avaliações
- FDTD: An Introduction: Prof. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum Prof. Rakhesh Singh KshetrimayumDocumento73 páginasFDTD: An Introduction: Prof. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum Prof. Rakhesh Singh KshetrimayumSonali MauryaAinda não há avaliações
- Special Relativity 3Documento17 páginasSpecial Relativity 3GeorgeLauAinda não há avaliações
- Topology Optimization For Shell Structures With Linear Buckling ResponsesDocumento6 páginasTopology Optimization For Shell Structures With Linear Buckling ResponsesAltairEnlighten100% (1)