Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
RS449 37 Pin Pinout
Enviado por
Abhishek KumarDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
RS449 37 Pin Pinout
Enviado por
Abhishek KumarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
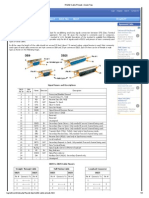
RS-449 (EIA-449) Serial 37 pin Connector Pinout
From AllPinouts
Connector pinout for: RS-449 (EIA-449) Serial 37 pin
37 pin D-SUB male connector at the DTE (Computer).
37 pin D-SUB female connector at the DCE (Modem). The RS449 interface is a generic connector specification. It's not an actual interface. The connector pinning was originally designed to support RS422 for balanced signals, and RS423 for the unbalanced signals. And should have been the successor of RS232. RS449 is a high speed digital interface - unlike RS232 which uses signals with reference to ground, RS449 V.11 receivers look for the difference between two wires. By twisting the two wires and making a "twisted pair" any stray noise picked up on one wire will be picked up on the other, because both wires pick up the same noise the RS449 differential interface just shifts in voltage level with reference to ground, but does not change with respect to each other. The receivers are only looking at the difference in voltage level of each wire to the other not to ground. The differential signals for RS449 are labeled as either "A and B" or "+ and -". In the case of RS449 wire A or + does not connect to B or -. Wire A always connects to A and B connects to B or + to + and - to -. If you do cross the wires you just inverted the data or clock in your interface and they don"t work - be sure to check the polarities. The EIA RS449 standard specifies the functional and mechanical characteristics of the RS449 interconnection between the data terminal equipment (DTE) in the data communications equipment (DCE) complying to EIA electrical interface standards RS 422 and RS 423.
Pin Name V.24
Dir
Description
Type
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 SI n/a SDSTRDRSRTCS-
101 112 103 114 104 105 115 106 141 107 109 140 125 113 142 102
OUT n/a OUT IN IN OUT IN IN OUT IN IN OUT IN OUT IN n/a
Shield Signal Rate Indicator unused Send Data (A) Send Timing (A) Receive Data (A) Request To Send (A) Receive Timing (A) Clear To Send (A) Local Loopback Data Mode (A) Terminal Ready (A) Receiver Ready (A) Remote Loopback Incoming Call Terminal Timing (A) Test Mode (A) Signal Ground Receive Common unused Send Data (B) Send Timing (B) Receive Data (B) Request To Send (B) Receive Timing (B) Clear To Send (B) Terminal In Service Data Mode (B) Terminal Ready (B) Receiver Ready (B) Select Standby Signal Quality New Signal
Ground Control Data Timing Data Control Timing Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Timing Control Ground Ground Data Timing Data Control Timing Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control
10 LL 11 DM12 TR13 RR14 RL 15 IC 17 TT18 TM19 SG 20 RC 21 n/a 22 SD+ 23 ST+ 24 RD+ 25 RS+ 26 RT+ 27 CS+ 28 IS 29 DM+ 30 TR+ 31 RR+ 32 SS 33 SQ 34 NS
108.2 OUT
16 SF/SR+ 126
IN/OUT Signal Freq./Sig. Rate Select. Control
102b 103 114 104 105 115 106 n/a 107 109 116 110 n/a OUT IN IN OUT IN IN OUT IN IN IN IN OUT
108.2 OUT
35 TT+ 36 SB 37 SC
113 117
OUT IN
Terminal Timing (B) Standby Indicator Send Common
Timing Control Ground
102a -
Name AA AB BA BB CA CB CC CD CE CF
Description Shield Ground Signal Ground Received Data
Function Also known as protective ground. This is the chassis ground connection between DTE and DCE. The reference ground between a DTE and a DCE. Has the value 0 Vdc. Data received by the DTE. Send by the DCE as a reply on the RTS after a delay in ms, which gives the DCEs enough time to energize their circuits and synchronize on basic modulation patterns. Known as DSR. Originated by the DCE indicating that it is basically operating (power on, and in functional mode). Known as DTR. Originated by the DTE to instruct the DCE to setup a connection. Actually it means that the DTE is up and running and ready to communicate. A signal from the DCE to the DTE that there is an incomming call (telephone is ringing). Only used on switched circuit connections. Known as DCD. A signal send from DCE to its DTE to indicate that it has received a basic carrier signal from a (remote) DCE.
Transmitted Data Data send by the DTE. Request To Send Originated by the DTE to initiate transmission by the DCE. Clear To Send DCE Ready DTE Ready Ring Indicator Received Line Signal Detector
Data Signal Rate Select CH/CI A control signal that can be used to change the transmission speed. (DTE/DCE Source> DA Transmit Signal Element Timing (DTE Source) Timing signals used by the DTE for transmission, where the clock is originated by the DTE and the DCE is the slave.
DB
Transmitter Signal Element Timing Timing signals used by the DTE for transmission. (DCE Source) Receiver Signal Element Timing (DCE Source) terminal In Timing signals used by the DTE when receiving data. Signal that indicates that the DTE is available for operation
DD IS
Service NS RC LL RL SB SC SF SS TM New Signal A control signal from the DTE to the DCE. It instructs the DCE to rapidly get ready to receive a new analog signal. It helps master-station modems rapidly synchronize on a new modem at a tributary station in multipoint circuits
Receive Common A signal return for receiver circuit reference Local Loopback / A control signal from the DTE to the DCE that causes the analog Quality Detector transmision output to be connected to the analog receiver input. Signal from the DTE to the DCE. The local DCE then signals the Remote Loopback remote DCE to loopback the analog signal and thus causing a line loopback. Standby Indicator Send Common Select Frequency Select Standby Test Mode Reserved for Testing Signal from the DCE to indicate if it is uses the normal communication or standby channel A return signal for transmitter circuit reference A signal from the DTE to tell the DCE which of the two analog carrier frequencies should be used. A signal from DTE to DCE, to switch between normal communication or standby channel. A signal from the DCE to the DTE that it is in test-mode and can"t send any data.
Você também pode gostar
- Rs 232 TutorialDocumento7 páginasRs 232 Tutorialapi-26695410100% (1)
- Rs-232 Interface: Computer TerminalDocumento4 páginasRs-232 Interface: Computer TerminalJames MojicaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 3Documento3 páginasAssignment 3Nutan NiraulaAinda não há avaliações
- RS232 Data Interface: A TutorialDocumento25 páginasRS232 Data Interface: A TutorialMr. SCIFIAinda não há avaliações
- AN83 Maxim Fundamentals of RS-232 Serial CommunicationsDocumento9 páginasAN83 Maxim Fundamentals of RS-232 Serial CommunicationsCarlos Roman Zarza100% (1)
- Tech Serial v1r0c0 PDFDocumento15 páginasTech Serial v1r0c0 PDFsalehimohsen13514969100% (1)
- RS232 Data Interface: A TutorialDocumento23 páginasRS232 Data Interface: A TutorialvinothvlbAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To Serial Port InterfacingDocumento25 páginasAn Introduction To Serial Port InterfacingAyushi GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- DB9 To DB25Documento3 páginasDB9 To DB25Bayu WiroAinda não há avaliações
- Pengantar RS232Documento26 páginasPengantar RS232beben honAinda não há avaliações
- OSI Physical Layer Components: Digital and Data CommunicationsDocumento28 páginasOSI Physical Layer Components: Digital and Data CommunicationsFranch Maverick Arellano LorillaAinda não há avaliações
- SignalsDocumento2 páginasSignalsRytis UrbonavičiusAinda não há avaliações
- WaterLog RS 232 Communications Technical NoteDocumento5 páginasWaterLog RS 232 Communications Technical NoteEng-ahmed ismail -مهندس كهرباءAinda não há avaliações
- Data Communication Over Telephone LinesDocumento3 páginasData Communication Over Telephone LinesAnand Asia100% (1)
- Serial Interfaces: RS-232 InterfaceDocumento3 páginasSerial Interfaces: RS-232 InterfaceIgnacio CatalanAinda não há avaliações
- Modes of Data TransmissionDocumento47 páginasModes of Data Transmissionadithya123456100% (1)
- Pinouts For Serial InterfacesDocumento7 páginasPinouts For Serial InterfacestuAinda não há avaliações
- DCT 03 Exp 01 Db9 ConnectorDocumento4 páginasDCT 03 Exp 01 Db9 ConnectorGia TríAinda não há avaliações
- RS232 Cable Pinouts - Quick TipsDocumento3 páginasRS232 Cable Pinouts - Quick TipsnixlynxAinda não há avaliações
- Serial Communication ProtocolsDocumento32 páginasSerial Communication ProtocolsVissu Sweet100% (1)
- RS 232 Specification StandardDocumento9 páginasRS 232 Specification StandardTetsusaigaAinda não há avaliações
- Application Note: App. Note Number: 1003 Title: RS-232 CommunicationsDocumento11 páginasApplication Note: App. Note Number: 1003 Title: RS-232 CommunicationsRamya VkAinda não há avaliações
- Appendix On Communication StandardsDocumento9 páginasAppendix On Communication StandardsTiến BùiAinda não há avaliações
- RS232Documento29 páginasRS232Pravish Sainath100% (1)
- RS-449 Serial Interface StandardsDocumento9 páginasRS-449 Serial Interface StandardsGlenda GragedaAinda não há avaliações
- Serial Communication Using Atmega16 MicrocontrollerDocumento4 páginasSerial Communication Using Atmega16 MicrocontrollerAnupam AkanshaAinda não há avaliações
- The X.21 InterfaceDocumento10 páginasThe X.21 InterfaceThakur Sahil NarayanAinda não há avaliações
- Serial Interfaces: RS-232 InterfaceDocumento3 páginasSerial Interfaces: RS-232 InterfacejkmaroAinda não há avaliações
- Ds92Lv16: Ds92Lv16 16-Bit Bus Lvds Serializer/Deserializer - 25 - 80 MHZDocumento21 páginasDs92Lv16: Ds92Lv16 16-Bit Bus Lvds Serializer/Deserializer - 25 - 80 MHZlur46Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2Documento29 páginasLecture 2Vinitha ViswanathanAinda não há avaliações
- RS232 Cable Pinouts - Quick TipsDocumento3 páginasRS232 Cable Pinouts - Quick TipsstudskirbyAinda não há avaliações
- Rs 232 & Rs 422 StandardDocumento27 páginasRs 232 & Rs 422 Standardpalak parmar100% (3)
- 8251 UsartDocumento14 páginas8251 Usartmohit mishraAinda não há avaliações
- History and Theory of Serial CommunicationsDocumento18 páginasHistory and Theory of Serial Communicationscam894Ainda não há avaliações
- What Is RS232 PDFDocumento4 páginasWhat Is RS232 PDFtjiangtjiangs100% (1)
- NE8392C Coaxial Transceiver Interface For Ethernet/Thin EthernetDocumento9 páginasNE8392C Coaxial Transceiver Interface For Ethernet/Thin Ethernetcatsoithahuong84Ainda não há avaliações
- GEM4000 - Interface ManualDocumento84 páginasGEM4000 - Interface Manual박수희Ainda não há avaliações
- DS2143/DS2143Q E1 Controller: Features Pin AssignmentDocumento44 páginasDS2143/DS2143Q E1 Controller: Features Pin AssignmentEngMohammedAMaqdamAinda não há avaliações
- RS232 CablesDocumento18 páginasRS232 CablesDoodyjonh Scott RockefellerAinda não há avaliações
- Single-Chip Modem Provides Low-Cost Data Communication: National Semiconductor Application Note 444 Wesley Lee July 1986Documento16 páginasSingle-Chip Modem Provides Low-Cost Data Communication: National Semiconductor Application Note 444 Wesley Lee July 1986Luis CarlosAinda não há avaliações
- Tda 10021 DatasheetDocumento17 páginasTda 10021 DatasheetWilly DacoAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Manual DAC-SignedDocumento10 páginasLab Manual DAC-Signedabidrk_21789100% (2)
- Industrial Data Communications - RS-232/RS-485: Tutorial 2Documento5 páginasIndustrial Data Communications - RS-232/RS-485: Tutorial 2Pedro Ferreira100% (4)
- Logic 1 and Is Historically Referred To As "Marking." Similarly, A High Level (+3V To +15V) Is Defined As Logic 0 and Is Referred To As "Spacing."Documento4 páginasLogic 1 and Is Historically Referred To As "Marking." Similarly, A High Level (+3V To +15V) Is Defined As Logic 0 and Is Referred To As "Spacing."Mohammad NadimAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamic Testing of Highspeed Adcs Part 2Documento17 páginasDynamic Testing of Highspeed Adcs Part 2ketkyhuAinda não há avaliações
- Netzer DS 247 128 SpecsheetDocumento8 páginasNetzer DS 247 128 SpecsheetElectromateAinda não há avaliações
- All IBM PC and Compatible Computers Are Typically Equipped With Two Serial Ports and One Parallel PortDocumento16 páginasAll IBM PC and Compatible Computers Are Typically Equipped With Two Serial Ports and One Parallel Port452bobAinda não há avaliações
- Interfacing HP Das (Rs-232) To Parallel Port of PC: D. Bhavsingh EC94001 M.Tech E.IDocumento23 páginasInterfacing HP Das (Rs-232) To Parallel Port of PC: D. Bhavsingh EC94001 M.Tech E.Ibhavsingh_pm007Ainda não há avaliações
- Technical Manual For Enhanced Data Switch Unit (EDSU) : HW Revision 1.2 SW Revision 2.1aDocumento22 páginasTechnical Manual For Enhanced Data Switch Unit (EDSU) : HW Revision 1.2 SW Revision 2.1aJon CornishAinda não há avaliações
- RS232 InterfaceDocumento3 páginasRS232 Interfacevairam81Ainda não há avaliações
- EDN Design Ideas 1998Documento166 páginasEDN Design Ideas 1998chag1956100% (4)
- 10-Bit Digital-To-Analog Converters: Features DescriptionDocumento22 páginas10-Bit Digital-To-Analog Converters: Features Descriptionwolvering2009Ainda não há avaliações
- T17 Interfaces: Chapter - 6Documento7 páginasT17 Interfaces: Chapter - 6lvsaruAinda não há avaliações
- Rs 232Documento16 páginasRs 232Nadeem YasirAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Ainda não há avaliações
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Nota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (3)
- Caterpillar Cat 303 CR Mini Hydraulic Excavator (Prefix DMA) Service Repair Manual (DMA00001 and Up)Documento21 páginasCaterpillar Cat 303 CR Mini Hydraulic Excavator (Prefix DMA) Service Repair Manual (DMA00001 and Up)kfmuseddk100% (6)
- Mini Camera User ManualDocumento4 páginasMini Camera User ManualAndronikus Marintan NapitupuluAinda não há avaliações
- Pipe Strut Vs Laced Strut - CSPDocumento39 páginasPipe Strut Vs Laced Strut - CSPAnonymous hhdd4mOmOh100% (1)
- Electrical System 3412C Engine: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic SymbolsDocumento2 páginasElectrical System 3412C Engine: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic SymbolsCarlos RamirezAinda não há avaliações
- Kubota BX2200 Operators Manual PDFDocumento64 páginasKubota BX2200 Operators Manual PDFСвятослав100% (1)
- HB-9500 User Manual (English)Documento8 páginasHB-9500 User Manual (English)mudkatAinda não há avaliações
- NXS 9750 Users Manual 2.8Documento54 páginasNXS 9750 Users Manual 2.8cradrodoliAinda não há avaliações
- Distribution Board Systems Made With ThermoplasticsDocumento9 páginasDistribution Board Systems Made With ThermoplasticsPhaniAinda não há avaliações
- 12.21.2019 Autowbrake Installaton FinalDocumento10 páginas12.21.2019 Autowbrake Installaton FinaljoeAinda não há avaliações
- Astm F855-2009 - 459Documento3 páginasAstm F855-2009 - 459EdsonHenriqueFerreiraAinda não há avaliações
- SM CR Orex PCCR 1417 Acl4 PDFDocumento77 páginasSM CR Orex PCCR 1417 Acl4 PDFVremedSoluCionesAinda não há avaliações
- Sony KDL 26 32 37 S5500 - CH - Ex2l SM PDFDocumento89 páginasSony KDL 26 32 37 S5500 - CH - Ex2l SM PDFP BAinda não há avaliações
- Manual de La Fire Power 260Documento24 páginasManual de La Fire Power 260jesus isturisAinda não há avaliações
- 793f, 797f, DO PDFDocumento2 páginas793f, 797f, DO PDFDennis Olaya100% (1)
- Earth-Fault and Short-Circuit Indicator Type: Elektro-MechanikDocumento5 páginasEarth-Fault and Short-Circuit Indicator Type: Elektro-MechanikMarius NagyAinda não há avaliações
- Protocolo AES EBUDocumento20 páginasProtocolo AES EBUEdson Francisco SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Philips 2Documento2 páginasPhilips 2mcrajpuraAinda não há avaliações
- Filabot Wee Pack Lists - Filabot Wee Kit Pack ListDocumento1 páginaFilabot Wee Pack Lists - Filabot Wee Kit Pack ListAzerie SabirAinda não há avaliações
- 84-1. GDM-19 Parts ListingDocumento16 páginas84-1. GDM-19 Parts ListingcarlosorizabaAinda não há avaliações
- Ahe58/59 Ac Servo System: Safely InstructionDocumento8 páginasAhe58/59 Ac Servo System: Safely InstructionDinh Nguyen100% (1)
- 18 Engine Lubrication - Unimog 435 Workshop ManualDocumento30 páginas18 Engine Lubrication - Unimog 435 Workshop ManualJuan JapAinda não há avaliações
- GP1850 Service Manual - FurunoDocumento24 páginasGP1850 Service Manual - FurunoCarlos Proaño100% (1)
- EASTMAN D2 Parts Manual PDFDocumento16 páginasEASTMAN D2 Parts Manual PDFFelipe VieiraAinda não há avaliações
- Armorblock 2-Port Ethernet/Ip Module: Installation InstructionsDocumento20 páginasArmorblock 2-Port Ethernet/Ip Module: Installation InstructionsJulio EcheverríaAinda não há avaliações
- Operating Instructions of ZLP Series Suspended Platform 1. OutlineDocumento29 páginasOperating Instructions of ZLP Series Suspended Platform 1. OutlineEpure Gabriel100% (1)
- Vibxpert Manual English PDFDocumento86 páginasVibxpert Manual English PDFRizki A-fAinda não há avaliações
- TUV Manual IEC2016 2022.04.11 PDFDocumento69 páginasTUV Manual IEC2016 2022.04.11 PDFFriedrichAinda não há avaliações
- 42,0426,0115, enDocumento72 páginas42,0426,0115, enMustafa KeleşAinda não há avaliações
- Servicemanual, Vp5000, EngDocumento60 páginasServicemanual, Vp5000, EngAugusto Vieira50% (2)
- Kwikee - Owners - Manual 888 For Series 32Documento12 páginasKwikee - Owners - Manual 888 For Series 32Benjamin WhighamAinda não há avaliações