Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Expt 1
Enviado por
gaurav142Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Expt 1
Enviado por
gaurav142Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
Experiment no 1
Aim: - Introduction to Power Supply, Multimeter, CRO & Function
generator
Theory: DC POWER SUPPLY
It is easy to use, low power, four output general purpose laboratory supply. It is suitable for experimental set-ups, circuit development and low voltage applications. The power supply delivers three dc outputs: 0-32V dc output, continuously variable, with 2 Amps capacity. This section is provided with panel meters to monitor output voltage and current separately. 5V preset dc output with 5 Amps capacity. A built-in over voltage protection circuit offers protection to the loads against over voltage. 15V preset dc output with 500mA capacity.
All the outputs are floating (i.e. neither any of +ve or-ve output terminals nor any point within the regulator circuitry is connected to ground). The power supply is designed to operate satisfactorily in ambient temperature of up to 50 oC and full power can be drawn if free air circulation is allowed. The unit works on main supply of 230v ac at 50 Hz. Panel control 32V SECTION: - Coarse & fine control are provided on the front panel for the setting of output voltage & current. 5V SECTION: - A single control is provided on the front panel to adjust the output voltage from 4.5V to 5.5V. 15V SECTION: - A single control is provided on the front panel to adjust output voltage from 12V to 15V.
Jaypee University of Information Technology, Waknaghat
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
FUNCTION GENERATOR
The HP33120 function generator is used to provide voltages that vary with time. It has four primary waveforms: sine, square, triangular and ramp. There are three parameters that can be varied for each waveform: 1. peak-to-peak voltage (2-20 V) 2. frequency (0.01 hz -1 MHz) 3. DC offset To set any of these features, press the button labeled with the feature you wish to modify. Notice that one of the digits is blinking, turning the dial will affect this digit, you may change which digit is flashing by pressing the left or right arrow keys. It is also possible to enter a number directly by pressing the button marked Enter Number. After pushing this button, you may enter a number on the key pad. Pressing enter immediately following will alter the setting to the new value.
DIGITAL MULTIMETER
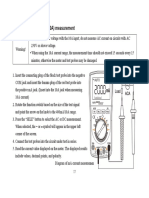
The HP34401 digital multimeter measures voltage, current and resistance. There are separate settings for measuring AC and DC values. If you examine the soft-key pad on the lower left of the multimeter, you will find primary functions in black and alternate functions in blue. The alternate functions are accessed by pressing the shift soft-key and then the function soft-key. For example, to measure DC voltage, you press the DC V soft-key. To measure DC current, you press the shift soft-key followed by DC I which is the same soft-key used for DC voltage. The multimeter also has the capability of measuring other quantities such as the frequency of periodic waveforms. There are three vertically aligned holes (banana jacks) in the multimeter located at the top right of the meter front panel. To measure voltage, place the positive terminal in the top hole, with the negative terminal in the center hole. The top hole is labeled Hi in red and V in black. To measure current, place the positive terminal (the terminal at which current enters the multimeter) in the bottom hole (labeled in red as I), and the other terminal in the center hole. Other than that, the operation of the digital multimeter is almost entirely automatic, simply set the multimeter to the type of measurement you wish to make by pressing the button labeled voltage, current, etc. and read the value from the display.
Jaypee University of Information Technology, Waknaghat
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering OSCILLOSCOPE
An oscilloscope is used to view a voltage waveform on a screen. An electron beam is generated in the cathode ray tube, directed at the back of the screen, and swept in time along the X-axis. A voltage applied to the scope probes is amplified and applied to a pair of horizontal metal plates through which the electron beam passes. This voltage deflects the beam in the vertical direction (Y-axis). The sweep in the electron beam combined with vertical deflection results in the appearance of a waveform on the screen of the scope. The scope has two probes: one for Channel 1 and one for Channel 2. Each channel has a vertical placement knob which moves the waveform for that channel up and down. Each channel also has a knob which selects the vertical scale of the waveform in terms of volts per division. Divisions are the visible grid lines on the oscilloscope screen. The knob which sets the horizontal scale in time per division controls both channels. The majority of all measurements made in this lab can be performed automatically with the HP54600 scope. To see the waveform, press Auto-scale. The Auto-scale button will be used more than any other on the scope. When you want to capture a waveform on the screen, the first thing to think of is Auto-scale. This takes the waveform at the input and displays it so that the entire peak-to-peak voltage is displayed as well as several periods are displayed. To measure voltage, push the button marked voltage which is located to the right of the screen near the top of the front panel. This will bring up a menu at the bottom of the screen, listing available voltage measurements. The first choice is to select either channel 1 or 2 for measurement. After that, you may select: Peak to Peak voltage (Vp-p), average voltage (Vave), or rms voltage (Vrms). By pressing the corresponding soft-keys, you will automatically get the selected measurement. For more choices, press the soft-key labeled Next Menu. The next menu will allow you to select: Vmax , V min , V top, V bot or V amp . Time measurements can be obtained by pressing the time button (located next to the voltage button). This will give you the following menu options: Frequency, Period, Duty Cycle, +Width, -Width, Rise Time, Fall Time, Delay and Phase Difference. The last command, Phase Difference, is useful for computing the difference in phase between waveforms on channels 1 and 2. Front Panel Controls POWER ON: Put the instrument to main supply with LED indication. INTENSITY: Control the brightness of the display. FOCUS CONTROL: - The sharpness of the display.
Jaypee University of Information Technology, Waknaghat
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
TIME BASE: - 18 step switch to enable selection of 18 calibrated sweep from 0.2 s/div in 1, 2, 3.sequence. TIME BASE VARIABLE: - In calibrated position (CCW) the selected sweep speed holds indicated calibration clockwise. CH1/Ch2: -Selects trigger signal in INT mode derived from either Ch1 and Ch2 inputs. AC/DC/GND: -Selects input coupling/grounding. TRACE: - Screw driver control to adjust horizontal tilt of the trace. AMPLIFIER MODE SWITCH: ALT/CHOP: - Selects switching mode for the two channels while in dual operation. DUAL/MONO(X-Y): - In dual, operates as a dual trace scope; in alt or chop mode, as selected. CT: - Converts scope into component tester
Precaution
Be careful with the DC power supply leads. Avoid letting them touch at all times. When they touch, a short circuit is formed. Consider what would happen if you shorted the wall socket, or a car battery! Short circuits can be dangerous, and care should be taken to avoid them.
Jaypee University of Information Technology, Waknaghat
Você também pode gostar
- Experiment 3Documento16 páginasExperiment 3Ashish patelAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Electronics Circuits: Experiment 1Documento9 páginasBasic Electronics Circuits: Experiment 1SavithaGnAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Session 01 Introduction To Laboratory Equipments: ObjectiveDocumento10 páginasLab Session 01 Introduction To Laboratory Equipments: ObjectiveHuma MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Ee 33 ProjectDocumento20 páginasEe 33 ProjectJozar TumabiniAinda não há avaliações
- notes-on-function-generator-1645711932Documento5 páginasnotes-on-function-generator-1645711932BEN KAPANSAAinda não há avaliações
- Lab EquipmentsDocumento7 páginasLab EquipmentsIbne FazalAinda não há avaliações
- 1Documento8 páginas1hanan adbelmoazeAinda não há avaliações
- Lab ManualDocumento65 páginasLab ManualHuma MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Use Oscilloscope Measure AC and DC VoltagesDocumento12 páginasUse Oscilloscope Measure AC and DC VoltagesSarah HarunAinda não há avaliações
- Multifunction Network Analyzer ManualDocumento13 páginasMultifunction Network Analyzer ManualDan Alexandru NeaguAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Oscilloscope MeasurementsDocumento5 páginasIntroduction to Oscilloscope MeasurementsSadiq IdrisAinda não há avaliações
- Time Varying SignalsDocumento17 páginasTime Varying SignalsDiego Cancino SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Measure Voltages and Currents Using a MultimeterDocumento16 páginasMeasure Voltages and Currents Using a Multimeterزينب عبد الناصر عاتي عبدالله الموحيAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 1: Introduction To Electronics InstrumentationsDocumento17 páginasExperiment 1: Introduction To Electronics InstrumentationsSharifah Syed HamzahAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To The OscilloscopeDocumento9 páginasIntroduction To The OscilloscopeStudentsHeartAinda não há avaliações
- Lab EE 1Documento6 páginasLab EE 1Mazlin AzuraAinda não há avaliações
- OscilloscopeDocumento9 páginasOscilloscopeQadeer Khan100% (1)
- Session 2: Practical Experiments in Phase MeasurementDocumento13 páginasSession 2: Practical Experiments in Phase MeasurementMaxAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Lab Equipment FunctionsDocumento10 páginasIntroduction to Lab Equipment Functionsdani chAinda não há avaliações
- CISE 204 Digital System Design Lab Manual PDFDocumento44 páginasCISE 204 Digital System Design Lab Manual PDFEng-Mohammed KayedAinda não há avaliações
- Current Rectifier DocumentationDocumento2 páginasCurrent Rectifier DocumentationManjula DeshpandeAinda não há avaliações
- FEEE Lab Manual Part 2-54-126Documento73 páginasFEEE Lab Manual Part 2-54-126Berlin JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Elr Emm 4 ManualDocumento8 páginasElr Emm 4 Manualthanhnguyen81Ainda não há avaliações
- Eca Ii Lab 1Documento14 páginasEca Ii Lab 1Tausif MinhasAinda não há avaliações
- Lab # 1 Introduction To Instruments. (Digital Oscilloscope and Digital Function Generator) and Software LtspiceDocumento23 páginasLab # 1 Introduction To Instruments. (Digital Oscilloscope and Digital Function Generator) and Software LtspiceMISBAH BATOOLAinda não há avaliações
- Oscilloscope and Rc-Circuits Physics 230, Lab 5 Objective: Name PartnerDocumento5 páginasOscilloscope and Rc-Circuits Physics 230, Lab 5 Objective: Name PartnerSanira LasanthaAinda não há avaliações
- LORAIN POWER PLANT MICROPROCESSOR CONTROL PANELDocumento22 páginasLORAIN POWER PLANT MICROPROCESSOR CONTROL PANELRajesh Sharma100% (1)
- 16.voltmeter Calibration Punzalan - Tuliao.dumangasDocumento87 páginas16.voltmeter Calibration Punzalan - Tuliao.dumangasjomar lipaopaoAinda não há avaliações
- DSO3 D12 OscilDocumento17 páginasDSO3 D12 OscilmassimipelleAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 1 Introduction To The Use of The Digilent'S Analog DiscoveryDocumento6 páginasLab 1 Introduction To The Use of The Digilent'S Analog DiscoveryFredy Alzate100% (1)
- Network Analyser MPR-53/53S Parameters FunctionsDocumento4 páginasNetwork Analyser MPR-53/53S Parameters FunctionscacojlAinda não há avaliações
- Faculty ManualDocumento60 páginasFaculty ManualCookiesAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 01: Lab 01: Introduction To InstrumentsDocumento9 páginasExperiment 01: Lab 01: Introduction To InstrumentsBilal KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Eee5451 Lab3Documento24 páginasEee5451 Lab3sekelanilunguAinda não há avaliações
- 1.2.1. Uso MultimetroDocumento13 páginas1.2.1. Uso MultimetroSamuel Gerardo AndericaAinda não há avaliações
- InnoCare T Service ManualDocumento19 páginasInnoCare T Service ManualTony NavaAinda não há avaliações
- CroDocumento4 páginasCroRajan SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 9Documento13 páginasLab 9Abu BakarAinda não há avaliações
- The OscilloscopeDocumento12 páginasThe OscilloscopeAzhar AliAinda não há avaliações
- AC/DC Clamp Meter User's ManualDocumento20 páginasAC/DC Clamp Meter User's ManualMartin OngAinda não há avaliações
- EE 442 Laboratory Experiment 1 Introduction To The Function Generator and The OscilloscopeDocumento22 páginasEE 442 Laboratory Experiment 1 Introduction To The Function Generator and The Oscilloscopehassam saeedAinda não há avaliações
- Function GeneratorsDocumento4 páginasFunction GeneratorsVarunKumarAinda não há avaliações
- How To Use The Power Supply, Digital Multimeter and NI ELVISDocumento25 páginasHow To Use The Power Supply, Digital Multimeter and NI ELVISAmb WaraichAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring Transient Response of RC CircuitsDocumento9 páginasMeasuring Transient Response of RC CircuitsEHTISHAM UL HAQAinda não há avaliações
- Hall-Effect Sensors Lab Counts Low PulsesDocumento12 páginasHall-Effect Sensors Lab Counts Low PulsesAbul Barkat Mollah Sayeed Ud DoulahAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 4: Measuring Instruments and Power/Signal Sources: 1-Digital MultimeterDocumento8 páginasLecture 4: Measuring Instruments and Power/Signal Sources: 1-Digital MultimeterHuzaifa RehanAinda não há avaliações
- Fluke 87 V Secret MenuDocumento8 páginasFluke 87 V Secret MenuMehmet Serdar TekeAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 2 - Introduction To The Oscilloscope and SBCDocumento8 páginasLab 2 - Introduction To The Oscilloscope and SBCOm PrakashAinda não há avaliações
- Using an oscilloscope to analyze audio signalsDocumento25 páginasUsing an oscilloscope to analyze audio signalsFnd MuorAinda não há avaliações
- Marbles' recipe for random musicDocumento16 páginasMarbles' recipe for random musicRJ BevyAinda não há avaliações
- Science Learning Center University of Michigan - Dearborn: Use of The OscilloscopeDocumento47 páginasScience Learning Center University of Michigan - Dearborn: Use of The OscilloscopebingAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Experiment 4 ReportDocumento2 páginasLab Experiment 4 ReportYuen WeipingAinda não há avaliações
- AC and DC Current (Ma, 10A) MeasurementDocumento17 páginasAC and DC Current (Ma, 10A) MeasurementRgfAinda não há avaliações
- ESE 211 Lab 3 Measurement of AC SignalsDocumento6 páginasESE 211 Lab 3 Measurement of AC SignalsHanzala NoumanAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Labmanual 1Documento78 páginasElectronic Labmanual 1bipul ahmedAinda não há avaliações
- User Manual Achook-1080, G726A, UM0084 - LatestDocumento24 páginasUser Manual Achook-1080, G726A, UM0084 - Latestprajith555Ainda não há avaliações
- Science Learning Center University of Michigan - Dearborn: Use of The OscilloscopeDocumento49 páginasScience Learning Center University of Michigan - Dearborn: Use of The OscilloscopeAlex ZadicAinda não há avaliações
- Tool FunctionGenerator TutorialDocumento5 páginasTool FunctionGenerator Tutorialimen boubechirAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Nota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Ainda não há avaliações
- Fabricación de Insertos de Carburo de TungstenoDocumento5 páginasFabricación de Insertos de Carburo de TungstenoRolando Nuñez MonrroyAinda não há avaliações
- Denison Hydraulics Goldcup Digital Hi-Iq Control: Electronic Control Card User Manual Software Version 2.2BDocumento62 páginasDenison Hydraulics Goldcup Digital Hi-Iq Control: Electronic Control Card User Manual Software Version 2.2BHassan Haghighi TajvarAinda não há avaliações
- Gearbox Efficiency and LubricationDocumento6 páginasGearbox Efficiency and Lubricationrashm006ranjanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to AMOS - Basic building blocks and getting startedDocumento1 páginaIntroduction to AMOS - Basic building blocks and getting startedtomo100% (1)
- Chainsaw SparesDocumento2 páginasChainsaw SpareswanttobeanmacccAinda não há avaliações
- DBMS Lab ExperimentsDocumento45 páginasDBMS Lab ExperimentsMad Man100% (1)
- Process Control Plan SCM100113Documento20 páginasProcess Control Plan SCM100113Rohit MakhijaAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Safety Handbook 3001.5Documento51 páginasDesign and Safety Handbook 3001.5phankhoa83Ainda não há avaliações
- Dynamic Architecture Journal ArticleDocumento11 páginasDynamic Architecture Journal Articlesakshi soniAinda não há avaliações
- Fls Brochure Usa v2 PDFDocumento4 páginasFls Brochure Usa v2 PDFXa ViAinda não há avaliações
- Basics of GD&T TrainingDocumento3 páginasBasics of GD&T TrainingShajil SAinda não há avaliações
- NFC 17102 - Lightning Protection - Protection of Structures and Open Areas Against Lightning Using Early Streamer Emission Air TerminalsDocumento58 páginasNFC 17102 - Lightning Protection - Protection of Structures and Open Areas Against Lightning Using Early Streamer Emission Air TerminalsLEONARDOAinda não há avaliações
- Adobe 2017 Download LinksDocumento4 páginasAdobe 2017 Download LinksDaśhīñg ÆžīAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Torch Parts: T100 ConsumablesDocumento2 páginasMachine Torch Parts: T100 Consumablesبسام الاغبريAinda não há avaliações
- Sap InputDocumento211 páginasSap InputdominscribdAinda não há avaliações
- OEM Industrial Air Handling Products CatalogDocumento31 páginasOEM Industrial Air Handling Products CatalogalexAinda não há avaliações
- Count rows in all tablesDocumento25 páginasCount rows in all tablessatya1401Ainda não há avaliações
- Mobile Robots & Kinematics: Session 2: Nicol As Ilich Samus February 27, 2014Documento5 páginasMobile Robots & Kinematics: Session 2: Nicol As Ilich Samus February 27, 2014Nicolás Ilich SamusAinda não há avaliações
- Anna University International Admissions GuideDocumento4 páginasAnna University International Admissions GuideAmir AzeezAinda não há avaliações
- 150-4059 - Rockbreaker Installation Manual PDFDocumento26 páginas150-4059 - Rockbreaker Installation Manual PDFDanny Joel Espinoza CastañedaAinda não há avaliações
- Richard GrisenthwaiteDocumento25 páginasRichard GrisenthwaitecaarthiyayiniAinda não há avaliações
- Extension To Existing Production Building Industrial Slab: Method StatementDocumento8 páginasExtension To Existing Production Building Industrial Slab: Method StatementSirb PetruAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrology Lecture01Documento24 páginasHydrology Lecture01Mohd. YunusAinda não há avaliações
- Catalogue 12V Ilss For Polis Bantuan Vehicles (Petronas)Documento7 páginasCatalogue 12V Ilss For Polis Bantuan Vehicles (Petronas)Afiq Muizz SallehhoudinAinda não há avaliações
- Morgan Parts Catalog 44p LRDocumento27 páginasMorgan Parts Catalog 44p LRArturo Zavala UrquidesAinda não há avaliações
- Postmodern Architecture Reinterprets Form & FunctionDocumento5 páginasPostmodern Architecture Reinterprets Form & FunctionNejra Uštović - PekićAinda não há avaliações
- FE Exam Formatted ProblemsDocumento12 páginasFE Exam Formatted ProblemsCarlo Galicia100% (1)
- Iec 61400 Justification: E30/70 PRODocumento60 páginasIec 61400 Justification: E30/70 PROoswalfAinda não há avaliações
- Process Capability AnalysisDocumento37 páginasProcess Capability Analysisabishank09100% (1)
- LDM CuNi7Zn39Pb3Mn2 MSDSDocumento4 páginasLDM CuNi7Zn39Pb3Mn2 MSDSmp87_ingAinda não há avaliações