Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
B4 Observation of Beats (TG)
Enviado por
Shirley SayDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
B4 Observation of Beats (TG)
Enviado por
Shirley SayDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
73667650.
doc
p.1/3
School Name Date
Class (No.) Subject Mark
AL Practical Physics
B4 Observation of beats
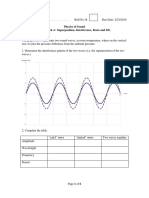
Procedure A. Beats from two tuning forks produced and compare it with the sound obtained by a single tuning fork. The single tuning fork produced the sound continuously and gradually decayed. When two tuning forks with slightly different frequencies were knocked, the sound intensity produced was rise and fall regularly and also slowly died away. B. Beats from two signal generators waveform as f1. 3. Knock the tuning forks 1 and 2 at the same time and hear their sound. Describe the sound
7. Turn on the CRO and adjust the Y scale to displace the whole waveform. Sketch the
8. Switch off the signal generator 1. Switch on the signal generator 2 and set the frequency to 260 Hz with the same amplitude as step 6. Sketch the waveform displaced on the CRO as f2.
New Way Physics for Advanced Level
Manhattan Press 2005
73667650.doc
p.2/3
9. Switch on the signal generator 1 and set the frequency to 250 Hz again. Sketch the combined waveform from loudspeakers 1 and 2 as f.
10. Set the frequency to 270 Hz in the signal generator 2. Sketch the combined waveform as f .
Results and Discussion 1. Describe the intensity and amplitude of the combined sound (beat) in Parts A and B. The combined sound with slightly different frequencies emitted the rise and fall sound intensity, which is called the sound beat. The difference of these two frequencies is the beat frequency. If the difference of the frequencies is large, there will be two separate sound notes instead of sound beat, i.e. no sound beat can be produced. 2. Explain why beats are formed by two waves of different frequencies. When two waves having slightly different frequencies meet at some place, their phases relative to each other are changing with time, i.e. repeatedly in phase and in antiphase. As a result, the successive constructive and destructive interference of two sound waves produced the rise and fall sound intensity.
New Way Physics for Advanced Level
Manhattan Press 2005
73667650.doc
p.3/3
3.
From Part B, calculate the beat frequencies f and f . Compare f and f and deduce the relationship between the beat frequency and the variation of individual frequency. f = 260 Hz 250 Hz = 10 Hz f = 270 Hz 250 Hz = 20 Hz
4. State the sources of error and suggest improvements for this experiment. (a) The speakers are not placed in parallel. (b) The microphone is not placed in the middle between the speakers. It is suggested to align the equipments properly in place. 5. Give a conclusion to this experiment. The sound beat frequency is produced from two sound waves with slightly different frequencies.
New Way Physics for Advanced Level
Manhattan Press 2005
Você também pode gostar
- Superposition and Standing Waves: Conceptual ProblemsDocumento88 páginasSuperposition and Standing Waves: Conceptual ProblemsnallilathaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 10.1 10.2garcia STEM2Documento3 páginasActivity 10.1 10.2garcia STEM2nino pabellanoAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 16 SMDocumento88 páginasChap 16 SMzenrocAinda não há avaliações
- Audio Fundamentals ChapterDocumento5 páginasAudio Fundamentals Chaptersumit ManeAinda não há avaliações
- Acoustic Theory Speech ProductionDocumento24 páginasAcoustic Theory Speech ProductionKittenlover1234100% (1)
- Homework 4 - Superposition, Interference, Beats and SILDocumento6 páginasHomework 4 - Superposition, Interference, Beats and SILimrp5Ainda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Word Chapter17Documento13 páginasMicrosoft Word Chapter17om123456789Ainda não há avaliações
- Transformer Core Noise CorrelationDocumento6 páginasTransformer Core Noise Correlationgiovanni MarzoloAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter No. 8 - WavesDocumento3 páginasChapter No. 8 - Wavesnazarin.nordinAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter19pp171 180 PDFDocumento10 páginasChapter19pp171 180 PDFInderMahesh0% (1)
- Chap 15Documento86 páginasChap 15noscribdyoucantAinda não há avaliações
- Waves and Sound WorksheetDocumento11 páginasWaves and Sound Worksheetsmartamjad89% (19)
- CH 10Documento8 páginasCH 10David BrantleyAinda não há avaliações
- Wave Generator WorksheetDocumento7 páginasWave Generator WorksheetJhen Ivy50% (2)
- Standing Wave Patterns and Sound Waves in Physics ExperimentsDocumento2 páginasStanding Wave Patterns and Sound Waves in Physics ExperimentsferAinda não há avaliações
- Waves and Sound PacketDocumento16 páginasWaves and Sound PacketKaito EspinaAinda não há avaliações
- Padolina - DYO Experiment PresentationDocumento8 páginasPadolina - DYO Experiment PresentationSweg SwegAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 11A Answer Key Physics Revision Sheets 1Documento6 páginasGrade 11A Answer Key Physics Revision Sheets 1fgdhAinda não há avaliações
- As Unit-2 Student Book (QuestionDocumento15 páginasAs Unit-2 Student Book (QuestionCostas Paschalides100% (2)
- 1 0wave1 11 2activityDocumento10 páginas1 0wave1 11 2activityNisa Hj MohamadAinda não há avaliações
- Factsheet Physics: Stationary Waves On Strings and in Air ColumnsDocumento3 páginasFactsheet Physics: Stationary Waves On Strings and in Air ColumnsPengintai100% (1)
- Waves and Sound WorksheetDocumento12 páginasWaves and Sound WorksheetprosenAinda não há avaliações
- Conceptual Problems from Chapter 15 Traveling WavesDocumento14 páginasConceptual Problems from Chapter 15 Traveling WavesNipun SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier Synthesis of Ocean Scenes 87 PDFDocumento8 páginasFourier Synthesis of Ocean Scenes 87 PDFavinashAinda não há avaliações
- ExamView - Waves and Sound - Practice TestDocumento9 páginasExamView - Waves and Sound - Practice TestMohan RajAinda não há avaliações
- Examview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Documento9 páginasExamview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Tajay Billings100% (1)
- GP1 - STEM - Q2 - W4 - SLK-4 - Mechanical Waves and SoundDocumento26 páginasGP1 - STEM - Q2 - W4 - SLK-4 - Mechanical Waves and SoundGrayka QuiapoAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 10 - Properties of WavesDocumento3 páginasIGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 10 - Properties of WavesAishath Waheeda0% (1)
- trialstpm2022KelantanP3Question-1Documento8 páginastrialstpm2022KelantanP3Question-1ASANAMMAH NACHIAR A/P PAKEER MOHAMED MoeAinda não há avaliações
- 1.5 Analysing Interference of WavesDocumento10 páginas1.5 Analysing Interference of WavesCik Rokiah GhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Sound and WavesDocumento11 páginasPhysics Sound and WavesCraft CityAinda não há avaliações
- Practice sheet - Sound and space fundamentalsDocumento1 páginaPractice sheet - Sound and space fundamentalsZAHRA NAUREEN NAUREEN100% (1)
- Introduction To AcousticsDocumento7 páginasIntroduction To AcousticsMuhammad ZubairAinda não há avaliações
- Classic Waveshapes and SpectraDocumento4 páginasClassic Waveshapes and SpectraDæveAinda não há avaliações
- Interference of Waves PrinciplesDocumento5 páginasInterference of Waves PrinciplesReiana YeoAinda não há avaliações
- Resonance: Sound Waves - 251Documento27 páginasResonance: Sound Waves - 251Ankit JhaAinda não há avaliações
- Wave Systems 2012solDocumento6 páginasWave Systems 2012solGabrielle TanAinda não há avaliações
- Physics and Musical InstrumentsDocumento13 páginasPhysics and Musical InstrumentsMax Zimmerman100% (1)
- 15 Superposition of Waves 15Documento5 páginas15 Superposition of Waves 15Ashani0001100% (1)
- Chapter 15 Traveling Waves Conceptual PRDocumento86 páginasChapter 15 Traveling Waves Conceptual PRk4dr0nAinda não há avaliações
- PHY 121 8 - Interference of WavesDocumento30 páginasPHY 121 8 - Interference of WavesChristopher NdamboAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 202 Practice ExamDocumento10 páginasPhysics 202 Practice Exampalace2022Ainda não há avaliações
- P2133500 PDFDocumento12 páginasP2133500 PDFxongassilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis and Reproduction of The Frequency SpectrumDocumento11 páginasAnalysis and Reproduction of The Frequency SpectrumramonbossAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Laser Fundamentals and CalculationsDocumento1 páginaPhysics Laser Fundamentals and CalculationsKool PrashantAinda não há avaliações
- 14 - Waves General Waves and Wave Intensity - 14Documento4 páginas14 - Waves General Waves and Wave Intensity - 14dil19860209Ainda não há avaliações
- An 1026Documento6 páginasAn 1026kuazuAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Evidence#5Documento9 páginasLearning Evidence#5felina.duran001Ainda não há avaliações
- EX 4.1 Rev1Documento8 páginasEX 4.1 Rev1MANAR -Ainda não há avaliações
- Wave MotionDocumento92 páginasWave Motionkit_yee_221Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolDocumento3 páginasUnit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolシューゴAinda não há avaliações
- Wave PropertiesDocumento122 páginasWave PropertiesschlemielzAinda não há avaliações
- Additional Tutorial 1Documento4 páginasAdditional Tutorial 1ChristinaAinda não há avaliações
- Solution To UK #2 "SOUND"Documento6 páginasSolution To UK #2 "SOUND"vtendeanAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsNo EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (4)
- Electromagnetic Time Reversal: Application to EMC and Power SystemsNo EverandElectromagnetic Time Reversal: Application to EMC and Power SystemsFarhad RachidiAinda não há avaliações
- Acoustic Signals and Hearing: A Time-Envelope and Phase Spectral ApproachNo EverandAcoustic Signals and Hearing: A Time-Envelope and Phase Spectral ApproachAinda não há avaliações
- Trading My Sorrows: Words & Music by Darrell EvansDocumento38 páginasTrading My Sorrows: Words & Music by Darrell EvansJuan Mario Claros QuispeAinda não há avaliações
- Restoration Suite 2: User GuideDocumento19 páginasRestoration Suite 2: User GuidekosarobAinda não há avaliações
- Taylor SwiftDocumento21 páginasTaylor Swiftapi-251902149Ainda não há avaliações
- Junior Cycle Learning OutcomesDocumento4 páginasJunior Cycle Learning OutcomesAengus RyanAinda não há avaliações
- Guatemalan Marimba TraditionsDocumento5 páginasGuatemalan Marimba TraditionsZach WadsworthAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Ribbon MicrophoneDocumento9 páginasDesign of Ribbon MicrophonemerrickAinda não há avaliações
- Recording Drummers and Frontline InstrumentsDocumento16 páginasRecording Drummers and Frontline InstrumentsR WilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- Ev Pa2400t PDFDocumento2 páginasEv Pa2400t PDFMuhiyadinAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Serviço - Aiwa NSX-D77, NSX-T76, NSX-T77Documento48 páginasManual Serviço - Aiwa NSX-D77, NSX-T76, NSX-T77fabioferraoAinda não há avaliações
- SooperLooper - Documentation - Command ReferenceDocumento4 páginasSooperLooper - Documentation - Command ReferenceGorillakoenigAinda não há avaliações
- Function, Construction and Quality of The GuitarDocumento106 páginasFunction, Construction and Quality of The Guitaradorno5Ainda não há avaliações
- Dolby 365 ManualDocumento37 páginasDolby 365 ManualDirk Lindemans0% (1)
- Music 7: Guided Learning Activity SheetsDocumento15 páginasMusic 7: Guided Learning Activity SheetsJethromelech Rodriguez100% (2)
- XV-3080 Qa SoundlistDocumento20 páginasXV-3080 Qa SoundlistcaptainpalmerAinda não há avaliações
- I Wish: Verse Main Groove W/ Drums Intro BasslineDocumento1 páginaI Wish: Verse Main Groove W/ Drums Intro BasslineSebastian BerruzAinda não há avaliações
- Module: Intro To Linguistics Ensb 2 Year English LiteratureDocumento4 páginasModule: Intro To Linguistics Ensb 2 Year English LiteratureYašmeeñę ŁębdAinda não há avaliações
- Summative Test Q3 M 3-4Documento6 páginasSummative Test Q3 M 3-4Virgen delas flores High SchoolAinda não há avaliações
- FLP10078 Norway FiddleDocumento9 páginasFLP10078 Norway FiddletazzorroAinda não há avaliações
- Entrance Exam For G7Documento9 páginasEntrance Exam For G7Sheryl Damo AguilarAinda não há avaliações
- Highschool Band Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginasHighschool Band Lesson PlanDaniel ScheetzAinda não há avaliações
- Sunon DC Brushless Fan & Blower - (240-A) PDFDocumento90 páginasSunon DC Brushless Fan & Blower - (240-A) PDFd4l170Ainda não há avaliações
- Ultrasonic Testing - Training NotesDocumento80 páginasUltrasonic Testing - Training NotesRobert Maxwell88% (8)
- Medieval Robin and Marion performance set in scenic backgroundDocumento4 páginasMedieval Robin and Marion performance set in scenic backgroundPhuamae SolanoAinda não há avaliações
- Silence, Music, Silent MusicDocumento268 páginasSilence, Music, Silent Music方科惠100% (3)
- Live Escalate 3 - What's on Your PlaylistDocumento29 páginasLive Escalate 3 - What's on Your Playlistsantiago gamboa 805Ainda não há avaliações
- ICSE-X Physics - Chap-7 (Sound)Documento12 páginasICSE-X Physics - Chap-7 (Sound)mohammedumar7864521Ainda não há avaliações
- Waves A Level Practice QuestionsDocumento6 páginasWaves A Level Practice QuestionsisaacsrandomsignupsAinda não há avaliações
- Noise Pollution in Dhaka CityDocumento23 páginasNoise Pollution in Dhaka CityMuhammad Mahadi100% (11)
- Questionsdoppler Model Aircraftstage AllDocumento1 páginaQuestionsdoppler Model Aircraftstage AllArshad KhanAinda não há avaliações