Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
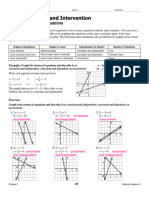
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations CH 13 Simultaneous Equations
Enviado por
Epic WinDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations CH 13 Simultaneous Equations
Enviado por
Epic WinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
Selected Solved Problems: Math B: Unit 5: Graphs and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations
G.MaB.13.1.1-4 VG.MaB.13.1.9 G.MaB.13.2.1-3 VG.MaB.13.2.13-14 VG.MaB.13.2.21 MVG.MaB.13.3.20 G.MaB.13.1.5-6 VG.MaB.13.1.10 G.MaB.13.2.5-6 VG.MaB.13.2.15-16 MVG.MaB.13.3.21 G.MaB.13.1.7 VG.MaB.13.1.11 G.MaB.13.2.7-9 VG.MaB.13.2.17-18 MVG.MaB.13.3.22 G.MaB.13.1.8 VG.MaB.13.1.12 G.MaB.13.2.10-12 VG.MaB.13.2.19-20 MVG.MaB.13.3.23
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
Summery: Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations:
Coefficient: The number in front of a letter is called coefficient. Simultaneous Equations: Two linearly independent equations together may form a pair of simultaneous equations. The solutions of the simultaneous equations are pair of numbers that satisfy both equations.
2 is the coefficient of x 2x x 1 is the coefficient of x x 1 is the coefficient of x 3 5x 5 is the coefficient of x 3 Solving by elimination: To eliminate a variable from a pair of equations, subtract when the coefficients are the same, and add when the coefficients are equal but of the opposite sign.
x + 2 y = 5 2 x y = 15 x + 2 y = 5 4 x 2 y = 30 // // x + 2 y + 4 x 2 y = 5 + 30 x + 4 x = 35 5 x = 35 35 x= 5 x=7 2 x y = 10 2 7 y = 15 14 y = 15 14 15 = y y = 1 Note that the pair of answers x = 7 , and y = 1 must both satisfy both equations.
Solving by elimination: We may solve a pair of simultaneous linear equations by eliminating one of the variables from the system. This may be achieved by properly multiplying both sides of one of the equations by a number and the subtracting or adding the equations. x + 2 y = 5 we may multiply To solve 2 x y = 15 both sides of the second equation 2 x y = 15 by 2 and then add the resultant equations to each other, and therefore eliminate (remove) y from the equation. The resulting equation is an equation of only one variable that may be solved accordingly.
Solving by substitution: To reduce a system of linear equations to an equation of only one variable, find one of the variables from one of the equations in terms of the other one, and then replace it in the second equation.
x + 2 y = 5 2 x y = 15 x + 2y = 5 x = 5 2y Substitute x by 5 2 y in the second equation 2 x y = 15 : 2 (5 2 y ) y = 15 10 4 y y = 15 5 y = 1 5 y = 15 10 5 y = 5 y = 5 x = 5 2 y x = 5 2( 1) = 5 + 2 x = 7
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
Solving by elimination: To eliminate a variable from a pair of equations, we may have to multiply both of the equations by a proper number and then subtract when the coefficients are the same, and add when the coefficients are equal but of the opposite sign. G.MaB.13.3.9 2 x + 3 y = 17 3x 2 y = 0.5 To eliminate y we may multiply the first equation by by 2 , and the second equation by 3 , and then add the resulted equations: 2 2 x + 2 3 y = 2 17 3 3x 3 2 y = 3 0.5 4 x + 6 y = 34 9 x 6 y = 1.5 (4 x + 6 y ) + (9 x 6 y ) = 34 1.5 // // 32.5 13 x = 32.5 x = x = 2 .5 13 Substitute x by its value x = 2.5 in one of the original equations to find the other variable: 2 x + 3 y = 17 2(2.5) + 3 y = 17 5 + 3 y = 17 3 y = 17 5 3 y = 12 12 y= y=4 3
3x + 2 y = 5 5 x + 3 y = 15 To eliminate y from the equations, we may multiply the first equation by the coefficient of y in the second equation, i.e. by 3 . Similarly the second equation must be multiplied by 2 , the coefficient of the y in the first equation. The resulting equations must be subtracted from one another: 9 x + 6 y = 15 10 x + 6 y = 30 9 x + 6 y (10 x + 6 y ) = 15 30 // // 9 x + 6 y 10 x 6 y = 15 x = 15 x = 15 Substitute x by its value x = 15 in one of the original equations to find the other variable: 3 x + 2 y = 5 3 15 + 2 y = 5 45 + 2 y = 5 40 2 y = 5 45 = 40 y = = 20 2 Answer: x = 15 , y = 20 Check: Note that the pair of answers obtained must satisfy also the second equation: 5 x + 3 y = 15 5 (15) + 3 ( 20 ) =15
?
75 60 =15 15 = 15 Checks!
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
G.MaB.13.1.1 Which ordered pair is in the solution set of x < 6 y ? (2) B (6, 0 ) (3) C (0, 5) (1) A (0, 6 ) Suggested solution: Answer: Alternative (3) C (0, 5) Point x <6 y? x 6 y A (0, 6 ) 0 6 6 = 0 No! B (6, 0 ) 6 6 0 = 6 No! C (0, 5) 0 6 5 = 1 Yes! 0 < 6 5 D (7, 0 ) 7 6 7 = 1 No!
(4) D (7, 0 )
G.MaB.13.1.2 Which ordered pair is not a member of the solution set of 2 x 3 y 12 ? (2) B ( 3, 6 ) (3) C (10, 3) (4) D (6, 0 ) (1) A (0, 4 ) Suggested solution: Answer: Alternative (3) C (10, 3) y Point 2x 3y 2 x 3 y 12 ? x 0 A (0, 4 ) Yes! 4 0 3( 4 ) = 12 B ( 3, 6 ) 3 6 2( 3) 3( 6 ) = 6 + 18 = 12 Yes! 10 3 C (10, 3) 2(10 ) 3(3) = 20 9 = 11 No! 6 0 D (6, 0 ) 2(6 ) 3(0 ) = 12 Yes!
G.MaB.13.1.3 The accompanying diagram shows the graph of which inequality? (2) y x 1 (3) y < x 1 (4) y x 1 (1) y > x 1
Suggested solution: Answer: Alternative (4) y x 1 We may first write the equation of the line. The y-intercept of the line is m = 1 . On the other hand the slope of the line is 0 ( 1) =1 k= 1 0 Therefore, the equation of the line is: y = x 1 The y-coordinates of all points in the green region satisfy y x 1
2 x + 2 y = 10 G.MaB.13.1.4 Solve the simultaneous equations: . 1 3x 2 y = 6 Suggested solution: Answer: x = 1 y = 6 2 x + 2 y = 10 x + y = 5 x + y = 5 x + y + 6 x y = 5 + 12 7 x = 7 y = 5 1 = 6 1 / / 6 x y = 12 x = 1 3x 2 y = 6
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
2 x = 8 5 y G.MaB.13.1.5 Solve the simultaneous equations: . x + y = 1 Suggested solution: Answer: x = 1 y = 2 2 x = 8 5 y 2 x + 5 y = 8 2x + 5 y 2x 2 y = 8 2 3y = 6 y = 2 / / x + y = 1 2 x + 2 y = 2
x + y = 1 x = 1 y = 1 2 = 1 y = 2 VG.MaB.13.1.6 a) On the same set of coordinate axes, graph the following equations x + y = 7 , 3 y 2 x = 6 , y = 2 b) Find the area of the triangle formed by the lines graphed in part (a)?
Suggested solution: Answer: Area = 45 (lu ) We may reorganize and rewrite the equations above as: y = 2 , 2 2 6 x + y = 7 y = 7 x , and 3 y 2 x = 6 3 y = 2 x + 6 y = x + y = x + 2 , 3 3 3 and finally simultaneously plot them as in the figure below:
2
The coordinates of the vertices of the triangle ABC are A ( 6, 2) , B (9, 2) , and C (3, 4) . The length of the base of triangle is:
b = AB = 9 ( 6) = 9 + 6 = 15 lu and its altitude is: h = 4 ( 2) = 4 + 2 = 6 lu
The area of the triangle is, therefore: Area =
b h 15 6 = 2 2
(lu )2 = 45 (lu )2
5
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.1.7 a) On the same set of axes, graph the following simultaneous system of inequalities: 3 y 2 x 6 . x + y > 7 b) Which ordered pair is in the solution set of graph drawn in answer to part (a)? (2) B (8, 1) (3) C (2, 6 ) (4) D ( 2, 7 ) c) (1) A (3, 4 )
Suggested solution: Answer: Alternative (3) C (2, 6 ) We may reorganize and rewrite the simultaneous system of inequalities as: 2 3 y 2 x 6 y x 2 3 x + y > 7 y > 7 x
2 x 2 and y = 7 x simultaneously on 3 the same coordinate system, and choose the regions satisfying 2 simultaneously y x 2 and y > 7 x . The green area in the figure below 3 is the one that satisfy both conditions simultaneously. Only the point C (2, 6 ) lies in this region.
Then we plot two straight lines of y =
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
G.MaB.13.1.8. Solve the equation 1.5 x 5.7 = 4.8 2 x by graphing two lines using a graphic calculator.
Suggested solution: Answer: x = 1.2 We may plot the two equations in the simultaneous equations below on the same coordinate system, simultaneously. Then using the following combination, we may calculate the intersection of the lines graphed: y = 1.5 x 5.7 y = 4.8 2 x 2 nd , CALC , 5 : intersection , ENTER , ENTER , ENTER . The solution of 1.5 x 5.7 = 4.8 2 x is x = 1.2 as illustrated in the figure below.
3 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 0 1 2 3 x
Analytical solution: Answer: x = 3.0
1.5 x 5.7 = 4.8 2 x 1.5 x + 2 x = 4.8 + 5.7 3.5 x = 10.5
y = 4 .8 2 x
y = 1.5 x 5.7
A (3; -1.2)
3.5 10.5 x = 3 .0 x= 3.5 3.5
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.1.9. Malins music CD collection includes jazz, and classical CDs. She has, at most, 14 Jazz and, at most 8 classical CDs. The combined number of jazz and classical CDs she has is not greater than 18. If x is the number of jazz CDs and y is the number of classical CDs, graph the region that contains the number of jazz and classical CDs in Malins music CD collection.
Suggested solution: We may express the data above as: x 14 , y 8 , x + y 18 y 18 x . Plot the lines x = 14 , y = 8 , and y = 18 x . The shaded region is the region of the interest that satisfy simultaneously the 3 restrictions organized in the equation system below: y 18 x x 14 y 8 Any combination of integer x and y in the green shaded area below is possible! This region is the one where all conditions listed above are simultaneously satisfied. This is illustrated in the figure to the right. The figure particularly could be confusing if viewed in black and white.
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.1.10 a) On the same set of axes, graph the lines y = 4 , and 2 x + y = 6 . b) Find the area, in square units, of the trapezoid in Quadrant IV bounded by the x-axis, the y-axis, and the lines graphed in part (a)
Suggested solution: Answer: Area = 16
(lu )2
a) We may first rewrite 2 x + y = 6 as y = 2 x + 6 and then plot y = 2 x + 6 and y = 4 on the same axis as in the figure illustrated below:
b) The area of the trapezoid ABCD may be calculated if the length of its height h = AB and its bases BC and AD are determined. h = 0 ( 4 ) = 4 lu
AD = 5 lu
BC = 3 lu Area =
(AD + BC ) h = (5 + 3) 4 = 16
2 2
(lu )2
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.1.11 a) On the same set of axes, graph the lines y = 2 , y = 6 , y = 2 x + 12 , and y = 2 x 12 b) Find the area, in square units, of the parallelogram formed by these lines.
Suggested solution: Answer: Area = 24 (lu )
2
a) The lines y = 2 , y = 6 , y = 2 x + 12 , and y = 2 x 12 are plotted above. Together these lines form a parallelogram ABCD . b) The area of the parallelogram ABCD may be calculated if the length of its height h and its base b are determined. h = 6 2 = 4 lu b = AD = 7 ( 5) = 7 + 5 = 12 lu b h 12 4 2 Area = = = 24 (lu ) 2 2
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
10
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.1.12 (modified) Two video rental stores offer two different membership plans: Store A charges $15 for membership and $2 for each video that is rented. Store B does not have a membership fee but charges $3.50 for each video that is rented. a) Write an equation that shows the total cost, C , of renting n video from store A . b) Write an equation that shows the total cost, C , of renting n video from store B . c) Construct a simultaneous equation system of the equations obtained above and solve it graphically. Interpret the results. d) Solve the equation system analytically. Interpret the results. Suggested solution: $C = 15 + 2 n Answer: $C = 15 + 2 n , $C = 3.5 n , , n = 10 , $C = $35 $C = 3.5 n a) The total cost, C , of renting n video from store A is $C = 15 + 2 n b) The total cost, C , of renting n video from store B is $C = 3.5 n $C = 15 + 2 n c) The intersection of the two lines is the solution of the $C = 3.5 n equation system: The cost of renting 10 videos is the $35 no matter which store they are rented from. As illustrated below, the store A is cheaper than store B if more than 10 videos are rented. It is, on the other hand more expensive if less than 10 videos are rented from. The results are consistent with the graphical solution of part C.
The cost of renting video 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 n (number of rented videos)
$C = 15 + 2 n 15 3.5 n = 15 + 2 n 3.5 n 2 n = 15 1.5 n = 15 n = d) = 10 1.5 $C = 3.5 n $C = 15 + 2 n $C = 15 + 2 10 = 15 + 20 = $35 The cost of renting 10 videos n = 10 is the $35 no matter which store they are rented from. As in part (c).
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
B
A
C (cost in $)
12
14
16
11
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
G.MaB.13.2.1 What is the solution set for the following system of equations? x = y x + 2 y = 6 (2) (2, 2 ) (3) (6, 6 ) (4) ( 6, 6 ) (1) ( 2, 2 ) Suggested solution: Answer: Alternative (4) ( 6, 6 ) We may use the substitution method to solve the problem. Replace x by x = y in the second equation x + 2 y = 6 : x + 2 y = 6 y + 2 y = 6 y = 6 x = y = 6 x = 6
G.MaB.13.2.2 What is the solution for x in the following system of equations? y = 2 x 3 y = x + 1 2 4 (2) 2 (3) (4) 4 (1) 3 3 Suggested solution: Answer: Alternative (2) x = 2 We may use the substitution method to solve the problem. Replace y by y = x + 1 in the first equation y = 2 x 3 : // / / // y = 2 x 3 ( x + 1) = 2 x 3 x 1 = 2 x 3 x 1 2 x + 1 = 2 x 3 2 x + 1 x = 2 x = 2 VG.MaB.13.2.3 What is the solution for y in the following system of equations?
3 2 = 4 x 6 x + y = 17 (1) 1
(2) 1
(3) 9
(4) 9
Suggested solution: Answer: Alternative (1) y = 1 We may rewrite the first equation by multiplying both sides of the equation by 4 x (or by cross multiplication): 8 3 2 3 2 / = 4 x = 4 x 3x = 8 x = / / 4 x 3 4 x / 8 Substitute x by x = in the second equation 6 x + y = 17 : 3 8 6 + y = 17 16 + y = 17 y = 17 16 y = 1 3
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
12
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
G.MaB.13.2.5 Solve the following system of equations algebraically and check: y + 5x = 0 3 x 2 y = 26 Suggested solution: Answer: x = 2 , y = 10 We may solve the problem by elimination method. We may eliminate y by multiplying the first equation by 2 and then adding the resulting equation to the second equation: 2 y + 2 5 x = 0 26 // // x=2 2 y + 10 x + 3 x 2 y = 26 13 x = 26 x = 13 3x 2 y = 26 Substitute x by x = 2 in the one of the equation, for example y + 5 x = 0 : y + 5(2 ) = 0 y + 10 = 0 y = 10 Check: Substitute x = 2 , and y = 10 in the second equation and check if LHS=RHS 3(2) 2( 10) = 26 6 + 20 = 26 26 = 26 : Checks!
?
VG.MaB.13.2.6 Solve the following system of equations algebraically and check: y x=0 4 2 y = 3 x + 7 7 28 Suggested solution: Answer: x = , y = 5 5 y We may multiply both side of the equation x = 0 by 4: 4 y 4x = 0 y = 4x Substitute y = 4 x in the second equation: 7 2 y = 3x + 7 2(4 x ) = 3x + 7 8 x = 3x + 7 8 x 3x = 7 5 x = 7 x = 5 7 28 y = 4x y = 4 y = 5 5 Check: 7 28 Substitute x = and y = in the second equation and check if LHS=RHS: 5 5 ? 28 ? 7 2 = 3 + 7 56 = 21 + 35 56 = 56 Checks! 5 5
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
13
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
G.MaB.13.2.7 Solve the following system of equations algebraically and check: a 2 =b 3 2a + 3b = 5
Suggested solution: Answer: a = 1 , b = 1 We may multiply both side of the equation
a2 = 3b a 2 = 3 b a = 3 b + 2 3 / Substitute a = 3 b + 2 in the second equation: 2a + 3b = 5 2 (3 b + 2 ) + 3b = 5 6 b + 4 + 3b = 5 9 b = 5 4 9 b = 9 9 b = b = 1 9 Substitute b = 1 in a = 3 b + 2 : a = 3 b + 2 a = 3 ( 1) + 2 a = 3 + 2 a = 1 Check: Substitute a = 1 and b = 1 in the first equation and check if LHS=RHS: ? ? ( 1) 2 = 1 3 = 1 1 = 1 LHS = RHS Checks! a2 =b 3 3 3
a2 = b by 3: 3
3 /
G.MaB.13.2.8 Solve the following system of equations algebraically and check: y 1 = x 7 y 3x = 1 Suggested solution: Answer: x = 2 , y = 1 y 1 = x 4 7 y 3 ( y 1) = 1 7 y 3 y + 3 = 1 4 y = 1 3 4 y = 4 y = 4 7 y 3x = 1 y = 1 x = y 1 = 1 1 x = 2 Substitute x = 2 , and y = 1 in the second equation and check if LHS=RHS 7( 1) 3( 2) = 1 7 + 6 = 1 1 = 1 LHS = RHS Checks! G.MaB.13.2.9 Solve the following system of equations algebraically and check: y x =1 7 y 11x = 5 Suggested solution: Answer: x = 3 , y = 4 y x = 1 y = 1+ x 7(1 + x ) 11x = 5 7 + 7 x 11x = 5 4 x = 5 7 4 x = 12 7 y 11x = 5 12 x= x = 3 y = 1+ x = 1+ 3 y = 4 4 Substitute x = 3 , and y = 4 in the second equation and check if LHS=RHS 7(4) 11(3) = 5 28 33 = 5 5 = 5 LHS = RHS Checks!
? ? ? ?
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
14
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
G.MaB.13.2.10 Solve the following system of equations algebraically and check: 0.3 y 0.2 x = 2.1 0.75 y = 2.25 x Suggested solution: Answer: x = 3 , y = 9 Multiply the first equation by 10, and the second one by 100, and divide it by 75: 0.3 y 0.2 x = 2.1 3 y 2 x = 21 3 y 2 x = 21 0.75 y = 2.25 x 75 y = 225 x y = 3x Relplace y = 3 x in the first equation: 21 x = 3, 3 y 2 x = 21 3 (3x ) 2 x = 21 9 x 2 x = 21 7 x = 21 x = 7 y = 3 x y = 3 3 y = 9 Substitute x = 3 , and y = 9 in the first equation and check if LHS=RHS 3(9 ) 2(3) = 21 27 6 = 27 27 = 27 LHS = RHS Checks! G.MaB.13.2.11 Five pens of the same type cost the same as two notebooks of the same type. If one pen and two notebooks cost $4.20 , what is the cost of one pen? P = $0.7 Suggested solution: Answer: N = $1.75 Data: P : Cost of one pen N : Cost of one notebook 5 pens cost the same as 2 notebooks: 5 P = 2 N one pen and two notebooks cost $4.20 : 1P + 2 N = $4.20 5P = 2 N P = $0.7 $4.20 5 P 5 $0.7 P + 5 P = $4.20 P = N= = = $1.75 6 2 2 P + 2 N = $4.20 2 N = 5 P G.MaB.13.2.12 Two angles are complementary. The difference between four times the measure of the smaller angle and the measure of the larger angle is 10. What are the measure of the angles? L = 50 Suggested solution: Answer: S = 40 Data: S : The smaller angle L : The smaller angle Two angles are complementary : S + L = 90 The difference between four times the measure of the smaller angle and the measure of the larger angle is 10: L S = 10 L + S = 90 L = 50 100 2 L = 90 + 10 2 L = 100 L = S = 90 50 = 40 2 L S = 10 L + S = 90
? ?
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
15
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.2.13 The denominator of a fraction exceeds its numerator by 7. If the numerator 4 is increased by 3 and the denominator is decreased by 2, the new fraction equals . Find the 5 original fraction.
N = 5 N 5 = Suggested solution: Answer: D 12 D = 12 D : The denominator of the fraction. Data: N : The numerator of the fraction. D of a fraction exceeds its N by 7: D = N + 7 If N is increased by 3 and D is decreased by 2, the new 4 N +3 4 fraction equals : = 5 D2 5 N +3 4 = Cross product: 4(D 2 ) = 5( N + 3) 4 D 8 = 5 N + 15 D2 5 4 D 5 N = 15 + 8 4 D 5 N = 23 D = N + 7 4(N + 7 ) 5 N = 23 4 N + 28 5 N = 23 N = 23 28 = 5 N = 5 4 D 5 N = 23
D = N + 7 D = 5 + 7 D = 12 N = 5
N = 5 N 5 = Answer: D 12 D = 12
VG.MaB.13.2.14 A club consisting of seniors and juniors has 15 members. After seven more seniors and three more juniors join the club, the ratio of juniors to seniors is 2 to 3. How many juniors were originally in the club?
Suggested solution: Answer: The club originally had J = 7 junior members. It has now J + 3 = 10 Junior members. Data: S : Number of senior members, originally. J : Number of senior members, originally. The club has 15 members: S + J = 15 After seven more seniors and three more juniors join the club, J +3 2 the ratio of juniors to seniors is 2 to 3: = S +7 3 J +3 2 = Cross product: 3( J + 3) = 2(S + 7 ) 3J + 9 = 2S + 14 3 J 2 S = 14 9 S +7 3 J + S = 15 2 J + 2 S = 2 15 35 2 J + 3J = 30 + 5 5 J = 35 J = J =7 J =7 5 3J 2S = 5 3J 2S = 5 S + J = 15 S = 15 J = 15 7 = 8 S =8 J + 3 = 7 + 3 = 10 Answer: The club originally had J = 7 junior members. It has now J + 3 = 10 Junior members.
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
16
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.2.15 (a) If t represents the tens digit of a two-digit number, and u represents the units digit, what is the two-digit number in terms of t and u ? (b) The units digit of a two-digit number is one more than its tens digits. The two-digit number is two less than five times the sum of its digits. What is the number?
Suggested solution: Answer: (a) 10t + u ,(b) The number is 23 Data: t : the tens digit of a two-digit number u : the units digit of the number The units digit of a two-digit number is one more than its tens digits: u = t + 1 The number is 2 less than 5 times the sum of its digits: 10t + u = 5(t + u ) 2 The two-digit number is: 10t + u 10t + u = 5(t + u ) 2 10t + u = 5t + 5u 2 10t 5t 5u + u = 2 5t 4u = 2 u = t + 1 5t 4(t + 1) = 2 5t 4t 4 = 2 t = 2 + 4 t = 2 u = 2 + 1 = 3 5t 4u = 2 Answer: The number is 23 t = 2, u = 3
VG.MaB.13.2.16 The length of a side of an equilateral triangle exceeds twice the length of a side of a smaller equilateral triangle by one. If the difference in the perimeters of the triangles is 15, (a) what is the length of a side of the large triangle? (b) what is the perimeter of the smaller triangle?
Suggested solution: Answer: (a) S = 4 lu , L = 9 lu (b) PS = 12 lu Data: S : length of a side of the small triangle L : length of a side of the large triangle L exceeds twice S by one: L = 2 S + 1 The difference in the perimeters of the triangles is 15: 3L 3S = 15 L = 2S + 1 S = 4 2S + 1 S = 5 S = 5 1 L = 2 4 +1 = 9 3L 3S = 15 L S = 5 L = 2S + 1 Answer: S = 4 lu , L = 9 lu The perimeter of the smaller triangle is PS = 3 4 = 12 lu Answer: PS = 12 lu
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
17
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.2.17 A store charges a fixed amount to fax one page and another amount to fax each additional page that is faxed to the same telephone number. If the cost of faxing 5 pages is $3.05 , and the cost of faxing 13 pages is $6.65 (a) What is the cost of faxing only one page? (b) What is the cost of faxing each additional page?
Suggested solution: Answer: (a) $1.25 , (b) P = $0.45 F : the fixed fee Data: P cost of each additional page Faxing 5 pages costs $3.05 : F + 5 P = $3.05 The cost of faxing 13 pages is $6.65 : F + 13P = $6.65 F + 13P = $6.65 F + 13P (F + 5P ) = $6.65 $3.05 13P 5 P = $3.6 8P = $3.6 F + 5P = $3.05
P=
F + 5P = $3.05 F = $3.05 5P F = $3.05 5 ($45) F = $3.05 $2.25 = $0.80 Therefore, the cost of faxing only one page is: $1.25 : Cost = $0.80 + 1 P Cost = $0.80 + 1 ($45) Cost = $0.80 + $45 Cost = $1.25 The cost of each additional page is P = $0.45
$3.6 P = $0.45 8
VG.MaB.13.2.18 In the triangle ABC , the measure of B is twice the measure of A . If the measure of A is subtracted from the measure of C , the difference is 20. Find the measure of the angles of the triangle.
Suggested solution: Answer: Answer: A = 40 , B = 80 , C = 60 Data: B is twice the measure of A : B = 2 A If A is subtracted from C , the difference is 20: C A = 20 A + B + C = 180 B = 2 A C A = 20 C = A + 20 160 A + B + C = 180 A + 2 A + A + 20 = 180 4 A = 180 20 4 A = 160 A = = 40 4
A = 40 B = 2A = 2 40 = 80 B = 80 C A = 20 C = A + 20 = 40 + 20 = 60 C = 60
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
18
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.2.19 There were 100 more balcony tickets than main-floor tickets sold for a concert. The balcony tickets sold for $4 , and the main-floor tickets sold for $12 . The total amount of sales for both types of tickets was $3056 . (a) Write a system of two equations that describes the given conditions. Define the variables. (b) Using the system of equations in part (a) find the number of balcony tickets, and the number of the floor tickets that were sold. B = F + 100 Suggested solution: Answer: (a) ; (b) F = 166 , B = 266 4 B + 12 F = 3056 Data: $4 each balcony ticket, total number of balcony tickets sold: B $12 each main-floor ticket, total number of main-floor tickets sold: F 100 more balcony tickets than main-floor tickets: B = F + 100 $3056 the total amount of sales: 4 B + 12 F = 3056 B = F + 100 4(F + 100) + 12 F = 3056 4 F + 400 + 12 F = 3056 16 F = 3056 400 4 B + 12 F = 3056 16 F = 3056 400 16 F = 2656 F = 2656 = 166 B = F + 100 = 166 + 100 = 266 16 Answer: F = 166 , B = 266
VG.MaB.13.2.20 The senior class at Northwest High School needed to raise money for the yearbook. A local sporting goods store donated hats and T-shirts. The number of T-shirts was three times the number of hats. The seniors charged $5 for each hat, and $8 for each T-shirt. If the seniors sold every item and raised $435 , What were the total number of hats and the total number of T-shirts that were sold? Suggested solution: Answer: H = 15 , T = 45 $5 each hat, num, total number of hats: H Data: $8 each T-shirt, total number of T-shirts : T The number of T-shirts was three times the number of hats: T = 3H $435 Total money raised: 5 H + 8T = 435 T = 3H 435 5 H + 8(3H ) = 435 5 H + 24 H = 435 29 H = 435 H = H = 15 29 5 H + 8T = 435 T = 3H T = 3 15 = 45 Answer: H = 15 , T = 45
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
19
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.2.21 In the accompanying diagram, ABCD is a parallelogram with mB = 120 , mD = 2 x + 5 y , and mA = 4 x + y . Find the values of x and y . Check your solution. (only an algebraic solution will be accepted.) C Suggested solution: Answer: B mB = 120 x = 10 , y = 20 Due to the fact that the figure is a parallelogram, the two opposite angle must be equal to each other, i.e. mD = mB = 120 , and mA = 4 x + y mD = 2 x + 5 y mA = mC = 60 . Therefore, the following system of two linearly A D independent equation system may be constructed. mB = 120 4 x + y = 60 4 x + y = 60 4 x + y = 60 mA = 4 x + y 2 x + 5 y = 120 2 2 x + 2 5 y = 2 120 4 x + 10 y = 240 mD = 2 x + 5 y
We may subtract the first equation from the second one. This will eliminate x and produce one linear equation of only a single variable y : 180 // // 4 x + 10 y (4 x + y ) = 240 60 4 x + 10 y 4 x y = 180 9 y = 180 y = = 20 9 4 x + y = 60 40 y = 20 4 x + 20 = 60 4 x = 60 20 4 x = 40 x = 4 y = 20 x = 10 Substitute x = 10 , and y = 20 in the secod equation and check if LHS=RHS
2(10) + 5(20)=120 20 + 100 =120 120 = 120 LHS = RHS Checks!
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
20
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.3.18 The accompanying table shows the number of grams of protein and the number of calories in a single serving of bran flakes cereal and milk. How many servings of a) cereal, and b) milk are needed to get a total of 35 g of protein and 470 cal ? Food Protein Calories Cereal 5 g 90 cal Milk 8 g 80 cal
Suggested solution: Answer: We may serve the cereal x = 3 times and the milk y = 2.5 . x : The number of serving of cereal Data: y : The number of serving of milk 5 x + 8 y = 35 g 5 x + 8 y = 35 12 9 x 5 x = 47 35 4 x = 12 x = 4 90 x + 80 y = 470 cal 9 x + 8 y = 47 x=3 We simplified, first, the second equation by dividing it by 10, then we eliminated y by subtracting the first equation from the second one. We may substitute x = 3 in any one of the equations to find y : 20 y = 2.5 5 x + 8 y = 35 8 y = 35 5 x 8 y = 35 5 3 8 y = 20 y = 8 Answer: We may serve the cereal x = 3 times and the milk y = 2.5 . This may be interpreted as serving the cereal and milk twice, and adding only half a portion of the milk to the third serving of the cereal.
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
21
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
VG.MaB.13.3.19 (modified) Allan rented a sprayer and a generator. On his first job, he used each piece of equipment for 6 h at a total cost of $90 . On his second job, he used the sprayer for 4 h and the generator for 8 h at a total cost of $100 . a) Write a system of two equations that describes the given conditions. Define the variables. b) Using the system of equations written above find the hourly cost of the generator and that of the sprayer. Suggested solution: s + g = $15 Answer: (a) , (b) g = $10 , s = $5 s + 2 g = $25 Data: s : The hourly rent of the sprayer g : The hourly rent of the generator $90 : The rent of 6 h use of each piece of equipment: 6 s + 6 g = $90 $100 : The rent of 4 h use of sprayer and 8 h use of the generator: 4 s + 8 g = $100 s + g = $15 6 s + 6 g = $90 4 s + 8 g = $100 s + 2 g = $25 We simplified the equation system by dividing the first equation by 6 and the second one by 25. To solve the problem, we may eliminate s by subtracting the first equation from the second one: s + g = $15 g = $10 s + 2 g (s + g ) = $25 $15 s + 2 g s g = $10 / / s + 2 g = $25 s + g = $15 s = $15 g s = $15 $10 s = $5
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
22
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
MVG.MaB.13.3.20 (modified) Oscar and Niklas went shopping at Price Extra. Oscar bought two jumbo rolls of aluminium foil and three packages of AA batteries for a total cost of $21.00 . Niklas bought five identical jumbo rolls of aluminium foil and two identical packages of AA batteries for a total cost of $25.00 . a) How much does one roll of aluminium foil cost? b) How much does one package of AA batteries cost? c) How much money does Natalie need to buy two identical jumbo rolls of aluminium foil and four identical packages of AA batteries? d) How much money does Terese need to buy x identical jumbo rolls of aluminium foil and y identical packages of AA batteries?
Suggested solution: Answer: (a) a = $3.00 , (b) b = $5.00 , (c) C = $26 , (d) $C = $3 x + $5 y a : The cost of one jumbo roll of aluminium foil Data: b : The cost of one package of AA batteries $21.00 : The cost of two jumbo rolls of aluminium foil and three packages of AA batteries: 2 a + 3 b = $21.00 $25.00 : The cost of five jumbo rolls of aluminium foil and two packages of AA batteries: 5 a + 2 b = $25.00 We may eliminate a , and therefore find b , by multiplying the first equation by 5 and the second one by 2 and then subtracting the second equation from the first:
2 a + 3 b = $21 5 2 a + 5 3 b = 5 $21 10 a + 15 b = $105 5 a + 2 b = $25 2 5 a + 2 2 b = 2 $25 10 a + 4 b = $50 $55 15 b 4 b = $105 $50 11 b = $55 b = b = $5.00 11 2 a + 3 b = $21 2 a = $21 3 b 2 a = $21 3 5 2 a = $6 a =
b = $5.00
$6 a = $3.00 2 x identical jumbo rolls of aluminium foil and y identical packages of AA batteries cost: $C = $3 x + $5 y $C = x a + y b = $3 x + $5 y 2 identical jumbo rolls of aluminium foil and 4 identical packages of AA batteries cost: C = $26 C = 3 2 + 5 4 = 6 + 20 = $26
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
23
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
MVG.MaB.13.3.21 (modified) At the local video rental store, Bashar rents two movies and three games for a total of $15.50 . At the same time, Kevin rents three movies and one game for a total of $12.05 . a) How much is the charge to rent one movie? b) How much is the charge to rent one game? c) How much money does Camilla need to rent a combination of one game and one movie from the same video rental store? d) How much money does Martina need to rent a combination of x game and y movie from the same video rental store?
Suggested solution: Answer: (a) M = $2.95 , (b) G = $3.20 , (c) C = $6.15 , (d) $C = $2.95 x + $3.20 y Data: M : The charge for renting one movie G : The charge for renting one game $15.50 for renting 2 movies and 2 games: 2 M + 3 G = $15.50 $12.05 for renting 3 movies and 1 game: 3 M + 1 G = $12.05 The cost for renting x movies and y games: $C = M x + G y We may eliminate G , and therefore find M , by multiplying the first equation by 3 and then subtracting the second equation from it:
3 M + 1 G = $12.05 3 3 M + 3 G = 3 $12.05 9 M + 3 G = $36.15 2 M + 3 G = $15.50 2 M + 3 G = $15.50 2 M + 3 G = $15.50 $20.65 9 M 2 M = $36.15 $15.50 7 M = $20.65 M = 7 3 M + 1 G = $12.05 G = $12.05 3 M G = $12.05 3 $2.95
M = $2.95 G = $3.20
The cost for renting x movies and y games: $C = $2.95 x + $3.20 y : $C = M x + G y = $2.95 x + $3.20 y The cost for renting 1 movie and 1 games: $C = $6.15 $C = $2.95 + $3.20 = $6.15
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
24
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
MVG.MaB.13.3.22 (modified) The cost of a taxi ride is calculated by adding a fixed amount 1 1 km of the trip. If 1 km trip costs $4.00 and a 1 km trip costs to a charge for each 4 2 $5.50 , a) what is the fixed fee for each trip? 1 km of the trip? b) what is the charge for each 4 c) what is the cost of a 3 km trip? d) what is the cost of an x km trip?
Suggested solution:
1 km of the trip , (c) The cost of 4 an 3 km trip is C = $10.00 , (d) The cost of an x km trip is $C = 1.00 + 3 x
Answer: (a) F = $1.00 , (b) a = $0.75 for each
Data:
F : The fixed fee for each trip 1 a : The charge for each km of the trip 4 $4.00 for 1 km trip: F + 1 4 a = $4.00 F + 4a = $4.00 1 3 3 $5.50 for 1 km = km trip: F + 4a = $5.50 F + 6a = $5.50 2 2 2 The cost for x km trip: C = $ F + x 4a = $ F + 4a x
F + 6a = $5.50 $1.50 6a 4a = $5.50 $4.00 2a = $1.50 a = a = $0.75 2 F + 4a = $4.00 1 a = $0.75 for each km of the trip 4 F + 4a = $4.00 F = $4.00 4a F = $4.00 4 0.75 = $4.00 3.00 F = $1.00
The cost of an 3 km trip is C = $10.00 $C = 1.00 + 3 3 = 1.00 + 9 = $10.00 The cost of an x km trip is $C = 1.00 + 3 x $C = F + 4a x = 1.00 + 4 0.75 x = 1.00 + 3 x
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
25
MaBNVCO08 Unit Five Graph and Transformations Ch 13 Simultaneous Equations NV-College
MVG.MaB.13.3.23 (modified) The cost of a long distance telephone call is determined by a flat fee for the first 5 minutes and a fixed amount for each additional minute. Pannos is charged $3.25 for a long distance call that lasts 15 minutes, and $5.17 for a long-distance call that lasts 23 minutes. At the same rate, a) what is the flat fee for the first 5 minutes? b) what is the fee for each additional minute? c) what is the cost of a long-distance telephone call that lasts 30 minutes? d) what is the cost of a long-distance telephone call that lasts t min ?
Suggested solution: Answer: (a) F = $0.85 , (b) x = $0.24 for each additional minute , (c) The cost of a long-distance telephone call that lasts 30 minutes is $6.85 , (d) The cost of a long-distance telephone call that lasts t min : $0.85 + 0.24(t 5) Data:
F : The flat fee for the first 5 minutes x : The fixed amount for each additional minute $3.25 for a long distance call that lasts 15 minutes: F + (15 5)x = $3.25 $5.17 for a long-distance call that lasts 23 minutes: F + (23 5)x = $5.17 The cost of a long-distance telephone call that lasts t min : $ F + (t 5)x
F + 18 x = $5.17 $1.92 18 x 10 x = $5.17 $3.25 8 x = $1.92 x = x = $0.24 8 F + 10 x = $3.25 x = $0.24 for each additional minute F + 10 x = $3.25 F = $3.25 10 x F = $3.25 10 ($0.24) = $3.25 $2.4 F = $0.85 The cost of a long-distance telephone call that lasts t min : $0.85 + 0.24(t 5) $ F + (t 5)x = $0.85 + 0.24(t 5)
The cost of a long-distance telephone call that lasts 30 minutes is $6.85 : $0.85 + 0.24(30 5) = $0.85 + 0.24 25 = $6.85
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Free to use for educational purposes. Not for sale.
26
Você também pode gostar
- Suggested Solutions Mab67Nvco10 Algebra, Geometry & FunctionsDocumento13 páginasSuggested Solutions Mab67Nvco10 Algebra, Geometry & FunctionsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Module 3 - L1 Math 602-1Documento18 páginasModule 3 - L1 Math 602-1Rillo Eunariza E.Ainda não há avaliações
- Cramer's Rule - The Method of DeterminantsDocumento10 páginasCramer's Rule - The Method of DeterminantsGanesh.MahendraAinda não há avaliações
- AI AA SL Core Diagnostic Test Ch. 1 3-5 Suggested SolutionsDocumento26 páginasAI AA SL Core Diagnostic Test Ch. 1 3-5 Suggested SolutionsAlexandr BostanAinda não há avaliações
- MaANVCO08Unit+Three+Algebraic+MethodsCh6 7-8-11Documento56 páginasMaANVCO08Unit+Three+Algebraic+MethodsCh6 7-8-11Epic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Solution+V1 G MaD6NVC08+Trigonometry+and+DerivativesDocumento9 páginasSolution+V1 G MaD6NVC08+Trigonometry+and+DerivativesEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Solution+Test MaBNVCO08 V2 Functions Algebra Geometry Quadratic Equations Simultaneous EquationsDocumento11 páginasSolution+Test MaBNVCO08 V2 Functions Algebra Geometry Quadratic Equations Simultaneous EquationsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- System of Linear Equation in Two Variables and Their GraphsDocumento38 páginasSystem of Linear Equation in Two Variables and Their GraphsRhealyn ABAinda não há avaliações
- Solution+V1 VG MVG MaD6NVC08+Trigonometry+and+DerivativesDocumento16 páginasSolution+V1 VG MVG MaD6NVC08+Trigonometry+and+DerivativesEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Graphing Linear EquationsDocumento18 páginasGraphing Linear Equationsat4machineAinda não há avaliações
- Equations and Inequalities of ModulusDocumento27 páginasEquations and Inequalities of ModulusLisaAinda não há avaliações
- Basics and Logarithm, Mod, WCMDocumento11 páginasBasics and Logarithm, Mod, WCMAbhishek AsthanaAinda não há avaliações
- Year 11 Methods Chapter 1Documento38 páginasYear 11 Methods Chapter 1JovicaSutevAinda não há avaliações
- BM Chapter 3Documento36 páginasBM Chapter 3Thevaka SatheeskumarAinda não há avaliações
- Warning: Chapter Test: Mathematical Reasoning Mathematics Course A Fall 2008: Maanvc08Documento11 páginasWarning: Chapter Test: Mathematical Reasoning Mathematics Course A Fall 2008: Maanvc08Epic WinAinda não há avaliações
- LinearDocumento16 páginasLinearAngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- LET-ExplanationDocumento8 páginasLET-ExplanationIrene Grace Edralin AdenaAinda não há avaliações
- 08 - Solving Linear Systems by Elimination 2 Student NotesDocumento2 páginas08 - Solving Linear Systems by Elimination 2 Student Notesapi-288090607Ainda não há avaliações
- 6 Linear Algebraic Equations PDFDocumento68 páginas6 Linear Algebraic Equations PDFAugusto De La Cruz CamayoAinda não há avaliações
- SimultaneousDocumento27 páginasSimultaneousLatchmi DeviAinda não há avaliações
- EC4001 - Becoming An Economist: Maths Diagnostic Test 2014/5Documento4 páginasEC4001 - Becoming An Economist: Maths Diagnostic Test 2014/5nishit0157623637Ainda não há avaliações
- Transformation of A Straight Line: MathematicsDocumento10 páginasTransformation of A Straight Line: MathematicsWilma Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Name:: Choosing The Best Method For Solving Systems of EquationsDocumento7 páginasName:: Choosing The Best Method For Solving Systems of EquationselegadoAinda não há avaliações
- Ch01 Linear FunctionsDocumento42 páginasCh01 Linear FunctionsLinoAinda não há avaliações
- Illustrating Quadratic Equation: Grade 9Documento6 páginasIllustrating Quadratic Equation: Grade 9Syril DuagAinda não há avaliações
- MATH 158: Mapua University - Department of MathematicsDocumento24 páginasMATH 158: Mapua University - Department of Mathematicsrc0952Ainda não há avaliações
- Decimal LsDocumento55 páginasDecimal LsZerihun IbrahimAinda não há avaliações
- N1te0p Lecture8 PDFDocumento14 páginasN1te0p Lecture8 PDFAbdulahi AbebeAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Equation in One VariableDocumento2 páginasLinear Equation in One VariableDanilo de MesaAinda não há avaliações
- 1-6 Study Guide and Intervention: Solving Systems of EquationsDocumento2 páginas1-6 Study Guide and Intervention: Solving Systems of EquationsAbdullah MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Solving Simultaneous Equations Class 9Documento21 páginasSolving Simultaneous Equations Class 9SANDEEP SINGHAinda não há avaliações
- Pascal's Math Practice TestDocumento6 páginasPascal's Math Practice TestERNANIE LLAVOREAinda não há avaliações
- Quadratic Equations MethodsDocumento18 páginasQuadratic Equations MethodsPaula FanaAinda não há avaliações
- bk9 13Documento29 páginasbk9 13Rahique ShuaibAinda não há avaliações
- Jain Engineering College Mathematics NotesDocumento24 páginasJain Engineering College Mathematics Notesdaredemon92Ainda não há avaliações
- Midterm ReviewDocumento30 páginasMidterm ReviewRolyn Grace Domagoso VergaraAinda não há avaliações
- Math Quest Math Methods VCE 12 (2016 Edition)Documento542 páginasMath Quest Math Methods VCE 12 (2016 Edition)NhiAinda não há avaliações
- Sia3e SSM 03Documento106 páginasSia3e SSM 03brianAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 1 SolutionDocumento17 páginasCBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 1 SolutionsanaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 13Documento38 páginasCH 13Bayley_NavarroAinda não há avaliações
- GE 111 Study Problems Part II SolutionsDocumento61 páginasGE 111 Study Problems Part II SolutionsKnowledgeIsTruePowerAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Math for IE: Linear & Nonlinear EquationsDocumento63 páginasAdvanced Math for IE: Linear & Nonlinear EquationsJi JiAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Math For IE - Chapter 1Documento16 páginasAdvanced Math For IE - Chapter 1Ji JiAinda não há avaliações
- Rmo 2012 Mumbai Region Previous Year Question Papers of Regional Mathematical Olympiad With SolutionsDocumento4 páginasRmo 2012 Mumbai Region Previous Year Question Papers of Regional Mathematical Olympiad With SolutionsAkshay PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Suggested Solutions Mabnvco10 Algebra and Geometry: InstructionsDocumento11 páginasSuggested Solutions Mabnvco10 Algebra and Geometry: InstructionsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Solutionbank C1: Edexcel Modular Mathematics For AS and A-LevelDocumento58 páginasSolutionbank C1: Edexcel Modular Mathematics For AS and A-LevelMaruf_007Ainda não há avaliações
- Addition and Subtraction of Fractions: College AlgebraDocumento12 páginasAddition and Subtraction of Fractions: College AlgebraLara GatbontonAinda não há avaliações
- Expression Vs EquatnsDocumento7 páginasExpression Vs EquatnsNanoManAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5Documento11 páginasLecture 5Red ManAinda não há avaliações
- Using A Graphing Calculator To Graph Linear Equations y MX + B Slope-Intercept Form Graph Table (2nd Graph) X-Y Table Find Intercepts Find PointsDocumento24 páginasUsing A Graphing Calculator To Graph Linear Equations y MX + B Slope-Intercept Form Graph Table (2nd Graph) X-Y Table Find Intercepts Find PointsmegantosAinda não há avaliações
- Ax + by D Found by Using The Method Above. Let Us Call TheDocumento2 páginasAx + by D Found by Using The Method Above. Let Us Call TheeibsourceAinda não há avaliações
- Solving Linear Equations and Constructing Mathematical ModelsDocumento626 páginasSolving Linear Equations and Constructing Mathematical ModelsElizabeth Dibanadane100% (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNo EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsNo EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (8)
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"No EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Nota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (2)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsAinda não há avaliações
- InequalitiesDocumento192 páginasInequalitiesEpic Win100% (2)
- Warning Signs of A Possible Collapse of Contemporary MathematicsDocumento12 páginasWarning Signs of A Possible Collapse of Contemporary MathematicsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- The Mystery of Stochastic MechanicsDocumento18 páginasThe Mystery of Stochastic MechanicsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- RomeDocumento7 páginasRomeEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Hilbert's Mistake: Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton UniversityDocumento27 páginasHilbert's Mistake: Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton UniversityEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- New 18Documento5 páginasNew 18Epic WinAinda não há avaliações
- IstDocumento34 páginasIstEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics and The Mind: Nelson/papers - HTMLDocumento6 páginasMathematics and The Mind: Nelson/papers - HTMLEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Syntax and Semantics: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLDocumento7 páginasSyntax and Semantics: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Ram RecDocumento8 páginasRam RecEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- HopeDocumento4 páginasHopeEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- FogDocumento5 páginasFogEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- OutlineDocumento7 páginasOutlineEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Intuitionism: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLDocumento20 páginasUnderstanding Intuitionism: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Nelson BibDocumento5 páginasNelson BibEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- ElemDocumento101 páginasElemEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Edward NelsonDocumento1 páginaEdward NelsonEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- FaithDocumento8 páginasFaithceceph354Ainda não há avaliações
- EDocumento9 páginasEEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- J. P. MayDocumento17 páginasJ. P. MayEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Zhang QDocumento15 páginasZhang QEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Set TheoryDocumento26 páginasInternal Set TheoryEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- WoolfDocumento9 páginasWoolfEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Zhang TDocumento4 páginasZhang TEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- WalijiDocumento6 páginasWalijiEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Probability Theory: 1 Heuristic IntroductionDocumento17 páginasProbability Theory: 1 Heuristic IntroductionEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- J-Spectra For A Quotient Group J of G. That Context Gives An Interesting SituationDocumento9 páginasJ-Spectra For A Quotient Group J of G. That Context Gives An Interesting SituationEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- WeinerDocumento6 páginasWeinerEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- VParticipantsDocumento1 páginaVParticipantsEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- WaddleDocumento10 páginasWaddleEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Math and SciencesDocumento227 páginasEngineering Math and SciencesMercy Joy PangadloAinda não há avaliações
- Adv Ex 16 InequalitiesDocumento4 páginasAdv Ex 16 InequalitiesLeroy ChengAinda não há avaliações
- Class 10 - IMO 2 PDFDocumento5 páginasClass 10 - IMO 2 PDFNeeraj Goyal100% (1)
- Mastery Test in Mathematics 10Documento2 páginasMastery Test in Mathematics 10JulianFlorenzFalconeAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra: Factoring PolynomialsDocumento2 páginasAlgebra: Factoring PolynomialsBianca Marie TataroAinda não há avaliações
- M - (X) 2. - (-Y) + X : Substitute The Given Value For The Variable and Evaluate. X - 4, y - 7, M 3Documento4 páginasM - (X) 2. - (-Y) + X : Substitute The Given Value For The Variable and Evaluate. X - 4, y - 7, M 3Hussain MustafaAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Mathematics MCQs 22-11-22Documento5 páginas10 Mathematics MCQs 22-11-22Kanishk ShakyawarAinda não há avaliações
- Squares and Square Roots 4Documento16 páginasSquares and Square Roots 4rajesh duaAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Sheet 2 (Multiple Integral)Documento3 páginasTutorial Sheet 2 (Multiple Integral)Dawa PenjorAinda não há avaliações
- SPM Matematik K1 2019 PahangDocumento17 páginasSPM Matematik K1 2019 PahangMat HuzainiAinda não há avaliações
- Changes Between Forms of Quadratic FunctionsDocumento4 páginasChanges Between Forms of Quadratic FunctionsCharalampidis DimitrisAinda não há avaliações
- Maths 2014 GR 8 Nov Vraestel 2 MemoDocumento6 páginasMaths 2014 GR 8 Nov Vraestel 2 MemoEstelle EsterhuizenAinda não há avaliações
- Theorems on Different Kinds of ParallelogramsDocumento9 páginasTheorems on Different Kinds of ParallelogramsErica SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Circles 3Documento24 páginasCircles 3Ateef Hatifa100% (1)
- Python Arithmetic, Area, Quadratic, Swap, Conversion ProgramsDocumento18 páginasPython Arithmetic, Area, Quadratic, Swap, Conversion ProgramsNimit GargAinda não há avaliações
- 50-Increase & Decrease of RatioDocumento6 páginas50-Increase & Decrease of RatioSameh SalahAinda não há avaliações
- Past Year Paper ACSIDocumento4 páginasPast Year Paper ACSIronghui009Ainda não há avaliações
- Understanding Fractions ConceptuallyDocumento36 páginasUnderstanding Fractions ConceptuallyJohan5539Ainda não há avaliações
- Group Tuition with Mr Arthur Lee APGP WS2 - GPDocumento22 páginasGroup Tuition with Mr Arthur Lee APGP WS2 - GPMichelle LouAinda não há avaliações
- Add Maths O Level Quick Revision Sheet With All FormulasDocumento16 páginasAdd Maths O Level Quick Revision Sheet With All FormulasÅzmâñ Khäñ50% (2)
- Trig Cheat Sheet 2Documento1 páginaTrig Cheat Sheet 2Jin HyungAinda não há avaliações
- Circle Theorems Exam QuestionsDocumento4 páginasCircle Theorems Exam QuestionsglennAinda não há avaliações
- Even/odd proofs: Practice problems SolutionsDocumento4 páginasEven/odd proofs: Practice problems SolutionsSaleem KholowaAinda não há avaliações
- 5 4 PacketDocumento6 páginas5 4 Packetapi-327561261Ainda não há avaliações
- NCERT Solutions For Class 1 To 12 - Free PDF DownloadDocumento13 páginasNCERT Solutions For Class 1 To 12 - Free PDF DownloadAnkit YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Maths CH 111Documento54 páginasMaths CH 111muscularindianAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics PracticeDocumento2 páginasMathematics PracticeHishq DhimanAinda não há avaliações
- Holiday Assignments for Class IXDocumento6 páginasHoliday Assignments for Class IXdevanshAinda não há avaliações
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 TrianglesDocumento39 páginasNCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Trianglesठाकुर अक्षय राघवAinda não há avaliações
- Seamo Past Paper D 2019Documento7 páginasSeamo Past Paper D 2019Quang Ha100% (7)