Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Roy Davis Ballard
Enviado por
1234567899999999999Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Roy Davis Ballard
Enviado por
1234567899999999999Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ballard Power Systems
Using Simplorer and Maxwell Tools to Validate Electric Drives for EV Applications, and Interactions with Rapid Prototyping Tools
Roy I. Davis Ballard Power Systems Dearborn, Michigan
Automotive Electromechanical Simulation Workshop 9 October 2003
Electric Drives for EV Applications - Outline
n n n n n n n n
Brief Overview of Ballard Electric Drives Design Process How Ansoft Tools Fit In at Ballard PM Motor Design Evaluation Control Design Motor Design Inverter Design Custom Power Module Design Rapid Prototyping Control Design Testing Motor Design Evaluation
18 December 2003
Electric Drives Design Process
Customer Specification
Controller
VDC DC Supply ID C
V AC
MM
Inverter
IA C
Motor
NM
MT Transmission N T
Transmission Assumptions
Load
Motor Requirements
Motor Electromagnetic Design
Performance Evaluation
Motor Mechanical Design Motor Thermal Design
Inverter Requirements Cost Evaluation Volume Estimate Mass Estimate
18 December 2003
Custom Power Module Design Inverter Design
Transmission Requirements
How Ansoft Tools Fit in at Ballard
Customer Specification
Controller
Simplorer
Transmission Assumptions
Load
VDC DC Supply ID C
V AC
MM
Inverter
IA C
Motor
NM
MT Transmission N T
Motor Requirements
Motor Electromagnetic Design
Performance Evaluation
Motor Mechanical Design Motor Thermal Design
Maxwell 3D Simplorer
Cost Evaluation Volume Estimate Mass Estimate
18 December 2003
Inverter Requirements
Custom Power Module Design Inverter Design
RMxprt Maxwell 2D
Maxwell Thermal
Transmission Requirements
PM Motor Design Evaluation
n
Maxwell 2D used to perform analysis
Calculation of Average Torque and Ripple Torque
Average value and peak-to-peak magnitude match well between test and FEA calculations. FEA Results (3.7 revs)
Maxwell 2D Torque vs. Time
Test Data (2.8 revolutions)
95
90
Torque, Nm
85
80
75
70 -0.10
-0.08
-0.06
-0.04
-0.02
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
Torque, Nm
Time, seconds
18 December 2003
Time, seconds
5
PM Motor Design Evaluation
n
Maxwell 2D used to perform analysis
Calculation of Back EMF
Harmonic content and magnitude matches well with experiments. FEA Results
Test Data
40 30
Back-EMF (V)
20 10 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -0.010 -0.008 -0.006 -0.004 -0.002 0.000 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.008
Time (s)
Equal time and voltage scales
18 December 2003 6
PM Motor Design Evaluation
n n
RMxprt used to enter motor design information Maxwell 2D used to perform analysis
Calculation of Ld and Lq (Energy or Vector Potential Method)
Flux Linkage Method:Ld versus Id
Flux Method: Lq versus Iq
4.50E-04 4.00E-04
2.5E-04 2.0E-04 1.5E-04 1.0E-04 5.0E-05 0.0E+00
3.50E-04 3.00E-04
Lq (H)
Ld(H)
2.50E-04 2.00E-04 1.50E-04 1.00E-04 5.00E-05 0.00E+00
100
200
300
400
500
600
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
Id(A) Ld (25 Turns) FEA
Iq (A)
Ld Test
18 December 2003
Lq (25 Turns) FEA
Lq,Test
7
Control Design Motor Design - General
n
Motor equivalent circuit parameters with saturation
Needed for control development Use Maxwell 2D to update estimates made earlier in design process Used to populate Simplorer model of PM motor PTPA (selection of id/iq trajectories) Maxwell & Simplorer Field weakening control Maxwell & Simplorer Interactions of control with dc bus variations due to load point changes (dynamic) - Simplorer Interactions of sensors and interface limitations on control performance Simplorer Etcetera
Ansoft tools are used to explore and understand:
Matlab/Simulink used as primary control development tool with autocode function for dSpace rapid prototyping hardware.
18 December 2003
Control Design Motor Design - Simplorer
Omega_Motor Viscous_Load
+
IA_Meas
A
OMEGA
Omega_GND
+
V
Ballard_IPM IB_Meas
A
I1Q
A B C 3~
MS
+
V
+
V V
LOAD
I1D V1Q V1D PHIM
T ransform_ab_alphabeta GND
0.4k 0.3k 0.2k
EQUBL
0.1k 0
Lin_IPM_25kW.MI [Nm] IQ_Rotor.VAL IQ_R_Ref.VAL Lin_IPM_25kW.I1Q Lin_IPM_25kW.I1D ID_R_Ref.VAL ID_Rotor.VAL Lin_IPM_25kW.I1A [A] IA_Filter.VAL
FB FA
Fbeta Falpha
GAIN
EQUBL
-0.1k -0.2k -0.3k 0 1m 2m 3m 4m 5.6m t [s]
COSINE
Half
EQUBL
P_over_2
GAIN
Norm_to_DC_Bus_C
LIMIT GAIN CONST
theta_electrical
SINE
ID_R_Ref IQ_R_Ref
CONST
Ibeta
Norm_to_DC_Bus_B
LIMIT GAIN
D_Q_Controller_Rotor_Frame
Vd_feedback Vq_feedback
NEG
Ialpha
Reciprocate
EQUBL
Vd_feedfwd Vq_feedfwd vdr Rotor_Speed_Mech Theta_Rotor_Mech D_feedback D_reference Q_feedback Q_reference
IQ_Rotor
Norm_to_DC_Bus_A
LIMIT GAIN
vqr C_voltage_reference B_voltage_reference A_voltage_reference
ID_Rotor
18 December 2003
Control Design Motor Design - Simplorer
10
GAIN
Ld
GAIN
Vq_feedfwd Rs1
10
NEG
GAIN
Q_feedback
10
q_integral
GAIN
CONST
Lamda_PM Q_reference q_proportional
10
Rotor_Speed_Mech
10
GAIN
Vq_feedback Rs
GAIN
10
Vd_feedfwd
Poles_over_21 Lq
10
NEG
GAIN GAIN
D_feedback
10
d_integral
GAIN
D_reference
d_proportional
10
Vd_feedback vd r
10 10
Poles_over_2
10
GAIN COSINE
vqr Cos
SINE
B_voltage_reference sqrt_3_over_2
GAIN
Theta_Rotor_Mech
10
Sin
NEG
v_beta
NEG
v_alpha
C_voltage_reference
10
10
GAIN
NEG
A_voltage_reference
one_half
18 December 2003
10
Control Design Motor Design Co-simulate
iq
Back-EMF Decoupling
PMSM physical model
e ^ m p 1 Ki S +
Resistance Decoupling
e pm
R + + + + -
iq *
+ Kp +
vq
1 Lq
1 S
iq
State Feedback Current Regulator
^ eL d
C rossCoupling Input Decoupling
eL d
1 Ki S
eL q
^ eL q
+ + R
Resistance Decoupling
id *
Kp
+ +
vd
+ + -
1 Ld
1 S
id
id
Current Regulator/Motor Block Diagram
Simulink Current Regulator
18 December 2003
11
Control Design Motor Design Co-simulate
n
Space Vector Modulation (SVM) with Overmodulation Modes 1-2 and Deadtime Compensation
Simulink Model of Modulation Systems
18 December 2003 12
Control Design Motor Design Co-simulate
Omega_Motor Viscous_Load IA_Meas
A
+ +
OMEGA
Omega_GND
+
V
IB_Meas
A
Ballard_IPM
A B C 3PHIDEG ~
MS
+
V
+
V
+
V
LOAD
EQU
V_DC
PHIM
FML1
PHI_MOD:=MOD(Lin_IPM_25kW.PHIDEG,360)
GND
60 40 20 0
EQUBL
-20 -40 -60
IQ_Rotor.VAL ID_Rotor.VAL SIMPLORER Link Interface Lin_IPM_25kW.MI [Nm] Viscous_Load.TORQUE [Nm] SIM2SIM1 Lin_IPM_25kW.OMEGA Lin_IPM_25kW.I1D -1 * Lin_IPM_25kW.I1Q
SiM2SiM SiM2SiM
EQUBL
-80 -0.1k -0.12k 0 2.5m 5m 7.5m 10m 13m 15m 18m 20m 23m t [s]
EQUBL
LIMIT
CONST
CONST1
LIMIT CONST
CONST2
LIMIT CONST
Ballard Pow e r Sys t e m s Roy Davis Simulation of IPM Drive 7 April 2003
CONST3
18 December 2003 13
Control Design Motor Design Co-simulate
Omega_Motor Viscous_Load IA_Meas
A
+ +
OMEGA
Omega_GND
+
V
IB_Meas
A
Ballard_IPM
A B C 3PHIDEG ~
MS
+
V
+
V
+
V
LOAD
EQU
V_DC
PHIM
FML1
PHI_MOD:=MOD(Lin_IPM_25kW.PHIDEG,360)
GND
60 40 20 0
EQUBL
-20 -40 -60
IQ_Rotor.VAL ID_Rotor.VAL SIMPLORER Link Interface Lin_IPM_25kW.MI [Nm] Viscous_Load.TORQUE [Nm] SIM2SIM1 Lin_IPM_25kW.OMEGA Lin_IPM_25kW.I1D -1 * Lin_IPM_25kW.I1Q
SiM2SiM SiM2SiM
EQUBL
-80 -0.1k -0.12k 0 2.5m 5m 7.5m 10m 13m 15m 18m 20m 23m t [s]
EQUBL
LIMIT
CONST
CONST1
LIMIT CONST
CONST2
LIMIT CONST
Ballard Pow e r Sys t e m s Roy Davis Simulation of IPM Drive 7 April 2003
CONST3
18 December 2003 14
Control Design Motor Design Co-simulate
Omega_Motor Viscous_Load IA_Meas
A
+ +
OMEGA
Omega_GND
+
V
IB_Meas
A
Ballard_IPM
A B C 3PHIDEG ~
MS
+
V
+
V
+
V
LOAD
EQU
V_DC
PHIM
FML1
PHI_MOD:=MOD(Lin_IPM_25kW.PHIDEG,360)
GND
60 40 20 0
EQUBL
-20 -40 -60
IQ_Rotor.VAL ID_Rotor.VAL SIMPLORER Link Interface Lin_IPM_25kW.MI [Nm] Viscous_Load.TORQUE [Nm] SIM2SIM1 Lin_IPM_25kW.OMEGA Lin_IPM_25kW.I1D -1 * Lin_IPM_25kW.I1Q
SiM2SiM SiM2SiM
EQUBL
-80 -0.1k -0.12k 0 2.5m 5m 7.5m 10m 13m 15m 18m 20m 23m t [s]
EQUBL
LIMIT
CONST
CONST1
LIMIT CONST
CONST2
LIMIT CONST
Ballard Pow e r Sys t e m s Roy Davis Simulation of IPM Drive 7 April 2003
CONST3
18 December 2003 15
Inverter Design Custom Power Module Design
n
Use Maxwell 3D to model power module layout
Objective is to compute parasitic module inductance to support module design layout decisions 2nd objective is to provide inductances for bridge circuit simulation Presently developing this process difficult to get accurate results
Upper I1 E3 -5 Switching Lstray S1
4.7
Lower
E4
E1 EMF := 17 3.3
E2
NEG
S2 EMF := 5
Also developing process for parameterizing the detailed models of IGBTs in Simplorer using this test circuit.
18 December 2003 16
Inverter Design Custom Power Module Design
Simplorer model of inverter, dc source, and motor used to:
Evaluate component stresses under realistic conditions
Switches Diodes Capacitors
Investigate effects of different/variable PWM algorithms Determine losses
18 December 2003
17
Rapid Prototyping Control Design
We use dSpace for rapid prototyping control design and motor performance evaluations on the dyno
Clean interface to Simulink/RTW with Control Desk
Simplorer model of motor and inverter easily integrated with Simulink model of control
Helps to debug any problems arising from interactions with inverter PM motor model easily allows use of saturable inductances as functions of current Easy to do what-if investigations Much easier and seemingly more reliable than Matlab Power System Toolbox to include detail model of inverter and PM motor.
18 December 2003
18
Testing Motor Design Evaluation
Unexplained or different behavior that occurs during testing can be examined in Maxwell or Simplorer to determine cause. Provides a feedback link to design tool usage that allows refinement of rules of thumb or development of design rules to be applied with the numerical design tools.
18 December 2003
19
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- GP1200 Ingles PDFDocumento253 páginasGP1200 Ingles PDFJuan Luis Romero Ramirez100% (1)
- SsangYong Actyon Sports Q149 2011.01 Electrical Wiring DiagramDocumento84 páginasSsangYong Actyon Sports Q149 2011.01 Electrical Wiring Diagramcelyoz100% (1)
- Technical Note 3882A: Fault Finding Sequential GearboxDocumento93 páginasTechnical Note 3882A: Fault Finding Sequential GearboxNvidia TV100% (1)
- Tesla Model 3 - Emergency First Responders Guide.Documento31 páginasTesla Model 3 - Emergency First Responders Guide.Iqtidar AAinda não há avaliações
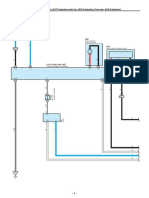
- EPS (TMT Made From Oct. 2017 Production Until Jan. 2018 Production, From Jan. 2018 Production)Documento8 páginasEPS (TMT Made From Oct. 2017 Production Until Jan. 2018 Production, From Jan. 2018 Production)Angel Rodríguez100% (1)
- Pradeep 11th Physics Guide DownloadDocumento2 páginasPradeep 11th Physics Guide DownloadSandeep Kaswan33% (3)
- On Virtual Doctor System For Health Monitoring FinalDocumento23 páginasOn Virtual Doctor System For Health Monitoring FinalChetu ChethanAinda não há avaliações
- Master Governance Plan SummaryDocumento21 páginasMaster Governance Plan SummaryMichelle SaverAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier Transform (For Non-Periodic Signals)Documento27 páginasFourier Transform (For Non-Periodic Signals)hamza abdo mohamoudAinda não há avaliações
- Sound Reinforcement Equipment Rack LayoutDocumento1 páginaSound Reinforcement Equipment Rack LayoutJeghiAinda não há avaliações
- Machinery Vibration Analysis-Introduction To Advanced TroubleshootingDocumento5 páginasMachinery Vibration Analysis-Introduction To Advanced TroubleshootingAbdulrahman AlkhowaiterAinda não há avaliações
- Pengaruh Social Media Marketing Terhadap Customer Bonding Dan Purchase To IntentionDocumento8 páginasPengaruh Social Media Marketing Terhadap Customer Bonding Dan Purchase To IntentionTya Asih Puji LestyaAinda não há avaliações
- Gammxfa 000027Documento981 páginasGammxfa 000027laurentAinda não há avaliações
- Summative Test 7Documento9 páginasSummative Test 7Gel Obenza BunedAinda não há avaliações
- Graco Supply Systems - 338921eneuDocumento16 páginasGraco Supply Systems - 338921eneuDanaAinda não há avaliações
- Productdatasheet Babsl 72 NBR 902Documento2 páginasProductdatasheet Babsl 72 NBR 902narayan46Ainda não há avaliações
- 2907-000Documento49 páginas2907-000swd14janAinda não há avaliações
- Fintech PresentationDocumento12 páginasFintech PresentationAnjali BhardwajAinda não há avaliações
- Magelis Advanced Panels: Hmi Gxo User ManualDocumento78 páginasMagelis Advanced Panels: Hmi Gxo User ManualcanAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report 1 Ese689 HakimDocumento10 páginasLab Report 1 Ese689 HakimMuhammad Asyraf Bin ZaininAinda não há avaliações
- NBMiner Crypto GPU Miner Log Output with AMD Ryzen CPU & RX 570 GPUDocumento2 páginasNBMiner Crypto GPU Miner Log Output with AMD Ryzen CPU & RX 570 GPUManish SawaiyanAinda não há avaliações
- RelationsDocumento60 páginasRelationsLawrence ChitandulaAinda não há avaliações
- Java Programming: From Problem Analysis To Program Design, 3eDocumento46 páginasJava Programming: From Problem Analysis To Program Design, 3eElla GiananAinda não há avaliações
- ABM Module C - Unit 25 HRM & ITDocumento6 páginasABM Module C - Unit 25 HRM & ITprjiviAinda não há avaliações
- Aechinesia Vol 7 Patana GalleryDocumento6 páginasAechinesia Vol 7 Patana GalleryNita AtiraAinda não há avaliações
- CS6K-265 - 270 - 275 - 280 P: Key Features Linear Power Output WarrantyDocumento2 páginasCS6K-265 - 270 - 275 - 280 P: Key Features Linear Power Output Warrantyadolfo escobarAinda não há avaliações
- MDU UIET 5TH SEM EE SyllabusDocumento59 páginasMDU UIET 5TH SEM EE SyllabusKshitij TyagiAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Cash Register Programming-ManualDocumento27 páginasElectronic Cash Register Programming-ManualRendy Adam FarhanAinda não há avaliações
- Prooccore Traınıng5Documento13 páginasProoccore Traınıng5ErkinAinda não há avaliações
- Lower Half Collapsing Lesson 12BDocumento3 páginasLower Half Collapsing Lesson 12BLIEW JIA KANG MoeAinda não há avaliações