Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Curriculm of Civil Engg& Allied Discipline
Enviado por
Muhammad Shakil JanDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Curriculm of Civil Engg& Allied Discipline
Enviado por
Muhammad Shakil JanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
PAKISTAN ENGINEERING COUNCIL Curriculum for Engineering Practice Examination (EPE) Civil Engineering & Allied Disciplines
(Civil Engineering/Transportation Engineering/Urban Engineering/Environmental Engineering/Building & Architectural Engineering)
Total Marks: 100 MAIN OBJECTIVE: The main objective of Engineering Practice Examination (EPE) is the assessment of competence, knowledge and skills of a Registered Engineer (RE), after having attained a minimum of five years of practical experience in relevant field of engineering from a recognized engineering organization, institution or allied service, and has earned requisite CPD (Continuing Professional Development) credit points. PART-I (COMMON TO ALL DISCIPLINES) This is common to all disciplines comprising of 30 questions of one mark each (total marks 30) with the duration of 2 hours, dealing with engineering related management, communication skills and ethics. MANAGEMENT (ENGINEERING RELATED) i. Quality Issues: fundamental concepts, application and role ii. Finance: cost analysis, financial discipline iii. Procurement/Legal: bidding, contracts, arbitration, guarantees, liabilities iv. Latest Trends: emerging technologies and their applications. Suggested Books: PEC bidding/contract documents (www.pec.org.pk; www.picc.org.pk) FIDIC documents W.G. Sullivan, J.A. Bontandelli and E.M. Wicks, Engineering Economy, 11th Ed., Prentice Hall Inc., 1999 Franklin and John Stermole, Economic Evaluation and Investment Decision Methods (9th Edition) Project Management Institute , A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) - Fourth Edition, Published by Project Management Institute, weblink: A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) - Fourth Edition, 2008. 33% 34%
2. WRITTEN COMMUNICATION SKILLS i. English Language Communication Skills Paragraph and essay writing
Academic and presentation skills Project/ research proposals Monitoring and evaluation Progress and financial reporting
ii. Technical Report Writing Skills
iii. Knowledge Management and Leadership Skills Suggested Books: Writing. Intermediate by Marie-Christine Boutin, Suzanne Brinand and Francoise Grellet. Oxford Supplementary Skills. Fourth Impression 1993. ISBN 0 19 435405 7 Pages 20-27 and 35-41 Hargie, O. (ed.) Handbbook of Communications Skills, Routledge Writing. Advanced by Ron White. Oxford Supplementary Skills. Third Impression 1992, ISBN 0 19 435407 3 Practical English Grammar by A.J. Thomson and A.V. Martinet. Exercises1, 3rd Ed., Oxford University Press, 1997. ISBN 0194313492 Ellen, K. 2002. Maximize Your Presentation Skills: How to Speak, Look and Act on Your Way to the Top, Prima Lifestyles - 2005 Oxford English Dictionary or equivalent, (Latest Edition) 33%
3. ETHICAL AND SOCIAL ISSUES i. Code of ethics ii. Professional obligation of engineers iii. Role of opportunity and conflict iv. Interpersonal relations, social stratification and culture Suggested Books:
PEC Code of Ethics (http://pec.org.pk/code_ethics.aspx) PEC Code of Conduct (http://pec.org.pk/code_conduct.aspx) Ethics in Engineering, Martin M. W., Martin M. and R. Schinzinger, McGraw-Hill, (Latest Edition) Ethics in Engineering Practice and Research, Whitbeck C., Cambridge University Press, (Latest Edition) Finchan, R., & Rhodes, P. (2003), Principles of Organizational Behavior, 3rd Ed., Oxford. Project Management Institute , A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) - Fourth Edition, Published by Project Management Institute, weblink: A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) - Fourth Edition, 2008.
PART-II (BREADTH) This part attempts to assess the breadth of Civil Engineering and allied disciplines including Civil, Transportation, Urban, Environmental, and Building & Architectural Engineering. The examination of this part would comprise 30 multiple choice questions (total 30 marks) for 2-hours duration.
1. MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS FOR ENGINEERS i. Fundamentals Coordinate System: cartesian and polar coordinate system Trigonometric functions Maxima and minima of functions Application of limit, continuity, differentiation and integration Complex numbers Binary arithmetic Sequence and series
10%
ii. Differential and Partial Differential (PD) Equations and their Solutions iii. Vectors, matrices and determinants, their properties and applications iv. Solution of Equations Solution of linear simultaneous equations Iterative methods for solution of linear simultaneous equations
v. Numerical Differentiation and Integration vi. Eigen Values and Eigen Vectors vii. Statistics & Probability Frequency curves and their types, frequency histograms Measure of dispersion (mean, mode, median, standard deviation) AM, GM, HM and their properties Simple and multiple regression Interpolation and its applications Basics of probability, types and methods
Suggested Books: George Brinton Thomas, Ross L Finney, Calculus & Analytical Geometry, Addison-Wesley, 1998 S M Yousif, Mathematical Methods, 2nd Edition, Ilmi Kitab Khana Hogg & Craig, Introduction to Mathematics &Statistics, Prentice Hall, 2004. Cagora S, Numerical Methods for Engineers, McGraw Hill, 2006. Erwin Kreyszig, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Ninth Edition, 2005, International Edition, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN: 0471728977. 10%
2. ENGINEERING MECHANICS i. Statics
General principles of statics Resultant, resolution and conditions of equilibrium of co-planer forces Types of supports and reactions Degree of restraints and static determinacy Friction
ii. Dynamics Velocity, acceleration and their units linear and angular motion inertia force, impulse, momentum and work power and energy
Suggested Books: Hibler, R.C. Engineering Mechanics, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall, 2006 Khurmi, R. S. Engineering Mechanics, 19th Ed, S. Chand, 1990 7%
3. SURVEYING i. Methods of surveying ii. Leveling, contouring, plane table surveying iii. Traversing iv. Tachometry
v. Basics of Geographic Information System (GIS) and Remote Sensing (RS) vi. Photogrametry vii. Basics of field astronomy viii. Surveying Instruments: levels, theodolite, Electronic Distance Meter (EDM), total station, GPS (Global Positioning System) ix. Practical problems x. Calculation of area and volume xi. Computations and setting out of curves xii. Tunnel surveying xiii. Hydrographic surveying Suggested Books: Irvine W, Surveying for Construction, McGraw Hill Inc., 4th edition1997. Bannister, Raymond S, Baker R, Surveying, Pearson Education and Dorling Kindersley Publishing Inc. (1998). Kanetkar T.P., 2008, Surveying & Leveling, Volume I & Volume II, Standard Publishers Distributors, India, 2008. Burrough P.A., and McDonnell R.A., Principles of Geographical Information Systems, 352 pages, Oxford University Press, 1998. Geographic information system, available on: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geographic_information_system 10%
4. CIVIL ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND CONSTRUCTION i. Construction Materials General civil engineering materials, performance requirements (strength, stiffness, durability, appearance)
Materials quality control and testing Concrete: cement, fine and coarse aggregates, properties of cement, aggregates and water, basic concrete mix design procedure, concrete admixtures Bricks: properties of brick making materials and methods, types/ specifications of bricks Stones: types, characteristics and uses of common construction stones Steel: production and properties of steel, steel grades, effect of alloys, protection from corrosion and fire Timber: properties, defects, durability and seasoning/preservation of timber Asphalt: types, properties and uses of asphalt Construction methodologies pertaining to in situ and pre-cast construction Mechanized construction techniques Layout, earthwork and construction Construction equipments
ii. Construction Methodologies
Suggested Books: R. C. Smith, Cameron K. Andres Materials of Construction, McGraw Hill Inc Ltd, 1998. M. Neville Properties of Concrete, Wiley John & Sons. 3rd Ed. 1994, ISBN: 0803133677 9%
5. FLUID MECHANICS i. Properties of Fluids (Statics and Dynamics)
ii. Fluid Properties Measuring Techniques: devices for the measurement of static pressure, velocity and discharge in pipes and open channels iii. Flow in Pipes: minor and major losses in pipelines, empirical formulae for pipe flow, solutions of pipe flow problems and pipe networks iv. Flow in Open Channels: formulae for flow in open channels and most efficient hydraulic cross-section v. Forces on Vanes, Turbines and Pumps: impulse momentum equation, forces on flat and curved vanes, components and operations of various turbines and pumps. Suggested Books: Finnemore,E.J & Franzini,J.B.,10th Edition. Fluid Mechanics with Engineering Application. McGraw Hill Book Co. Singapore. Jain, A.K. Fluid Mechanics. Khanna Publishers, New Delhi, India,1990. S.S. Rattan, Fluid Machines Khanna Publishers, New Delhi, India, 1994.
6. MECHANICS OF SOLIDS i. Fundamental Laws and principles of stress and strain
10%
ii. Stresses in composite bars and relationships between elastic constants iii. Shear Force (SF), Bending Moment (BM), SF and BM diagrams, point of contra flexure and point of inflation iv. Theory of simple bending, moment of resistance, section modulus, flexural formula v. Shear stresses in beams vi. Torsion of solid and hollow circular shafts vii. Strain energy viii. Experimental stress analysis Suggested Books: Pytel, A. & F.L.Singer, Strength of Materials, 4th Ed, Harper & row Publishers, 1987. G H Ryder, Strength of Materials, 3rd Edition, Macmillan, 1969. 10%
7. HYDROLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES i.
Water Resources and Hydrologic Cycle: Water Resources of Pakistan, hydrologic cycle, precipitation, evaporation, evapotranspiration, interception and infiltration
ii. Surface Flow: water stage measurement, stream flow routing, surface runoff, floods hydrographs iii. Groundwater: groundwater resources, flow and water table iv. Flow in Open Channels and Pipes: specific energy and critical depth. Water surface profiles, hydraulic jump, humps and contractions, water hammer v. Hydraulic Structures: bridges, cross drainage structures, types of reservoirs. Suggested Books: Awan, N.M. Surface Water Hydrology, National Book Foundation, Islamabad, 1981. Linsely, R.K., Kohler, Hydrology for Engineers, SI. Ed.1996, McGraw Hill Driscoll, F.G., Groundwater and Wells, Johnson Division, USA, 1987. Franzini, J.B. and Finnemore, E.J., Fluid Mechanics with Engineering Application , McGraw Hill Book Co., Singapore, 2003. Iqbal Ali Irrigation and Hydraulic Structures: Theory, Design and Practice, Publisher, Institute of Environmental Engineering & Research, NED University of Engineering &Technology, Karachi, 1993, ISBN: 9698160000
8. GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING i.
10%
Subsurface Exploration: common drilling methods and Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
ii. Soil Properties iii. Classification of Soil: particle size distribution, atterberg limits, unified soil and AASHTO classification systems iv. Compaction: theory and practice, standard and modified proctor test, Field Density Test (FDT) v. Permeability: Darcys Law and coefficient of permeability vi. Stresses in a Soil Mass: total and effective stresses, pressure bulb and 2:1 Method vii. Settlement of Soil: types and determination of settlement viii. Shear Strength of Soil: shear strength parameters and determination ix. Lateral Earth Pressure and Retaining Structures x. Shallow and Deep Foundations: types, bearing capacity and settlement determination xi. Embankment Dams: types and materials for construction. Suggested Books: Das, B.M. Principles of Geotechnical Engineering, 4th edition, PWS Publishing Company, 1998. Craig, R.F, Soil Mechanics, Van Nostrand Reinhold (UK) Co. Ltd.1983. Bowles, J.E Foundation Analysis and Design, McGraw Hill Publishing Company, 1988. 7%
9. ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING i.
Public Health Engineering Wastewater Treatment: wastewater flow rates, characteristics of sewage, sewage treatment and disposal Water Quality: water impurities and their health significance, WHO guidelines Water Treatment: treatment of surface and ground water.
ii. Environmental Engineering Solid Waste Management: sources, classifications, characteristics, generation rates, collection and disposal of solid waste Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), legislation and regulations Introduction to noise and air pollution.
Suggested Books: Terence J McGhee, Water Supply and Sewerage, 6th Edn, McGraw Hill, 1991, ISBN: 0070609381
Metcalf and Eddy, Waste Water Engineering, 4th Edn, McGraw Hill, 2002 Mackenzie L. Davis, David A. Cornwell, Introduction to Environmental Engineering 4th Ed., McGraw Hill, 2000. 7%
10. TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING i. Railway Engineering
Railway station, site selection and layout, railway track, gauges, sleepers and ballast Points, crossings and signaling Airport site selection, classification, layout and drainage systems Runway configurations
ii. Airport Engineering
iii. Types of Harbors, Docks and Ports iv. Highway Engineering Highway route surveys, classifications, material specifications and testing Typical cross-sections of roads Geometric design: Horizontal, vertical, and transition curves, curve widening, at-grade and grade-separated intersections Sight distance requirements, super elevation, gradients and cambers Highway maintenance Traffic studies and control devices v. Pavement Engineering Types of pavements, Load distribution characteristics, wheel loads, load repetition and impact factors Concept of rigid and flexible pavement design.
Suggested Books: Jason C., Yui, Elsevier, Transportation Engineering, Introduction to Planning, Design and Operations Latest Edition. Paul H. Wright McGraw Hill, Planning and Design of Airports Highway Engineering Latest Edition. Dr. L. R. Kadyali, Dr. N. B. Lal Khanna Principles and Practices of Highway Engineering (including Expressway and Airport Engineering), 2010, ISBN: 8174091653 B. L. Gupta, Amit Gupta. Roads, Railways, Bridges, Tunnels and Harbour-Dock Engineering. 10%
11. STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND DESIGN i.
Types of structures and structural idealization, types of loads and beams, degree of indeterminacy
ii. Analysis of determinate structural members, arches, cables and bridges iii. Design philosophy and design codes
iv. Methods of design (working stress and ultimate strength design) of structural members, behavior of reinforced concrete members in flexure v. Design concepts of beam, column, slab, footing, retaining walls, tanks, stairs. Suggested Books: Wang, C.K. Intermediate Structural Analysis, McGraw Hill, 1983. Wang, C.K. & Charles G.S. Reinforced Concrete Design, 7th Ed, John Wiley & Sons, 2006. Aurthor H. Nilson, Design of Concrete Structures, Mc-Graw Hill, 2003 Lothers JE, Steel Structures, National Book Foundation, 1972.
PART-III (DEPTH) This part aims to assess the depth of Civil Engineering and allied disciplines including Civil, Transportation, Urban, Environmental, and Building & Architectural Engineering. The examination of this part would comprise 40 multiple choice questions for 3-hours duration. Each candidate can attempt the only opted area of practice, among the followings. 1. STRUCTURES i. Advanced Methods of Structural Analysis Stiffness matrix method Flexibility matrix method Finite element method Fundamentals of structural design Specifications and codes of practice of ASD (Alternate Stress Design) and LRFD (Load and Resistance Factor Design) methods Fabrication and erection methods of steel structures, hot rolled, cold formed and built up sections LRFD Method: Factor Of Safety (FOS), loads and load combination, concept of load and resistance factors, plastic design and limits on design, analysis and design of tension members, calculation of net area, analysis and design of columns, lacing and slay plates, Euler's buckling load in columns, design concept and methodologies for various structural members Design: design philosophy, design codes, design loads (i.e. dead load, live load, construction loads, wind loads, earthquake load, moving loads, snow loads, impact loads, load combinations), factor of safety and load factors Working stress method: serviceability criteria and checks for deflection, crack width and crack spacing Ultimate strength method: design of prismatic and non-prismatic sections in flexure, compatibility based analysis of sections and code requirements for flexure
ii. Steel Structures
iii. Reinforced Concrete
Slabs: types of slabs, design for flexure of one-way and two-way solid and ribbed slabs Shear and Tension: shear stress in reinforced concrete sections, design for diagonal tension Bond, Anchorage & Development Length: design and detailing for bond, anchorage, development length, laps and splices Columns: analysis of sections in pure compression, design of short columns under pure compression and with eccentric loading, slender columns Footing and Foundation: types of footing, design of square, rectangular and combined footing, design of eccentric, strap, strip and raft footings, piles and pile caps, bridge piers Stairs: analysis and design of various types of stairs and staircases Design of shear and retaining walls Prestressed Concrete: prestressing principles & design philosophy, analysis and design of simply supported prestressed beams for flexure and shear Concept and design procedure for earthquake resistant structural members.
Suggested Books Hassoun, M. N. Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures, PWS Engineering, 1985. Nilson A.H., Design of Reinforced concrete structures , John Wiley and Sons.1987. Nilson A.H., Design of Prestressed concrete 2nd Ed, John Wiley and Sons.1987. Lothers, J.E. Steel Structures, National Book Foundation, 1972.
2. TRANSPORTATION i. Modes of transportation and their comparison, transportation planning process, inter-modal transportation. ii. Railways Engineering Track alignment and surveys Geometric design of railway track Modern methods for construction of tracks, maintenance, tools and organization Sleeper density, spacing and stiffness of track Welding of rails Formation failures with remedial measures Creep and wear of rail Points and crossings various layouts Cross drainage work: types, monitoring and maintenance Signaling and inter-locking. Types and layouts of airport terminal buildings
iii. Airport Engineering
Types of runways: capacities and exits Types of aprons Design and evaluation of flexible and rigid pavements for airfields. Types, capacity and level of service of highways Motorways and expressways: definition, points of difference, typical crosssection with measurements Types, analysis and design of intersections Pedestrian facilities Highway failures: evaluation and rehabilitation Pavement design: empirical and mechanistic approaches Human, vehicular and traffic characteristics Traffic volume/time delay studies Speed zoning and restriction Types of parking facilities and design of car park Types and functions of traffic control devices, traffic signs, markings, traffic signal design Traffic accident and their patterns, analysis and remedial safety measures Traffic Impact Assessment Technique.
iv. Highways and Traffic Engineering
Suggested Books: Jason C., Yui, Transportation Engineering Introduction to Planning, Design and Operations, Elsevier, Latest Edition. Horon Jeff, R. Planning and Design of Airports, McGraw Hill, Latest Edition. Gregory P. Tsinker, Port Engineering Planning Construction Maintenance and Security, John Wiley, 2004. Paul H. Wright McGraw Hill Highway Engineering, Latest Edition. Dr. L. R. Kadyali, Dr. N. B. Lal Khanna Principles and Practices of Highway Engineering (including Expressway and Airport Engineering) B. L. Gupta, Amit Gupta.Roads, Railways, Bridges, Tunnels and Harbor-Dock Engineering Croney D. Design and performance of road pavements 3rd Ed. ISBN: 978-0070144514
3. GEOTECHNICAL i. Subsurface Exploration Drilling and sampling procedures: methods and comparison of drilling methods, split spoon sampler, shelby, pitcher, denison and pistons, coring of rocks Field tests: In-situ Density Test, Standard Penetration Test (SPT), Cone Penetration Test Boring log interpretation. Proctor tests/ relative density tests Factors affecting compaction Field compaction equipment Site control procedure using sand cone/ core cutter methods.
ii. Compaction
iii. Classification of Soil Particle size distribution, uniformity coefficient, coefficient of curvature Atterberg limits Soil correlation and phase relations Unified classification system AASHTO classification system. Darcys Law Hydraulic conductivity Flow nets, calculation of seepage, critical hydraulic gradient Capillarity in soils Well analysis (steady flow only). Principle of effective stress Stresses in soils Vertical stress increase due to various types of loadings. Odometer test, void ratio, log pressure plots, normally consolidated & over consolidated soils Settlement and consolidation Pre-compression of ground Sand drains. Mohr-Coulomb failure criteria Laboratory determination of shear strength parameters. Active, passive and at rest earth pressure Rankine and Coulomb earth pressure theories Gravity and cantilever walls Braced cuts. Finite and infinite slopes Pseudo static analysis Tolerable, total and differential settlement Angular distortion Plate load tests. Estimation of pile capacity (single pile and pile groups) Pile load tests Pile construction.
iv. Permeability
v. Stresses in Soil Mass
vi. Consolidation
vii. Shear Strength of Soil
viii. Lateral Earth Pressure and Earth Retaining Structures
ix. Slope Stability
x. Shallow Foundations
xi. Deep Foundation
xii. Earthquake Engineering
Seismic zoning of Pakistan Dynamic soil parameters Liquefaction. Types and components of earth dams Design considerations Stability and seepage analysis.
xiii. Embankment Dams
xiv.Soil Improvement Techniques, Dewatering Methods, Sheet piles: Suggested Books: Das, B.M., Principles of Geotechnical Engineering, 4th edition, PWS Publishing Company, 1998. Craig, R.F, Soil Mechanics, Van Nostrand Reinhold (UK) Co. Ltd.1983. Bowles, J.E., Foundation Analysis and Design, McGraw Hill Publishing Company, 1988. Karl Terzaghi, Ralph Brazelton Peck, Gholamreza Mesri Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice John Wiley and Sons, 1996.
4. CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT i. Quality Control Cost and values of quality company structure policies and objectives engineering designs and specifications communications reporting and data processing Control of non-compliances Contractor relations, client relations Measurement of quality and quality documentation Concrete maturity & early strength evaluation Quality measurement, improvement and auditing Construction methodologies pertaining to in situ and pre-cast construction Dewatering and pumping Mechanized construction techniques: lifting & rigging, crane selection, erection & stability Earthwork construction & layout: site layout and control, excavation and embankment (cut & fill), borrow pit volumes, temporary erosion control Temporary structures: construction loads, formwork, false work, scaffolding, shoring and reshoring. Cost estimating Engineering economics.
ii. Construction Methodologies
iii. Estimating Quantities & Cost
iv. Project Management / Scheduling
Construction sequencing Activity time-analysis Resource scheduling Time-cost trade-off. Types and conditions of contracts Contract administration during construction: variation orders, extension of time, engineering decisions, dispute resolution Tendering process and evaluation.
v. Contracts and Tendering
Suggested Books: R. L. Peurifoy, W. B. Ledbetter , C. J. Schexnayder , Cliff J. Schexnayder, Construction Planning, Equipment and Methods, By:, McGraw-Hill Inc Ltd.1996. Project Management Institute , A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) - Fourth Edition, Published by Project Management Institute, weblink: A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) - Fourth Edition, 2008. Construction Planning for Engineers By: F. H. Griffis , John V. Farr , M. D. Morris , Fletcher Griffis , John Farr, McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math (1999), ISBN-10: 0073033278. PEC Standard Bidding/Contract Documents, (weblink: http://www.pec.org.pk/downloads.aspx, www.picc.org.pk).
5. WATER RESOURCES i. Hydraulics and Irrigation Steady flow in open channels: specific energy and critical depth, classification of water surface profiles, design of hydraulic jump and its practical applications, flow over humps and through contractions Unsteady flow: discharge through orifices, weirs under varying heads, unsteady flow through pipes, water hammer, instantaneous and slow closure of valves, design of surge chambers Dams and Water Power Engineering: types of storage dams, site selection for reservoirs, forces on dams, design of gravity dams, selection of waterpower sites, components and layout of waterpower schemes Hydraulic modeling: types of models, similitude in physical model testing, model techniques, analysis and scale effects Irrigation: methods of irrigation (surface, drip and sprinkler), design of lined and unlined channels, sediment transport in channels, types of lining, maintenance of canals, estimation of water requirement for crops Irrigation works: function and design of canal head regulators, meter flumes, outlets and cross drainage works, design of weirs and barrages Waterlogging, salinity, land reclamation techniques and drainage system design.
ii. Hydrology and Water Resources Precipitation: types and measurement of precipitation, factors necessary for the formation of precipitation, Interpretation of precipitation data Evaporation and infiltration: factors affecting evaporation and evapotranspiration, measurement of evaporation and evapotranspiration, factors affecting interception and infiltration, measurement of interception and infiltration Stream flow and surface runoff: water stage and its measurement, Selection of site for stage record, selection of control and metering section, methods of measurement of stream flow, telemetry and SCADA, interpretation of stream flow data, flood, frequency and duration analysis, flood routing, factors affecting runoff, estimating the volume of storm runoff, characteristics of hydrographs, components of a hydrographs, hydrograph separation, factors affecting hydrograph shape, derivation and application of unit hydrograph Groundwater: groundwater sources, discharge, assessment and formations/aquifers, types of wells and design.
Suggested Books: Finnemore, E.J & Franzini, J.B., Fluid Mechanics with Engineering Application 10th Edition, McGraw Hill Book Co. Singapore. Chow, V.T. Open Channel Hydraulics Mc. Graw-Hill International Book Company Punmia, B.C., Pande, B. B.Lal, Irrigation and Water Power Engineering, Standard Publisher Distributors, Delhi, 1984. Iqbal Ali. Irrigation and Hydraulic Structures: Theory, Design and Practice, Publisher, Institute of Environmental Engineering & Research, NED University of Engineering &Technology, Karachi Awan, N.M. 1981. Surface Water Hydrology, National Book Foundation, Islamabad. Linsely, R.K., Kohler, Hydrology for Engineers, SI. Edition, McGraw Hill, 1996. Driscoll, F.G. Groundwater and Wells, Johnson Division, USA, 1987.
6. ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING i. Public Health Engineering Water Supply and Sewerage System Design Water Quality: physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of water, water borne diseases and their control, water quality guidelines/standards, water quality monitoring Water Treatment and Design: screening, plain sedimentation, sedimentation aided with coagulation and flocculation, filtration, disinfection, water softening, removal of colours, odours and tastes from waters, removal of iron and manganese from water, fluoridation and de-fluoridation of water, desalination of brackish water Waste Water Treatment and Design: estimation of sewage quantities, characteristics of sewage, effluent disposal guidelines and standards, types of reactors, unit operations and processes, physical, chemical and biological treatment processes, biological nitrification and de-
nitrification, advance treatment (e.g. phosphorous removal, wetland treatment), sludge treatment (anaerobic) and disposal, re-use of sewage, environmental legislation and regulations. ii. Environmental Engineering Solid Waste Management and Design: types and characteristics of solid waste, sources and quantities of solid waste, collection, disposal and recycling of solid waste Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): Definitions of EIA, IEE, EIS, methods, techniques and procedures of EIA, format for the organization of EIA report, legislative and regulatory considerations Environmental Legislation and Regulations Noise and Air Pollution: noise pollution (sources, causes and control, noise quality standards in Pakistan, test procdures), air pollution(sources, causes and control, air pollution and human health, air quality standards, legislation and regulation in Pakistan, elementary study of dispersion models, haze, fog, smog).
Suggested Books: Terence J McGhee, Water Supply and Sewerage, 6th Ed, McGraw Hill, ISBN: 0070609381 Metcalf and Eddy, Waste Water Engineering, 3rd Ed, McGraw Hill Mackenzie L. Davis, David A. Cornwell, Introduction to Environmental Engineering, 4th Ed. McGraw Hill, 2000. Canter L. W. EIA?? ------------------------
7. URBAN ENGINEERING
1. Urban Sociology
Urban and rural; family, household and clan Types and formats of social relationship Urban communities Space and its types (physical, social and economic); Social infrastructure Sociology and development (social and psychological characteristics)
Suggested books: Bard John W., Urban Sociology, Illinois, F. E. Peacock.
2. Urban Planning and Management i. Urban Planning and Management Context Current planning process in Pakistan with special focus on Karachi; Inter-governmental relationships in local planning its complexity and unresolved issues Basic Studies of Urban Planning Population/demographic study
ii.
iii.
Land use study
Implementation, Policies, Plans, Programs, Regulation and Renewal Definitions of development objectives, policy and planning program Comprehensive plan and its related documentation process Programming of community development and capital intensive projects of government Urban zoning issues; Land subdivisions (both at formal and informal level)
Suggested books: Kenneth J.Davay, Elements of Urban Management (1993), UMPUNCHS. David E.Dowall and Giles Clarke, A Framework for Reforming Urban Land Policies in Developing Countries (Aug.1996), UMPUNCHS. William J.Fox, Strategic Options for Urban Infrastructure Management, UMP-UNCHS. John Ratcliffe, Introduction to Town & Country Planing, Hutchinson & Co. Ltd. London. 3. Advanced Technologies and Disaster Management i. Constructional Technologies Latest development in trenching and excavation e.g. trench less technology; Specialized formworks Technologies for building deep waterproof basements Mechanized construction methods and equipments Maintenance Rehabilitation & Repair Disaster Management Strategies for protection Loss estimation Risk and Vulnerability Analysis Disaster Mitigation
ii.
Suggested books: W. Ronald Hudson, Infrastructure Management: Integrating Design, Construction, Maintenance Rehabilitation and Renovation, John Wiley and Sons. Steven K. Kramer, An Introduction to Trench less Technology, Van Nostrand Reinhold C. M. Barrit, Advanced Building Construction, Trans-Atlantic Publications
4. Law and Regulatory Control Studies i. Building plans Submission of Building applications and drawings
Procedural checks: ownership verification; planning application forms; Drawing fees, No objection certificates, Advertisement; etc. Site visits Serving of notices Fines and compounding of violation Analysis of building proposals: conformity with the development plans, land use zoning planning criteria building bylaws, design guidelines, building line / parking requirements, chamfer requirements, construction over cultivators etc
Suggested books: Sindh Building Control Ordinance 1979, 1979, Sindh Government Press Karachi Building and Town Planning Regularities (Parts I & II), Sindh Government Press Karachi Building and Town Planning Regularities 2002, 2002, Sindh Government Press Sindh Local Government Ordinance 1979, 1979, Sindh Government Press 5. Financial Resource Management i. Capital financing and Allocation Difference between sources of capital Equity and borrowed capital Banking and specialized Credit Institution Functions of Bank and Credit Institution Documentation related to International and Domestic Banks Financial and funding Institutions
ii.
Suggested books: Eugene F. Brigham, Financial Management Theory & Practice, Harcourt College 8. i. BUILDING AND ARCHITECTURAL ENGINEERING Structures Plain cement concrete: materials, properties, production, testing, batching, curing, admixtures, mechanics and behavior, simple & TBeam design, axially loaded columns, codes provision, reinforcement detailing Reinforced and prestressed concrete design: design of structural system of RC Frames, beam design in flexure shear and torsion, slabs & columns design, prestressed concrete analysis and design, losses of prestress
Structural Dynamics and Earth Quake Engineering: free and forced vibration, SDOF and MDOF system, earthquake resistance structures, seismic zoning of Pakistan
Foundation Engineering: stress distribution, earth pressure, bearing capacity, foundations and structural design of footings, ground improvement techniques
Steel Structures: types of structural steel, design & analysis of structural components, allowable stress design, plastic analysis and design
Suggested Books: Concrete Technology by A.M. Neville Design of concrete structures by A.H.Nilson 13th Edition Design of Concrete structures (part I, II) by Prof Zahid A Siddiqui Dynamics of Structures by Anil K Chopra Fundamental structural steel design by ASD by Thomas Burns Design of steel structures by Gaylord & Gaylord Steel structre design & behavior CG Sollman and John E Johnson
ii. Water Supply and Sewerage System Design for Buildings: Water Supply Systems: design period, population and estimation of quantity, hydraulics and design of water distribution system, type of pipe materials Waste water collection systems: sanitary and storm sewers, pumping stations, hydraulics and design of sanitary and storm sewers Plumbing Design: plumbing elements, layout and design of water supply and drainage pipes, systems for fire prevention, detection and control Water Treatment: drinking water quality, standards and public health, sedimentation, coagulation, filtration and disinfection Waste water treatment: primary and secondary treatment methods Environmental protection: solid waste, air control and environmental remediation.
Suggested Books: Water Supply and Sewerage by TJ McGhee & EW Steel
iii. Building HVACs System Sesign Building Air Systems: air transportation system used in heating, ventilation and air conditioning Building Hydraulics System: water transportation system used in building, heating and cooling Building Thermal Systems: thermal energy flow in building and building systems HVAC system: HVAC equipment description, HVAC system types and its applications in buildings Engineering design and performance analysis: mechanical systems and energy conservation techniques
Suggested Books: Air Conditioning Principles & systems by Edward G Pita ASHRAE HANDBOOK FUNDAMENTALS
iv. Building Electrical System Design: Electrical equipment ratings: voltage and current Interior wiring systems: cables, conductors and enclosures Busway/busduct: light duty busway, flat cable assembly, lighting track Cable tray/raceways: steel, aluminum, flexible, non metallic, conduits, raceway and wiring systems Communication and security systems: materials and installation systems Voice and data communication system: data communication systems, terminal host system, local area network, video network. Electronic Security System: level of security, types of security technologies communications types,
Suggested Books: Modern Wiring Practice by WE Steward
Electrical Installation Calculations by A J Watkins
v. Building Construction and Management Introduction: building construction, site and sitework Masonry: structural properties, construction system, materials under stresses Concrete: structural properties, construction system, concrete wall, roof systems, materials under stresses Steel: structural properties, floor systems, wall systems, roof systems. Timber: structural properties, floor systems, wall systems, roof systems Construction Management: organizational structures, contract and procurement, management Construction Laws, ISO 9000 and total quality
Suggested Books: Barry's Introduction to Construction of Buildings Building Construction Handbook by Ray Chudley & Roger Greeno Mitchell's Structure & Fabric Part 2 Building Construction by B C Punima Project Management by J R Meredith and S J Mantel
Você também pode gostar
- Syllabus Abd Books For Semester As Per ManitDocumento3 páginasSyllabus Abd Books For Semester As Per ManitAviral UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- Cover & Table of Contents - Fundamentals of Structural Analysis (2nd Edition)Documento14 páginasCover & Table of Contents - Fundamentals of Structural Analysis (2nd Edition)braveknight940% (1)
- 58D6D3 Storm Water Inlet Design Curb Inlets Us UnitsDocumento2 páginas58D6D3 Storm Water Inlet Design Curb Inlets Us UnitsMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Building Economics Group AssignmentDocumento12 páginasBuilding Economics Group Assignmentapi-323157773Ainda não há avaliações
- Suspended ScaffoldsDocumento29 páginasSuspended ScaffoldsJason Leo100% (1)
- Main Seawater Pump Overhaul ReportDocumento7 páginasMain Seawater Pump Overhaul ReportPrakhyati RautAinda não há avaliações
- 04 Marl Chemical Park PDFDocumento36 páginas04 Marl Chemical Park PDFAnusha Rajagopalan100% (1)
- Renovating a House Guide: Essentials for Your ProjectDocumento15 páginasRenovating a House Guide: Essentials for Your ProjectM iqbalAinda não há avaliações
- Concrete Batch Plant Control Plan PDFDocumento42 páginasConcrete Batch Plant Control Plan PDFkatfy1Ainda não há avaliações
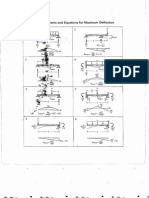
- Curriculm of Civil Engg& Allied DisciplineDocumento21 páginasCurriculm of Civil Engg& Allied DisciplineAbbasabbasiAinda não há avaliações
- Curriculum of Chemical EnggDocumento23 páginasCurriculum of Chemical Enggfaizfrasat123Ainda não há avaliações
- Automobile Enginneering SyllabusDocumento139 páginasAutomobile Enginneering SyllabusJinu Madhavan100% (1)
- PAKISTAN ENGINEERING COUNCIL EPE SYLLABUSDocumento5 páginasPAKISTAN ENGINEERING COUNCIL EPE SYLLABUSTaimur AkhtarAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed SyllabusDocumento81 páginasDetailed Syllabuspankajchandre30Ainda não há avaliações
- EN09 301: Engineering Mathematics IIIDocumento9 páginasEN09 301: Engineering Mathematics IIIArjun CpAinda não há avaliações
- Minor CivilDocumento4 páginasMinor Civilabdelhak AouadiAinda não há avaliações
- CSE Syl BOS 14-15 Draft-41-80Documento40 páginasCSE Syl BOS 14-15 Draft-41-80prasathAinda não há avaliações
- B.Tech. (1 Year) - 2012-13: (And ElectronicsDocumento21 páginasB.Tech. (1 Year) - 2012-13: (And ElectronicsSidharth SabyasachiAinda não há avaliações
- BE - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SEMESTER 1 SUBJECTSDocumento72 páginasBE - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SEMESTER 1 SUBJECTSmenilanjan89nLAinda não há avaliações
- PUC Summer Courses SyllabusDocumento10 páginasPUC Summer Courses SyllabusHoney AliAinda não há avaliações
- CIVIL ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE 1st Semester Anna UniversityDocumento25 páginasCIVIL ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE 1st Semester Anna UniversityJinu Madhavan100% (1)
- M Tech (Structural) SyllabusDocumento17 páginasM Tech (Structural) SyllabusAlfares AlmogedAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Madras, ChennaiDocumento2 páginasDepartment of Civil Engineering, IIT Madras, ChennaiAnonymous C3bCbLBfOaAinda não há avaliações
- 16MGU-Btech2010 PEDocumento127 páginas16MGU-Btech2010 PEPaul AugustineAinda não há avaliações
- 0 CE 7930 CG Teach Final 21Documento2 páginas0 CE 7930 CG Teach Final 21GoudaAinda não há avaliações
- NotificationDocumento4 páginasNotificationNayeem SheikAinda não há avaliações
- Civil IVDocumento14 páginasCivil IVDivya RajasekarAinda não há avaliações
- I year 2nd semester subjectsDocumento15 páginasI year 2nd semester subjectspranavateja12399Ainda não há avaliações
- Civil New34Documento21 páginasCivil New34preeti sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus ETR 2019 20 Part BDocumento62 páginasSyllabus ETR 2019 20 Part BrajuAinda não há avaliações
- 1st - & - 2nd - Sem - Diploma SyllabusDocumento50 páginas1st - & - 2nd - Sem - Diploma Syllabusvj4249Ainda não há avaliações
- Asian Institute of Technology Electronic Documentation FormDocumento7 páginasAsian Institute of Technology Electronic Documentation FormspratiwiaAinda não há avaliações
- SEMESTER 3 OutlineDocumento6 páginasSEMESTER 3 OutlineHamza MughalAinda não há avaliações
- Degree in MechDocumento26 páginasDegree in MechRaj AnooshAinda não há avaliações
- Ph.D. Course Work Syllabus in Civil Engg.Documento15 páginasPh.D. Course Work Syllabus in Civil Engg.arunachelamAinda não há avaliações
- B Arch Syllabus I IV 14 15Documento38 páginasB Arch Syllabus I IV 14 15Teenesh VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus ETR 2019 20 Part BDocumento53 páginasSyllabus ETR 2019 20 Part BBoban MathewsAinda não há avaliações
- Uit RGPV First Year SyllabusDocumento19 páginasUit RGPV First Year SyllabusYasir MujtabaAinda não há avaliações
- Cons Engg PDFDocumento22 páginasCons Engg PDFkanithaAinda não há avaliações
- Top 30 Chemical Engineering TextbooksDocumento28 páginasTop 30 Chemical Engineering TextbooksAnonymous 8pCXXsAinda não há avaliações
- Draft - Syllabus For S1 and S2 - KTUDocumento56 páginasDraft - Syllabus For S1 and S2 - KTUvpzfarisAinda não há avaliações
- Epe ExaminationDocumento20 páginasEpe ExaminationZohaib Alam WarraichAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd Year Eng - Outline PDFDocumento7 páginas3rd Year Eng - Outline PDFkingAinda não há avaliações
- ME PE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus 06.07.11Documento25 páginasME PE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus 06.07.11Kanishka BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- M Arch ArchitechtureDocumento31 páginasM Arch ArchitechtureManjul PratapAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus June 2010Documento76 páginasSyllabus June 2010shreya1106Ainda não há avaliações
- A Syllabus in CE 41Documento7 páginasA Syllabus in CE 41CONNIE INQUIGAinda não há avaliações
- ECE Sem 4 SyllabusDocumento12 páginasECE Sem 4 SyllabusDaksh SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- MCESC Structural Engineering and Construction ManagementDocumento23 páginasMCESC Structural Engineering and Construction ManagementsonofalexanderAinda não há avaliações
- (Electrical Engineer) Part I & II: Detailed Syllabus of Technician Membership ExaminationDocumento20 páginas(Electrical Engineer) Part I & II: Detailed Syllabus of Technician Membership ExaminationRavi BoparaiAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Engineering Body of KnowledgeDocumento34 páginasIndustrial Engineering Body of KnowledgeSolinx ChannelAinda não há avaliações
- Aerospace Engineering SyllabusDocumento144 páginasAerospace Engineering SyllabusMaster WayneAinda não há avaliações
- VTU Syllabus Analysis and DesignDocumento13 páginasVTU Syllabus Analysis and DesignSwamy ManiAinda não há avaliações
- BTech 4th Year 8th Semester SyllabusDocumento6 páginasBTech 4th Year 8th Semester SyllabusM RoyAinda não há avaliações
- SE5 M.Sc. INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYDocumento93 páginasSE5 M.Sc. INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYwwea1234Ainda não há avaliações
- Shepherd-SurveyingProblemsSolutions Text PDFDocumento677 páginasShepherd-SurveyingProblemsSolutions Text PDFbkpanda23100% (3)
- Reference BooksDocumento4 páginasReference BooksSri WatsonAinda não há avaliações
- Semester 1 Subjects for 09F101 EnglishDocumento28 páginasSemester 1 Subjects for 09F101 EnglishRohan KhilareAinda não há avaliações
- RVR & JC - ECE - First Year Text BooksDocumento11 páginasRVR & JC - ECE - First Year Text Booksg3murtuluAinda não há avaliações
- Gtu Be Civil First YearDocumento14 páginasGtu Be Civil First YearHR Divya RanaAinda não há avaliações
- MTech Infrastructure Engg R13 RegulationsDocumento28 páginasMTech Infrastructure Engg R13 RegulationsRavi Shankar KolluruAinda não há avaliações
- Models in Planning: An Introduction to the Use of Quantitative Models in PlanningNo EverandModels in Planning: An Introduction to the Use of Quantitative Models in PlanningNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (2)
- Mathematical Theory of Connecting Networks and Telephone TrafficNo EverandMathematical Theory of Connecting Networks and Telephone TrafficAinda não há avaliações
- Optimization Techniques: With Applications to Aerospace SystemsNo EverandOptimization Techniques: With Applications to Aerospace SystemsAinda não há avaliações
- Statistical Techniques for Transportation EngineeringNo EverandStatistical Techniques for Transportation EngineeringNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- 1 s2.0 S2588912518300262 MainDocumento15 páginas1 s2.0 S2588912518300262 MainJunaid ArshadAinda não há avaliações
- Final Evaluatio Report Testing Service Pg1Documento1 páginaFinal Evaluatio Report Testing Service Pg1Muhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- (Total Plots Allotted) : Successful Applicants Wapda Employees - 05 MarlaDocumento25 páginas(Total Plots Allotted) : Successful Applicants Wapda Employees - 05 MarlaMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Tit TocDocumento7 páginasTit TocMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Federal Government Employees Housing FoundationDocumento2 páginasFederal Government Employees Housing FoundationMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Table With Lat Lon To Shapefile ArcGIS v10.1Documento2 páginasTable With Lat Lon To Shapefile ArcGIS v10.1Muhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- SR 421 Mainstreaming Pakistan Federally Administered Tribal AreasDocumento20 páginasSR 421 Mainstreaming Pakistan Federally Administered Tribal AreasNida HammadAinda não há avaliações
- JP Project Manager-She Can LeadDocumento8 páginasJP Project Manager-She Can LeadMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges of FATA MergerDocumento5 páginasChallenges of FATA MergerMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Programme Detail MS Management SciencesDocumento2 páginasProgramme Detail MS Management SciencesMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Invitation to Bid for Goods, Works and Non-Consulting ServicesDocumento1 páginaInvitation to Bid for Goods, Works and Non-Consulting ServicesMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Harmonized World Soil DatabaseDocumento43 páginasHarmonized World Soil DatabaseMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- GM GSC For PermissionDocumento1 páginaGM GSC For PermissionMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- NTDCL Casual Leave Application FormDocumento1 páginaNTDCL Casual Leave Application FormMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Application Form Enlistment DrillerDocumento3 páginasApplication Form Enlistment DrillerMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Sen 1968 Sen's Slope MethodDocumento12 páginasSen 1968 Sen's Slope MethodMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Application For SWH-DataDocumento2 páginasApplication For SWH-DataMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Mann KendallDocumento4 páginasMann KendallOm Prakash SahuAinda não há avaliações
- Mann 1945Documento16 páginasMann 1945Muhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Specifications For BeadingDocumento1 páginaSpecifications For BeadingMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Rainfall DataDocumento36 páginasRainfall DataMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Bisma NazDocumento2 páginasBisma NazMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Curriculum Vita Amber NewDocumento8 páginasCurriculum Vita Amber NewMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Upgrading 100 Primary Schools in Khyber PakhtunkhwaDocumento2 páginasUpgrading 100 Primary Schools in Khyber PakhtunkhwaMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Boq AliaDocumento126 páginasBoq AliaMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- BoqDocumento37 páginasBoqMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- 5FEAF3 Storm Water Inlet Design Gutter Inlets Si UnitsDocumento2 páginas5FEAF3 Storm Water Inlet Design Gutter Inlets Si UnitsMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Bill of QuantityDocumento2 páginasBill of QuantityMuhammad Shakil JanAinda não há avaliações
- Earth Pressure CalculationsDocumento35 páginasEarth Pressure Calculationskeddy lamarAinda não há avaliações
- Never-Seez® India Call +91-891-6666482Documento2 páginasNever-Seez® India Call +91-891-6666482Project Sales CorpAinda não há avaliações
- Basalt FRP Reinforcing Bars For Concrete StructuresDocumento6 páginasBasalt FRP Reinforcing Bars For Concrete StructuresSuresh ShanmugavelAinda não há avaliações
- Rab Venturi Wet Scrubber 00Documento2 páginasRab Venturi Wet Scrubber 00rudiawanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Cold FormingDocumento54 páginasIntroduction To Cold FormingRestu SihotangAinda não há avaliações
- Cable Element Analysis TechniquesDocumento16 páginasCable Element Analysis TechniquesPankaj_Taneja_9684Ainda não há avaliações
- Handouts of The Presentations - Seminar On Introduction To New Guidelines For Seismic Design of Road BridgesDocumento105 páginasHandouts of The Presentations - Seminar On Introduction To New Guidelines For Seismic Design of Road BridgesChaitu Rishan100% (1)
- Concrete Mix Design Methods, Verification StudyDocumento26 páginasConcrete Mix Design Methods, Verification StudyAhmed M AminAinda não há avaliações
- TH255C Engine CAT PartsDocumento134 páginasTH255C Engine CAT PartsKevine KhaledAinda não há avaliações
- Lts-Cvg-P01-16-0005-A4 Daar PDFDocumento32 páginasLts-Cvg-P01-16-0005-A4 Daar PDFSanjoy SanyalAinda não há avaliações
- Carrier Infinity Control Owners ManualDocumento35 páginasCarrier Infinity Control Owners ManualsunshineorthodocAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials-II 2-2 Set-3 (A)Documento18 páginasStrength of Materials-II 2-2 Set-3 (A)Sri DAinda não há avaliações
- 02-04 Chap GereDocumento12 páginas02-04 Chap GereSri DAinda não há avaliações
- 17 4Documento2 páginas17 4fedaquiAinda não há avaliações
- Ruelco Fuse Plug LiteratureDocumento3 páginasRuelco Fuse Plug Literaturenk1.testmailAinda não há avaliações
- Catalogue Tylo Sauna RoomsDocumento28 páginasCatalogue Tylo Sauna RoomsVictor NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Structural steel design guide contentsDocumento1 páginaStructural steel design guide contentsNeeraj DubeyAinda não há avaliações
- SABP-Q-010 Mix Design and Construction of Sulfur Extended Asphalt ConcreteDocumento26 páginasSABP-Q-010 Mix Design and Construction of Sulfur Extended Asphalt ConcreteMr. Moses Imagoro100% (1)
- Cold-Formed Steel Shear Wall DesignDocumento8 páginasCold-Formed Steel Shear Wall DesignjmiguelmenaAinda não há avaliações
- Workshop 2011 - 03121936Documento551 páginasWorkshop 2011 - 03121936FR100% (2)
- Assignment-10 CE39 NOC20Documento7 páginasAssignment-10 CE39 NOC20jayadeep ksAinda não há avaliações
- NEC 316.10 Ampacity Table For Cable Conductor SizingDocumento1 páginaNEC 316.10 Ampacity Table For Cable Conductor SizingHumayun RazaAinda não há avaliações
- Presentasi Ahu DXDocumento17 páginasPresentasi Ahu DXpt.esasurya arcapadaAinda não há avaliações