Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Pa Tho Physiology
Enviado por
Joshina AnnDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Pa Tho Physiology
Enviado por
Joshina AnnDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
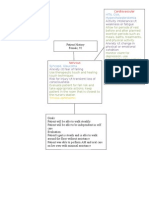
Pathophysiology: Definition: Hip replacement surgery is a procedure in which a doctor surgically removes a painful hip joint with arthritis
and replaces it with an artificial joint. It usually is done when all other treatment options have failed to provide adequate pain relief. Management of hip replacement: Use an abduction pillow or splint to prevent adduction after surgery if the patient is very restless or has an altered mental state. Keep the patient's heels off the bed to prevent pressure ulcers. Do not rely on fever as a sign of infection; older patients often have infection without fever. Decreasing mental status typically occurs when the patient has an infection. When assisting the patient out of bed, move him or her slowly to prevent orthostatic (postural) hypotension. Encourage the patient to deep breathe and cough, and use the incentive spirometer every 2 hours to prevent atelectasis and pneumonia. As soon as permitted, get the patient out of bed to prevent complications of immobility. Anticipate the patient's need for pain medication, especially if he or she cannot verbalize the need for pain control. Expect a temporary change in mental state immediately after surgery as a result of the anesthetic and unfamiliar sensory stimuli. Reorient the patient frequently. Observe for possible signs of hip dislocation, which include increased hip pain, shortening of the affected leg, and leg rotation. The most potentially life-threatening complication after THA is venous thromboembolism (VTE), which includes deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Older patients are especially at increased risk for VTE because of age and compromised circulation before surgery Post operative care: The surgeon also requests periodic hemoglobin and hematocrit (H&H) tests to assess for anemia. Check and document color, temperature, distal pulses, capillary refill, movement, and sensation. To prevent hip dislocation, ensure that he or she does not flex the hips beyond 90 degrees The length of stay in the acute care hospital is typically 3 days Teach Patient: Teach patient to keep from flexing hips more than 90 degrees and should use high chairs to sit on and walkers to move around. Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired physical mobility r/t musculoskeletal impairment and surgery - Before activity, observe for and, if possible, treat pain with massage, heat pack to affected area, or medication. Ensure that the client is not oversedated.
- Help the client achieve mobility and start walking as soon as possible if not contraindicated. Risk for injury r/t altered mobility
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocumento4 páginasFluid Volume ExcessTamil Villardo100% (2)
- Communicating With A Sleeping PersonDocumento104 páginasCommunicating With A Sleeping PersonPeterMoranAinda não há avaliações
- Liberation From Mechanical VentilationDocumento21 páginasLiberation From Mechanical VentilationRins Chacko50% (2)
- Leadership PP Version 3Documento24 páginasLeadership PP Version 3Joshina AnnAinda não há avaliações
- Drug ClassificationsDocumento10 páginasDrug ClassificationsJoshina AnnAinda não há avaliações
- 9 NovemberDocumento1 página9 NovemberJoshina AnnAinda não há avaliações
- Chapters 1 2Documento41 páginasChapters 1 2Joshina AnnAinda não há avaliações
- Apnea of PrematurityDocumento8 páginasApnea of PrematuritypatriaindraAinda não há avaliações
- Filum Platyhelmintes I. DefinitionDocumento38 páginasFilum Platyhelmintes I. DefinitionNsc Rhyrin 'syafa' LestariniAinda não há avaliações
- Abdominal IncisionsDocumento8 páginasAbdominal IncisionsdkasisAinda não há avaliações
- f3 Chapter 1Documento110 páginasf3 Chapter 1miracleambitiousAinda não há avaliações
- Acupuncture in India:: As Defined by The National Institutes of HealthDocumento3 páginasAcupuncture in India:: As Defined by The National Institutes of Healthmanikandan16Ainda não há avaliações
- Regulation of BPDocumento17 páginasRegulation of BPLemon CatbaganAinda não há avaliações
- 1289 - Andrology Labratory ManualDocumento245 páginas1289 - Andrology Labratory ManualJuragang PotilAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Stress in PlantsDocumento22 páginasHeat Stress in PlantsPao GabrielAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Amino AcidsDocumento25 páginas3 Amino AcidsrlznrecurAinda não há avaliações
- The Welfare of Cattle Kept For Beef ProductionDocumento150 páginasThe Welfare of Cattle Kept For Beef ProductionIsabel CarrilloAinda não há avaliações
- A Primer For The Primary FANZCA ExaminationDocumento62 páginasA Primer For The Primary FANZCA ExaminationAnnie100% (1)
- Assessment: Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocumento3 páginasAssessment: Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDelaine Mae MierAinda não há avaliações
- GENITOURINARYDocumento24 páginasGENITOURINARYrlinaoAinda não há avaliações
- Peng Kaji AnDocumento54 páginasPeng Kaji Anmabuhay crewAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus For The Post of Physical Education TeachersDocumento2 páginasSyllabus For The Post of Physical Education Teachersஅருள் முருகன்Ainda não há avaliações
- Aromatherapy SyllabusDocumento12 páginasAromatherapy SyllabusMyat Htun SoeAinda não há avaliações
- Nervous System NotesDocumento6 páginasNervous System NotesAlex Whitwam100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemDocumento4 páginasAnatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemJordz PlaciAinda não há avaliações
- Vedio 3Documento20 páginasVedio 3أحمد الكنديAinda não há avaliações
- ISMST Shockwave Medical Papers 2012Documento24 páginasISMST Shockwave Medical Papers 2012Dr-Gehad Samy Halwagy100% (1)
- Cansuje National High School: Quarter 3 Summative Test No. 1 in Science 10Documento3 páginasCansuje National High School: Quarter 3 Summative Test No. 1 in Science 10Jannet FuentesAinda não há avaliações
- July 6Documento13 páginasJuly 6Hanzelkris CubianAinda não há avaliações
- Simple AnatomyDocumento13 páginasSimple AnatomyNicky DaymondAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Exam-Health Specialist EditDocumento9 páginasDiagnostic Exam-Health Specialist EditAyuy Welliss MedusaAinda não há avaliações
- 67Documento57 páginas67Neeruam Ellehcim Aled ZurcAinda não há avaliações
- PathologyDocumento36 páginasPathologySayeed KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology of Local Anesthetics IDocumento93 páginasPharmacology of Local Anesthetics IAlshaimaa AhmedAinda não há avaliações