Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Explain and List Down The Factors Affecting Sight Clarity
Enviado por
Nizam MuhamadDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Explain and List Down The Factors Affecting Sight Clarity
Enviado por
Nizam MuhamadDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Inno
University Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Human Factor
Explain and list down the factors affecting sight clarity/sharpness vision
Muhammad Nizam Bin Muhamad Class: 7 Bachelors 3 Date of submission: 28 July 2011
53259208167
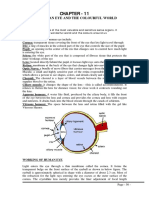
The eye is one of the most sensitive senses of the human body. This is shows by having an approximately of 1.2 billion nerve cells from the retinas to the area of the brain. Being this sensitive, there are various factors that can affect the clarity of someones vision. The figure below is showing the normal anatomy of an eye.
A normal person would have 20/20 vision acuity. This means that the person would be able to see and clarify the detail at 20 feet. If a person has acuity of 20/40 this means that the person can see what a normal person can see at 40 feet. The person with 20/40 acuity is short sighted. The 20/40 is showing the ratio of a person sharpness vision to what a normal persons sharpness vision. There are various factors that will affect a persons acuity. These factors are: I. II. III. IV. Physical factors The influence of ingested foreign object Environmental factors Factors associated with object being viewed.
Physical Factors
The
first
physical
factor
is
Hypemetropia
also
known
as
as farsightedness, longsightedness or hyperopia. Hypermetropia is a defect of vision caused by an imperfection in the eye (often when the eyeball is too short or the lens cannot become round enough), causing difficulty focusing on near objects, and in extreme cases causing a sufferer to be unable to focus on objects at any distance. As an object moves toward the eye, the eye must increase its optical power to keep the image in focus on the retina. If the power of the cornea and lens is insufficient, as in hyperopia, the image will appear blurred. In a hypermetropic eye, the light is not bent sufficiently so that it focuses at a point behind the retina. Here a person sees well for distance but near vision is difficult and causes strain. Hence hypermetropic people are called long-sighted. This is illustrated in the figure below.
Secondly is Myopia. It is a refractive defect of the eye in which collimated light produces image focus in front of the retina when accommodation is relaxed. In simpler terms, myopia is a condition of the eye where the light that comes in does not directly focus on the retina which is in the back of the eye. Because of this, the image that one sees is out of focus when looking at a distant object but comes into focus when looking at a close object. Eye care professionals most commonly correct myopia through the use of corrective
lenses, such as glasses or contact lenses. It may also be corrected by refractive surgery, though there are cases of associated side effects. The corrective lenses have a negative optical power (i.e. are concave) which compensates for the excessive positive diopters of the myopic eye.
The influence of ingested foreign object Vision can be adversely affected by the use of certain drugs and medication, alcohol, and smoking cigarettes. With smoking, carbon monoxide which builds up in the blood stream allows less oxygen to carried in the blood to the eyes. This is known as hypoxia and can impair rapidly the sensitivity of the rods.
Environmental Factors Vision can be improved by increasing the lighting level but only up to a point, as the law of diminishing returns to operate. Also increased in illumination could lead to result in increased glare. Older people are more affected by the glare of the reflected light then younger people. Moving from an extremely bright environment to a dimmer one has an effect of vision being severely reduced until the eyes get use to less light being available. This is because eyes have become light adopted. If an engineer works in a dark environment for a very long time, his eyes becomes gradually dark adapted allowing better visual acuity. This can take about 7 minutes for the cones and 30 minutes for the rods. As a consequence, moving between a bright hangar to a dark apron at night can mean that the maintenance engineer have to wait for his eyes to adjust. In low light condition, it is easier to focus if you look closely to one sight of an object. This allows the image to fall outside the fovea and onto the part of the retina which has many rods. Any airborne particle such as dust, rain or mist can interfere with the transmission of light through the air, distorting what is seen. This can be even worse when spectacles are worn as they are susceptible of getting dirty, wet, misted up or scratched. Engineers who wear contact lenses should take advice from their optician associated with the maximum wear time usually 8 to 18 hours. Goggle should be worn whenever necessary. Factors associated with object being viewed
Many factors associated with the object being viewed can also influence vision. We use information from the objects we are looking at to help distinguish what we are seeing. These are known as visual cues. Visual cues often refer to the comparison of object of known size to known objects. An example of this is that we associate small objects with being further away. Similarity, if an object does not stand out well from its background, it is harder to distinguish its edges and hence its shape. Movement and relative motion of an object, as well as distance and angle of the object from the viewer, can all increase visual demands.
Você também pode gostar
- Anatomy of Peripheral RetinaDocumento29 páginasAnatomy of Peripheral RetinaNeelam Khatwani100% (1)
- Human EyeDocumento72 páginasHuman EyeDhananjayAinda não há avaliações
- The Human Eye and The Colourful World: Anchli Singh, Class XADocumento17 páginasThe Human Eye and The Colourful World: Anchli Singh, Class XAshashank100% (1)
- TBL 1 - Refractive Error SlidesDocumento66 páginasTBL 1 - Refractive Error SlidesAmirah Azman100% (4)
- Reffractive ErrorsDocumento13 páginasReffractive ErrorsSagiraju SrinuAinda não há avaliações
- 7.1 Gradual Loss of VisionDocumento19 páginas7.1 Gradual Loss of VisionparugandooAinda não há avaliações
- Spectacle Prescription by DR Harbansh LalDocumento52 páginasSpectacle Prescription by DR Harbansh LalJatinderBaliAinda não há avaliações
- Krishna Gata RogaDocumento10 páginasKrishna Gata Rogathiru thirumakal100% (1)
- Phoropter HandoutsDocumento8 páginasPhoropter Handoutsjehn02992% (12)
- Comparative Animal Physiology: Philip C. WithersDocumento7 páginasComparative Animal Physiology: Philip C. WithersWwwanand111Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 4 Visual ImpairmentDocumento61 páginasModule 4 Visual ImpairmentMina Agarwal100% (5)
- Energetic Eyehealing - The New Paradigm of Eye Medicine CategoriesDocumento6 páginasEnergetic Eyehealing - The New Paradigm of Eye Medicine CategoriesMadon MariaAinda não há avaliações
- About EyesDocumento5 páginasAbout Eyeshisyer11Ainda não há avaliações
- HypermetropiaDocumento5 páginasHypermetropiaAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHAinda não há avaliações
- Eye Diseases: An Investigatory Project by Shrikanth Pillai XII BDocumento11 páginasEye Diseases: An Investigatory Project by Shrikanth Pillai XII BCR7STUDIO 7100% (1)
- 9.2 Human Performance and LimitationsDocumento66 páginas9.2 Human Performance and LimitationsAlfian DwiAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Medical Device?Documento5 páginasWhat Is A Medical Device?Jan Kenneth BarazonAinda não há avaliações
- Slides For Chapter 2 Human FactorDocumento41 páginasSlides For Chapter 2 Human FactorVisan NaiduAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Eye Disorders-1Documento11 páginasIntroduction To Eye Disorders-1bhavani GAinda não há avaliações
- The Eye and VisionDocumento70 páginasThe Eye and VisionLedkos SLAinda não há avaliações
- Human Eye PDFDocumento12 páginasHuman Eye PDFMothi KarunaAinda não há avaliações
- Class10 Science Unit11 NCERT TextBook English EditionDocumento12 páginasClass10 Science Unit11 NCERT TextBook English Editionshraddha0603Ainda não há avaliações
- Eyesight ProblemsDocumento2 páginasEyesight ProblemsMridul DevkotaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Class X For 2017 18Documento22 páginasPhysics Class X For 2017 18KalaiAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Investigatory Project (On Eye Diseases)Documento22 páginasBiology Investigatory Project (On Eye Diseases)sagar0% (1)
- Biology Investigatory Project On Eye DiseasesDocumento18 páginasBiology Investigatory Project On Eye DiseasesBHALAJI KARUNANITHI100% (1)
- Resume CataractDocumento3 páginasResume CataractFadila PadmariniAinda não há avaliações
- Certificate: Study of Eye DiseasesDocumento20 páginasCertificate: Study of Eye DiseasesDhruvAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocumento19 páginasBiology Investigatory ProjectGopikrishna united67% (3)
- The EyeDocumento7 páginasThe EyeTavvia HenryAinda não há avaliações
- Correct of Eye DefecDocumento15 páginasCorrect of Eye Defeceboigbeeghosa7Ainda não há avaliações
- Incu AssignDocumento2 páginasIncu AssignmintuwondeAinda não há avaliações
- FactsAbout REFRACTIVE ERRORS 2013Documento4 páginasFactsAbout REFRACTIVE ERRORS 2013Vidhya NairAinda não há avaliações
- Investrigatory Project (Term I) : Subject - BIOLOGYDocumento20 páginasInvestrigatory Project (Term I) : Subject - BIOLOGYRehan RazaAinda não há avaliações
- Name - Krishna Chouhan CLASS - 12th B: Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2 IndoreDocumento11 páginasName - Krishna Chouhan CLASS - 12th B: Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2 IndoreKrishna ChouhanAinda não há avaliações
- Phys ProjDocumento11 páginasPhys Projben-jAinda não há avaliações
- Human EyeDocumento9 páginasHuman EyeNimish MalhotraAinda não há avaliações
- HUMAN FACTORS Chapt 4, 5 & 6Documento162 páginasHUMAN FACTORS Chapt 4, 5 & 6Johnson MangumaAinda não há avaliações
- CommunicationDocumento16 páginasCommunicationbitchass niggaAinda não há avaliações
- Onisha Biology Project 14 10 15Documento14 páginasOnisha Biology Project 14 10 15Jelani GreerAinda não há avaliações
- The Human EyeDocumento38 páginasThe Human EyeDarlo HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- MyopiaDocumento3 páginasMyopiaAbu RidhuwanAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Eye ReportDocumento1 páginaAnatomy Eye ReportbrylleAinda não há avaliações
- Jahandar Hajiyev-1Documento33 páginasJahandar Hajiyev-1aze2005aze2020Ainda não há avaliações
- Human EyeDocumento4 páginasHuman EyeLit Central DreamsAinda não há avaliações
- Human Eye and The Colorful World PDFDocumento12 páginasHuman Eye and The Colorful World PDFJyothi DeepakAinda não há avaliações
- 11.human Eye and Colourful WorldDocumento19 páginas11.human Eye and Colourful WorldJagpreet SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocumento52 páginasOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDShahar ShababAinda não há avaliações
- PresbiopiDocumento4 páginasPresbiopiapriyani ramahliaAinda não há avaliações
- About Short-Sightedness .: Normal VisionDocumento5 páginasAbout Short-Sightedness .: Normal VisionSyuhaida AdenanAinda não há avaliações
- Project 220209165249Documento32 páginasProject 220209165249Lakshmanan RAinda não há avaliações
- Light Sensitivity Photophobia 2019Documento13 páginasLight Sensitivity Photophobia 2019rgrr feAinda não há avaliações
- Blindness and Low VisionDocumento5 páginasBlindness and Low VisionCurt LaurenceAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Investigatory Project: Samiksha Subhashish SarkarDocumento35 páginasBiology Investigatory Project: Samiksha Subhashish SarkarSamiksha SarkarAinda não há avaliações
- SightDocumento26 páginasSightapi-703497157Ainda não há avaliações
- CL X Physics Ch-11 The Human EyeDocumento12 páginasCL X Physics Ch-11 The Human EyeDeepanshu BindalAinda não há avaliações
- CH 11Documento30 páginasCH 11piyushAinda não há avaliações
- Visual Factors Which Affect Reading AchievementDocumento14 páginasVisual Factors Which Affect Reading AchievementqwedcxzAinda não há avaliações
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocumento11 páginasHuman Eye and Colourful WorldSahishna SurapaneniAinda não há avaliações
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocumento52 páginasOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDHidayadAinda não há avaliações
- Aeas 455 - Chapter - 2 - Human Performance and LimitationDocumento82 páginasAeas 455 - Chapter - 2 - Human Performance and LimitationMd Jalal Uddin RumiAinda não há avaliações
- Phy098 Problem Solving AssignmentDocumento12 páginasPhy098 Problem Solving AssignmentMUHAMMAD FIKRI BATHURUL ZAMAN SHAHAinda não há avaliações
- Far-Sightedness, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo EverandFar-Sightedness, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Examination of EyeDocumento33 páginasExamination of EyeSumit YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Glaucoma Management Approach: Simple Literature ReviewDocumento4 páginasGlaucoma Management Approach: Simple Literature ReviewElrach CorpAinda não há avaliações
- KERATOKONUSDocumento15 páginasKERATOKONUSLusyAlwiAinda não há avaliações
- SOLIX Essential BrochureDocumento12 páginasSOLIX Essential BrochureHaag-Streit UK (HS-UK)Ainda não há avaliações
- Structure and Function of EyesDocumento11 páginasStructure and Function of EyesSamar Ameen SialAinda não há avaliações
- Eyelid Surgery Los AngelesDocumento2 páginasEyelid Surgery Los AngelesVeronica HinmanAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges in Pediatric RefractionDocumento68 páginasChallenges in Pediatric RefractionOptom. Sarbind Kumar YadavAinda não há avaliações
- 2.4.2 Student Response Sheet Visual Perception LabDocumento4 páginas2.4.2 Student Response Sheet Visual Perception LabHarsh KaushikAinda não há avaliações
- Early Photocoagulation For Diabetic Retinopathy: ETDRS Report Number 9Documento20 páginasEarly Photocoagulation For Diabetic Retinopathy: ETDRS Report Number 9Bernardo RomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Kyoto Kagaku - Eye Examination Simulator PDFDocumento2 páginasKyoto Kagaku - Eye Examination Simulator PDFJuan Carlos SuarezAinda não há avaliações
- Fercher - Ophthalmic Laser InterferometryDocumento4 páginasFercher - Ophthalmic Laser InterferometryGeorge E. BozinisAinda não há avaliações
- A Comparison of Tests For Quantifying Sensory Eye DominanceDocumento10 páginasA Comparison of Tests For Quantifying Sensory Eye DominanceBONAinda não há avaliações
- Relationship Between Color and Emotion ADocumento11 páginasRelationship Between Color and Emotion Amerve çetakAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Mamta Dept of Ophthalmology RNT Medical College, UdaipurDocumento56 páginasDr. Mamta Dept of Ophthalmology RNT Medical College, UdaipurGideon IrwandaAinda não há avaliações
- Free Cmyk Chart Printable Download A4Documento1 páginaFree Cmyk Chart Printable Download A4grafica bituAinda não há avaliações
- Homonymous Hemianopia - UpToDateDocumento6 páginasHomonymous Hemianopia - UpToDateSonali GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of The Possible Prognostic Factors For Visual OutcomesDocumento11 páginasImpact of The Possible Prognostic Factors For Visual OutcomesBima RizkiAinda não há avaliações
- A Cataract Is A Clouding of The EyeDocumento5 páginasA Cataract Is A Clouding of The EyeHikari 光 ShidouAinda não há avaliações
- A Study of Outcome of Rose K Lenses in KeratoconusDocumento4 páginasA Study of Outcome of Rose K Lenses in KeratoconusInternational Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research (IJCBR)100% (1)
- Plus Cylinder Refraction StepsDocumento2 páginasPlus Cylinder Refraction StepsDeanna PresnellAinda não há avaliações
- Gillam 1986 EnglishDocumento13 páginasGillam 1986 EnglishFelipe do NascimentoAinda não há avaliações
- De Valois1993 - A Multi-Stage Color Model.Documento13 páginasDe Valois1993 - A Multi-Stage Color Model.AnkanAinda não há avaliações
- CH 15Documento8 páginasCH 15naguguAinda não há avaliações
- Elkins - SAQA Munsell ColorDocumento7 páginasElkins - SAQA Munsell ColorLaura DuqueAinda não há avaliações